Dose-Response Curves
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Agonists
bind to receptor at endogenous ligand site and activates it
full agonist
gives 100% efficacy at full receptor occupy
partial agonist
gives partial efficacy at full-receptor occupancy
allosteric agonist (positive allosteric modulator)
binds to receptor at a different site than the endogenous ligand site, but enhances the binding affinity and efficacy to the endogenous ligand
antagonist
binds to receptor and reduces agonist effect, intrinsic activity zero
inverse agonist
binds receptor and reverses (reduces) constitutive activity
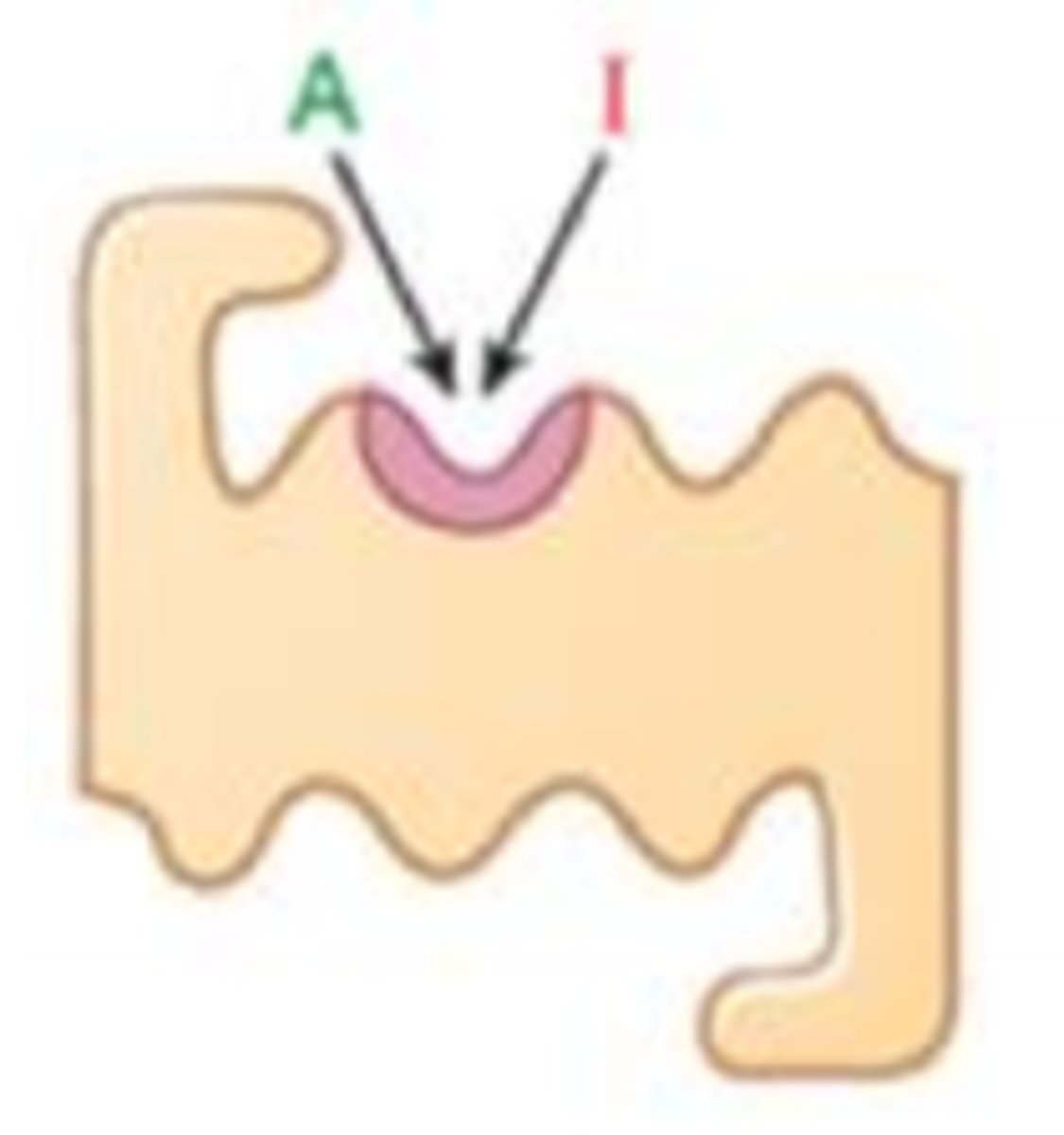
