Chapter 5: Macromolecules {Campbell Biology}
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
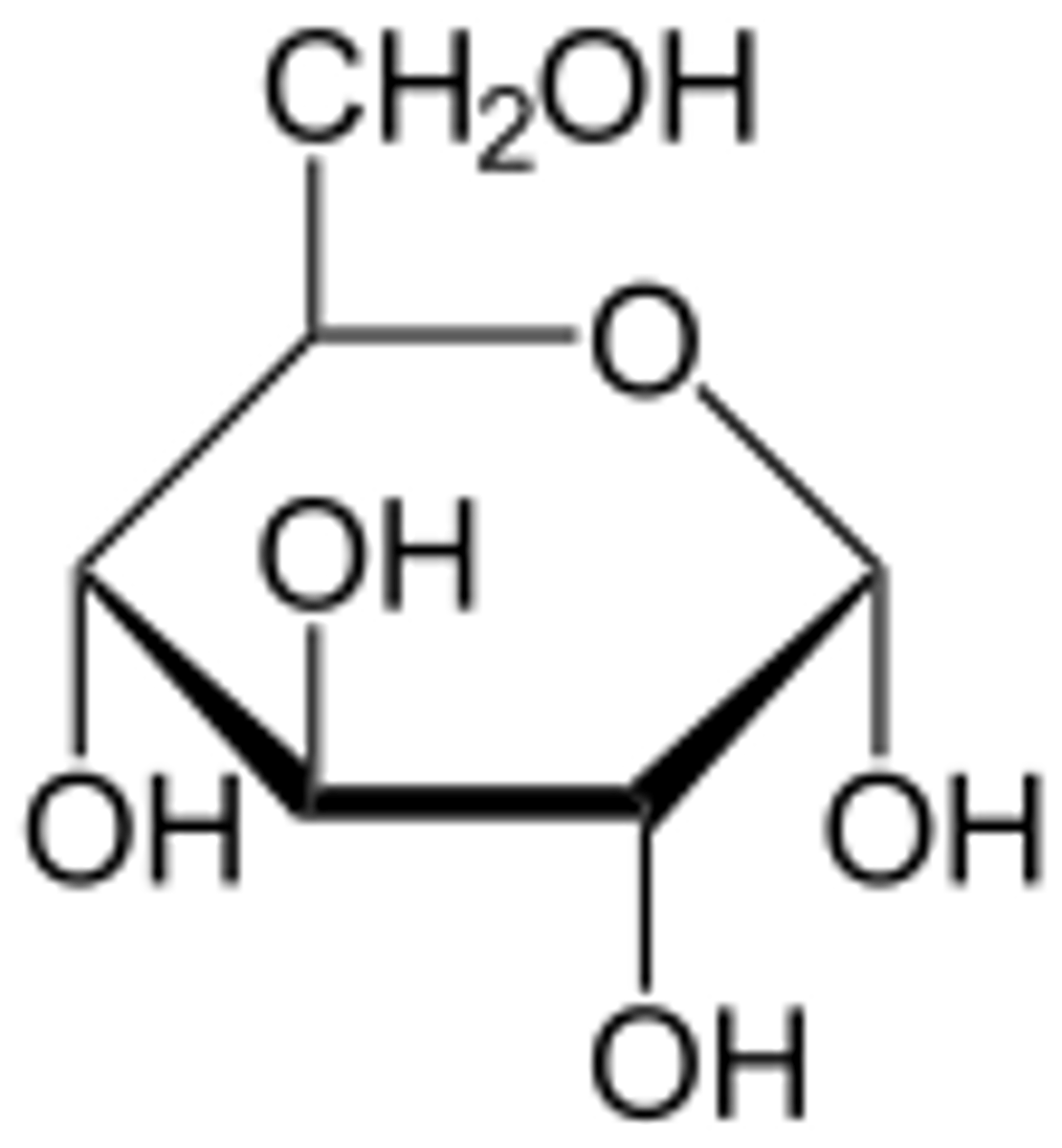
Monosaccharide
A simple sugar that is the basic subunit of a carbohydrate
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
polysaccharide
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
glycosidic linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
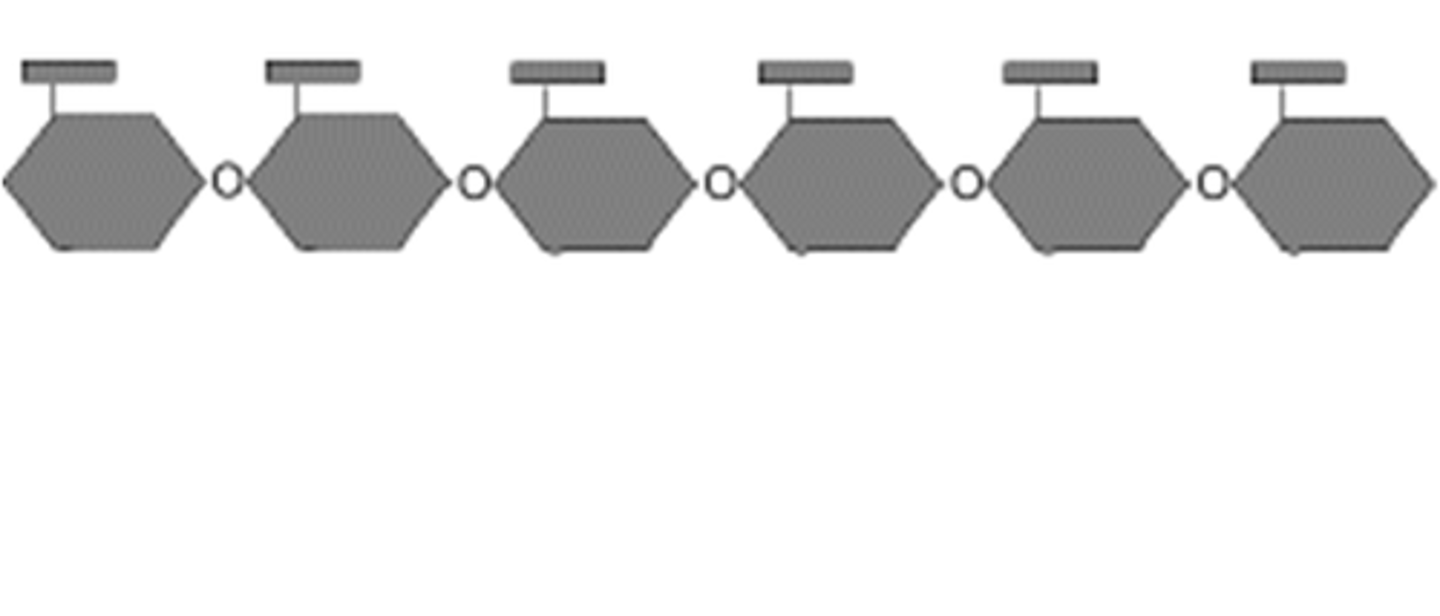
starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of α glucose.
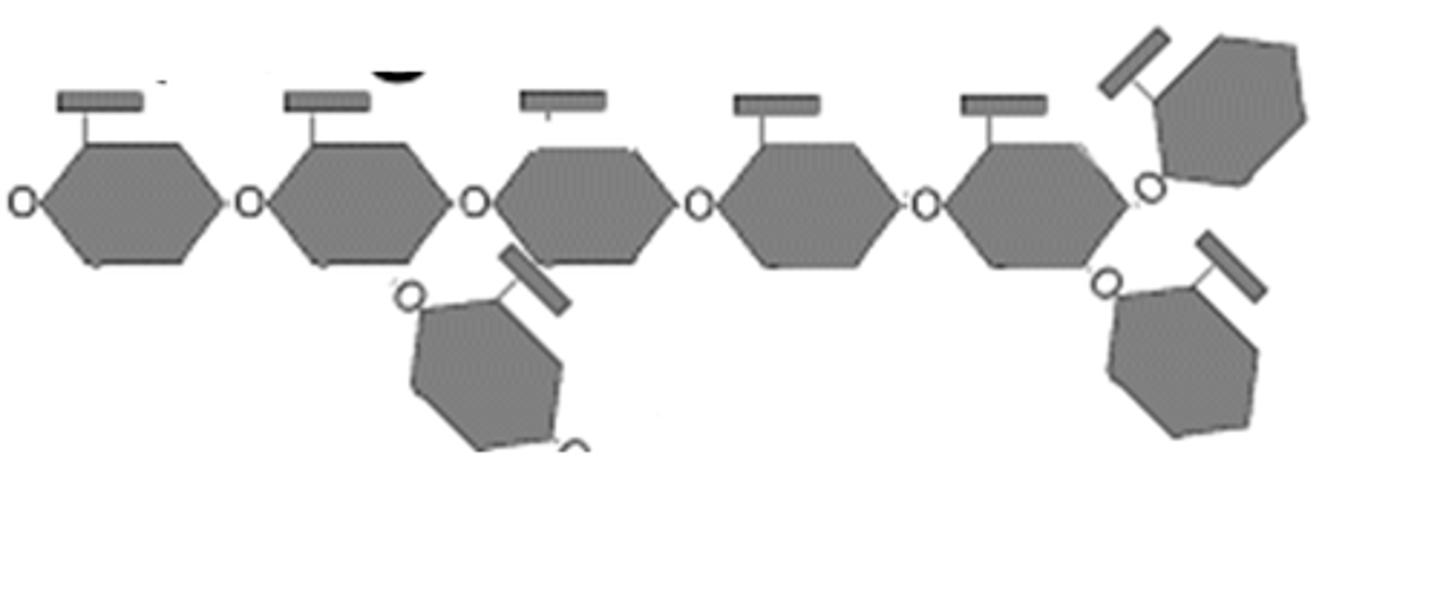
glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
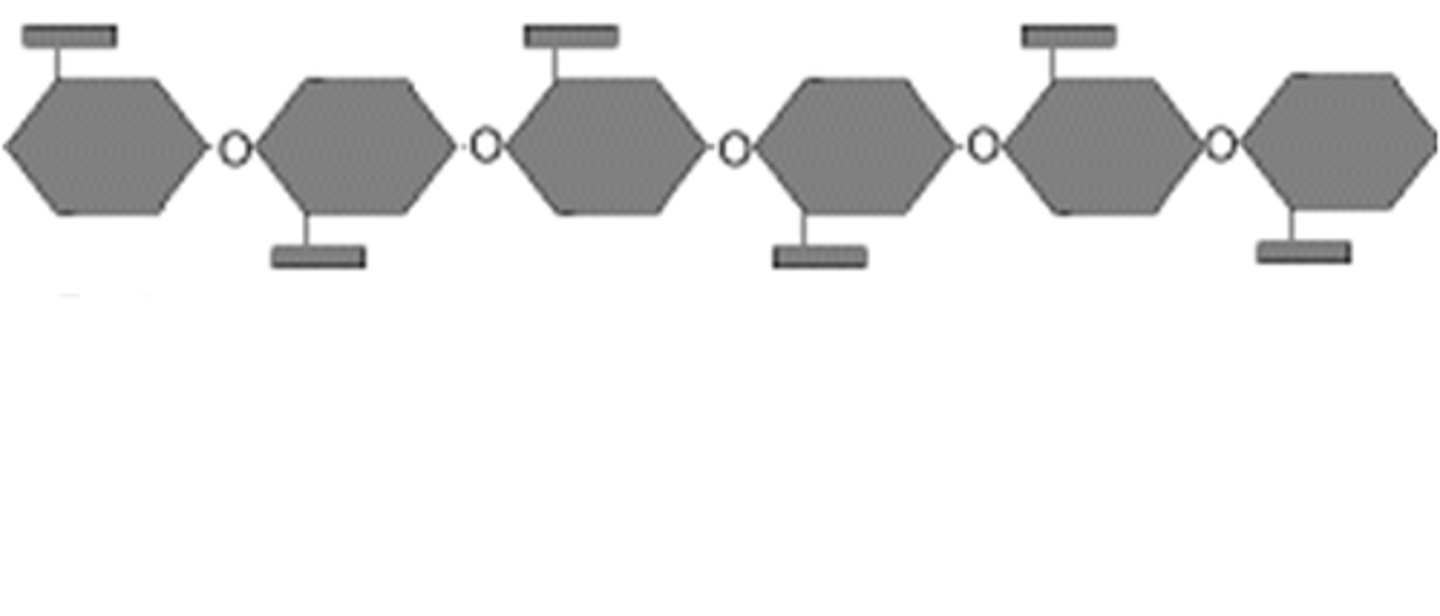
cellulose
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting of β glucose
chitin
A polysaccharide that makes up the exoskeleton in arthropods and the cell wall in fungi
maltose
Two glucose monomers form this disaccharide
sucrose
Glucose + fructose form this disaccharide
lactose
milk sugar
fructose
fruit sugar
glucose
C₆H₁₂O₆ ; primary energy source in cell metabolism
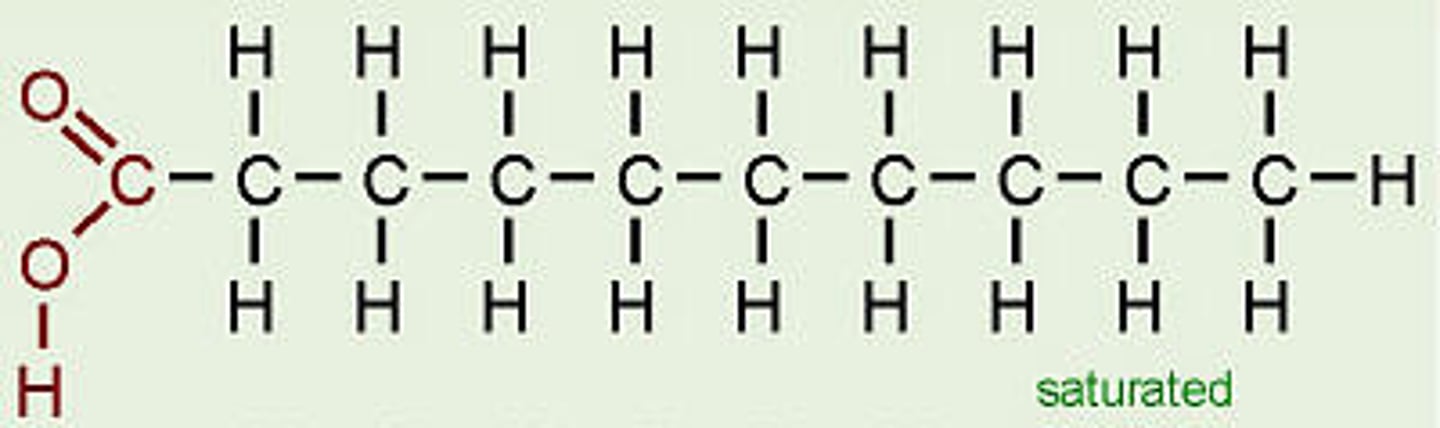
fatty acid
A hydrocarbon chain bonded to a carboxyl (COOH) functional group.
