Day 3 - The Octet Rule
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
The Octet Rule
Atoms of other elements do not have a full valence shell of electrons. Atoms react with other atoms to create a stable octet. This is called the octet rule.
valence
In this example, sodium has lost an electron and gains a charge of +1.
This charge is called its valence. Sodium (Na) has become a sodium ion (Na+).
The flame test
A flame test allows chemists to
determine the identify of unknown
metallic ions
Elements with Multiple Ionic Charges
A multivalent element can form two
or more stable ions. Most of the
transition metals (found in the middle
of the periodic table) can form more
than one type of ion.
Polyatomic Ions
An ion that contains more than one
atom is called a polyatomic ion.
Ionic bonds
Ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons is transferred from one atom to another atom.
chemical bond.
The force of attraction holding two atoms or ions together
Covalent bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when one
or more electrons are shared between
two atoms.
Formation of Ionic Compounds
• Ionic compounds are usually metals chemically bonded to non-metals.
• Metals tend to lose electrons to become cations (positive charge) and non-metals tend to gain electrons to become anions (negative charge).
• We can draw the Lewis structures of ions. Add square brackets around the element symbol and place the ion charge outside the brackets to show that the atom has become on ion.
• An ionic compound is not made of a single
positive ion and single negative ion. Instead
an ionic compound is made of anions and
cations in a fixed ratio.
electrostatic force
The atoms are held together by electrostatic force – the force of attraction between two objects with opposite charge
Properties of Ionic Compounds
1) Solid at room temperature
2) Hard and brittle
3) Have high melting and boiling points
4) Conduct electricity when molten liquids, but not as solids
5) Conduct electricity when dissolved in water
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Ionic compounds have high melting points because their ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces (ionic bonds). Melting the solid requires breaking the electrostatic forces.
Why are ionic compounds hard and brittle?
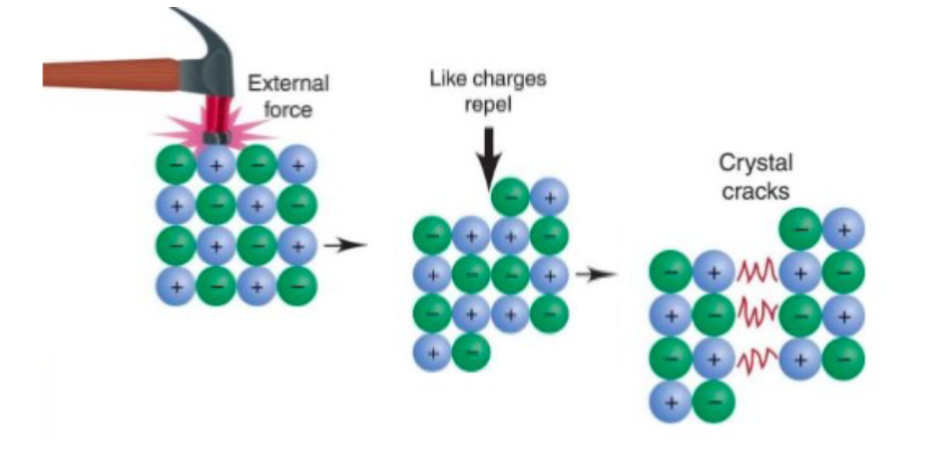
• Ionic compounds are hard and brittle because their bonds resist being
stretched.
• Ionic compounds are easily cracked because if the crystal lattice is offset,
ions of the same charge end up side by side and repel each other.
Why can ionic compounds carry electric?
When soluble in water, they form good electrolytes. Water molecules surround each ion and separate it from its crystal. The free-floating ions are able to move and carry and electric charge through the water.
Uses of Sodium
• Sodium ions, Na+, are required for nerves to transmit signals throughout our bodies, help our muscles contract, and control how much water stays in our blood and how much water is lost in urine.
• We get sodium from foods like salt (NaCl), cheese, and preservatives. Many people with Western diets eat more salt than required. This leads to increased water retention, high blood pressure, and an increased risk of heart disease.
Uses of Potassium
Potassium ions, K+, help maintain normal levels of fluid inside our cells, helps muscles to contract, and supports normal blood pressure. Many fruits and vegetables are high in potassium.

What is this and why people need this?
Gatorlyte is an electrolyte beverage designed for rapid rehydration. It contains a blend of five electrolytes
People who may need Gatorlyte include:
Athletes during or after intense workouts or competitions.
Individuals participating in endurance events like marathons or triathlons.
People who work in hot environments and sweat a lot.
Anyone recovering from dehydration due to illness or other causes.