Allosteric Potentiator (agonist)
Drug binds to the receptors allosterically and enhances (potentiates) the effect of the endogenous agonist, effecting both potency and efficacy
shifts left
effect of allosteric potentiators on dose response curve
increases
effect of allosteric potentiators on max response
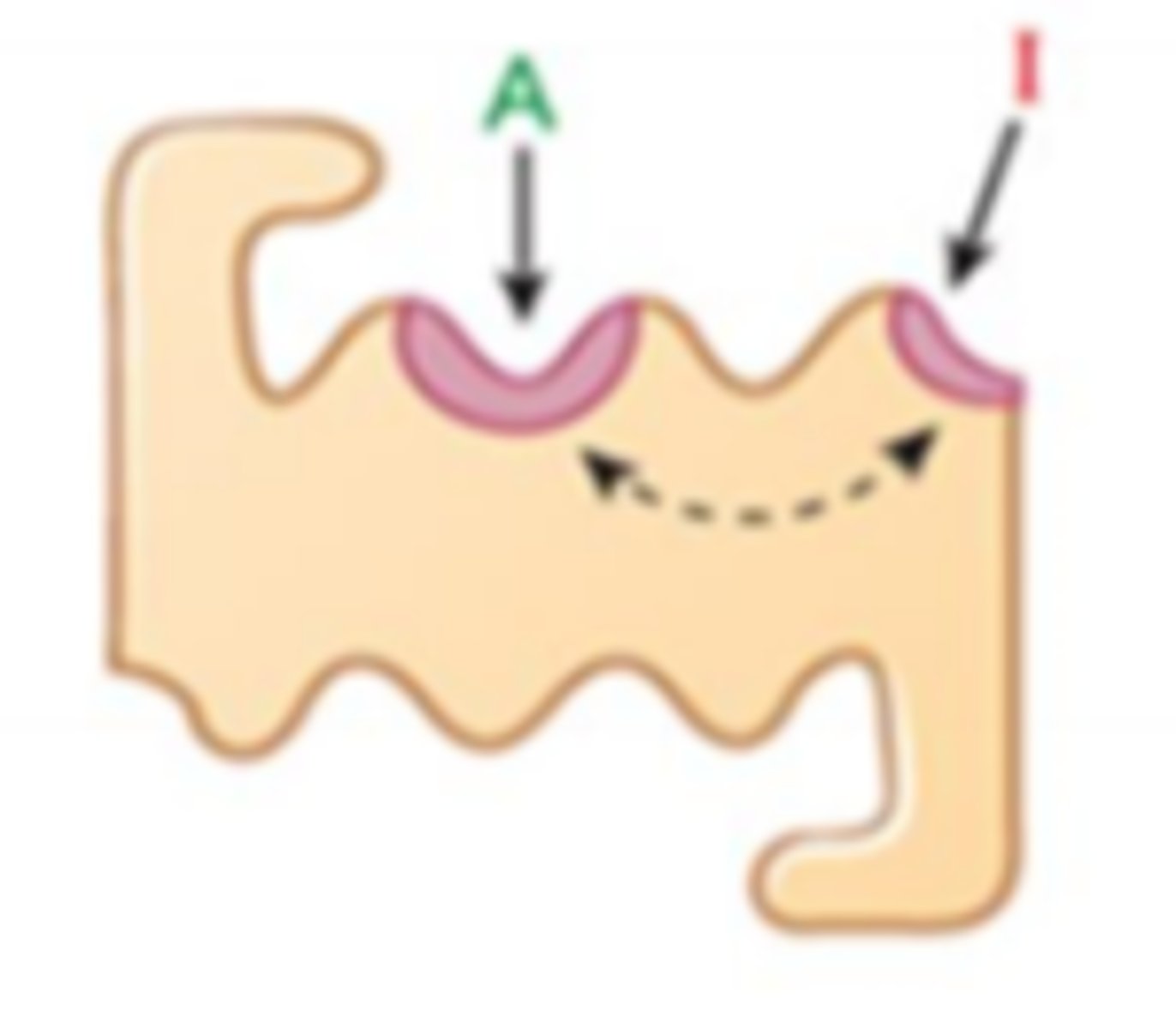
competitive antagonist
drug competes with agonist for the same receptor binding site; can be overridden with high concentration of agonist
shifts right
effect of competitive antagonist on dose response curve
does not change
effect of competitive antagonist on maximum response
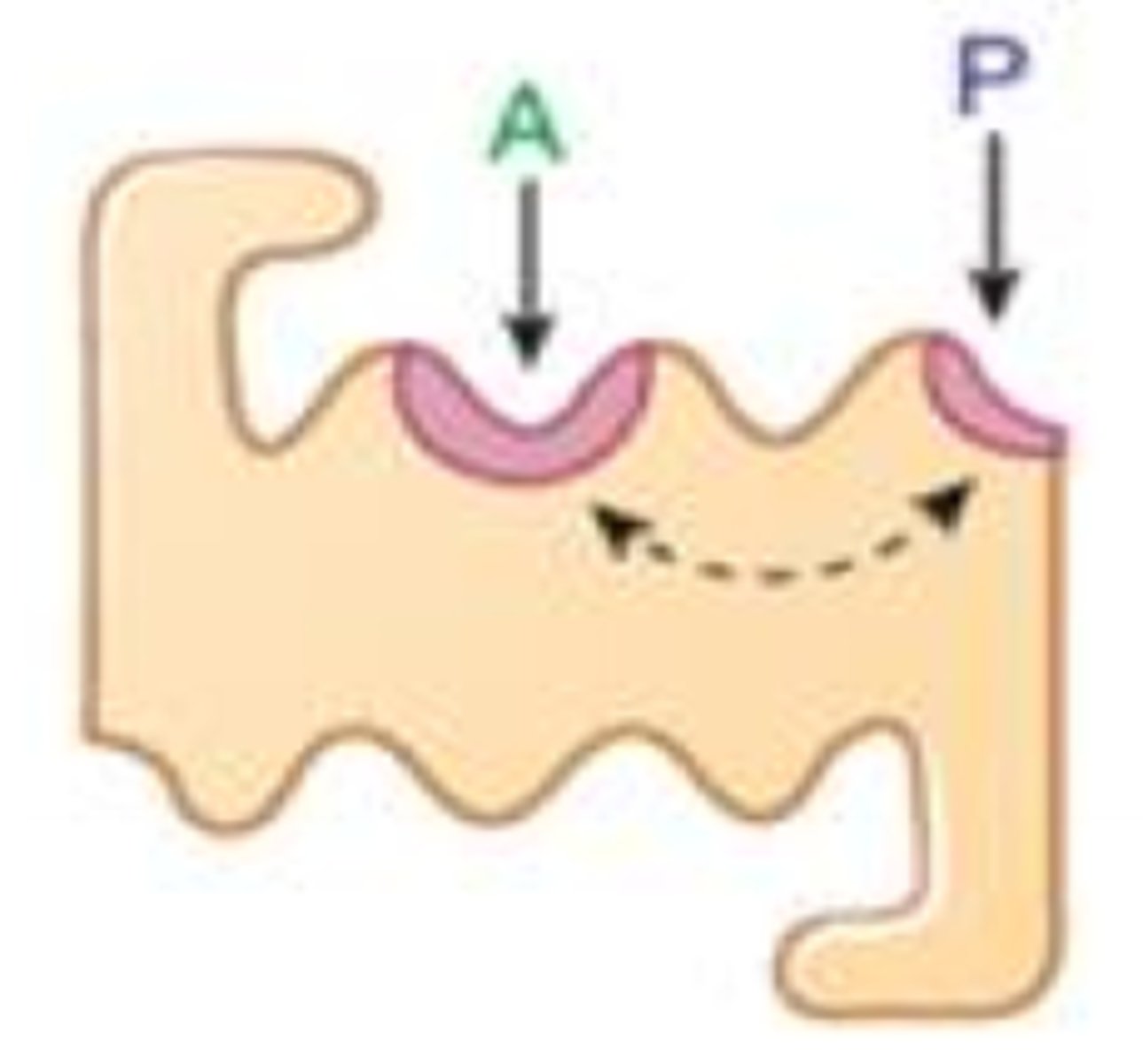