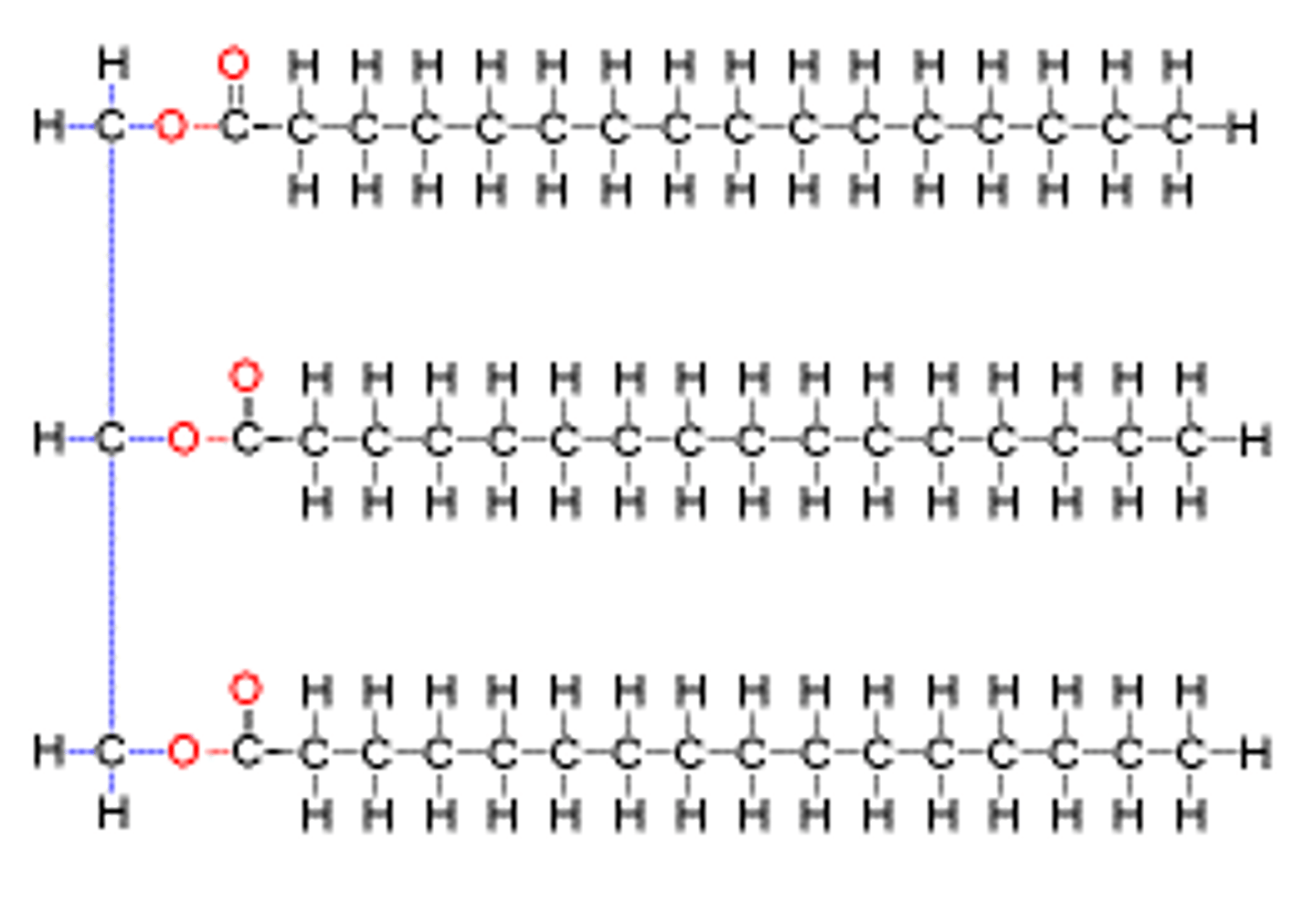
triglyceride
lipids that consist of three fatty acid (hydrocarbons) chains and one glycerol
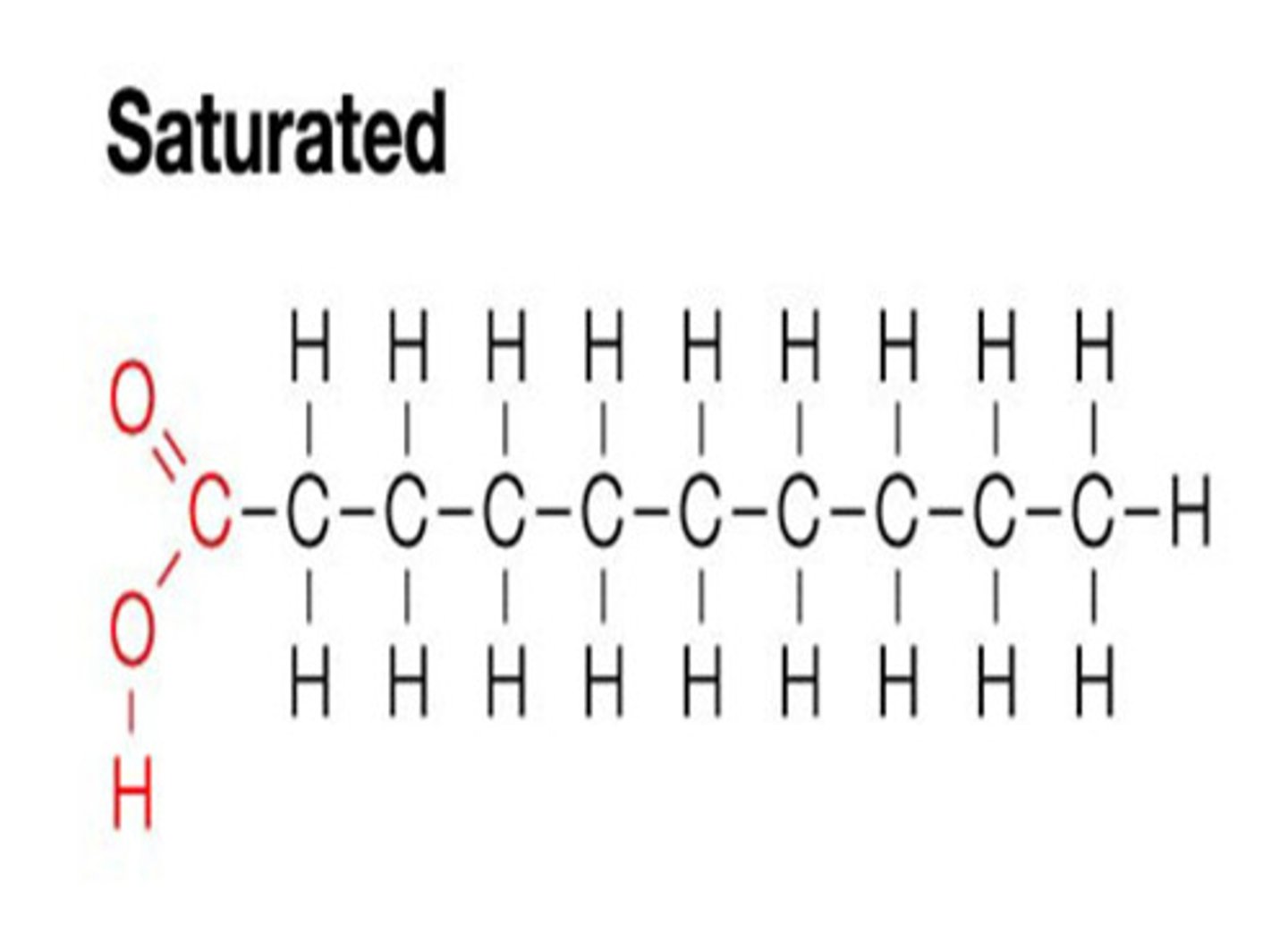
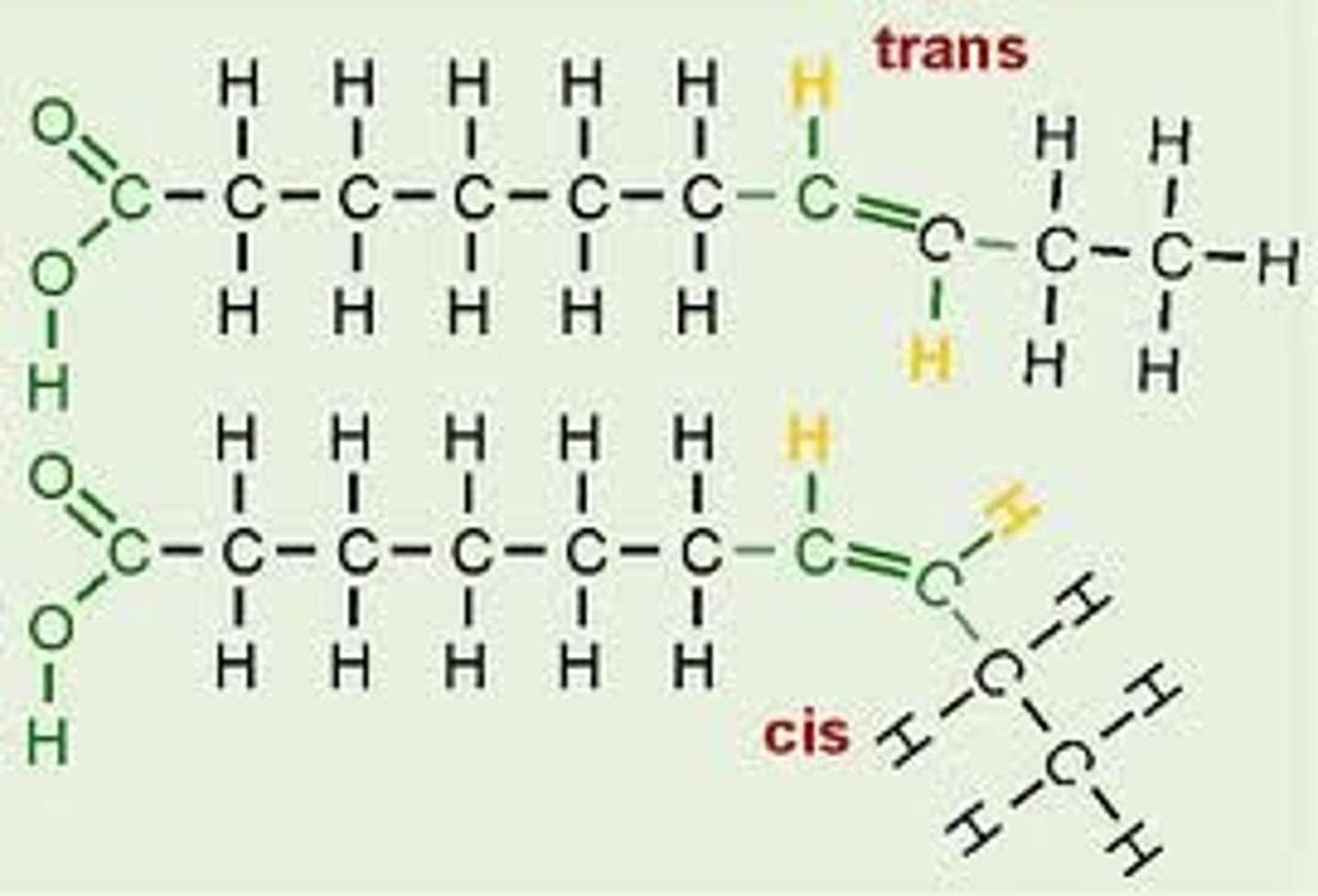
saturated fat
Example: Lard and butter
Solid at room temp because single bonds allow molecules to pack close together
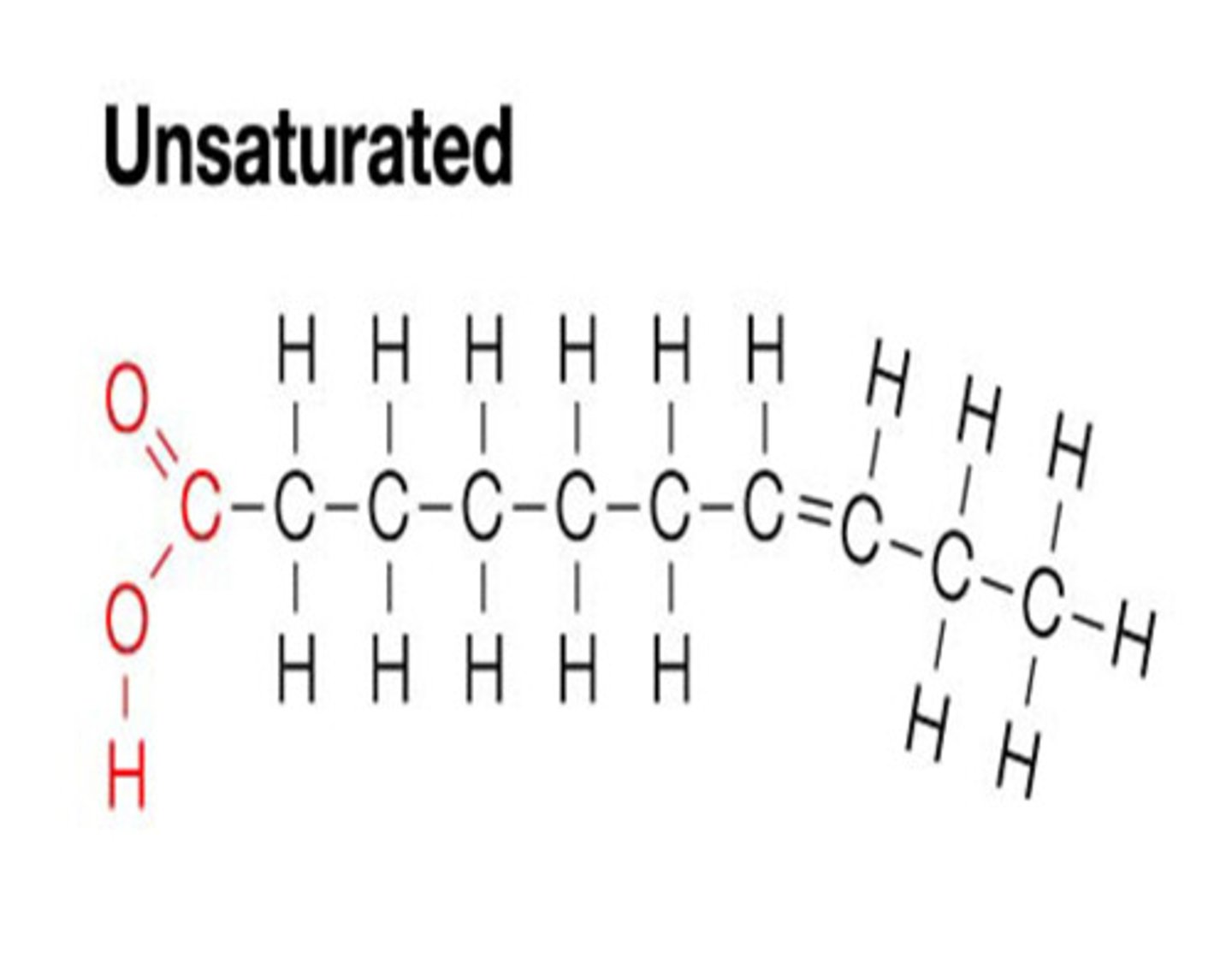
unsaturated fat
Example: Olive oil
Liquid at room temp because presence of cis double bonds prevent molecules from being close together
ester linkage
Bond in fats, between glycerol and the three fatty acids.
