3amino acid neurotransmitters: glutamate an GABA
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What type of drugs are etomidate and propofol, and how do they act on GABAa receptors?
They are intravenous anesthetics that enhance GABAa receptor activity, increasing Cl⁻ influx and causing sedation and loss of consciousness.
How do etomidate and propofol affect GABAa receptor function?
They amplify GABAergic inhibition through GABAa receptors, leading to anesthetic effects like sedation and unconsciousness.
What is the mechanism of action of barbiturates like pentobarbital at GABAa receptors?
They prolong the duration of Cl⁻ channel opening and can directly activate the receptor at high doses, enhancing inhibition.
How do barbiturates influence chloride channels in GABAa receptors?
They keep the Cl⁻ channels open longer, strengthening inhibitory signals — even without GABA at high doses.
What effects do barbiturates produce through their action on GABAa receptors?
They have sedative, anticonvulsant, and potentially life-threatening effects at high doses.
what are the therapeutic and toxic effects of barbiturates?
Useful as sedatives and seizure treatments, but dangerous in overdose due to risk of coma or respiratory depression.
What do benzodiazepines do at GABAa receptors?
They increase the frequency of Cl⁻ channel openings, enhancing GABA’s inhibitory effect.
How do benzodiazepines modulate GABAa receptor activity?
They boost GABA’s action by making the Cl⁻ channels open more often, but only when GABA is present.
What are the major clinical effects of benzodiazepines?
They act as anxiolytics, hypnotics, anticonvulsants, and muscle relaxants.
What symptoms or conditions can benzodiazepines help manage?
Anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and muscle tension due to their GABA-enhancing effects.
What are neurosteroids, and how do they act on GABAa receptors?
neurosteroids are hormone-derived compounds (e.g. from progesterone) that modulate GABAa receptors and enhance inhibition.
How do naturally occurring neurosteroids influence GABAergic transmission?
they increase GABA receptor activity, providing sedative and anticonvulsant effects, especially under hormonal changes or stress.
What type of receptor is the GABAb receptor?
It is a metabotropic receptor, meaning it signals through G-proteins, not ion channels.
: How is a GABAb receptor classified based on its signaling mechanism?
it is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that causes slower, indirect effects on the cell.
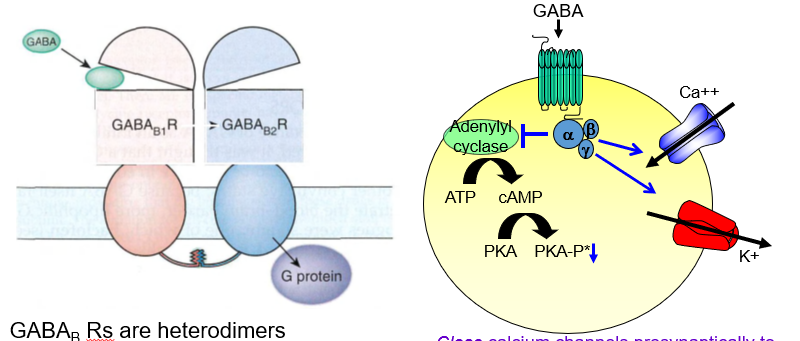
What is the structural composition of GABAb receptors?
They are heterodimers, made up of two different subunits: R1 and R2.
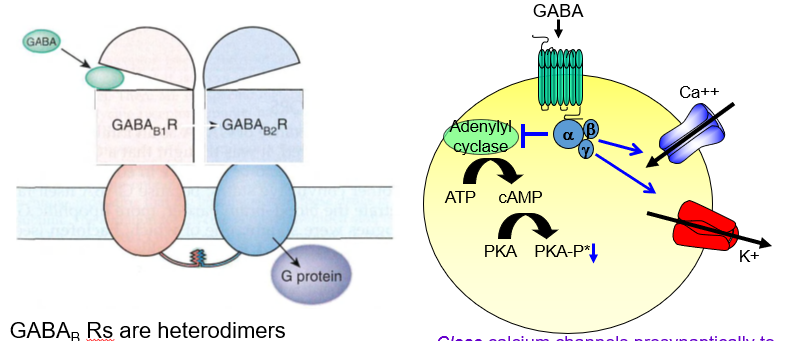
What subunit arrangement defines a functional GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor?