non-competitive antagonist
drug binds to receptor irreversibly, pseudo irreversibly, or allosterically
shift right
effect of non-competitive antagonist on dose response curve
decrease
effect of non-competitive antagonist on max response
partial agonist
result in a ceiling-limited pharmacological effect that is lower than the maximum tissue response; get a patient off of the full agonist
ED50
median effective dose
LD50
median lethal dose
safer
the higher the TI, the _____________ the drug
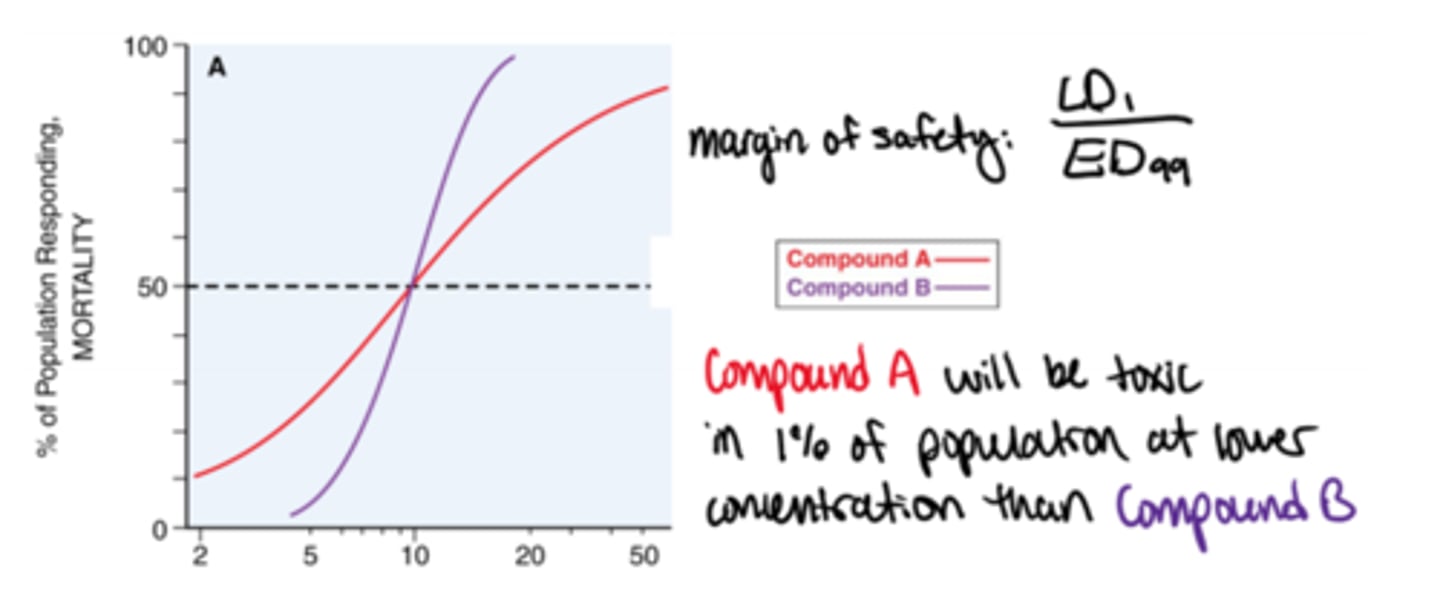
margin of safety
used to compare two drugs that have same LD50; takes into consideration at which concentration the drug first becomes toxic