trans fat
Unsaturated fats with trans double bonds that cause atherosclerosis
4 functions of fats
1. Storage
2. Insulation
3. Protection
4. Structure Formation
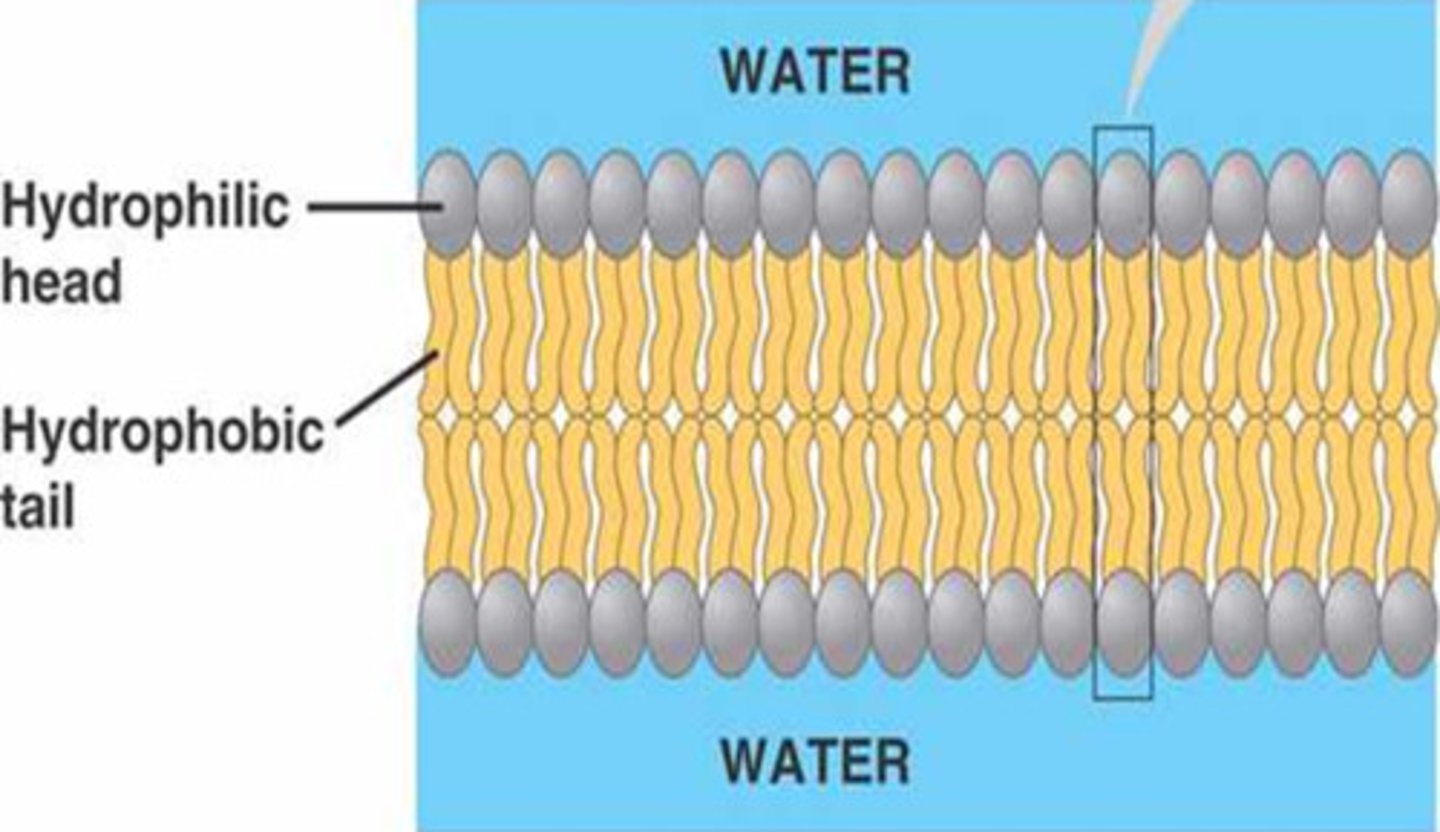
phospholipid
A lipid with a phosphate group in its hydrophilic head, and two nonpolar fatty acid tails; main constituent of cell membranes
steroid
Lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton containing four fused rings.
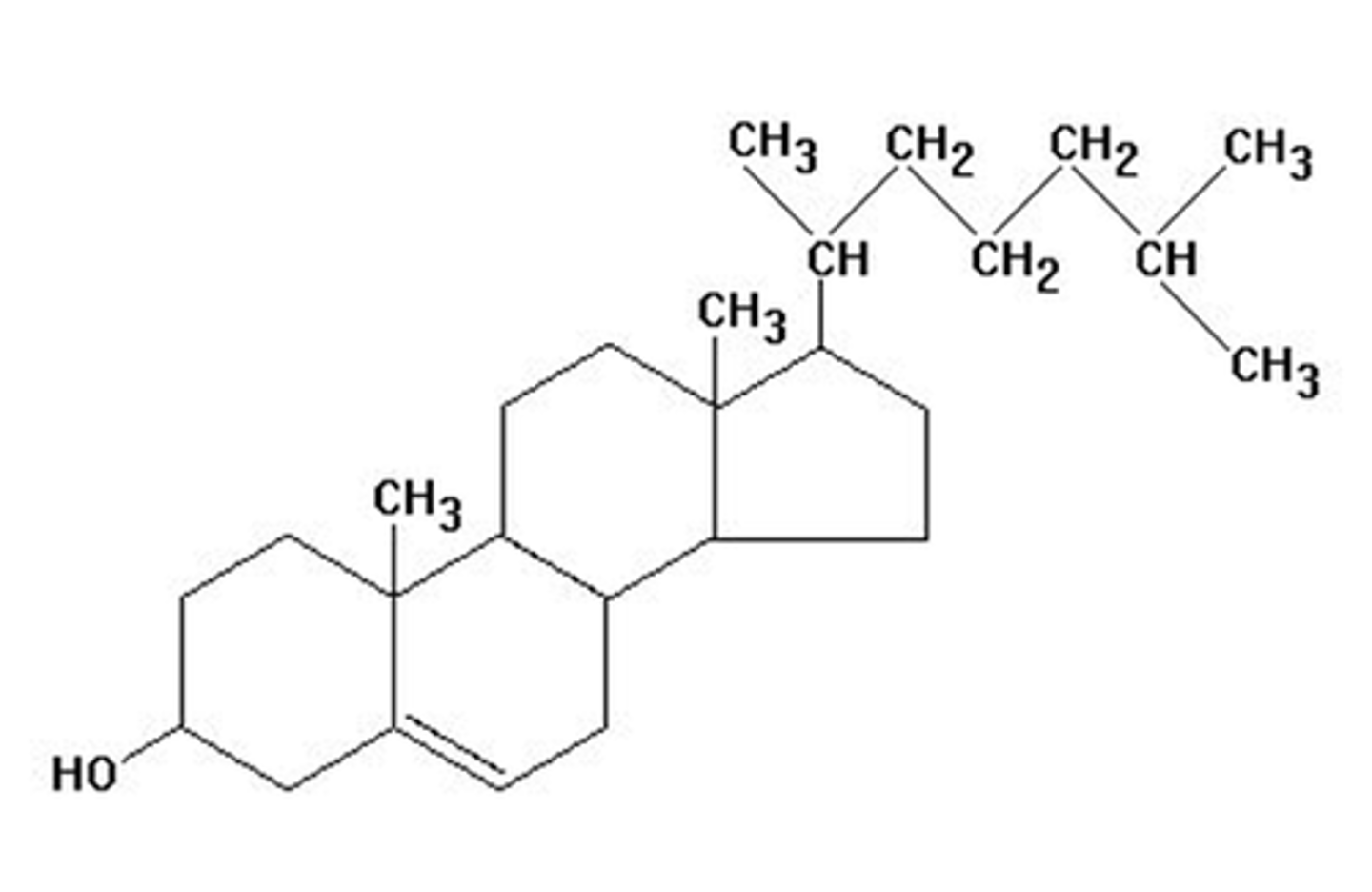
cholesterol
Crucial molecule in animals; is a component of membranes; example of a steroid
catalyst
A substance that affects the reaction rate without being used up in the reaction.
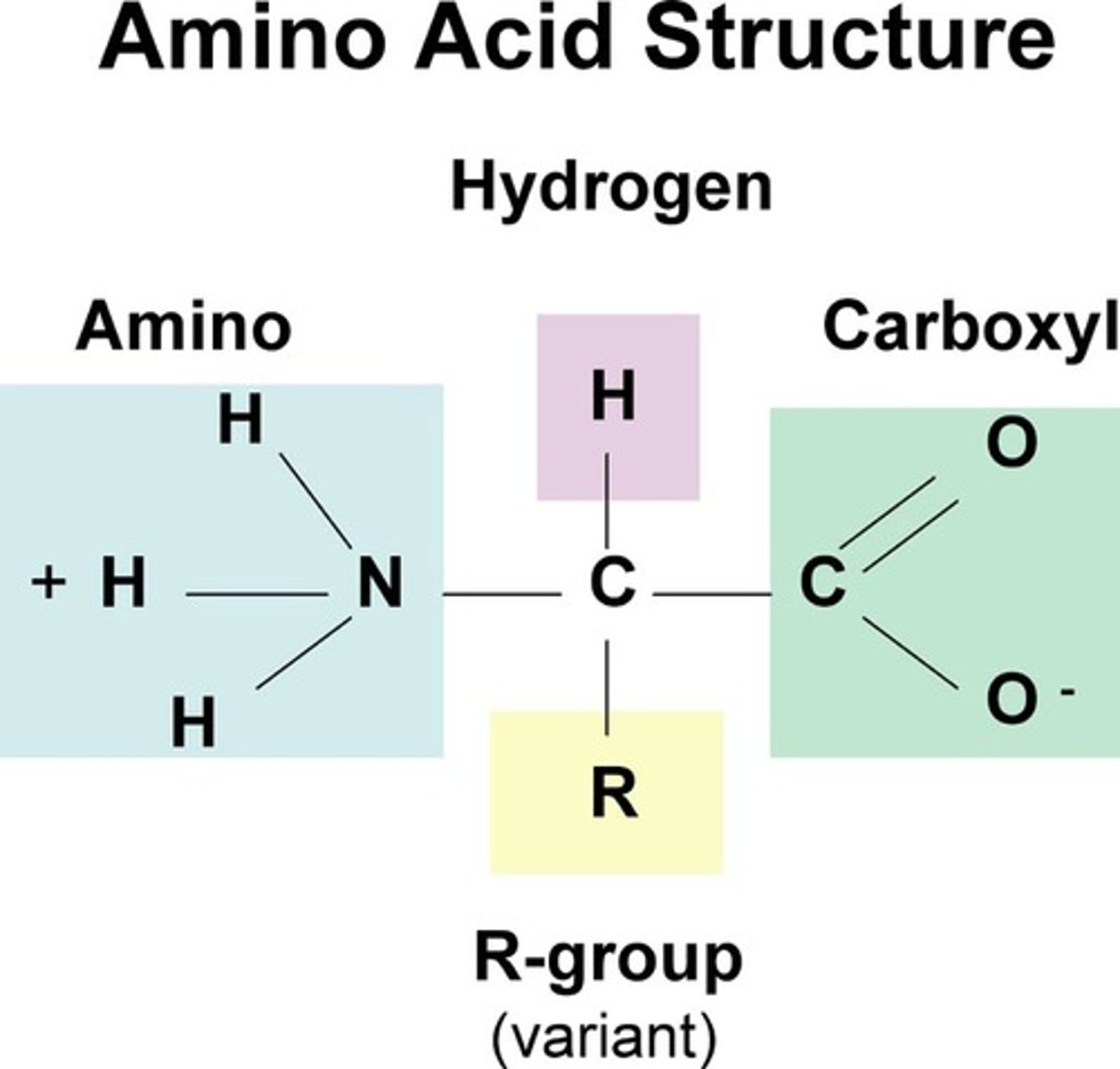
amino acid
A compound that contains both an amino group, a carboxylic acid group, alpha carbon and hydrogen; monomers from which proteins are built.
