Lecture 15: Nervous System Spinal Cord, Reflexes, Ear
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is described as a slender nerve column that passes downward from the brain into the vertebral canal?
spinal cord
Where does the spinal cord start?
just outside the skull (foramen magnum)
Where does the spinal cord end?
between the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae
Spinal cord consists of ______ segments which gives rise to spinal nerves
31
What can happen if the spinal cord is damaged?
can lead to paralysis
What are the major functions of the spinal cord?
connects body to brain via nerve impulses
center for spinal relfexes
What are the tracts of the spinal cord?
Ascending tract (spinothalamic)
descending tract (corticospinal)
What spinal tract carries sensory information via afferent neurons to the brain?
Ascending tract
What spinal tract is associated with motor impulses from the brain to muscles and glands via efferent neurons?
Descending tract
Ascending tract =
towards brain
Descending tract =
away from brain
What divides the right and left halves of the spinal cord?
anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus
What does the gray matter part look like?
butterfly core
what are posterior horns?
where afferent (sensory) fibers enter
What are anterior horns?
where efferent (motor) fibers exit
__________ surrounds the gray matter
white matter
On the spinal cord, large wings are which side?
ventral/anterior side
On the spinal cord, small wings are which side?
dorsal side
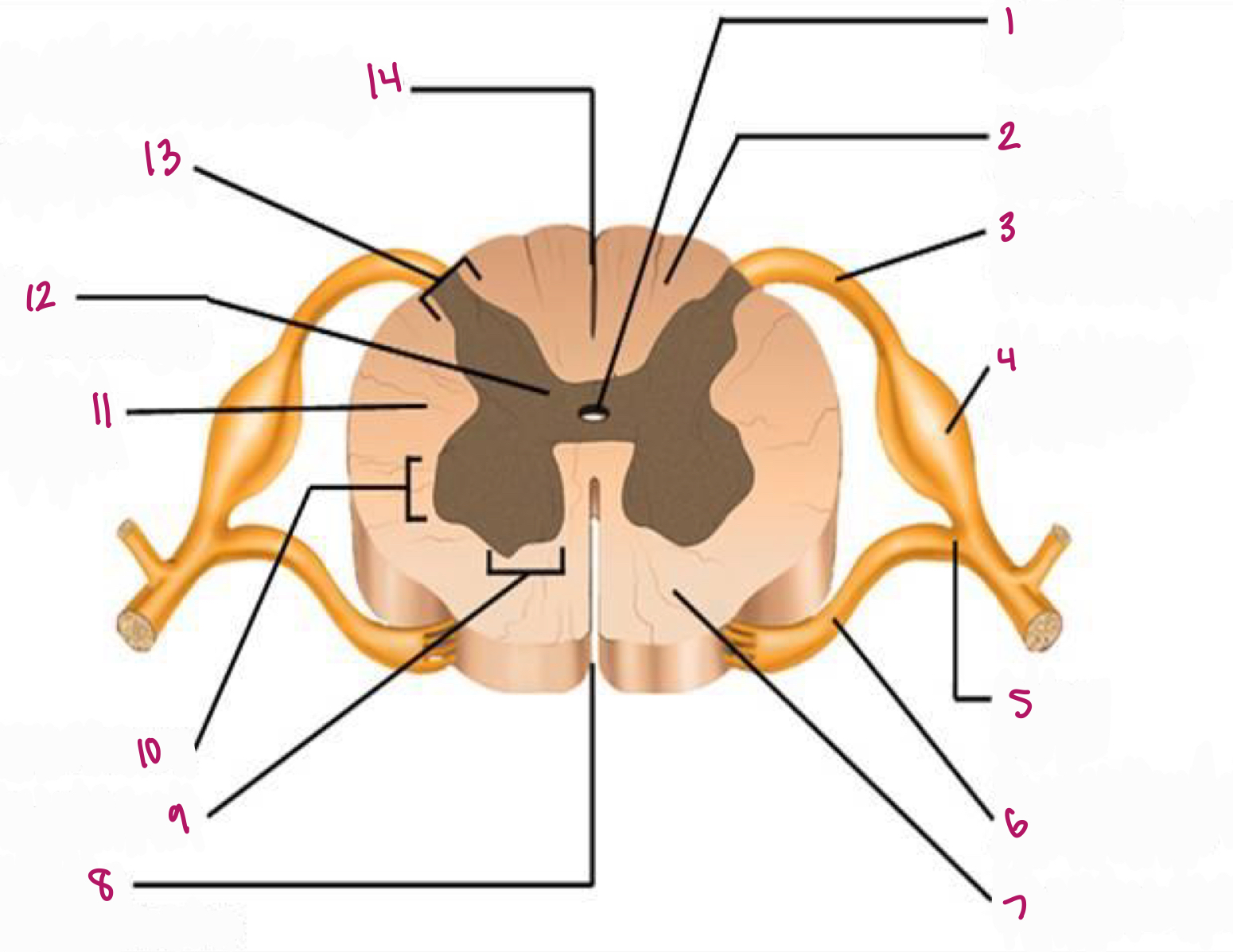
Label figure 1.
