Bio 110 Exam 2 Protists, Mitosis, Translation and Transcription
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Where is the Nucleus located?
Inside the cell’s cytoplasm, surrounded by a cell membrane called the nuclear envelope. Hold our DNA and gene expression
What is the flow of proteins in our endomembrane system?
Either SER (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) or RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum)
Smooth ER deals with toxins and breaks them down
Rough ER has ribosomes on the surface and receives proteins and synthesizes them (packages) from Nucleus either exports them or keeps them
Transports proteins through vesicles to Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus tells protein where to go, exports out of the cell or exports inside the cell to somewhere else also through vesicles.
What is the function of Lysosomes in the cell?
Breaks down waste materials by engulfing them. Hydrolase enzymes initially degrade the content.
What type of molecule are gangliosides? How can the accumulation of them cause Tay-Sachs disease?
It is a lipid molecule, neuronal cell that regulate the accumulation of gangliosides. Tay-Sachs destroy these neuronal cells leading to increases gangliosides.
Proteins that help transport molecules across the phospholipid bilayer most likely have R-groups that are _______.
both hydrophobic and hydrophilic
A cell that secretes proteins acquires a mutation that results in polypeptides bypassing the Golgi apparatus. What will be wrong with the proteins secreted from this cell?
They will be missing post-translational sugars.
Based upon what you have learned about the cytoskeleton in the tutorial, how is taxol most likely to kill a dividing cancer cell?
Taxol disrupts normal formation of the mitotic spindle necessary for chromosome movement during cell division. The cells does not split/divide and eventually just dies.
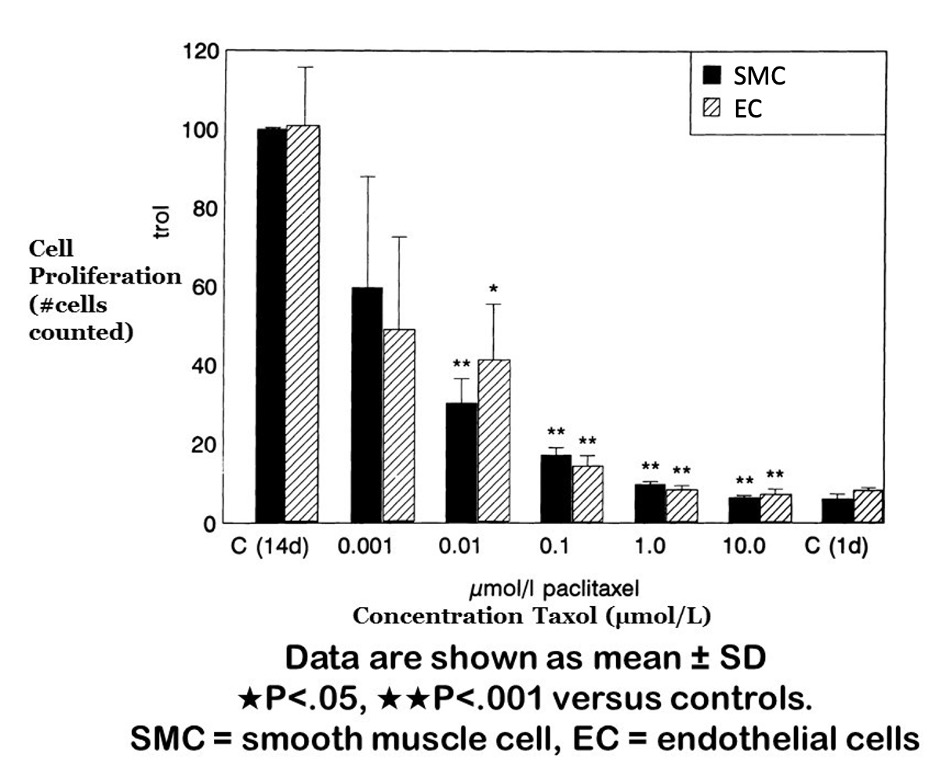
How does cell proliferation change with increasing concentrations of paclitaxel (taxol)?
There is a significant decrease in cell proliferation for both SMC and EC at taxol concentrations >0.01.
What are Microtubules made from and what process are they used for?
they are made from tubulin molecules and are used in Meiosis and Mitosis to drag/move chromosomes to each side of the cell
What are intermediate filaments and what is an example of them in action?
They are fibrous proteins that help reinforce cell structure by anchoring the organelles and resist the cell from tearing/splitting until ready
What are Microfilaments and what is an example of them in action?
They are tiny polymerized proteins and they are used in muscle contraction, help maintain cell structure
Which of these supports the idea that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once prokaryotic symbionts? Select all that apply.
