iGCSE Edexcel Chemistry Inorganic Part 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
when acids are added to water...
they form positively charged hydrogen ions (H⁺)
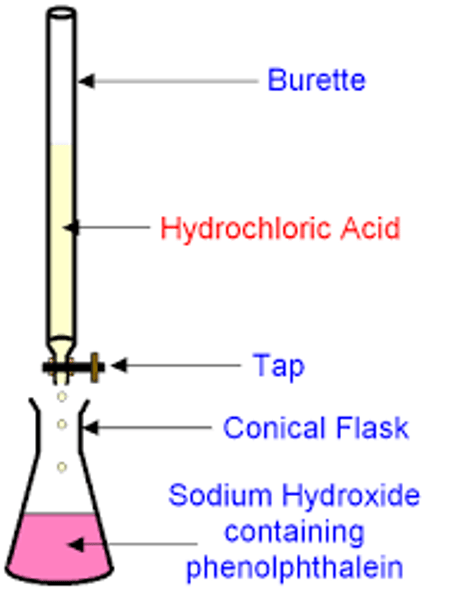
describe the method of performing a titration
Use the pipette and pipette filler and place exactly 25 cm3 sodium hydroxide solution into the conical flask
Place the conical flask on a white tile so the tip of the burette is inside the flask
Add a few drops of a suitable indicator to the solution in the conical flask
Perform a rough titration by taking the burette reading and running in the solution in 1 - 3 cm3 portions, while swirling the flask vigorously
Quickly close the tap when the end-point is reached (sharp colour change) and record the volume, placing your eye level with the meniscus
Now repeat the titration with a fresh batch of sodium hydroxide
As the rough end-point volume is approached, add the solution from the burette one drop at a time until the indicator just changes colour
Record the volume to the nearest 0.05 cm3