peptide bond
Bond between an amine group and a carboxyl group of two amino acids, forming bond between C-N
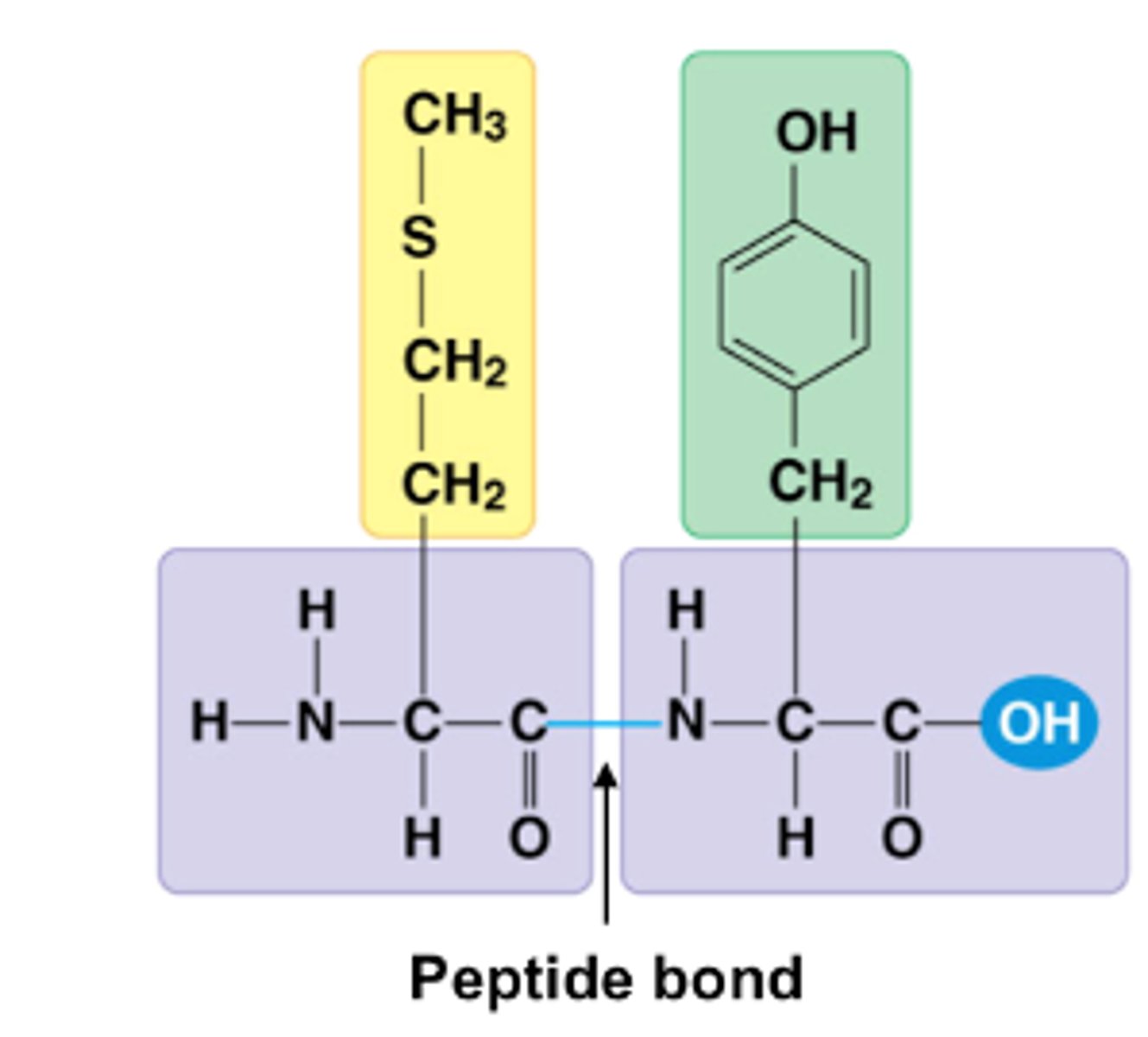
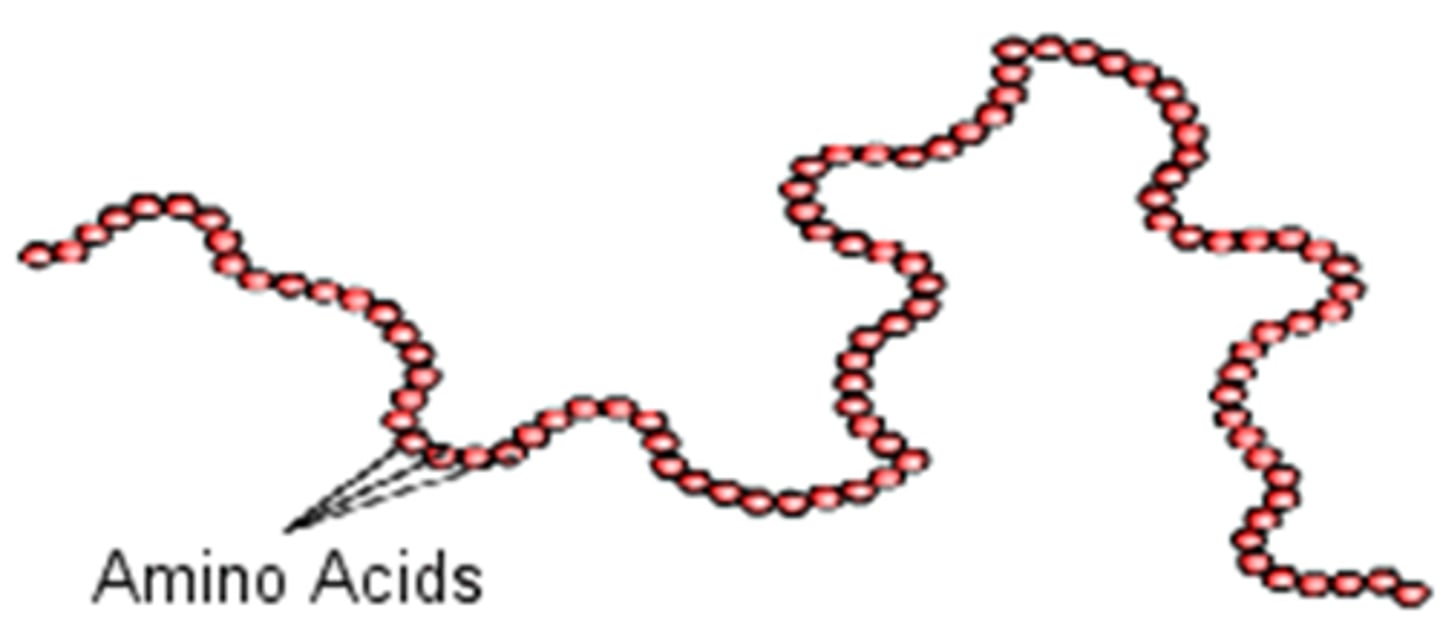
primary structure
the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide

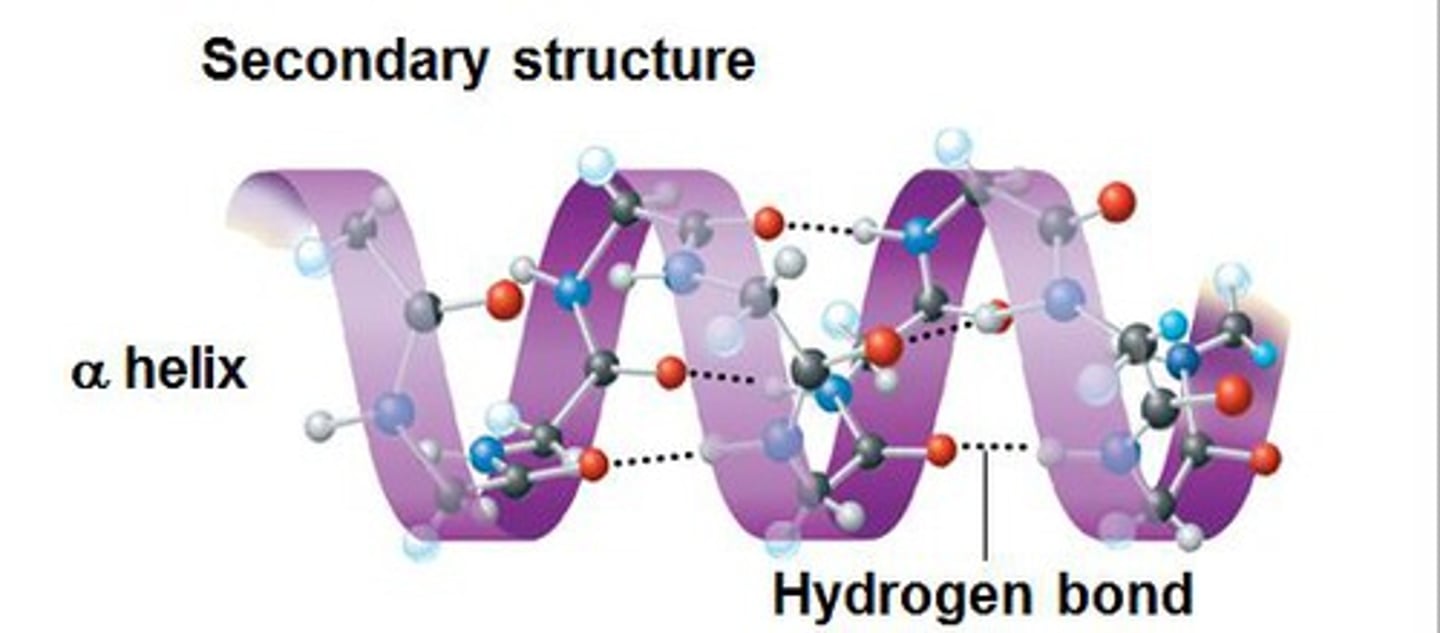
secondary structure
Alpha-helix (twisting formation) or Beta-pleated sheet (where the it lies alongside itself). Reinforced by hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl oxygen and the hydrogen on the amino group.
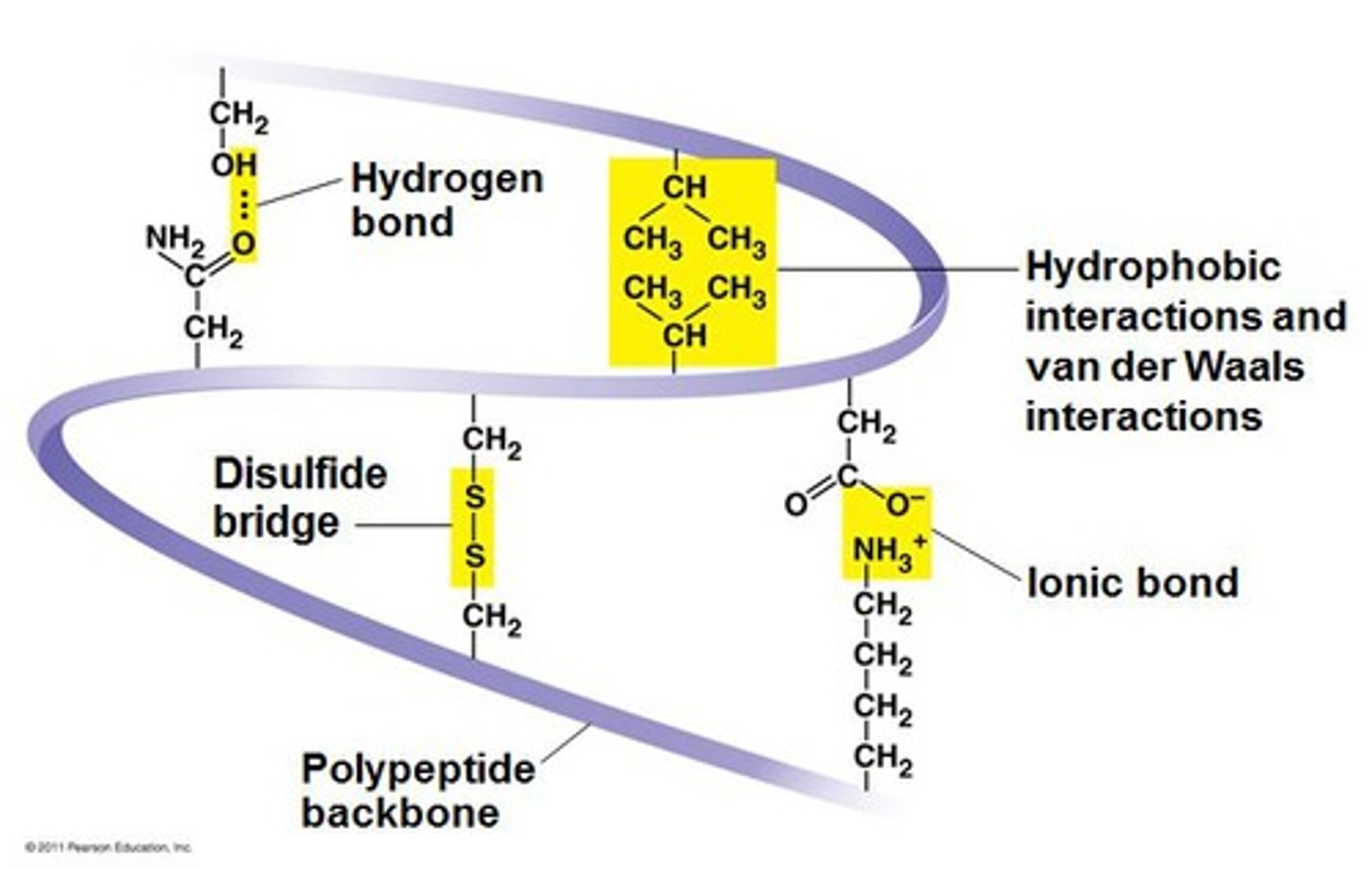
tertiary structure
Overall shape of a polypeptide resulting from interactions between R-groups
- Hydrophobic interactions lead some to hide in center
- Disulfide bridges form between two cysteine groups
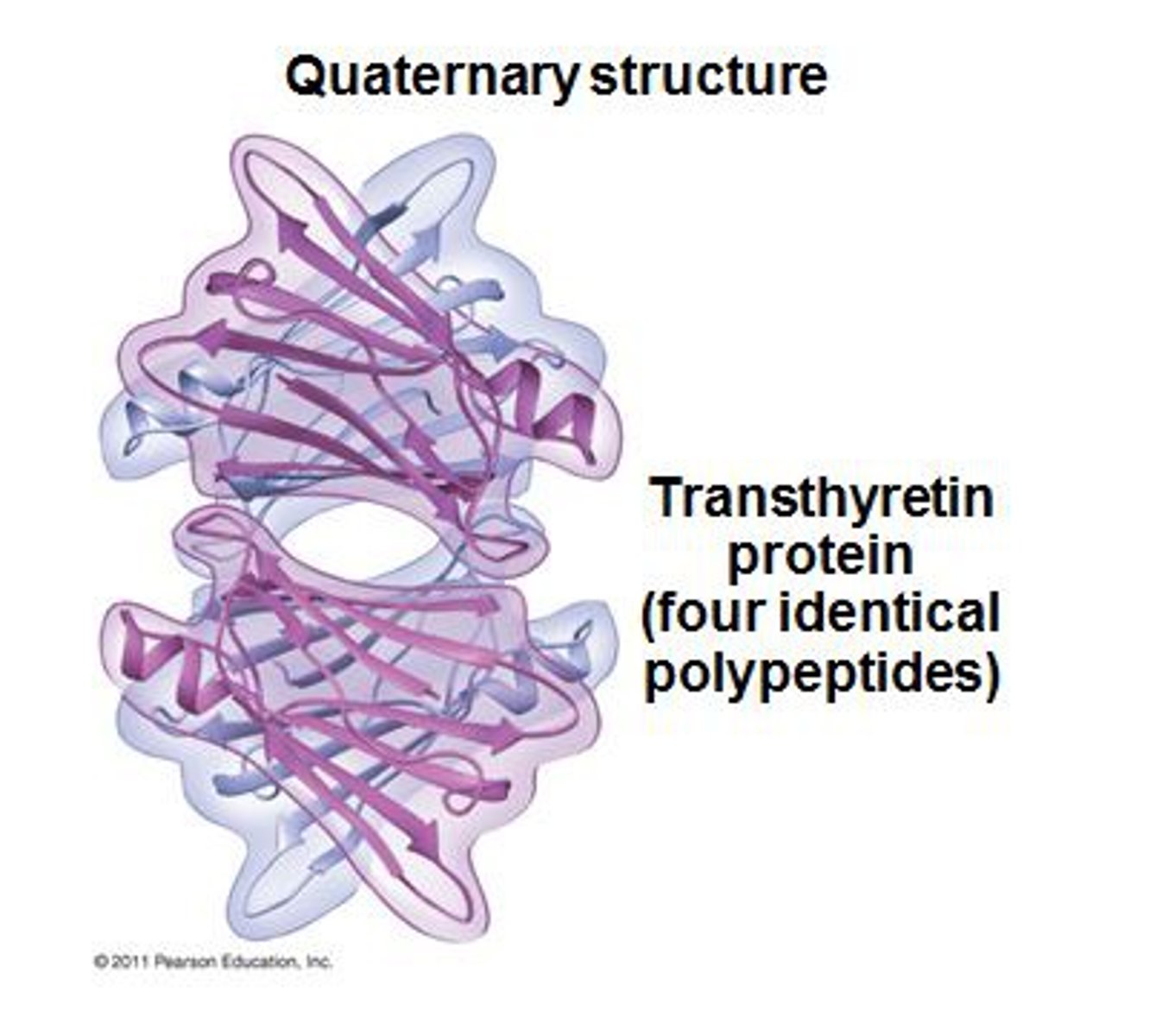
quaternary structure
When two or more globular polypeptide chains bind together. Same forces in tertiary structure at work in quaternary structure.
alpha helix
A spiral shape constituting one form of the secondary structure of proteins, arising from a specific hydrogen-bonding structure.