Their size is comparable to a prokaryote.
They have a circular DNA molecule.
They reproduce by binary fission.
Which of the following is a hypothesized selective pressure for the endosymbiotic theory for mitochondria?
Increasing atmospheric levels of oxygen that can damage molecular bonds, pushed Mitochondria to use O2 for more energy production
What is Central Dogma?
the description of DNA to RNA and RNA to proteins processes
What is Central Dogma in a Prokaryotic cell? In a Eukaryotic cell?
Transcription of DNA to mRNA
Translation of mRNA to proteins using a ribosome and a polypeptide is attached
Transcription of DNA to mRNA
Pre-RNA is attached called RNA processing
Translation of mRNA using a polypeptide and ribosome and attaches it to RER
Sent to Golgi Apparatus
Where do the proteins go after DNA is transcribes and translated inside the Nucelus?
Transported inside a vesicle enters the RER to be synthesized (re-arranges proteins to where they are needed) send to Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus receives protein and packages the protein in vesicles to either outside the cell or inside
How did Eukaryotes evolve from Prokaryotes?What were the first types of Eukaryotes?
Through a endosymbiotic relationship.
Protists
Which of the following statements about “protists” is true?
a All “protists” are prokaryotes.
b All “protists” are unicellular.
c Some “protists” are capable of photosynthesis.
d Some “protists” can be photoheterotrophs.
e All except A are true.
C. Some “protists” are capable of photosynthesis
Describe the basic characteristics of Protists, are Protists Eukaryotic or Prokaryotic?
Protists are Eukaryotic but some of them are unicellular some are multi-cellular, they are photoautotrophs and chemoheterotrophs.
What kind of organism causes Malaria? Why has it been so hard to develop treatments or vaccines for this disease?
Plasmodium, a parasitic protists, they have a complex life cycle and high genetic variability, they also hide in liver and blood cells
True or False: The cell of a typical single-celled “protist” is much less complex than an animal cell.
False. Single-celled “protists” must carry out all basic life functions in their single cell.
Euglena gracilis is a single-celled species of protist that can use sunlight or organic matter as an energy source. This organism is best classified as a______________.
Mixotroph. Uses both photoautotroph and chemoheterotroph
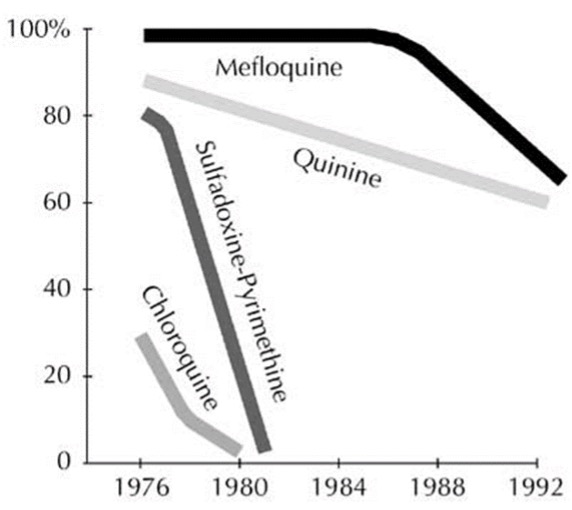
What does the graph indicate about the effectiveness of the anti-malarial drug mefloquine over time?
Effectiveness decreases
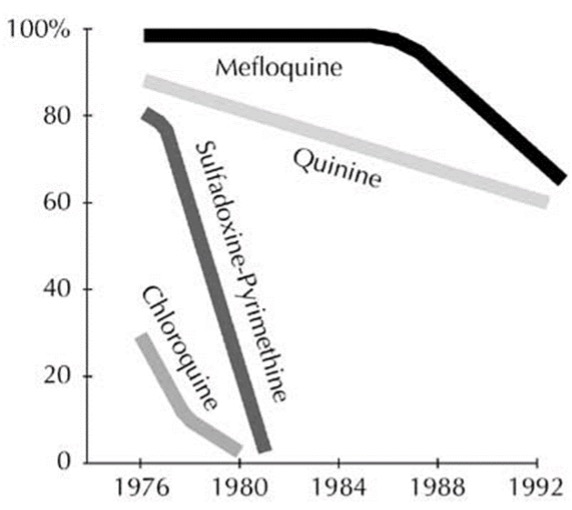
What is true about the malarial resistance to mefloquine?
Within the parasite population, some individuals are more resistant to mefloquine, and will survive and reproduce at a greater rate than less resistant individuals.
What is most accurate about mosquito resistance to insecticides?