Repeat until you achieve two concordant results (two results that are within 0.1 cm3 of each other) to increase accuracy

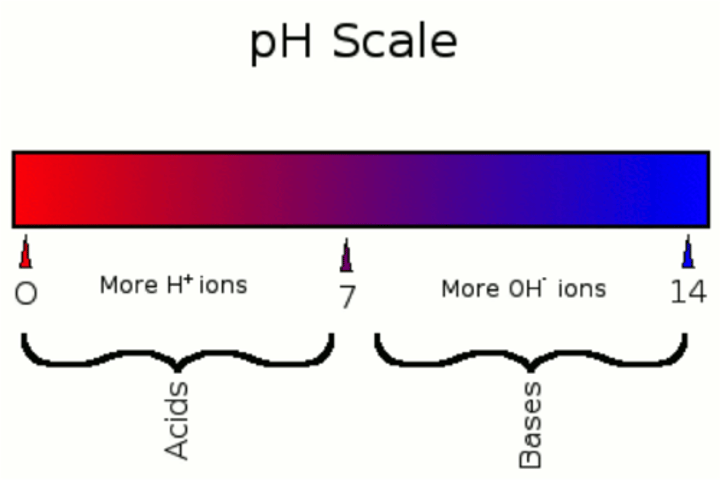
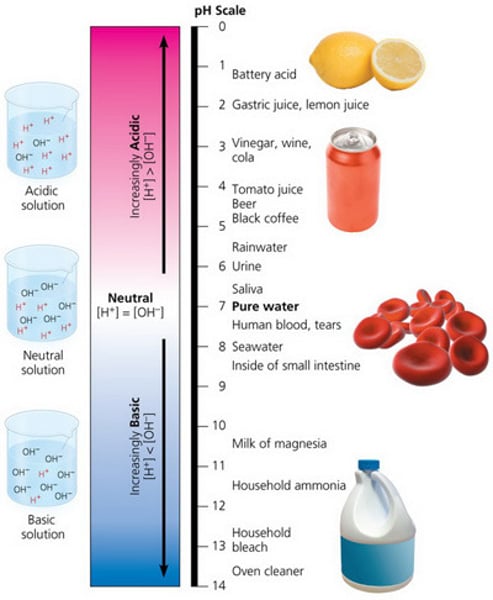
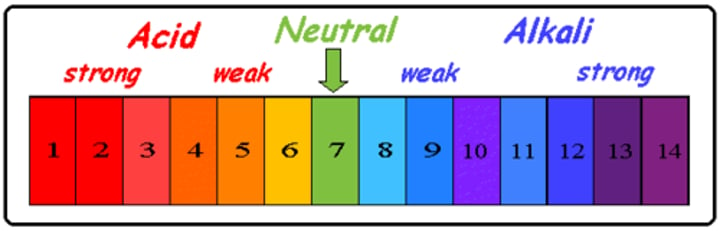
acidic
pH below 7
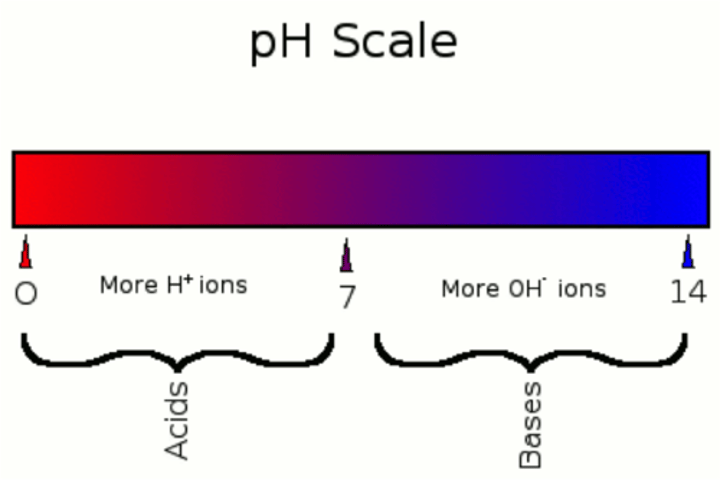
basic
pH greater than 7
litmus
red in acid, blue in alkali
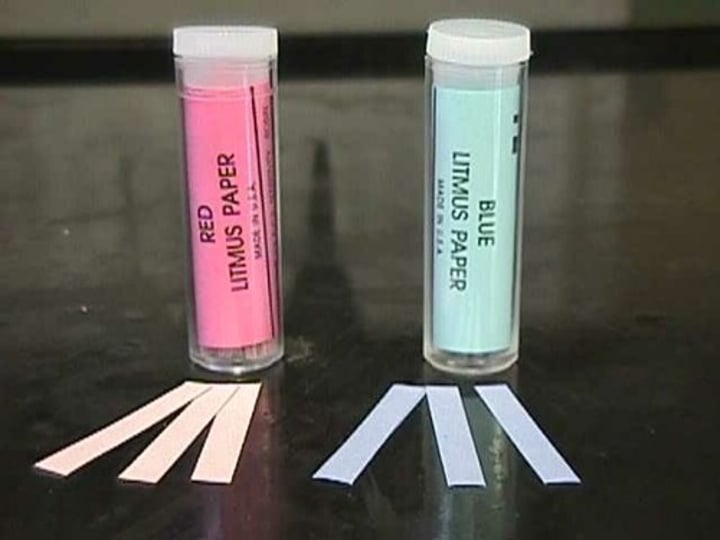

phenolpthalein
colorless in acid, pink in alkali
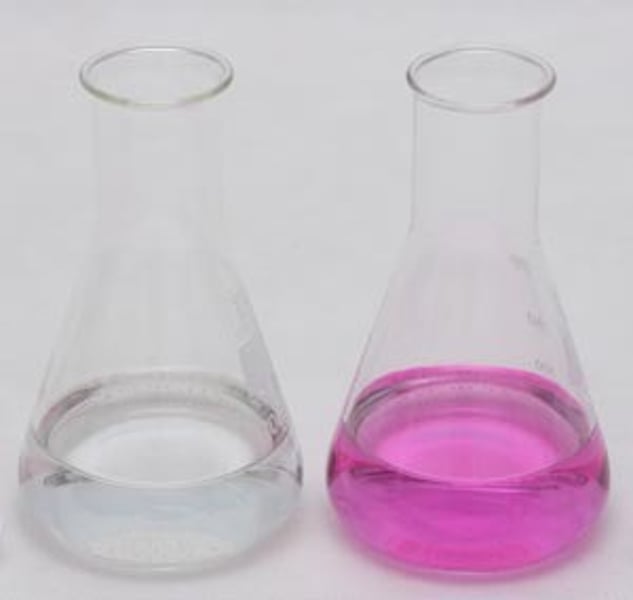

methyl orange
red in acid, yellow in alkali

neutralisation
when an acid reacts with an alkali
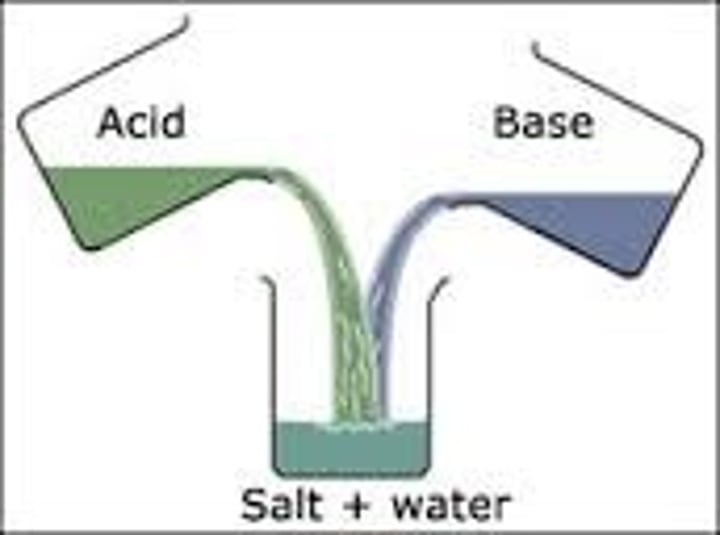
titrations
method of analysing the concentration of solutions
universal indicator
a wide range indicator and can give only an approximate value for pH
when alkalis are added to water...
they form negative hydroxide ions (OH⁻)
acid + base ->
salt + water
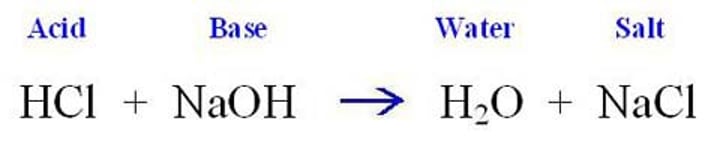
test for ammonia gas
damp red litmus paper turns blue

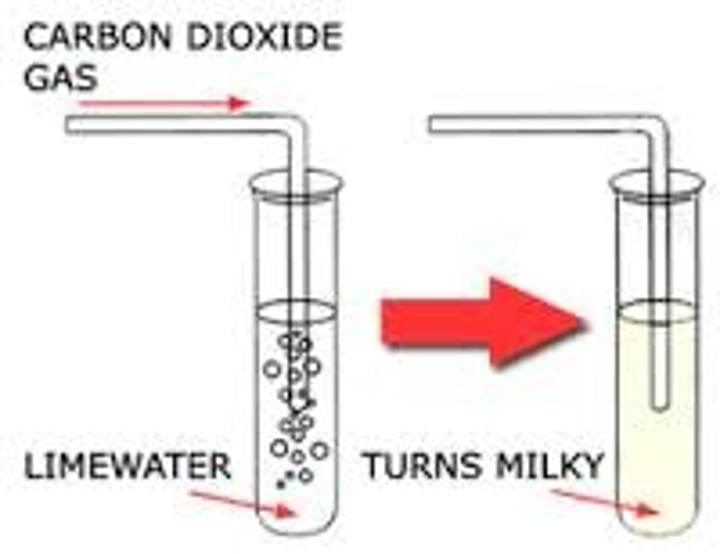
test for carbon dioxide gas
bubble through lime water; lime water turns milky/cloudy
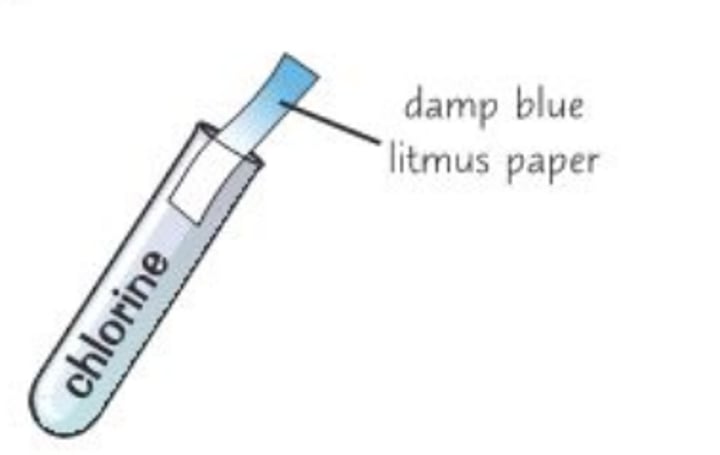
test for chlorine gas