It requires two different parts (R1 and R2) to form a working receptor.
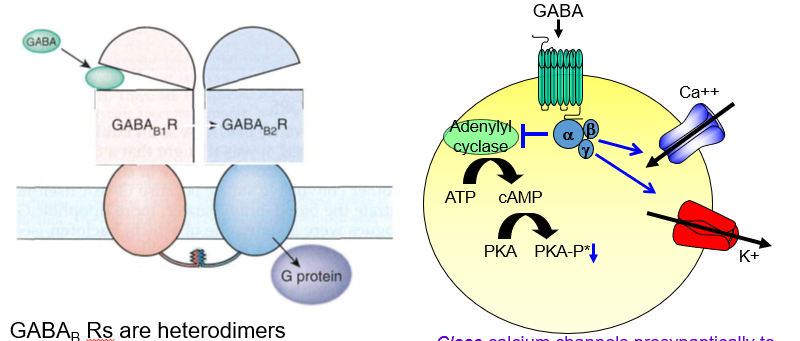
What is the role of the R1 subunit in GABAb receptors?
R1 contains the GABA binding site, often called the “venus fly trap” domain.
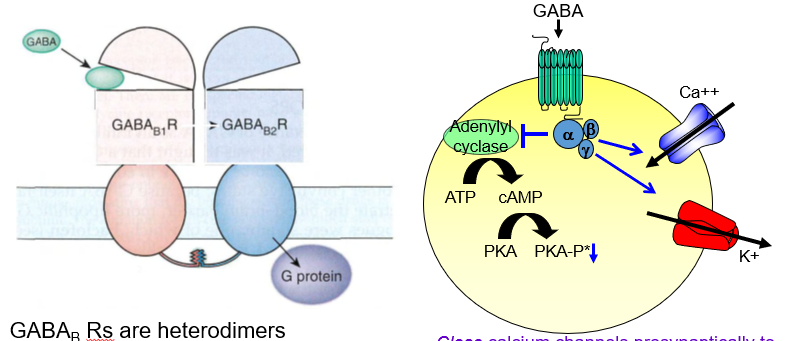
Where does GABA bind on the GABA b receptor?
It binds to the R1 subunit, which has a venus fly trap–like shape that captures the molecule.
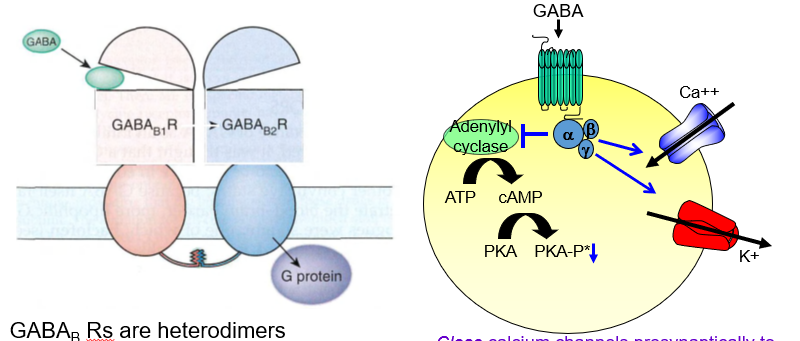
What does the R2 subunit of GABA b do?
R2 helps traffic the receptor to the cell surface so it can function.
Why is the R2 subunit important in GABAb receptors?
It’s needed to move the receptor to the membrane, allowing it to respond to GABA.