Within the mosquito population, some individuals are more resistant to insecticides and will survive and reproduce at a greater rate than less resistant individuals.
Wolbachia is a symbiont that lives in mosquito’s cells and can make them resistant to Plasmodium how does the bacterium help in the fight against malaria?
It makes mosquitoes resistant to infection by Plasmodium.
What are photosynthetic protists and how are they primary producers?
They use light energy and convert CO2 into sugars and make O2 as a product, allowing O2 in water and soil.
What is coral bleeching?
The lack of zooxanthellae that give nutrients to coral, coral lose their color due to pollution and radiation
In recent years, shrimp have declined in the Gulf of Mexico. What do you think might be the reason why shrimp have disappeared from the Gulf of Mexico?
Pollution has killed off shrimp populations
Aquatic ecosystems are most likely to be limited by what element?
Nitrogen b/c it is one of the key components to life, think macromolecules. So less N, less life.
What is a harmful algal bloom? What conditions contribute to the development of one of these blooms?
If algal blooms are dangerous, red tides/blue-green blooms can produce toxins and limit resources for other marine animals.
True of False if Algae respond to the increase of nutrients in their environment by increasing their reproductive rate this is an example of evolution.
False, populations can respond to change in their environment without evolving, most likely just a response.
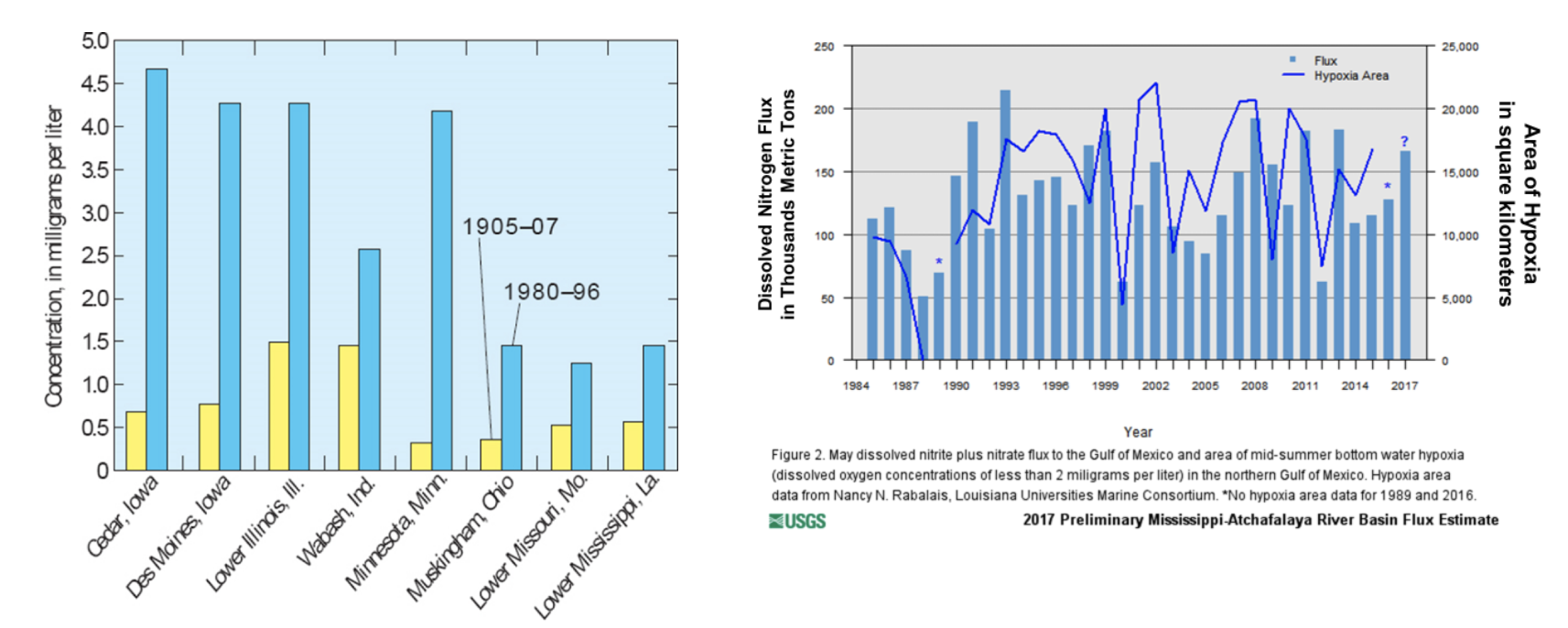
What do the figures below tell you about the runoff into the Mississippi River basin? Select all that apply.