damp blue litmus paper is bleached
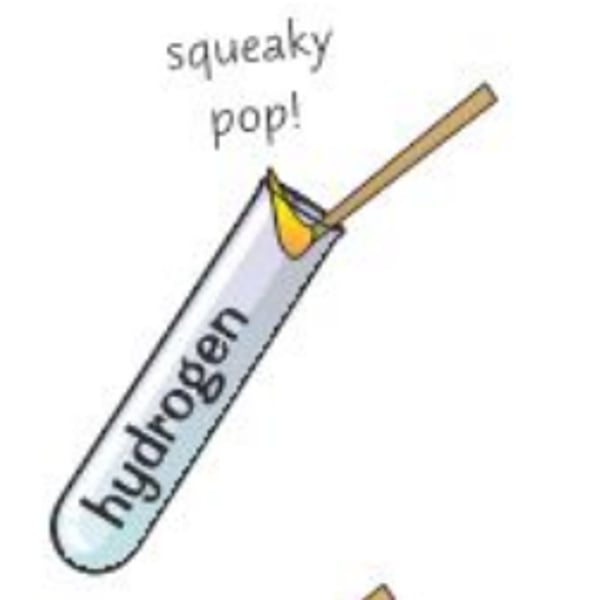
test for hydrogen gas
hold a lighted splint in mouth of test tube; burns with a 'squeaky pop' sound
test for oxygen gas
hold a glowing splint; splint relights

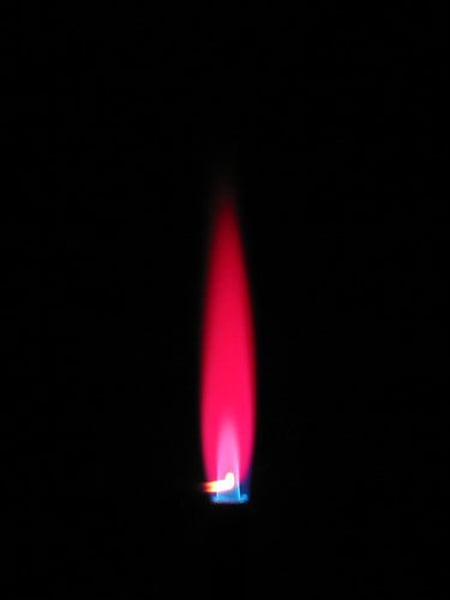
flame test result for lithium
red

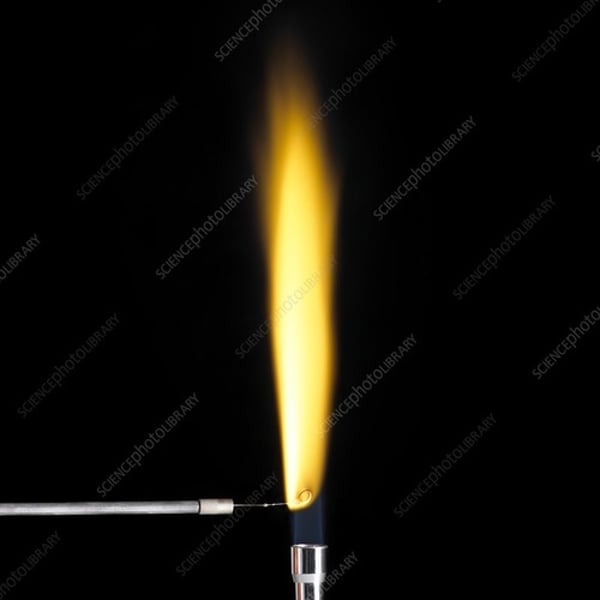
flame test result for sodium
yellow

flame test result for potassium
lilac
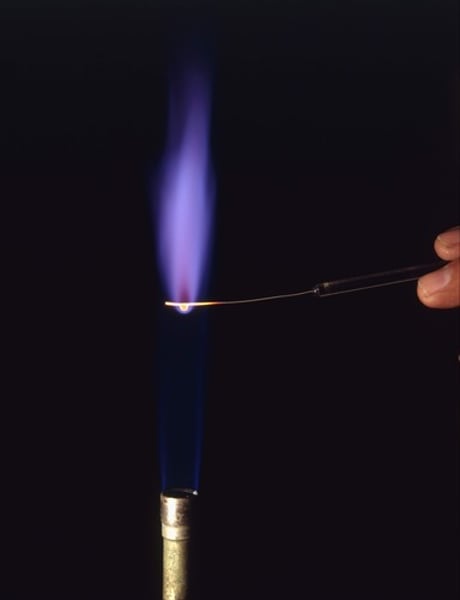

flame test result for calcium
orange-red
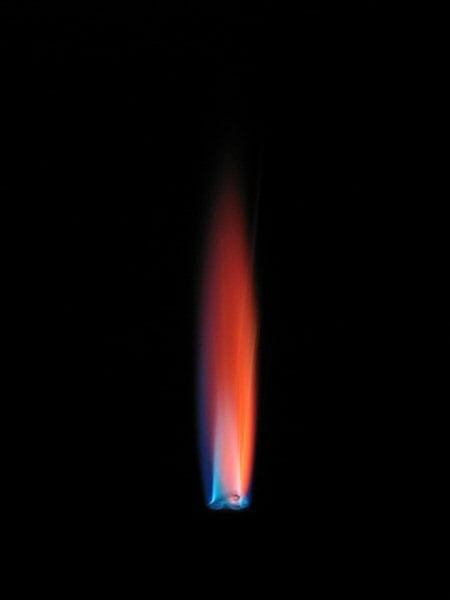

flame test result for copper
blue-green

describe the method of flame tests
Dip the loop of the wire in dilute hcl
hold it in the blue flame
Dip the loop of the wire in the sample
place loop back into the blue flame
result of hydroxide test for ammonium
ammonia gas produced turns damp red litmus blue
result of hydroxide test for copper (II)
light blue precipitate formed
result of hydroxide test for iron (II)
green precipitate formed
result of hydroxide test for iron (III)
red-brown precipitate formed
how are metal cations identified in aqueous solution?