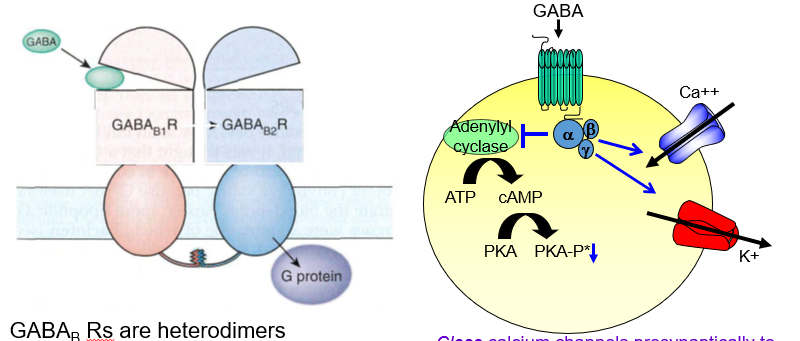
What is the presynaptic effect of GABAb receptor activation?
It closes calcium channels, reducing neurotransmitter release — acting as an autoreceptor.
How do GABAb receptors decrease neurotransmitter release presynaptically?
By blocking Ca²⁺ entry, they stop the neuron from releasing more transmitters.
What is the postsynaptic effect of GABAb receptor activation?
It opens potassium channels, causing slow hyperpolarization and inhibition.
How do GABAb receptors inhibit postsynaptic neurons?
They let K⁺ out, making the inside more negative and harder to excite.
What is spasticity in neurological terms?
It’s an exaggerated response of the stretch reflex pathways, often due to loss of inhibitory control.
How can spasticity be described in terms of reflex function?
It’s when the stretch reflex becomes overactive, leading to excessive muscle contraction.
What causes spasticity after a spinal cord injury?
Loss of descending inhibition from the brain increases reflex activity in the spinal cord.
Why does spasticity occur following spinal damage?
Because the brain’s normal inhibitory control is removed, allowing reflexes to become hyperactive.
what drug is commonly used to treat spasticity and acts on GABAb receptors?
Baclofen, a GABA b receptor agonist.
Which GABA b receptor drug helps reduce spasticity?
Baclofen — it mimics GABA and activates inhibitory GABAb receptors.
What conditions is baclofen commonly used to treat?
Spasticity in motor disorders like multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury.
In which disorders is baclofen an effective treatment?
It’s used for spasticity in MS, spinal injuries, and other motor system diseases.
Why is sedation a side effect of baclofen?
Because it crosses the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and affects CNS inhibition.
What causes the sedative side effect of baclofen?
It enters the brain and enhances inhibition, which can make patients feel drowsy or sedated.
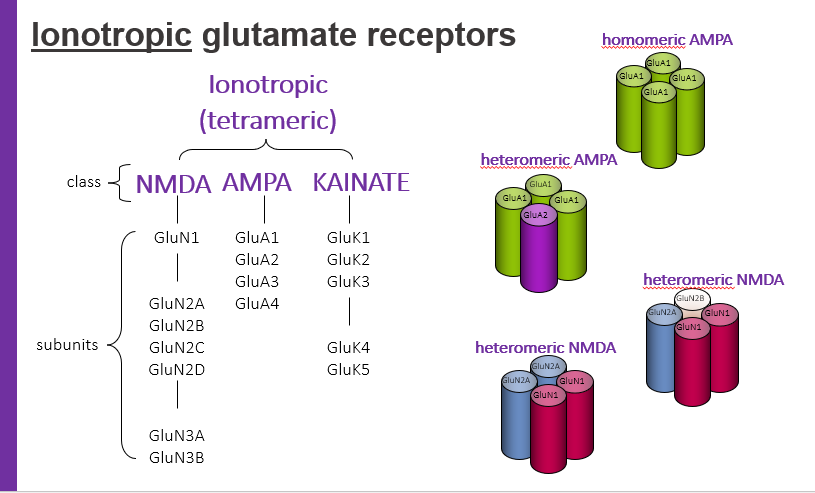
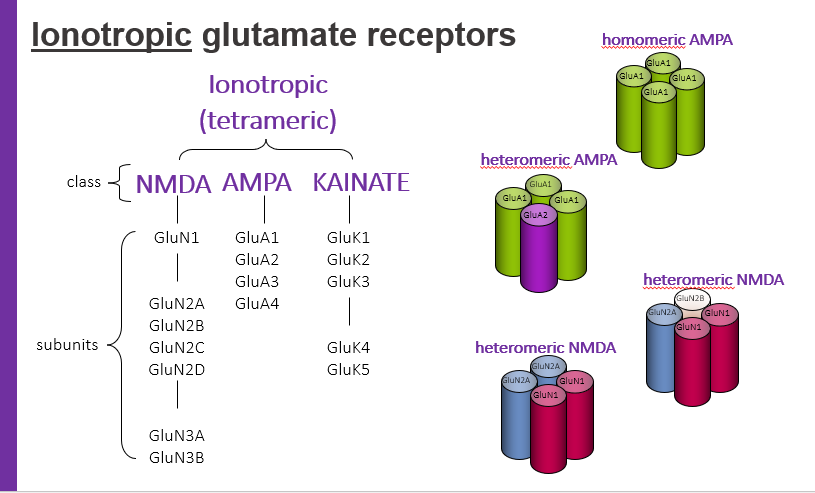
ionotropic glutamate receptors, tetrameric have classes. what are 3 classes?