A. Annual nitrate rate concentrations have increased over time
C. Dissolved N affects size of the hypoxic area in Louisiana’s coastal waters
E. The biggest sources of nitrates tend to be away from the Gulf of Mexico.
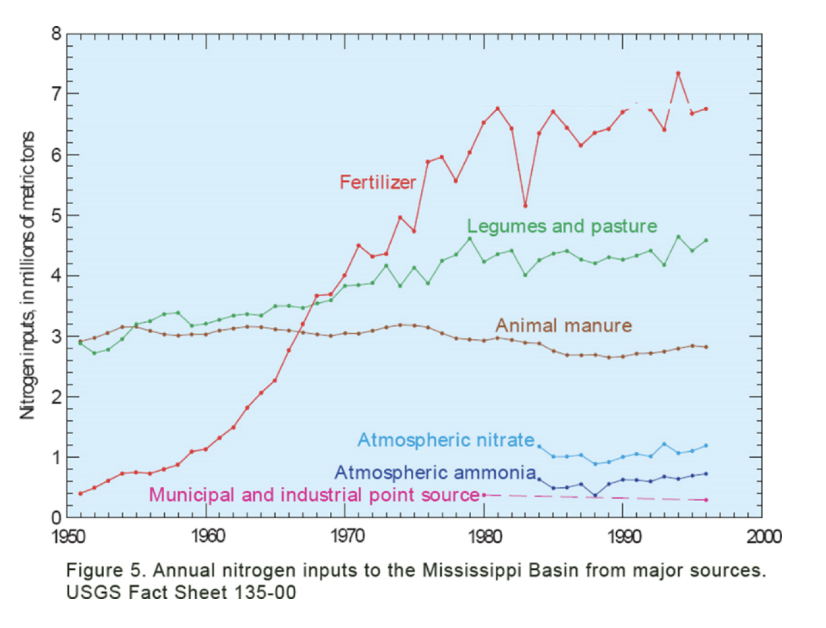
What is the greatest source of nitrogen in runoff to the Mississippi Basin?
Fertilizer that has a lot of Nitrogen in it, increasing the phytoplankton populations. The increase in population=more dead phytoplankton that was no consumed and eventually leads to less O2 being produced (Hypoxia)
What is Convergent Evolution?
when two completely different populations are affected by the same problem and have the same outcome.
Ex: Lactose Tolerance in different populations in Africa and Europe have the same phenotype but different gene mutation due to the increase in dairy products
What is DNA replication and what phase does it occur in?
When DNA is replicated from 46 chromosomes to 92 sister chromatids (still 46 chromosomes). Happens in S-phase of interphase
What is Mitosis?
duplicating DNA from parent to two identical diploid daughter DNA mitotic chromosomes (2n)
What are the different parts of interphase and what do they do?
G1- plans for DNA replication
S-phase-DNA replication
G2- final preparation makes microtubules for the spindle fibers before entering Mitosis
What is a chromosome, what are sister chromatids? What is a homologous chromosome?
chromosome- contains our DNA, single before replicated
sister chromatids- two identical copies of a chromosome attached by a centromere after replication
homologous chromosome- two similar chromosomes (one from mom, one from dad) have the same genetic info but different versions (alleles) Ex: eye color
Explain the steps of DNA replication?
Helicase splits the DNA strands (5’ to 3’ and 3’ to 5’)
They single strand binding proteins (SSBP) keep strands straight and stable
Primase lays down short RNA primers on both strands to provide a free 3’ hydroxyl group
The leading strand is continuous because DNA can only be placed from 5’ to 3’ and lays down complementary nucleotides
The lagging strand is non-continuous and DNA polymerase lays down in parts called Okazaki fragments
Ligase is only used on the lagging strand to close the gaps between the fragments
What are the pairings for the nucleotides Thymine, Adenine, Cytosine, and Guanine?
T=A
C=G
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is found to be composed of 30% thymine (T), what percentage of guanine (G) would you expect to find in the same molecule?
30% of Adenine which means 40% remains for Guanine and Cytosine and 40/2 is 20%.
Which of following statements are true about nuclear DNA replication in a cell that is preparing to divide? Select all that apply.
Occurs during S-phase and interphase and results in sister chromatids
DNA Polymerase always synthesizes a new strand of DNA in which direction?
5’ to 3’ only
In a cell, suppose that the gene coding for ligase becomes mutated and results in the production of a nonfunctioning ligase enzyme. Which of the following would you expect to occur?
Okazaki fragments will not be joined together
True or False mutations are always harmful?
False some mutations are useful
ex: lactose tolerant
True or False: A mutation always results in a change in protein shape.
False; there could be no protein there=mutation too
True or False; Mutations are random and rare events
True
True or False; in multicellular organisms, mutations that occur in somatic cells can be passed to offspring.