the colour of the precipitate formed on addition of NaOH
result of halide test for chloride
white precipitate formed
result of halide test for bromide
cream precipitate formed
result of halide test for iodide
yellow precipitate formed
result of sulphate test for sulphate
white precipitate formed
result of carbonates test for carbonate
effervescence, gas produced is CO2 which turns limewater mily
carbonate test
add dilute acid and test the gas released
sulphate test
acidify with dilute niric acid and add aqueous barium nitrate
halide test
acidify with dilute niric acid and add aqueous silver nitrate
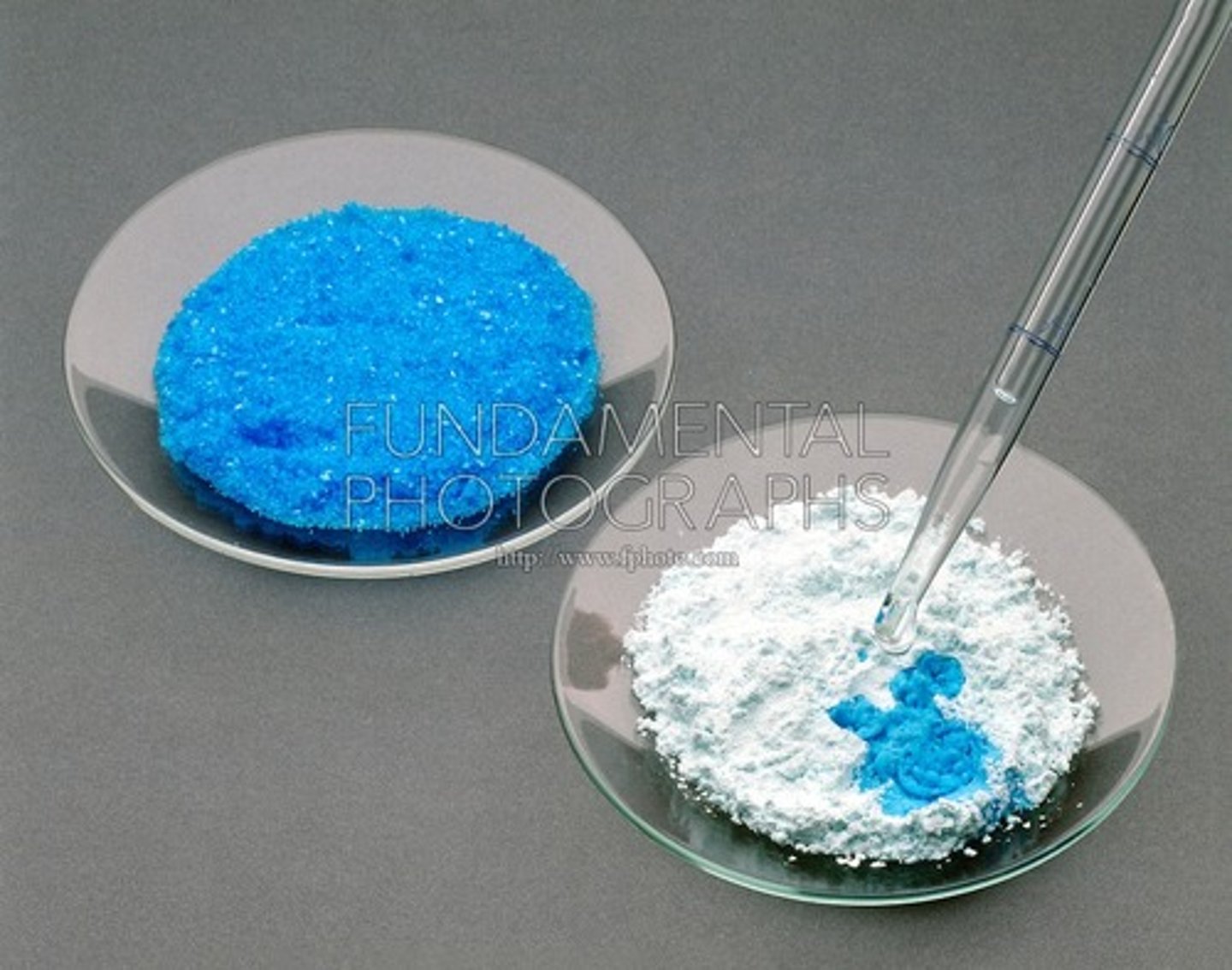
chemical test for water
anhydrous copper(II) sulfate turns from white to blue on the addition of water

physical test for water
aphysical test to see if a sample of water is pure is to check its boiling point
A sample of the liquid is placed in a suitable container such as a boiling tube and gently heated
Using a thermometer, you can check if the boiling point is exactly 100 oC