NMDA
AMPA
KAINATE
homomeric AMPA
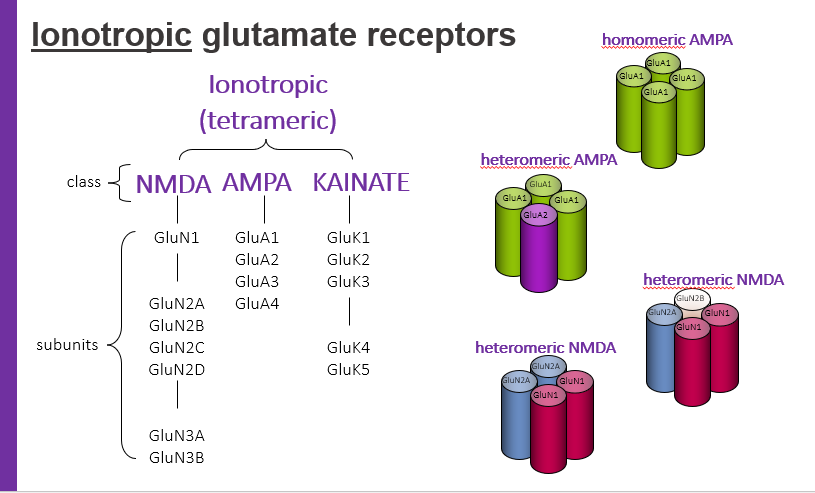
hetermeric AMPA
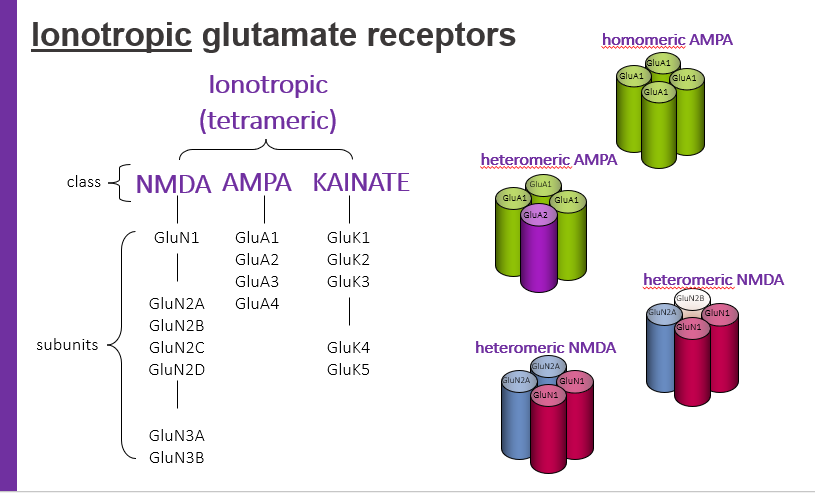
hetermeric NMDA
what type of ion channels are glutamatergic ionotropic receptors?