False; only mutations in gametes can be passed down to offspring
Which of the following sequences of DNA was produced using this strand as a template?
Write the corresponding sequence following base pairing and polarity rules on the line below, before selecting your answer.
5’ ACAGTCGAGCCTCGT 3’
3’ TGTCAGCTCGGAGCA 5’
Which of the following is true of mitosis in a diploid cell?
A. It results in two haploid daughter cells.
B. It does not require replication of the cell's DNA before cell division.
C. It results in two diploid daughter cells.
D. Multicellular organisms use it for reproduction.
C. results in two diploid daughter cells
What happens if a DNA is mutated?
If DNA is mutated it either is missing a nucleotide, wrong pairing, or just a misshapen protein. DNA polymerase will fix the mistakes but some still get through resulting in a mutation that cannot be fixed.
What are the three ways DNA polymerase repairs mistakes?
Mismatch repair
Base excision repair
Nucleotide excision repair
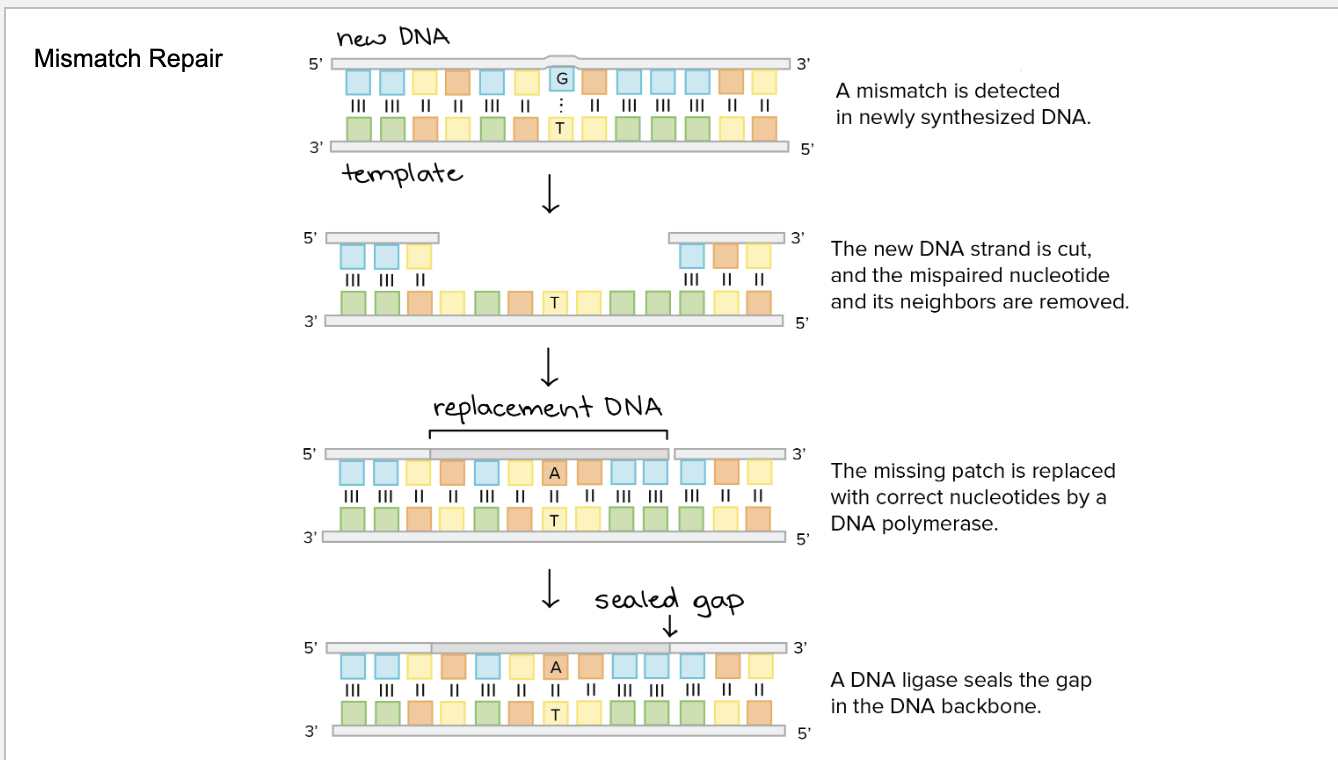
What is Mismatch repair?