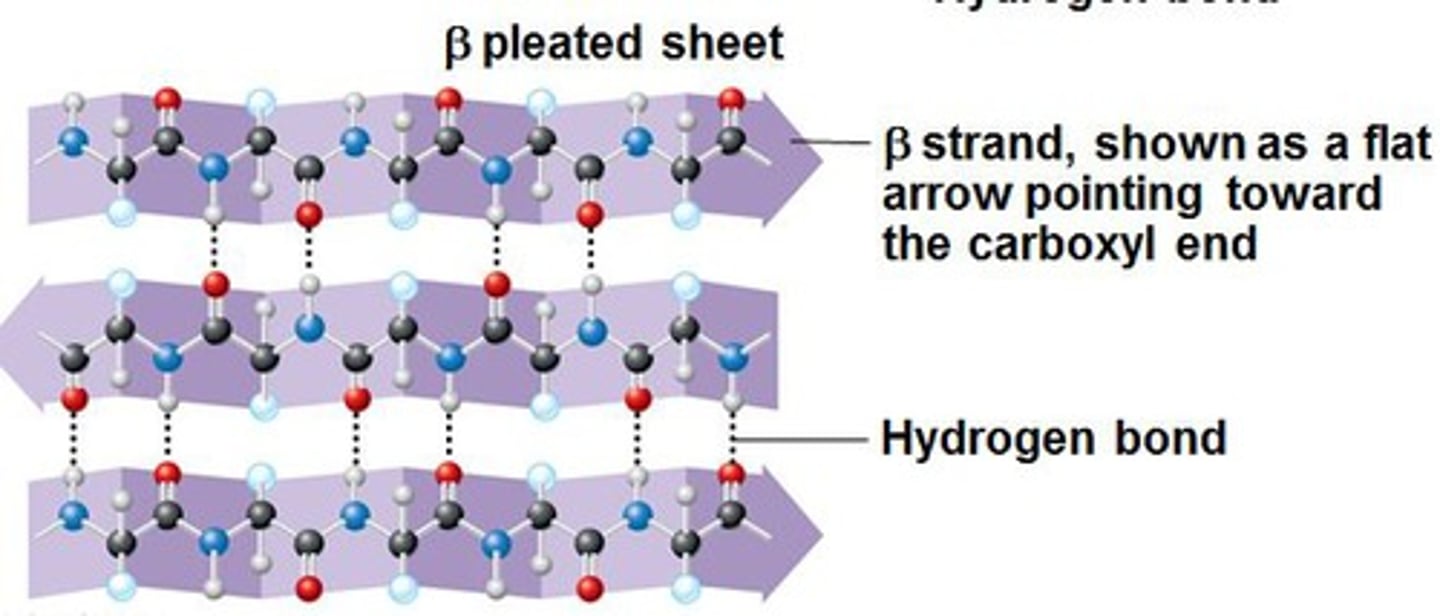
beta pleated sheet
One form of the secondary structure of proteins in which the polypeptide chain folds back and forth, or where two regions of the chain lie parallel to each other and are held together by hydrogen bonds.
denaturation
When a protein's chemical bonds and interactions are altered due to...
1. change in pH
2. change in temperature
3. change in salt concentration
and becomes misshapen, preventing it from fulfilling its duties
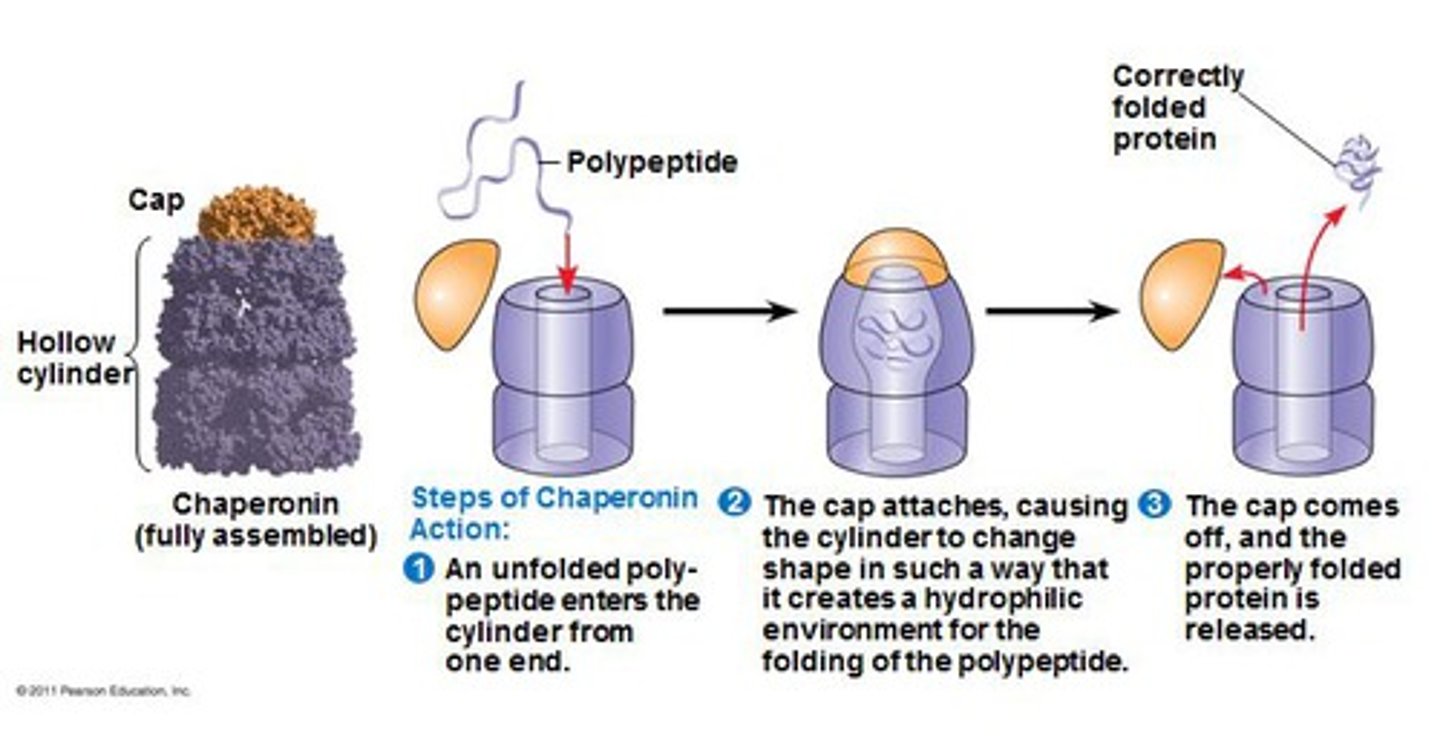
chaperonin
Proteins that assist in the proper folding of proteins
DNA
Deoxyribose, ATCG, double stranded, stores hereditary information
RNA
Ribose, AUCG, single stranded, gene expression and protein synthesis
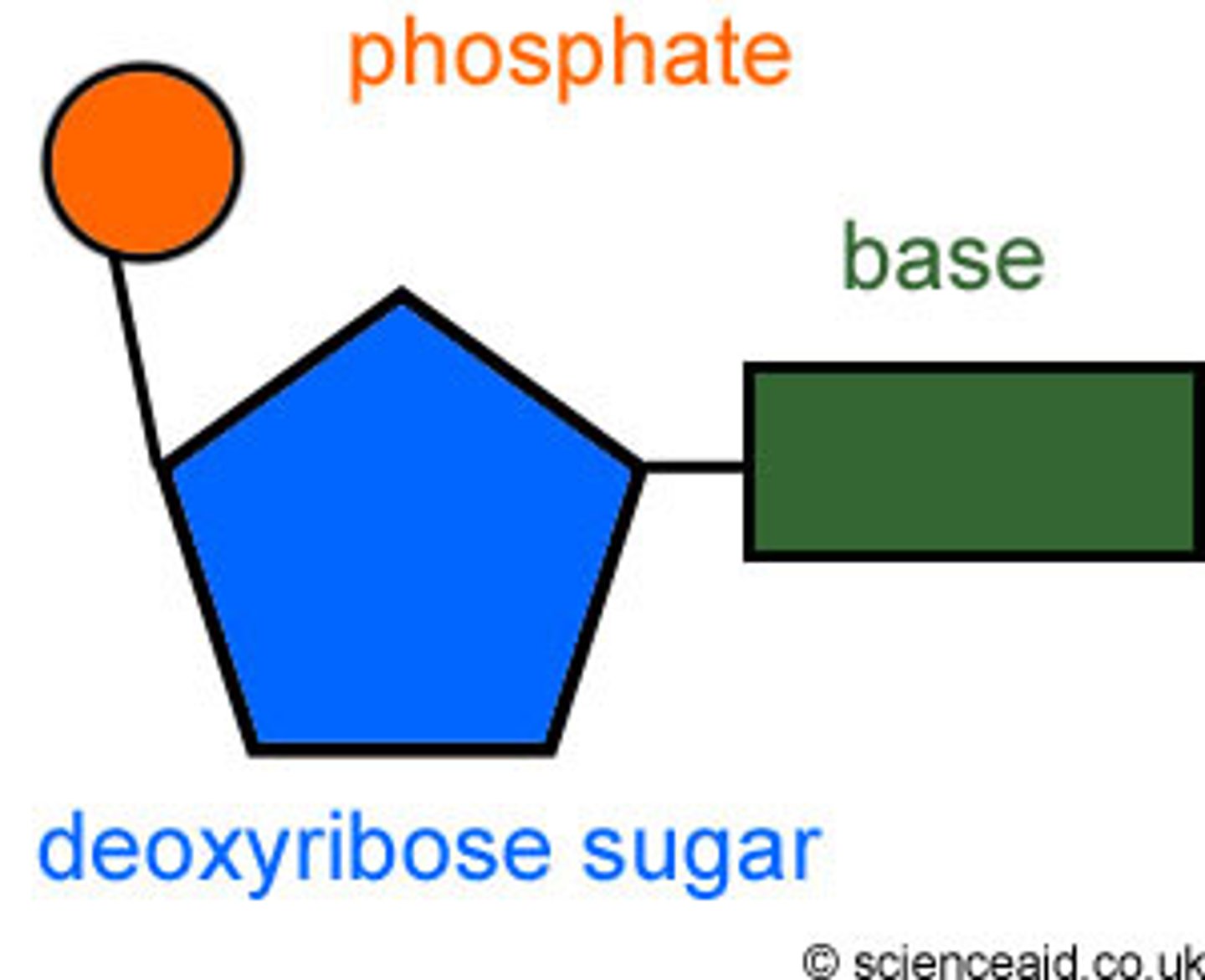
nucleotide
consists of a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Guanine (purine), Uracil (pyrimidine), Thymine (pyrimidine), and Cytosine (pyrimidine).