Any impurities present will usually tend to raise the boiling point and depress the melting point of pure substa
acid + metal ->
salt + hydrogen
acid + metal carbonate ->
salt + water + carbon dioxide
SPAN
sodium, potassium, ammonium and nitrate

bases examples
usually oxides, hydroxides or carbonates of metals; ammonia is an usual base
solubility rules
-SPAN compounds are soluble
-chlorides are soluble, except silver + lead (II)
-sulphates are soluble except for those of barium, calcium + lead (III)
-carbonates are insoluble
-hydroxides are insoluble
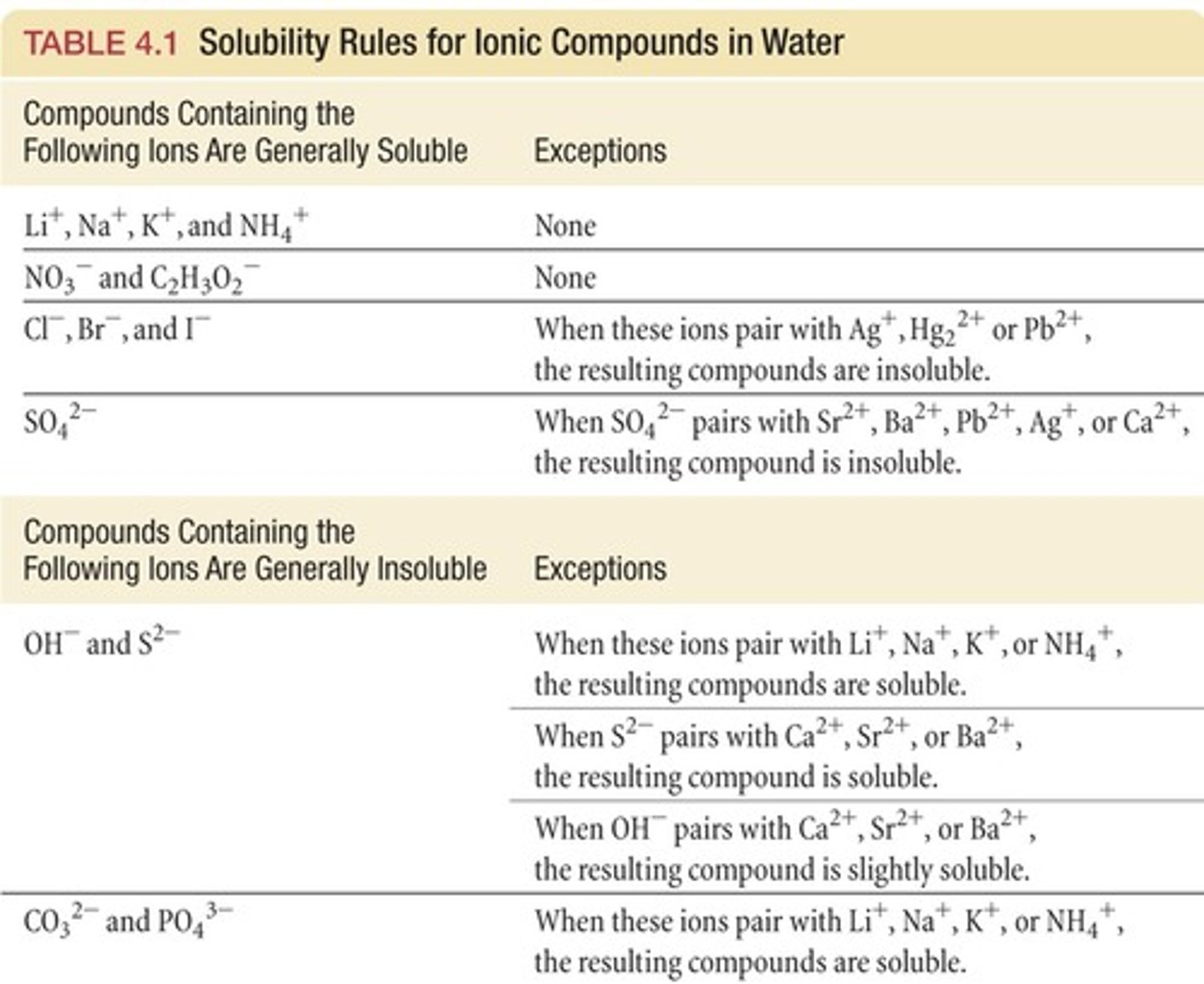
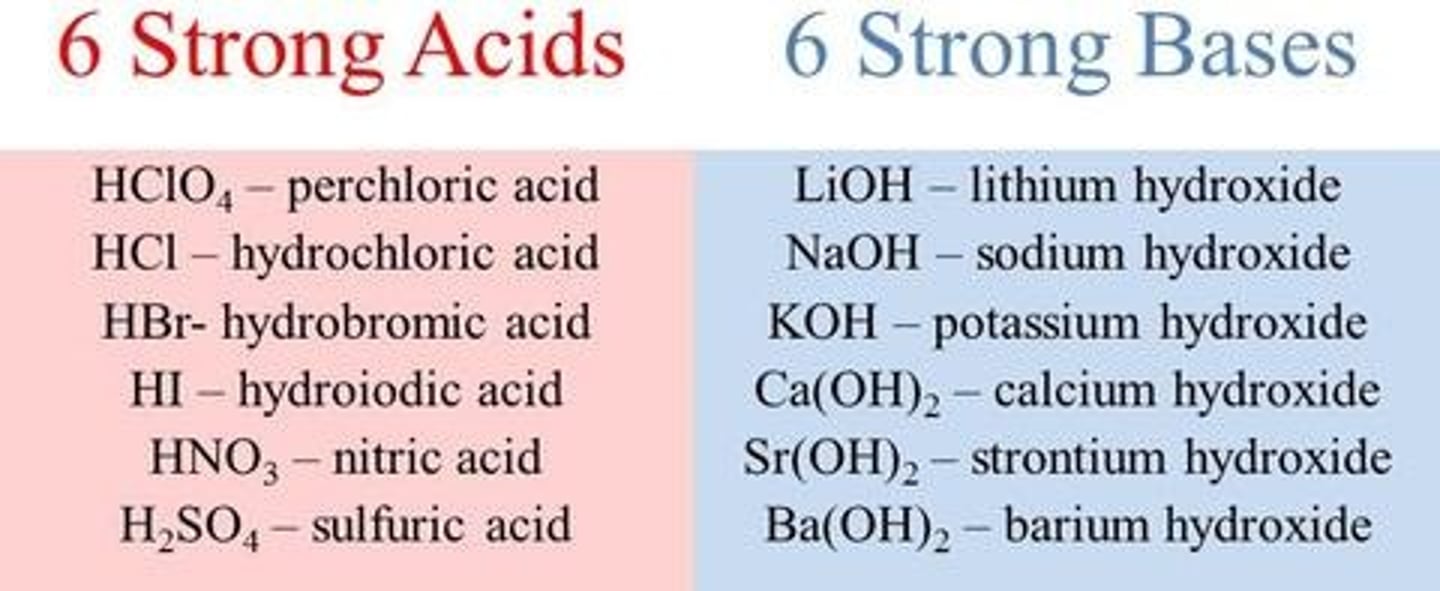
strong acids
dissociate completely in water
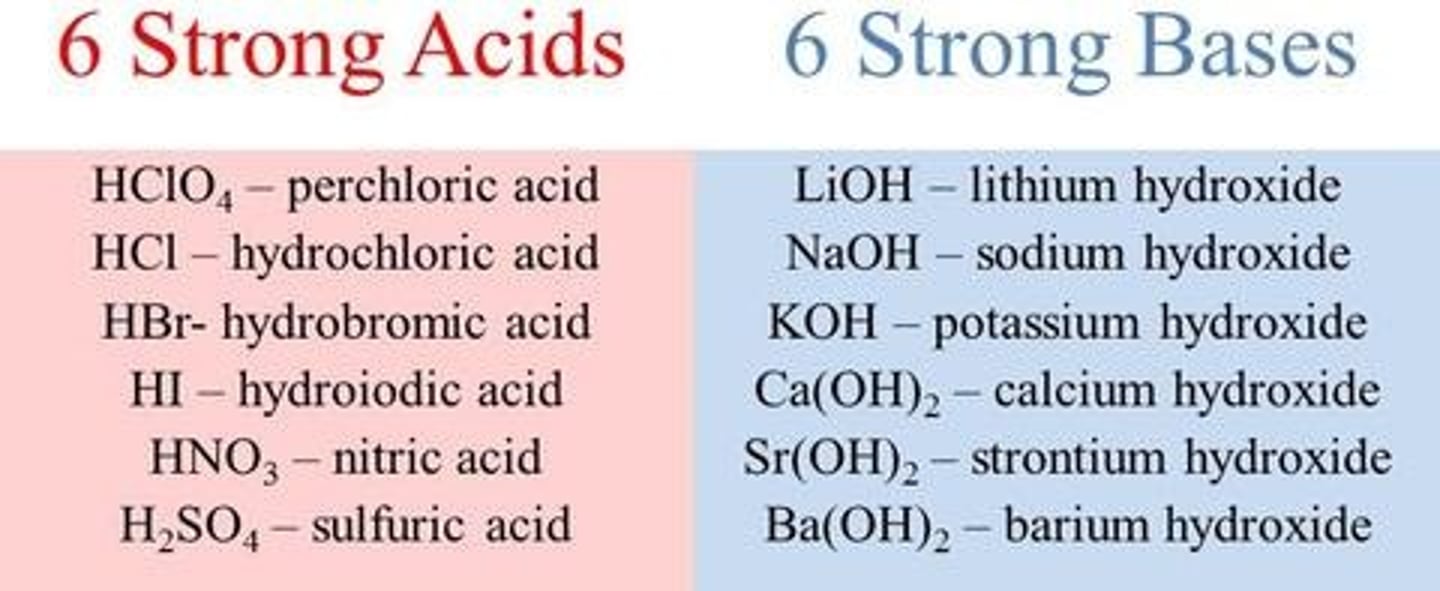
weak acids
partially dissociate in water
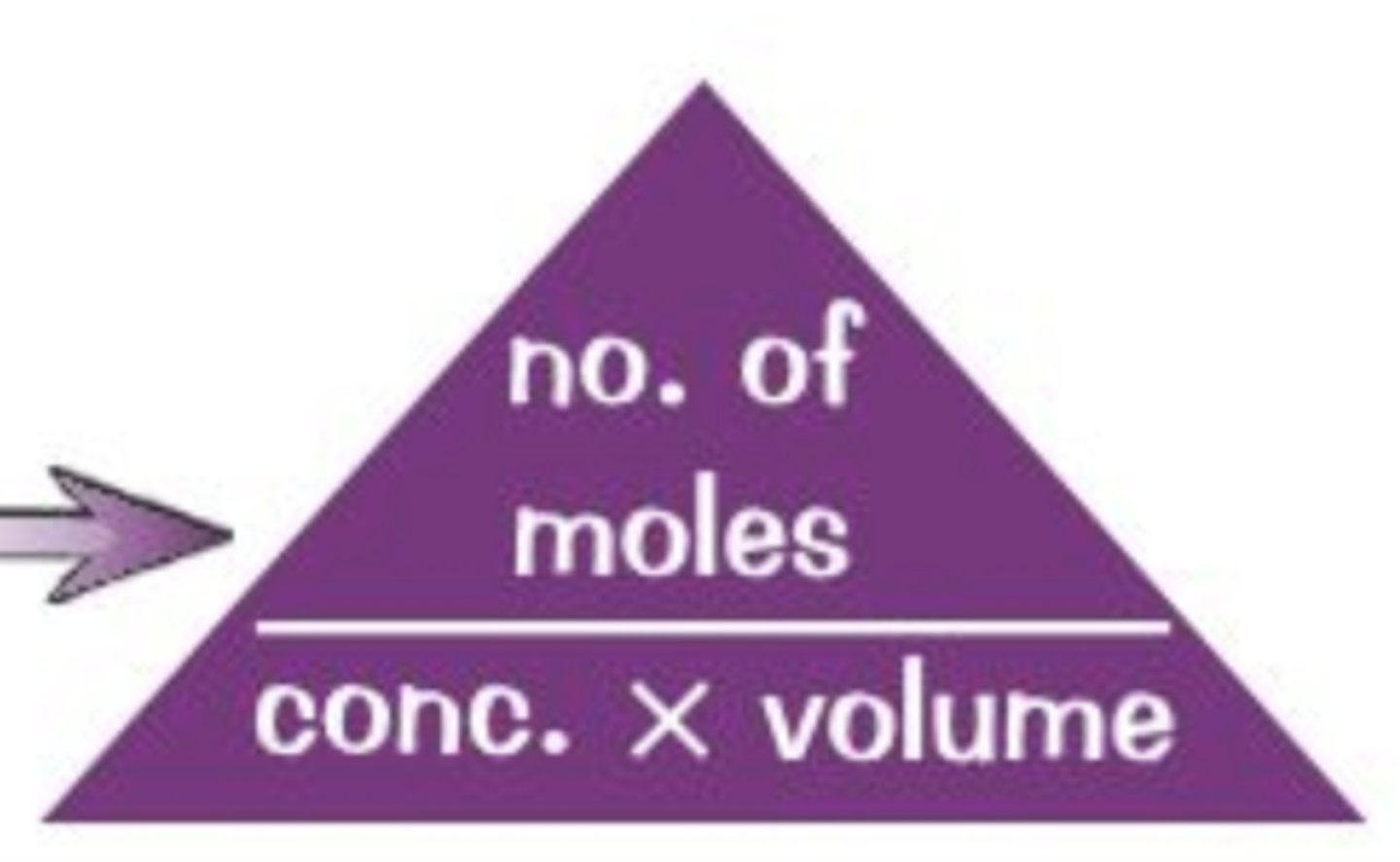
formula linking moles, concentration and volume
moles(mol)=concentration(mol/dm^3)*volume(dm^3)
formula linking moles, mass and RFM
moles(mol)=mass(g)/RFM
dm^3=xcm^3
1000cm^3
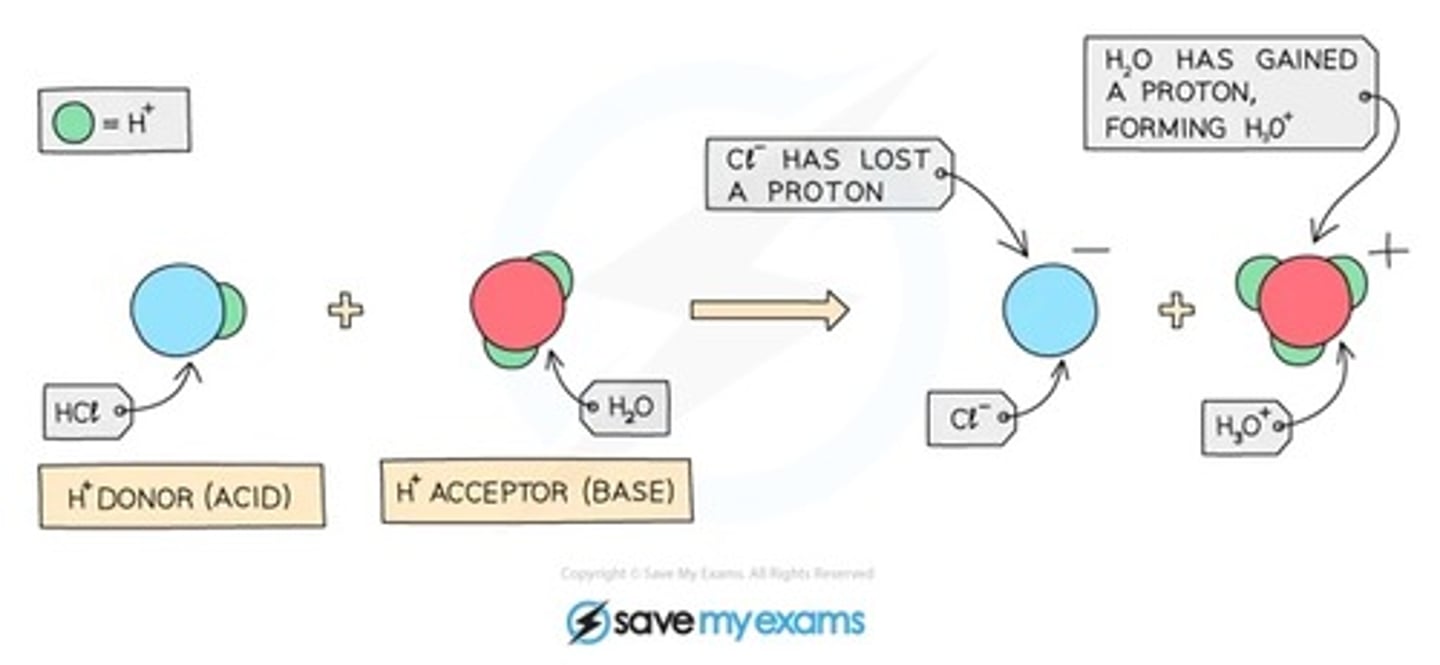
acids are proton...
donors
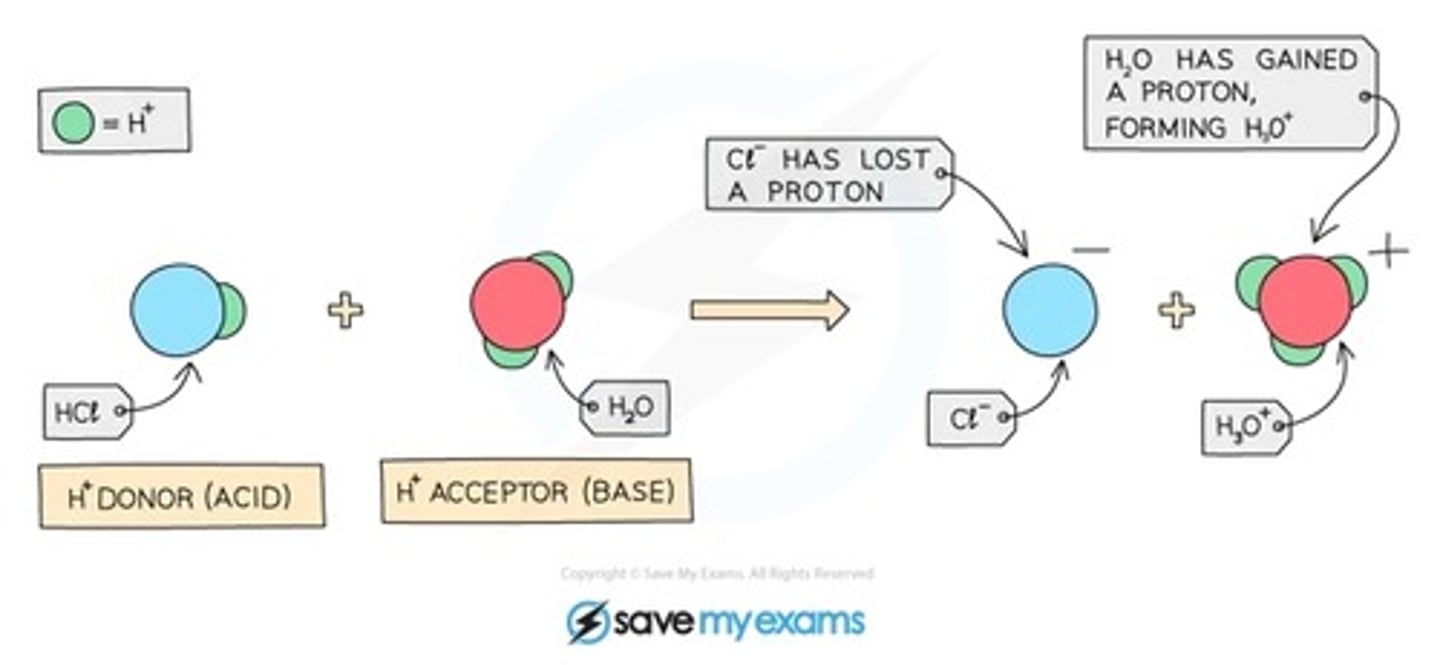
bases are proton...