mismatch of nucleotides is recognized by DNA polymerase
DNA strand is cut and the neighboring nucleotides are also cut
Mismatched strand is replaced with correct order
DNA ligase seals the strand together
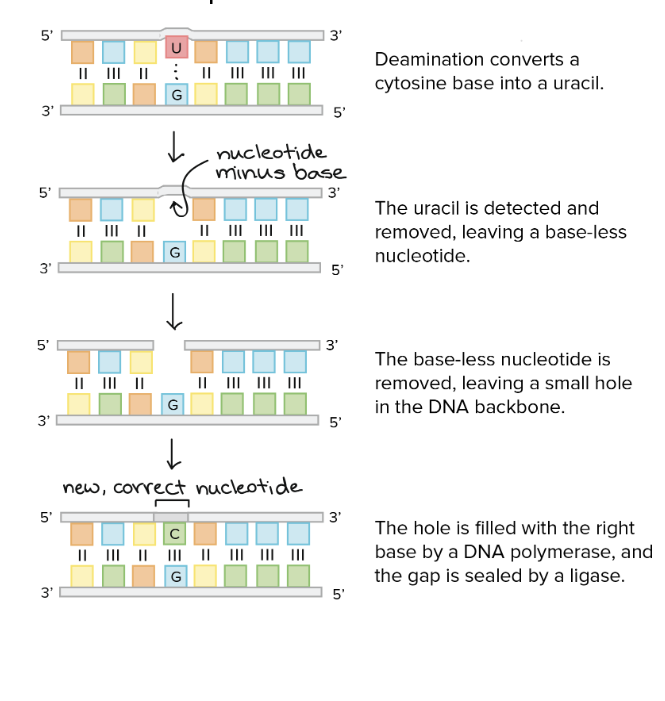
What is Base excision repair?
Deamination converts a Cytosine base to a Uracil
Uracil is detected and removed leaving a baseless nucleotide
DNA backbone is left with a missing nucleotide
DNA polymerase recognizes this and adds the matching base pair
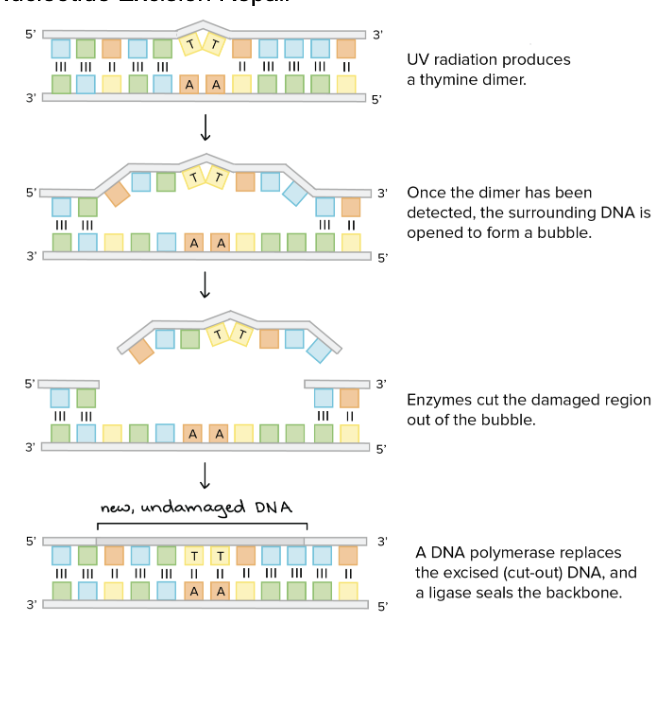
What is Nucleotide excision repair?
UV radiation produces a thymine dimer
Once the dimer is detected, surrounding DNA forms an open bubble
Enzymes cut out the damaged region that is the DNA bubble
DNA polymerase replaces segment with new DNA
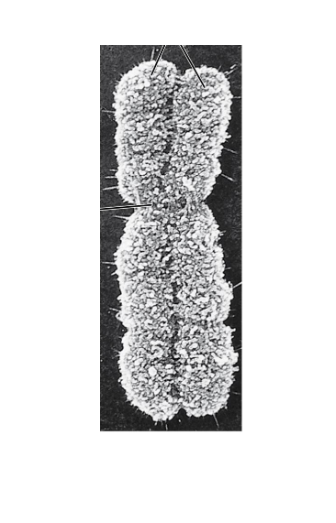
During what part of the cell cycle would you see a chromosome that looks like this?
M-phase
You discover a new species of snakes that glow in the dark. You want to see if they utilize the same
Green Fluorescent protein (GFP) as in jellyfish. You need to:
(1) Isolate the gene, (2) Amplify it, (3) Confirm the sequence
PCR (isolate the and amplify by making a lot of copies)
Electrophoresis (taking a piece of a specific place and amplifying it)
DNA sequencing (dNTPs terminate DNA polymerase to stop and allows to read what the sequence is)
A research team has isolated a DNA sample from a patient with a suspected genetic disorder caused by a point mutation. They are considering two techniques to analyze the DNA:
Method 1: Use gel electrophoresis to compare the size of DNA fragments.