LD1/ED99
wider
the __________ the therapeutic window, the safer the drug
narrower
the _________ the therapeutic window, the less safe the drug
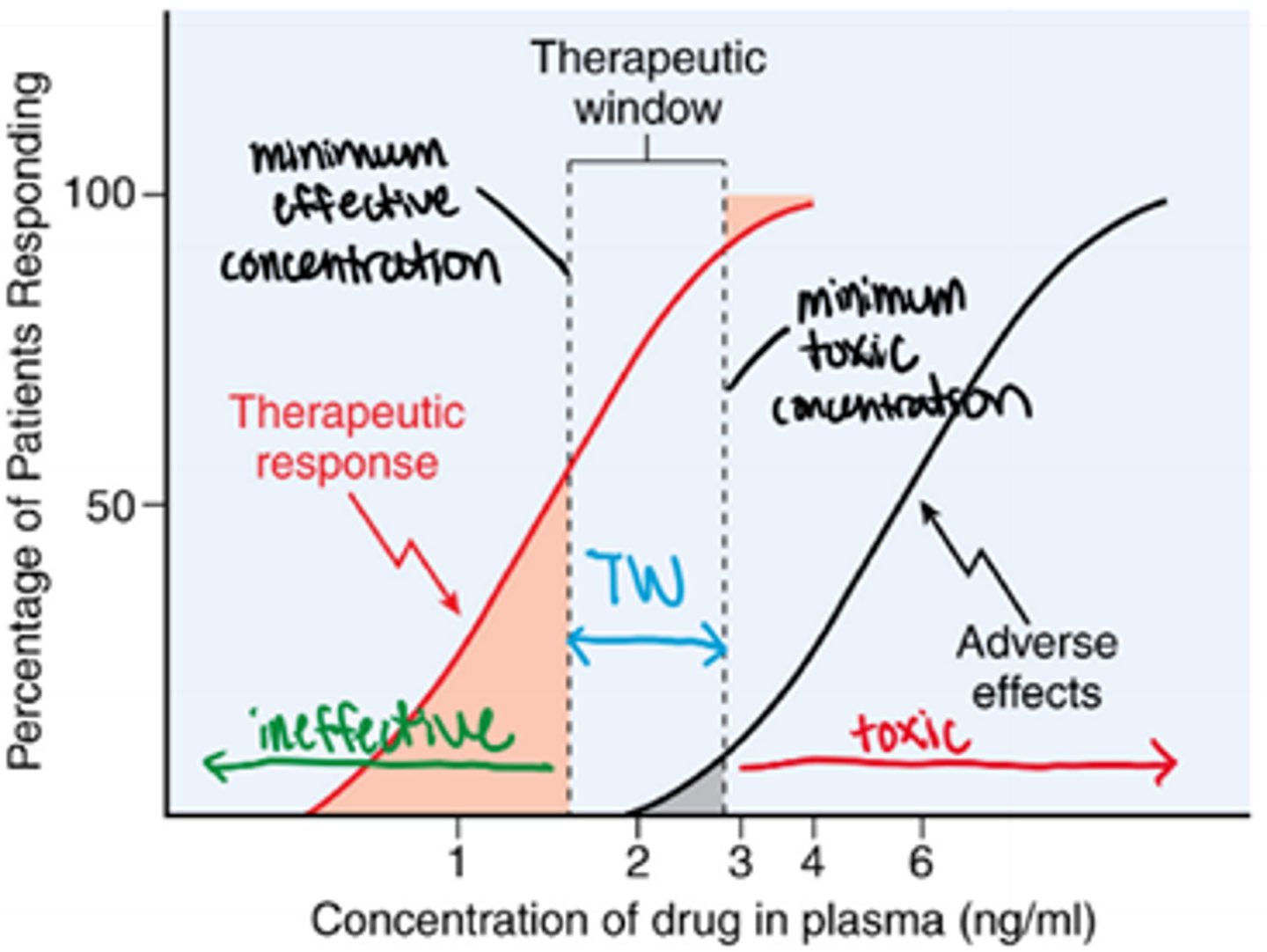
therapeutic window
The range of steady state drug plasma concentration that provides therapeutic efficacy with minimum adverse effects
aminoglycosides, warfarin, phenytoin
drugs with a narrow therapeutic window
1. Start low and go slow (titrate dose slowly)
2. Tight drug serum concentration monitoring
3. Drug-drug interactions
Precautions with drugs with narrow therapeutic window
hyporeactivity
intensity of drug effect in individual patient is diminished compared to that seen in most individuals
hyperreactivity
intensity of drug effect in individual patient is increased compared to that seen in most individuals
hypersensitivity
usually refers to allergic or other immunologic responses to drugs
Tolerance
decrease in responsiveness as result of continued drug administration (NOT addiction)
Tachyphylaxis
responsiveness to drug diminishes rapidly after administration
paradoxical response
effect opposite to the expected one (ex: antihistamines in children)
sensitive
Polymorphisms in CYP2C9 lead to warfarin __________________ phenotype
resistant
Polymorphisms in VKORC1 leads to warfarin ______________ phenotype