acceptors
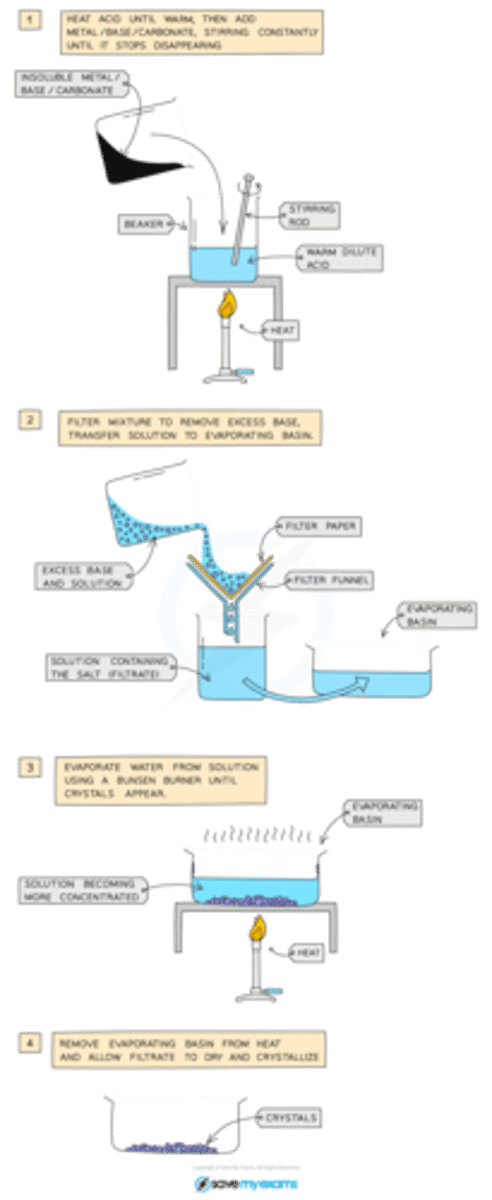
how to prepare a soluble salt
reaction of an acid with an insoluble salt
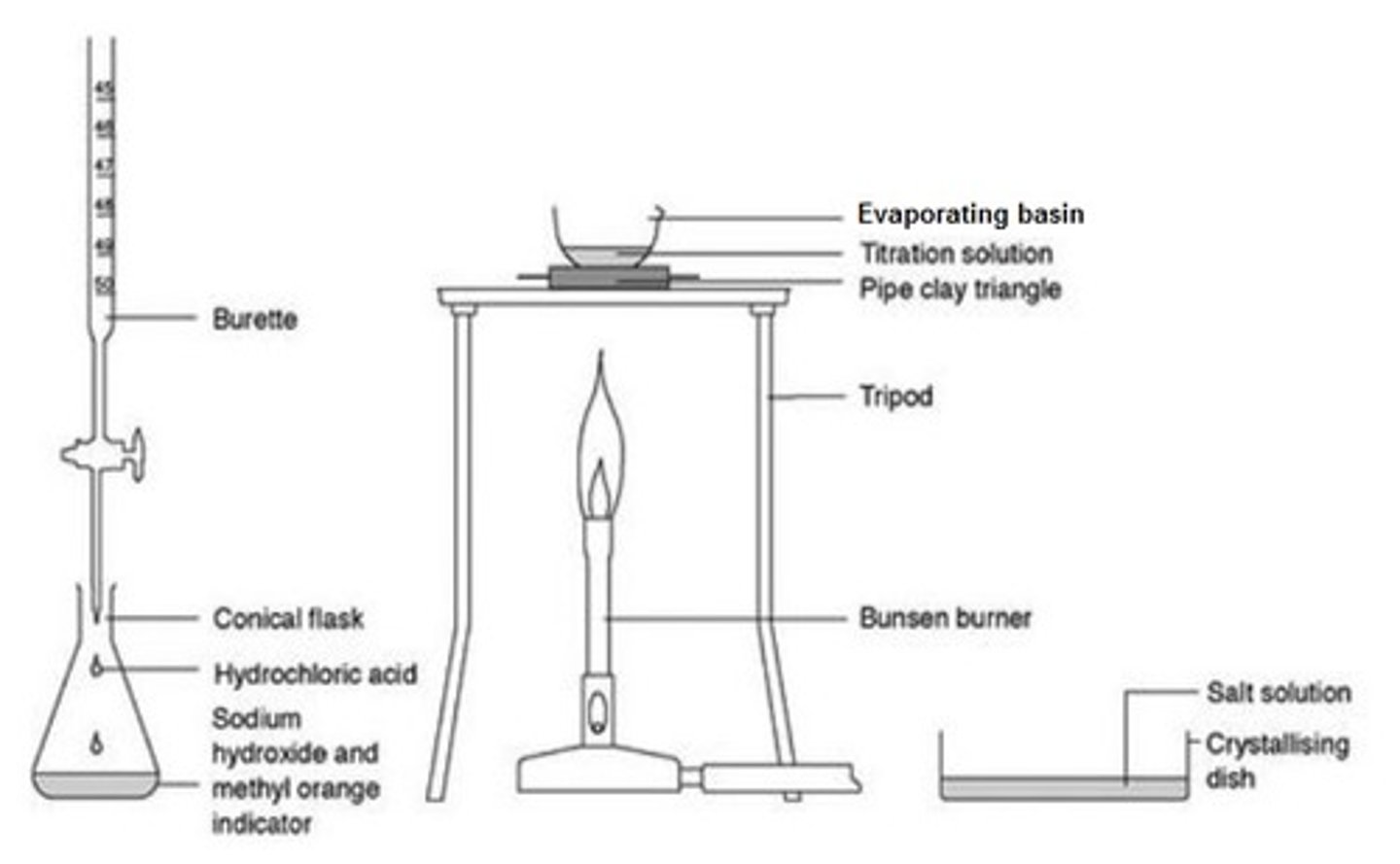
how to prepare an insoluble salt
two soluble salts