They are cation channels that allow positively charged ions to enter the neuron.
Which type of ions pass through glutamate-activated ionotropic receptors?
Positive ions (cations) such as Na⁺ and Ca²⁺.
What happens when cations enter the postsynaptic neuron through glutamatergic ionotropic receptors?
The membrane depolarizes, creating an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP).
What effect does glutamate have on the postsynaptic membrane potential?
It causes depolarization, generating an EPSP that can trigger an action potential.
What is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)?
A small depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that brings the neuron closer to firing an action potential.
How does an EPSP influence neuron firing?
It increases the likelihood of the neuron reaching threshold to fire an action potential.
Why is ionotropic glutamatergic neurotransmission considered "fast"?
Because the receptor directly opens an ion channel, allowing for rapid response within milliseconds.
What makes ionotropic receptors suitable for quick neural signaling?
Their direct channel-opening mechanism enables immediate excitatory effects.
What are NMDA receptors?
NMDA receptors are a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor that is highly permeable to Ca²⁺ and involved in synaptic plasticity and excitotoxicity.
What role do NMDA receptors play in the nervous system?
They mediate slow excitatory neurotransmission, are Ca²⁺ permeable, and are key in learning, memory, and excitotoxic damage.
Why are NMDA receptors described as voltage-sensitive?
Because Mg²⁺ blocks the channel at resting potential, but the block is removed upon depolarization.
What happens to Mg²⁺ in the NMDA receptor when the neuron depolarizes?
Mg²⁺ unblocks the channel, allowing Ca²⁺ and Na⁺ to flow through.
What is required to activate NMDA receptors?
Binding of both glutamate and glycine, and membrane depolarization to relieve Mg²⁺ block.
Which three conditions must be met for NMDA receptor activation?
Presence of glutamate, glycine, and depolarization to remove the Mg²⁺ block.
What is an orthosteric site on NMDA receptors?
The primary active site where endogenous ligands like glutamate or glycine bind.
Where do natural neurotransmitters bind on NMDA receptors?
: At the orthosteric site, the main activation site.
What are allosteric sites on NMDA receptors?
Sites other than the orthosteric site where molecules can modulate receptor activity.
how do allosteric modulators influence NMDA receptor function?
By binding to non-primary sites, they enhance or inhibit receptor activity indirectly.
: What are NMDA receptor antagonists?
Drugs that block NMDA receptor activity, either at the channel, orthosteric, or allosteric sites.
How do NMDA antagonists affect neurotransmission?
They inhibit NMDA receptor function, reducing Ca²⁺ influx and excitatory signaling.
What are examples of clinically useful NMDA receptor antagonists?
Ketamine and memantine.
Which NMDA antagonists are used therapeutically?
Ketamine (anesthetic/depression) and memantine (Alzheimer’s disease).
What are channel-blocking NMDA antagonists?
: Drugs that physically block the ion channel of NMDA receptors, preventing ion flow.
How do channel blockers inhibit NMDA receptor function?
By plugging the channel, stopping Ca²⁺ and Na⁺ influx.
What are glycine antagonists in the context of NMDA receptors?
Compounds that block the glycine co-agonist site, preventing receptor activation.
What happens when glycine antagonists bind to NMDA receptors?
They prevent glycine binding, thereby inhibiting receptor activation
What are polyamines and their role in NMDA receptor function?
Endogenous modulators that bind to allosteric sites, influencing receptor activity.
How do polyamines affect NMDA receptors?
They modulate channel activity by binding to non-orthosteric sites.
What do polyamine antagonists do?
They block the action of polyamines, altering NMDA receptor function.
How do polyamine antagonists modulate NMDA activity?
By inhibiting polyamine effects, which may decrease receptor activity.
Why are NMDA receptors the most studied glutamate receptors?
Because they have multiple modulatory sites, play roles in learning, memory, and are linked to neurological disorders.
What makes NMDA receptors a key target in neuroscience research?
Their complex regulation, critical brain functions, and role in disease make them highly studied.