Method 2: Use DNA sequencing to determine the exact order of nucleotides in the gene of interest
Method 2; because it provides more detailed information and reveals the exact DNA sequence
What is the function of Mitosis in a single cell vs. multi-cell
Single cell=reproduction
Multi-cell= growth, development, repair (Meiosis is for reproduction)
From prophase through metaphase of mitosis, each chromosome has _____ DNA molecule(s), while from anaphase through telophase of mitosis, each chromosome has _____ DNA molecule(s).
2;1
Mitosis is a process of cell division in which one call goes through a cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically __________.
Identical
List the cell cycle in order.
Interphase (G1, S-phase, G2)
Mitotic phase (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase)
Cytokinesis
What is Cytokinesis?
the process of splitting the cytoplasm and cell membrane happens after telophase
What is Karyokinesis?
Division of Nucleus during all of Mitotic phase and happens before Cytokinesis
What happens in each part of the M-phase?
Prophase- chromosomes become condensed
Metaphase-chromosomes move to the middle of the cell
Anaphase- spindle fiber attached to the centromere split the sister chromatids to each end of the cell
Telophase- chromosomes begin to decondense/elongate and parts of the cell wall begin to split
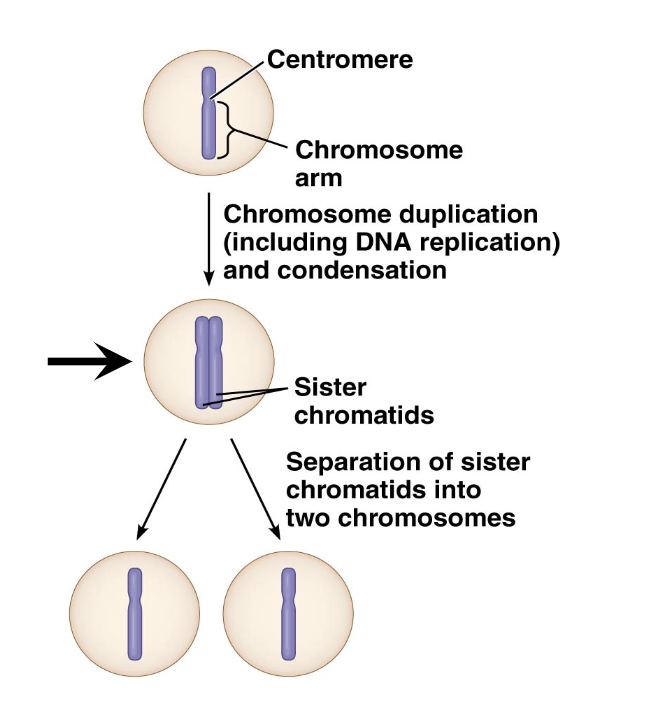
How many duplicated chromosomes are in middle cell (arrow)?
1
Some cells have several nuclei per cell. How could such multinucleate cells be explained?
The cell underwent repeated karyokinesis, but cytokinesis did not occur.
What does G0 phase mean?
Cells are currently not actively duplicating/dividing
What are some irreversible G0 cells?
Terminally differentiated Stem cells: sex cells, neurons, immune cells, fat cells, muscle cells, bone cells
What is the monomer of a protein? How many different types of this specific monomer are there and why is this important?
Amino acids make up proteins, there are about 20 different “R” groups which means there is a lot of variation of proteins for specific things.
What are the four levels of protein structure? Which ones are hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Nonpolar= hydrophobic, “R” group likes to fold into itself
Polar= hydrophilic, “R” group likes to extend its head outside
Charged (acidic or basic)= hydrophilic, “R” group likes to extend its head outside
What is the differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in terms of where transcription and translation occur?
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus so they transcribe and translate in cytoplasm
Eukaryotes have a nucleus they transcribe in the nucleus and then translate in the cytoplasm.
What is the relationship between the DNA template strand and the coding strand?
The DNA template is the DNA that will be translated by the coding strand, the coding strand is complementary to the template strand, it helps tell the mRNA what sequence it will be in
What is the relationship between the DNA coding strand and the mRNA molecule that is produced?
DNA coding strand is the exact same as the mRNA molecule sequence other than replacing T with U.