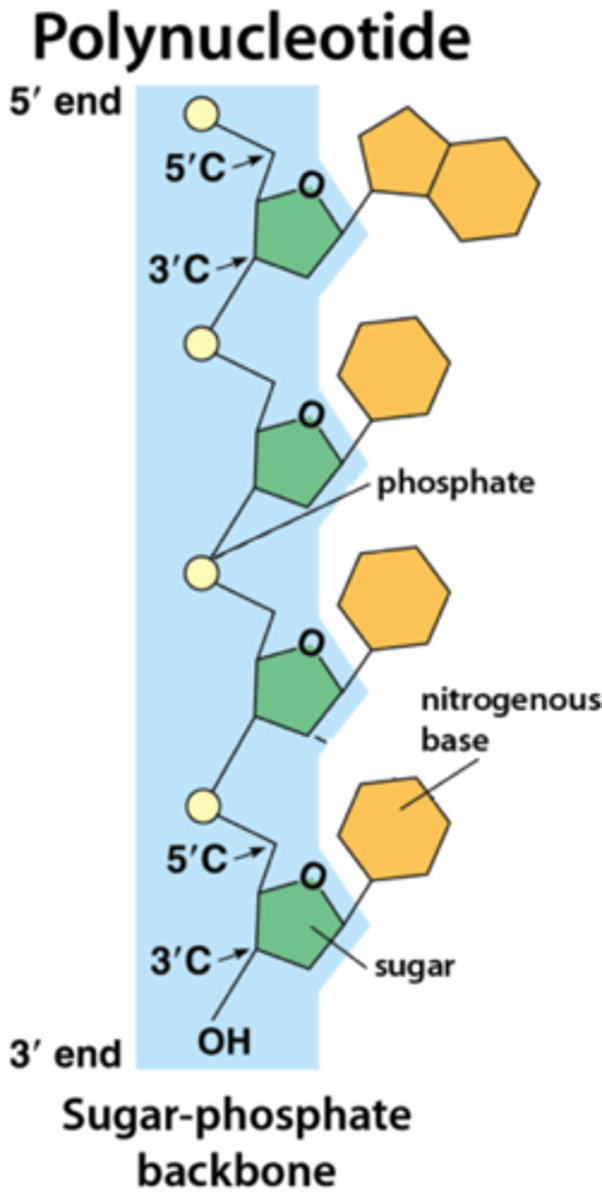
polynucleotide
DNA nucleotides combined together
purine
Adenine and Guanine, has 2 rings
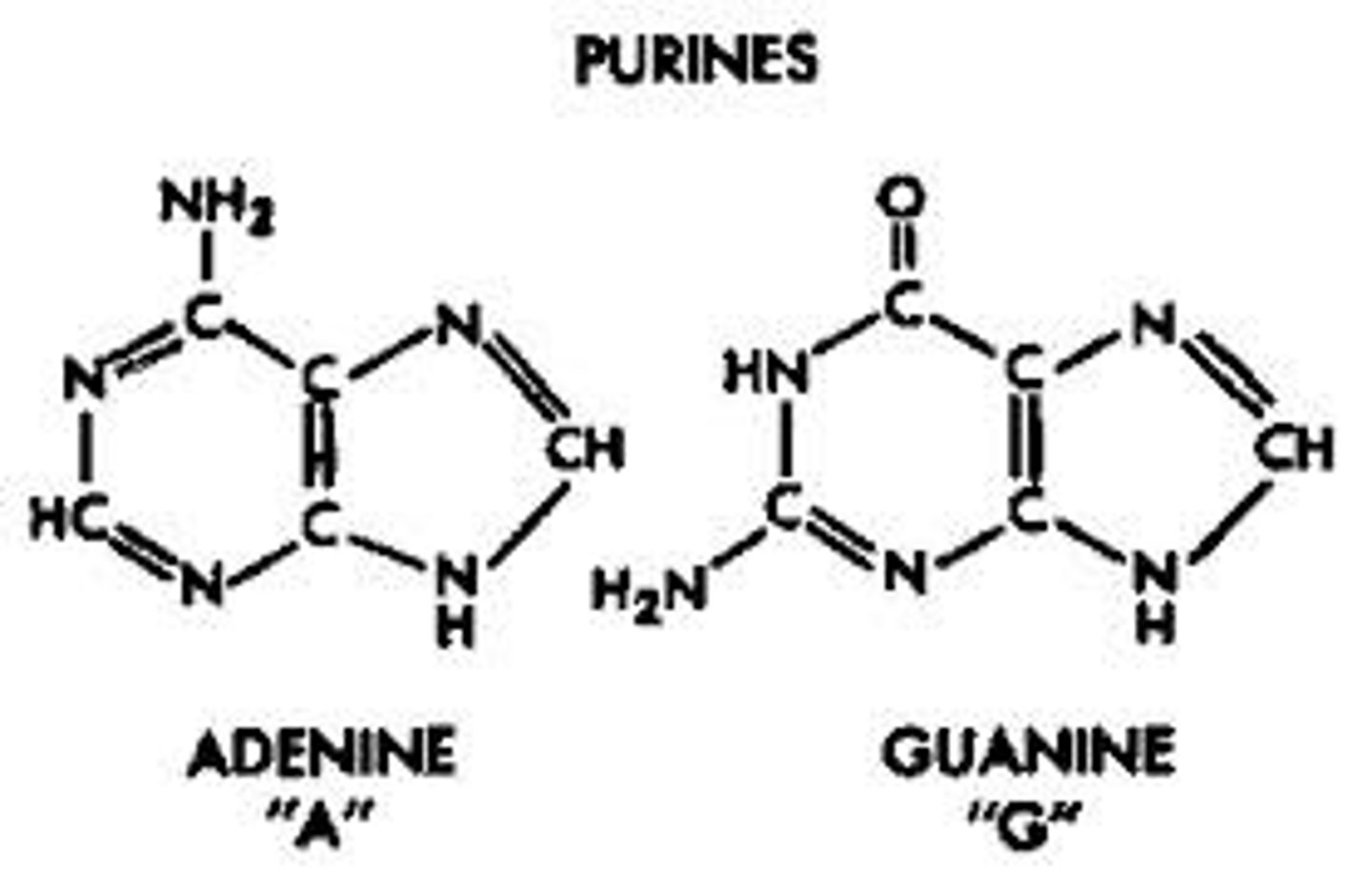
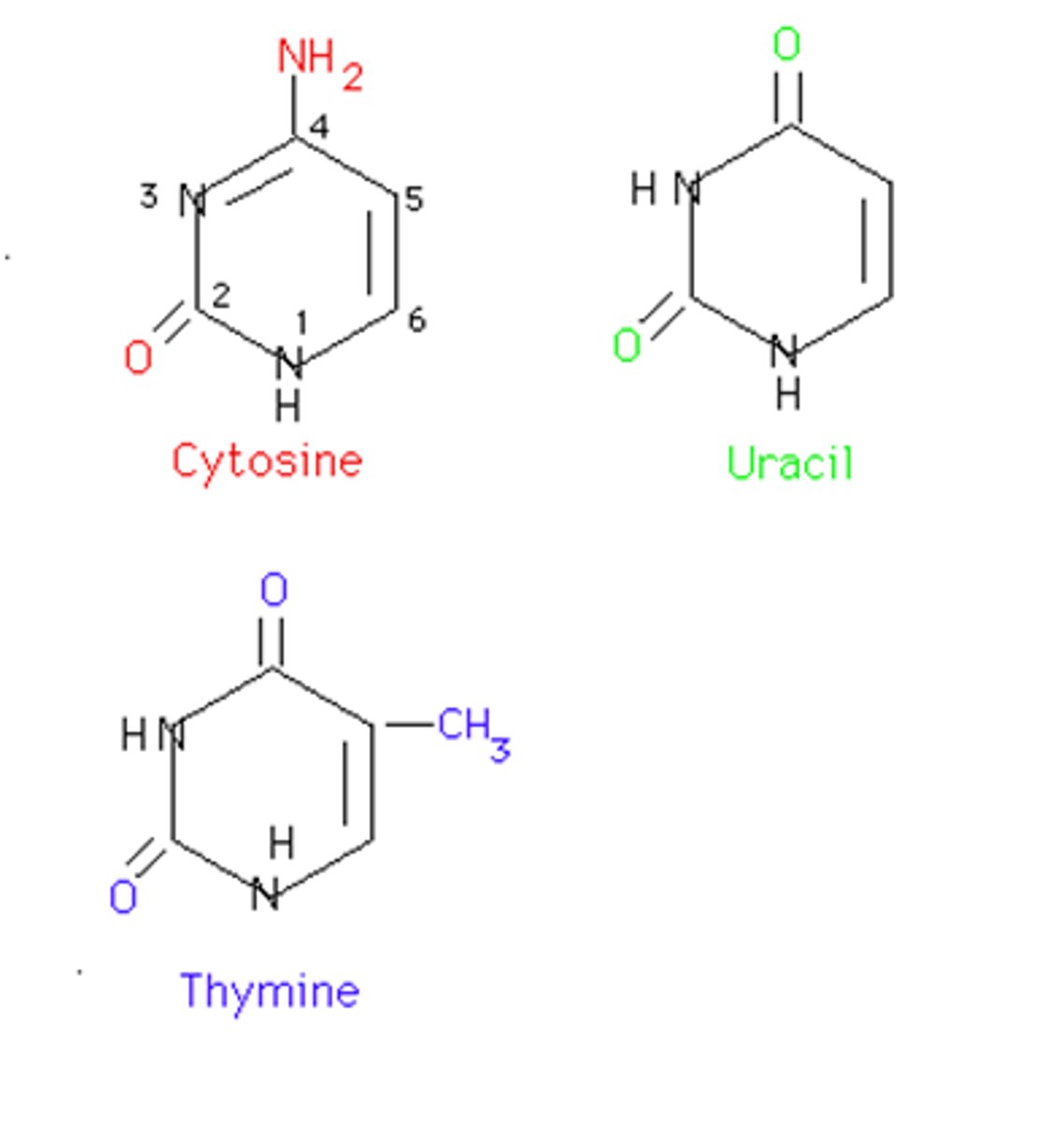
pyrimidine
Thymine, Cytosine, and Uracil, one ring
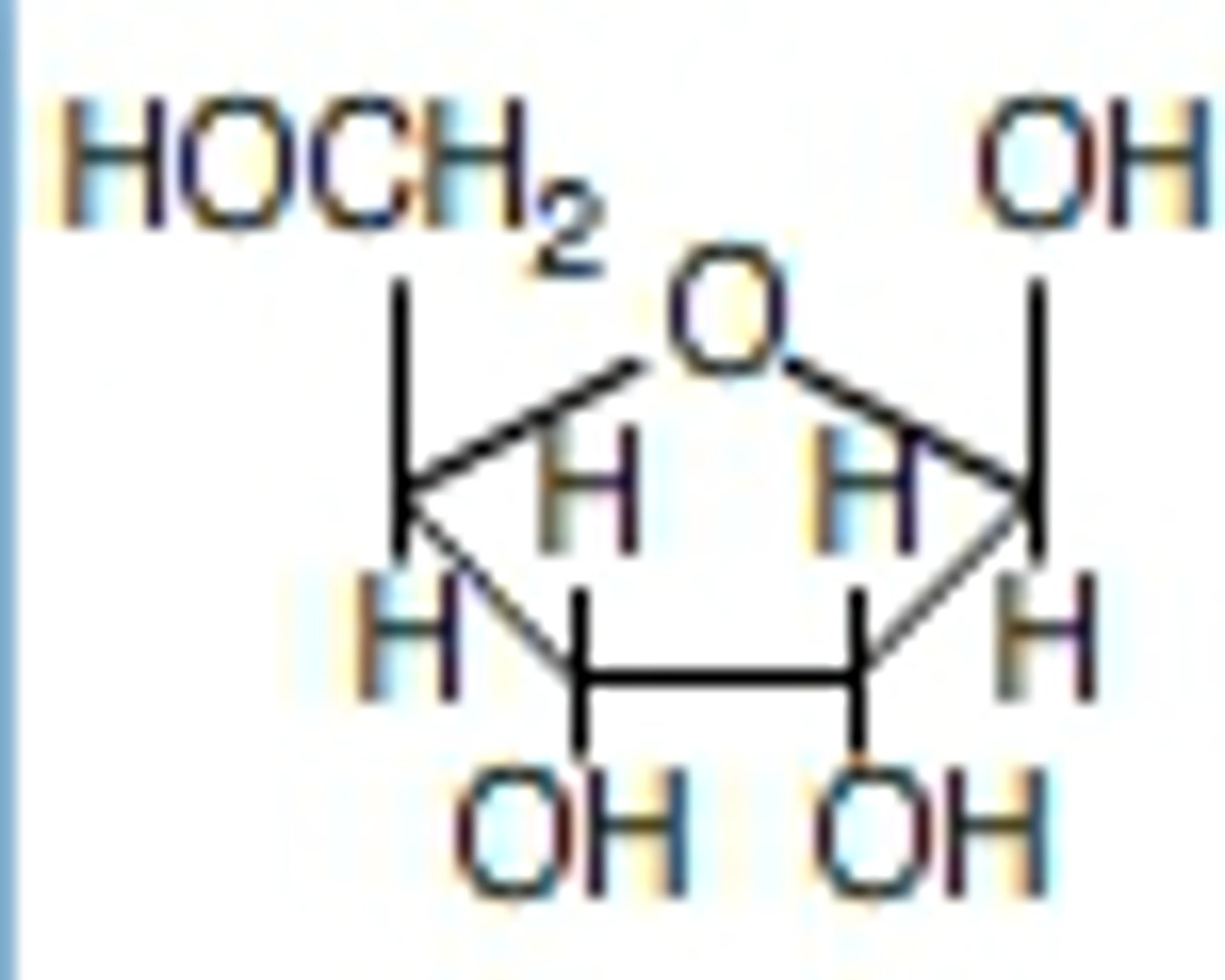
ribose
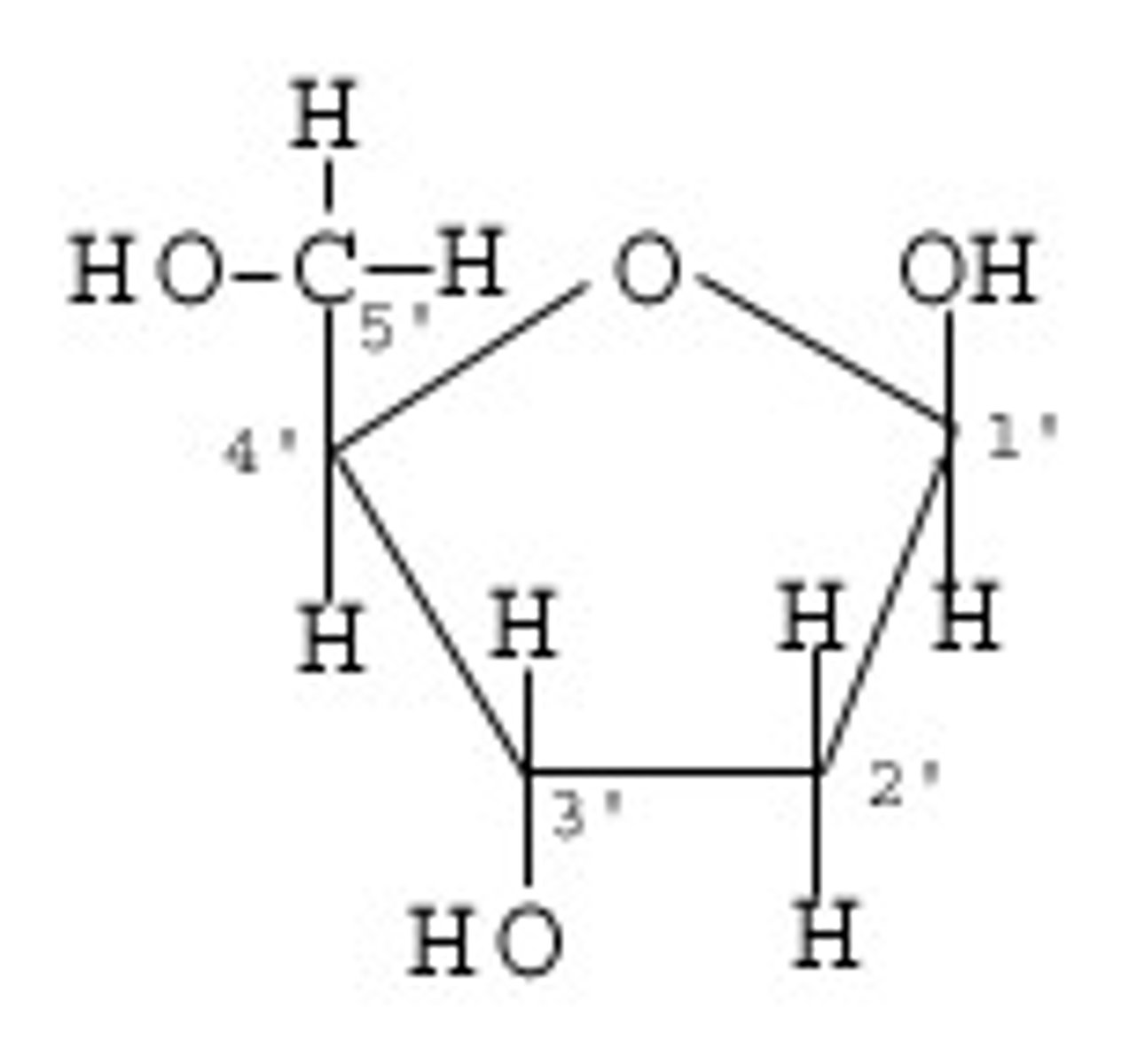
deoxyribose
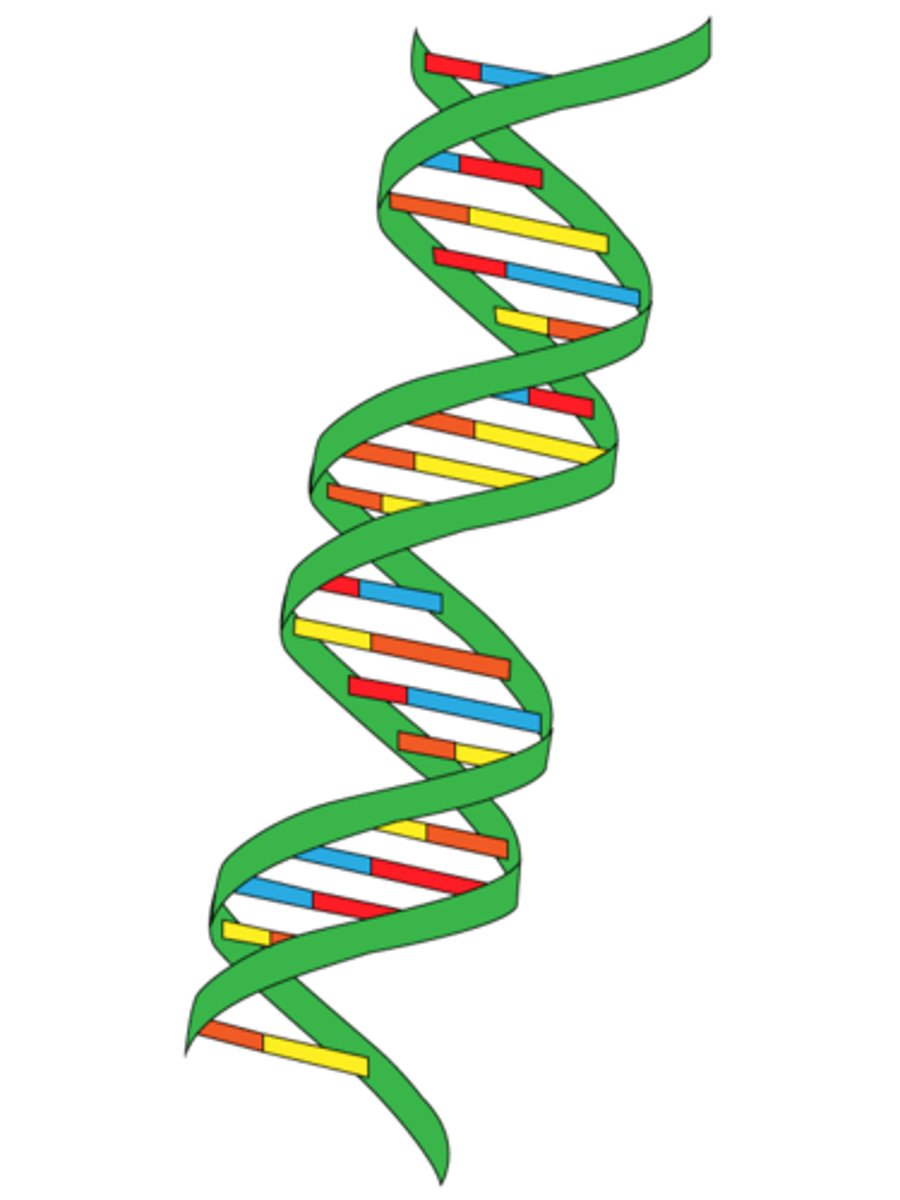
double helix
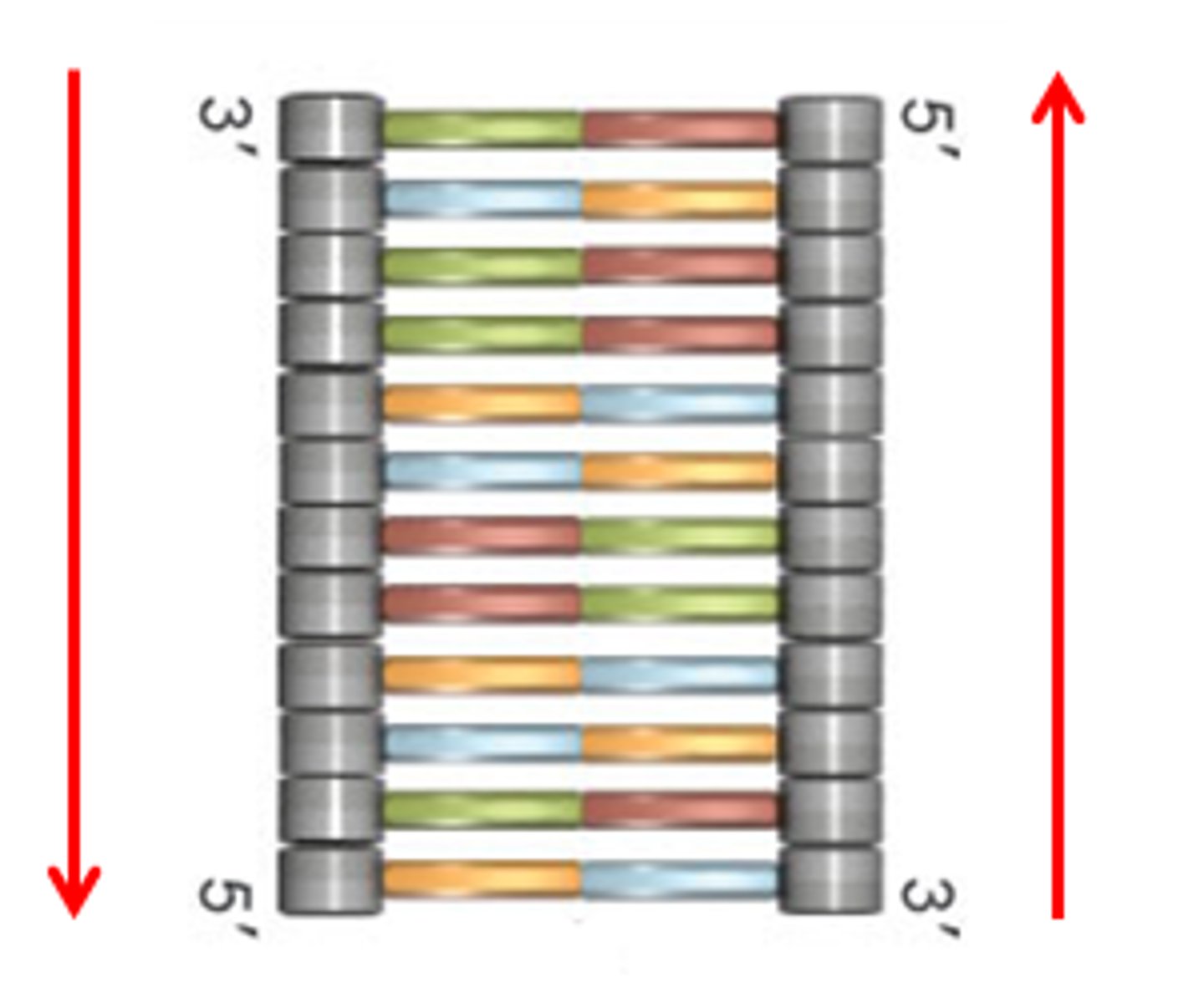
antiparallel
the 5' end of one strand will align with the 3' end of the other strand
Enzymatic protein
Protein that accelerates chemical reactions.