Which way does RNA polymerase lay down mRNA?
from 5’ to 3’
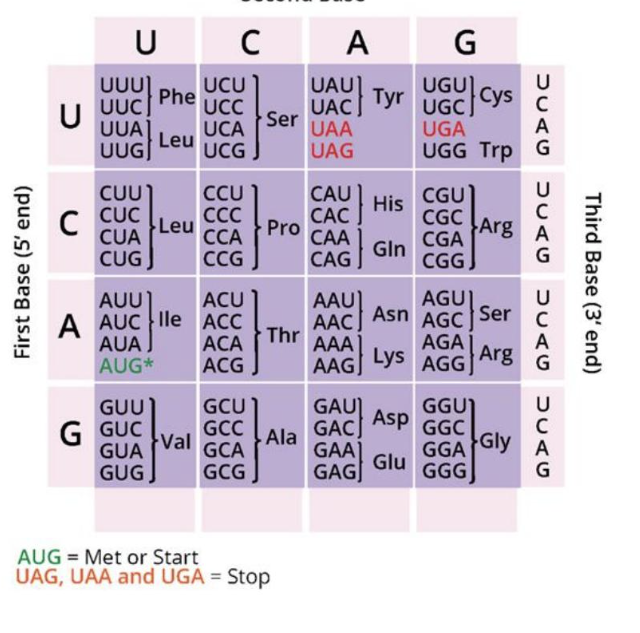
What molecules contain the codons that are translated from nucleotides to amino acids?
messenger RNA
True or False: the primary sequence of a protein will begin with the code AUG; amino acid (Met).
True
What is the “triplet code” what does it mean that the code is universal, unambiguous, and redundant?
Every 3 nucleotides codes for 1 amino acid.
Universal= every living thing follows genetic code this way
Unambiguous= cannot change genetic code
Redundant= multiple different nucleotides (codons) can code for the same amino acid
True or False; the entire chromosome gets trancribed?
False; only specific DNA is transcribed
What enzymes and materials are needed for Transcription to occur?
RNA Polymerase- builds RNA strand and reads DNA template strand
Helicase- splits DNA strand
Transcription Factors- bind to promoter to tell polymerase where to start
RNA Polymerase II- adds nucleotides to the 3’ end
What enzymes and materials are needed for Translation to occur?
rRNA- structural component of ribosomes, place where translation happens forming the peptide bonds and amino acids
tRNA- transports amino acids to growing peptide chain
What would be the coding strand of this DNA template strand?
3’ TACCGTTAGCGGAAGAAA 5’
5’ ATGGCAATCGCCTTCTTT 3’
What would the mRNA strand be of this DNA template strand?
3’ TACCGTTAGCGGAAGAAA 5’
5’ AUGGCAAUCGCCUUCUUU 3’
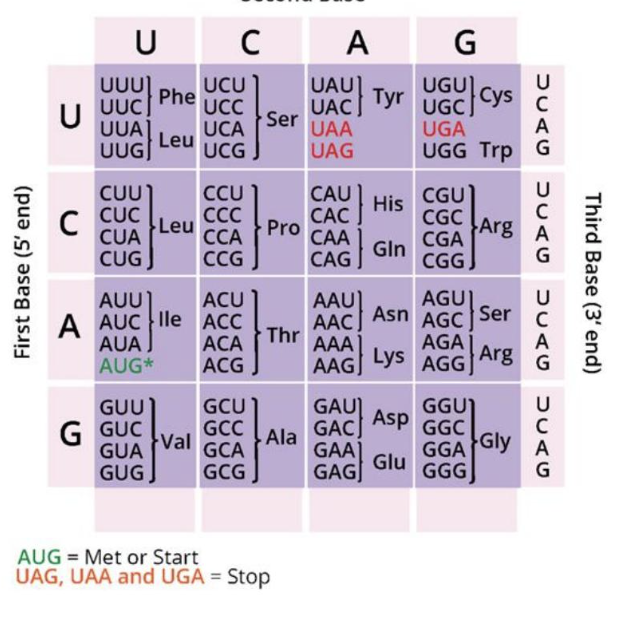
What is the sequence of the polypeptide encoded by this DNA template strand?
3’ TACCGTTAGCGGAAGAAA 5’
first find the mRNA strand:
5’ AUGGCAAUCGCCUUCUUU 3’
then use the table to find the amino acids:
start| Ala| Ile | Ala | Phe | Phe
What are the different types of mutations?
Point Mutation- a single nucleotide is changed
Frameshift Mutation- addition/deletion of several nucleotides resulting in the entire protein is shifted
Silent Mutations- there is a change in DNA code but it codes for the same amino acid
Missense Mutation-change of amino acid to another
Nonsense Mutation- a cut off/stop amino acid instead of a normal one