Ex. digestive enzymes catalyze hydrolysis to digest food
Storage protein
Protein that stores amino acids
Ex. Casein is a milk protein that is a source of a.a. for baby mammals
Hormonal protein
Protein that coordinates organism's activities
Ex. Insulin regulates blood sugar concentration
Motor protein
Protein that is responsible for movement
Ex. Actin and myosin contract muscles
Defensive protein
Protein that protects against disease
Ex. antibodies destroy viruses and bacteria
Transport protein
Protein that transports substances
Ex. Hemoglobin transports oxyen in blood
Receptor protein
Protein that tells the cell to respond to chemical stimuli
Ex. Receptors in nerve cells detect signalling molecules
Structural protein
Protein that supports structures
Ex. Keratin makes up hair, horns, feathers, etc
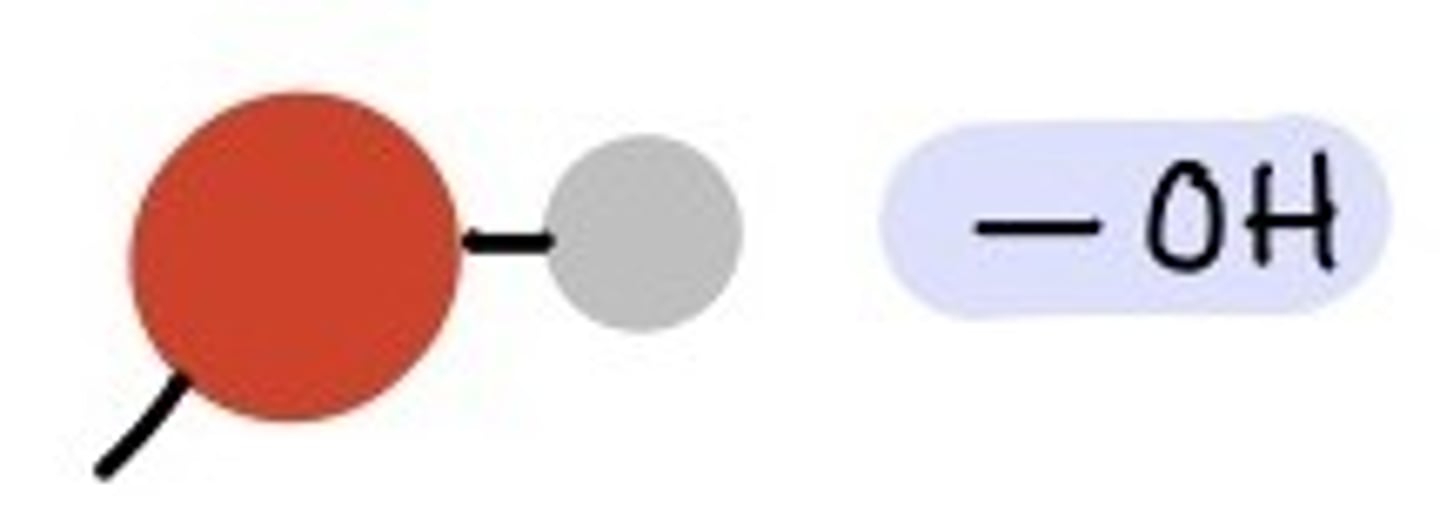
Hydroxyl
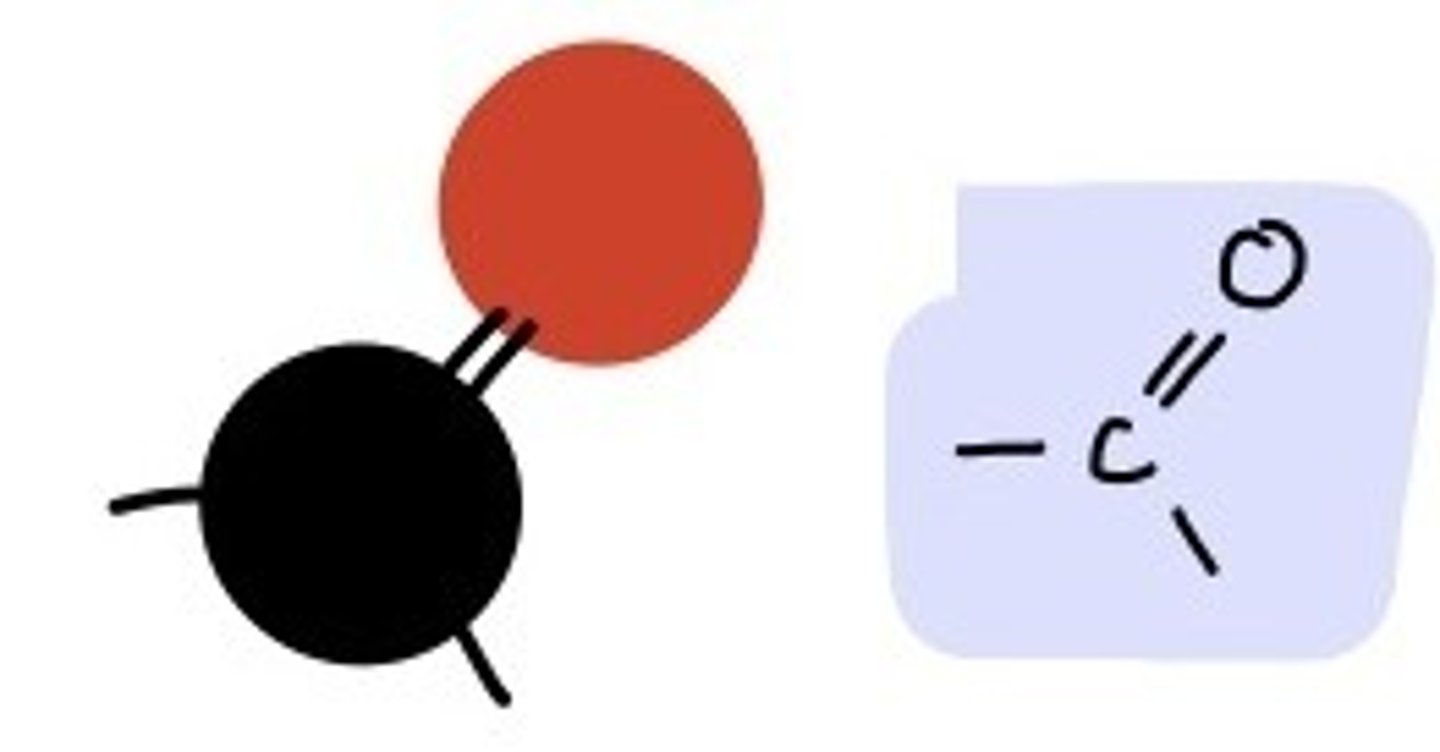
Carbonyl
Carboxyl
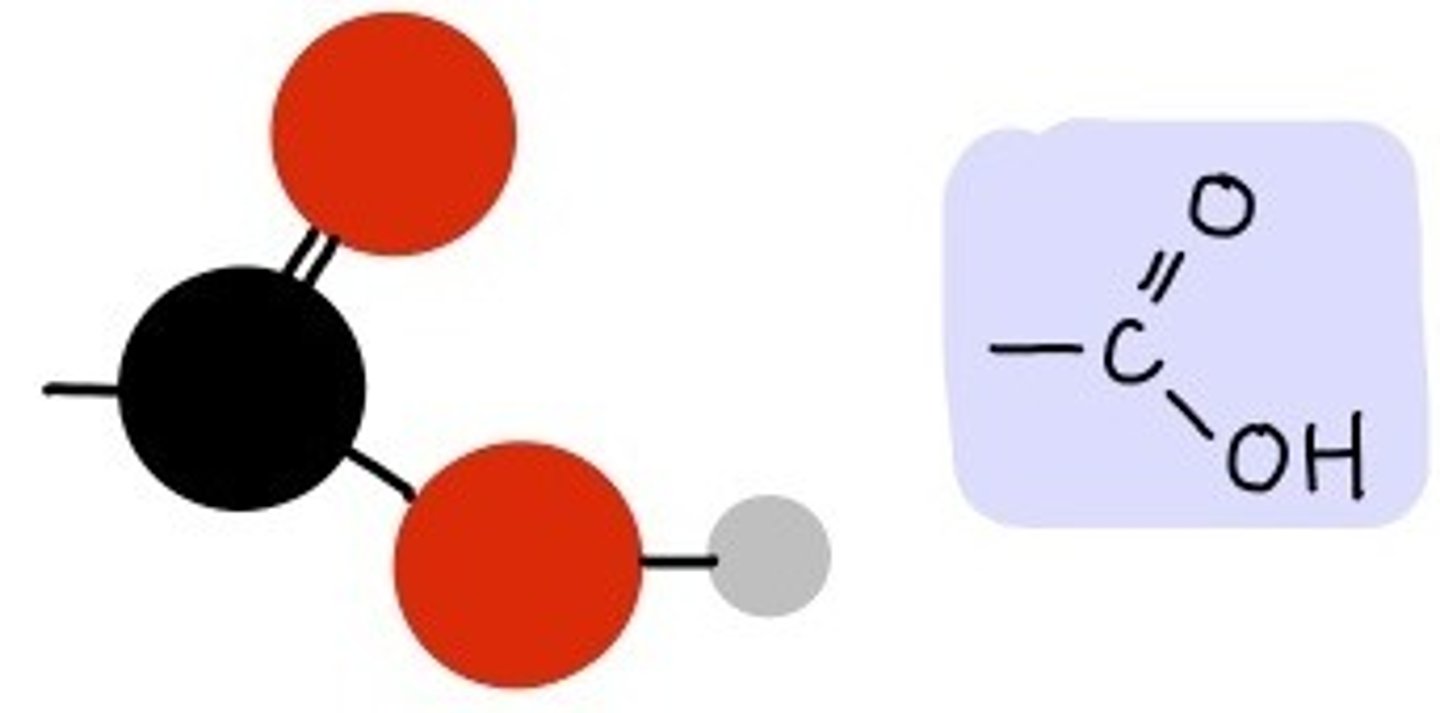
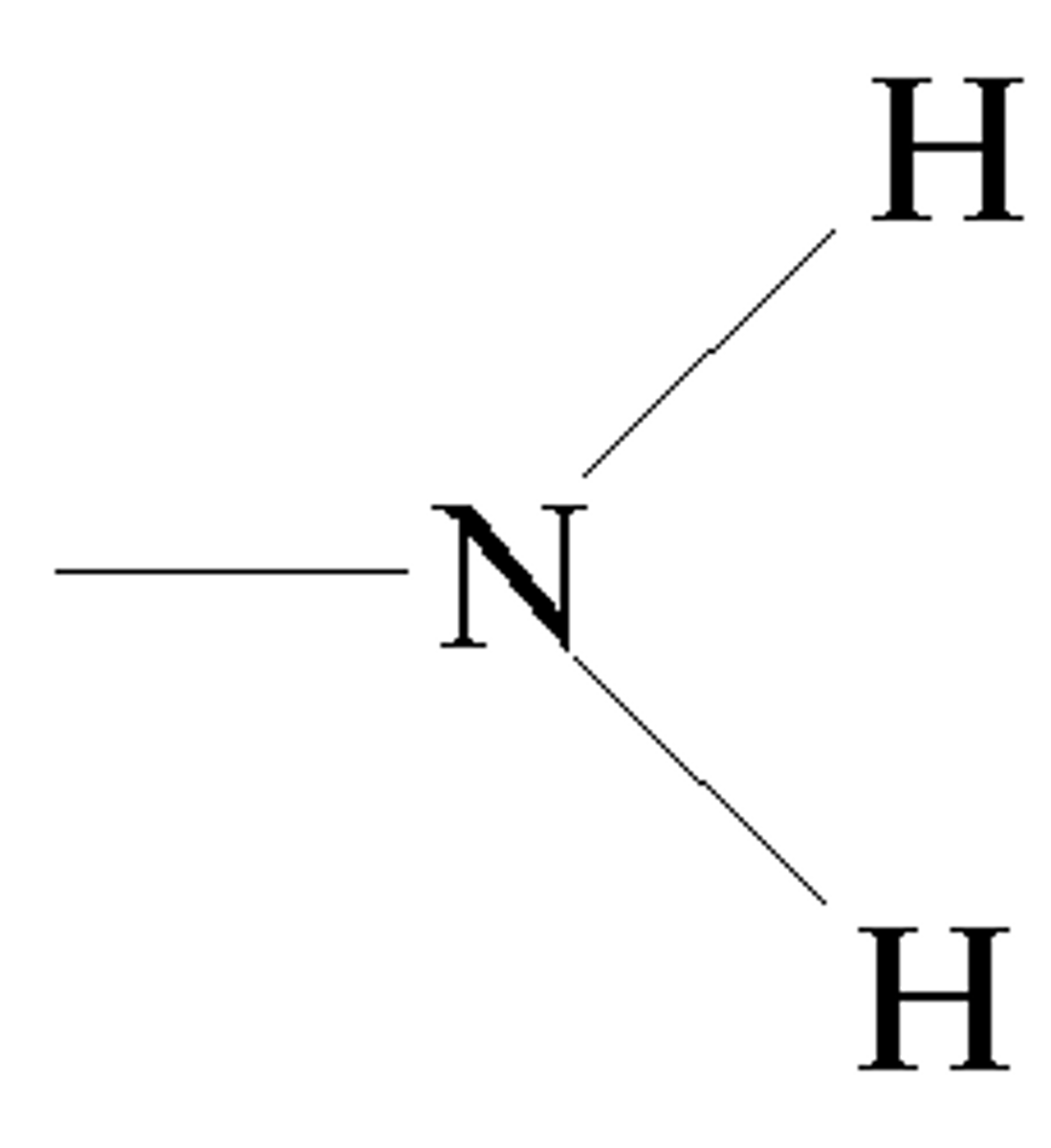
Amino
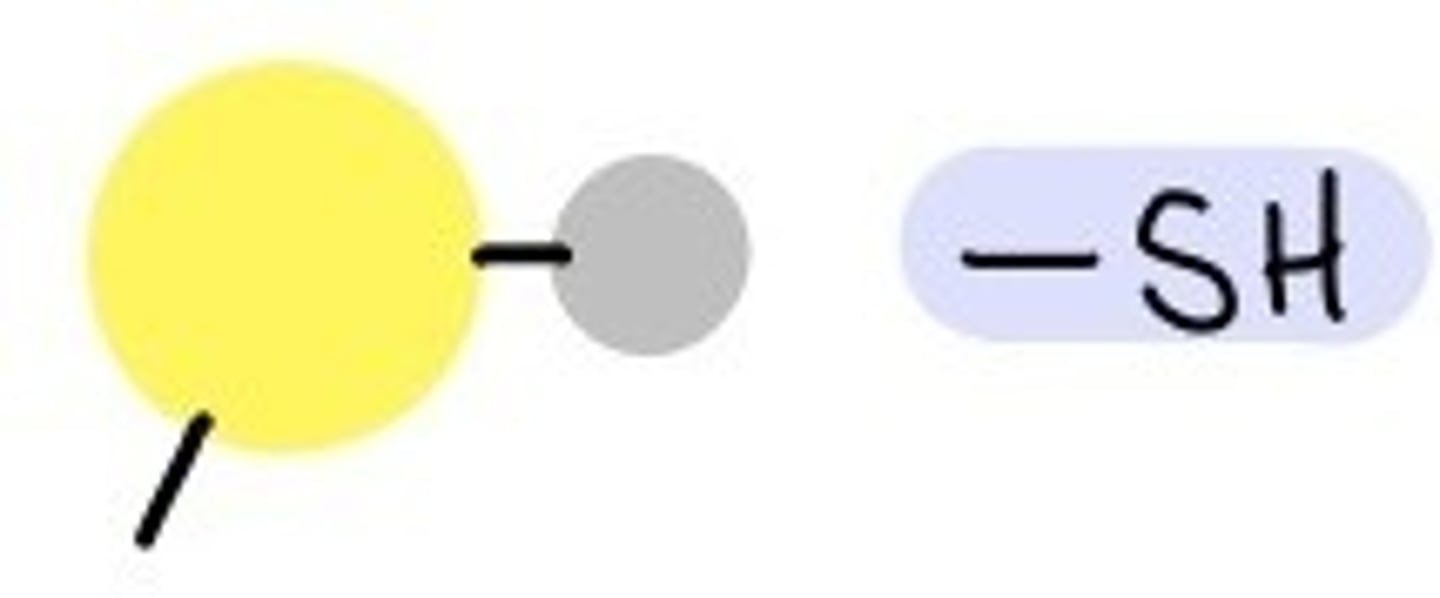
Sulfhydryl
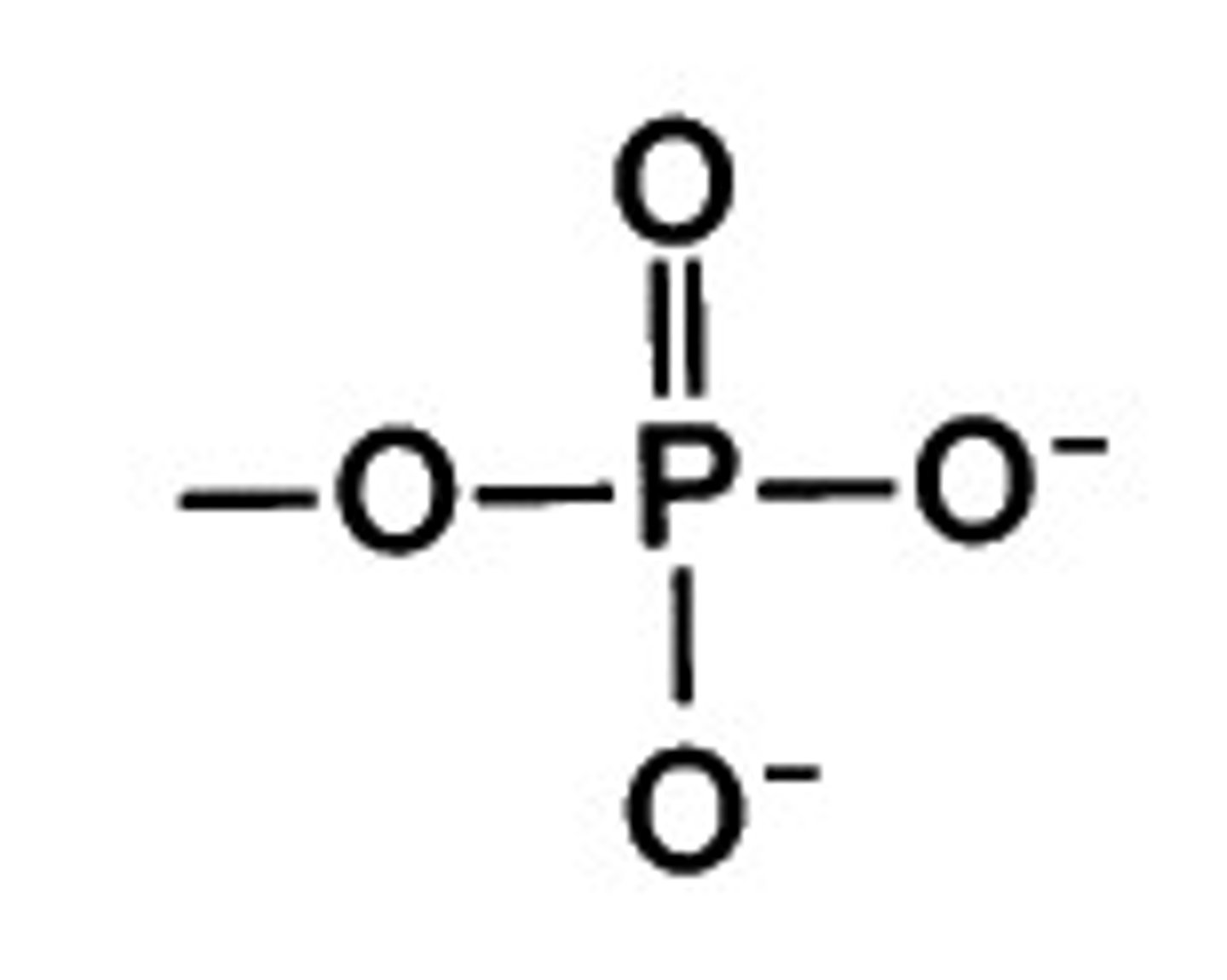
Phosphate
Methyl
Dehydration reactions
Create polymers from monomers by removing water
Hydrolysis
Water is added to split large molecules
Carbohydrate
Simple sugars and polymers; CH₂O