central canal
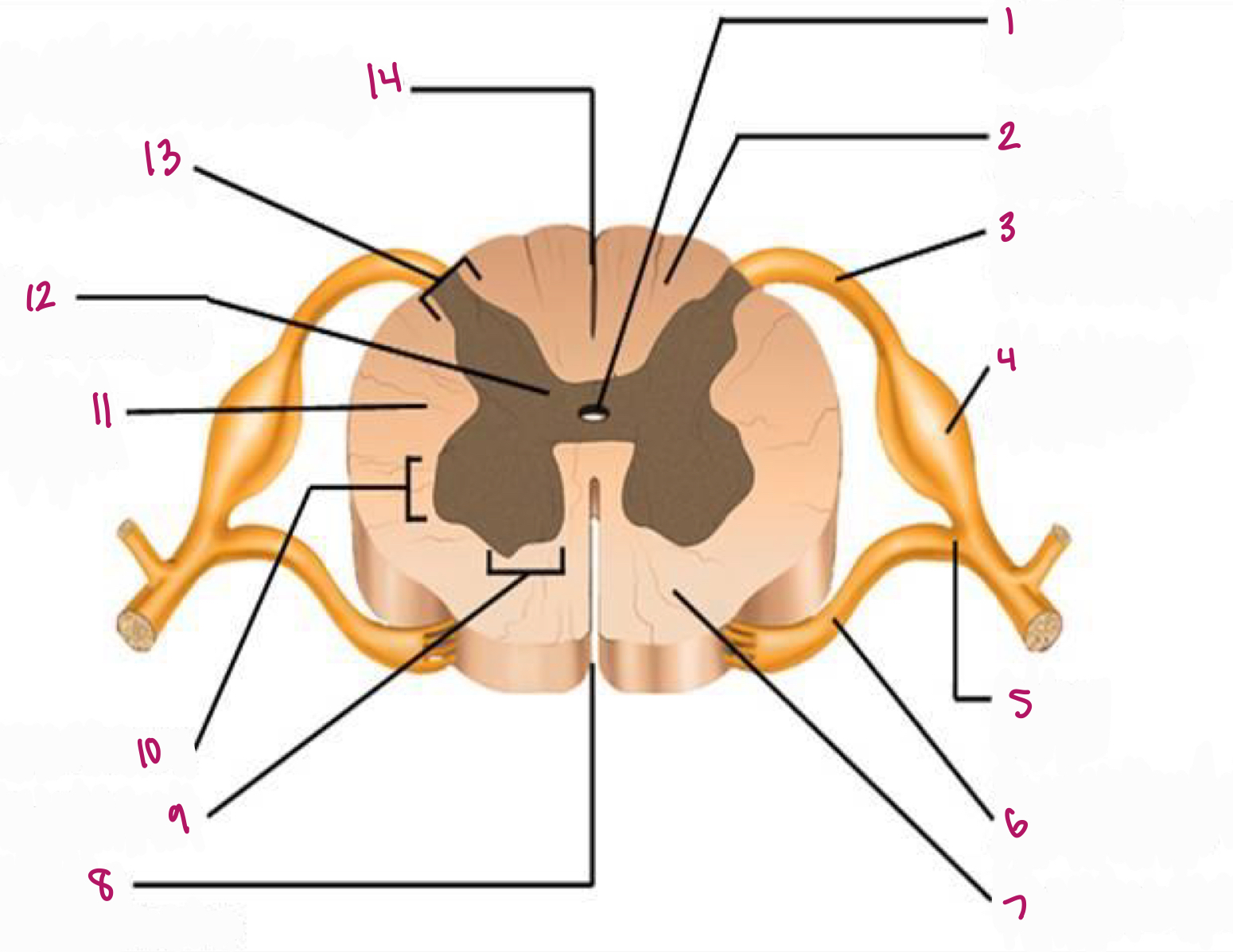
Label figure 2.
dorsal column
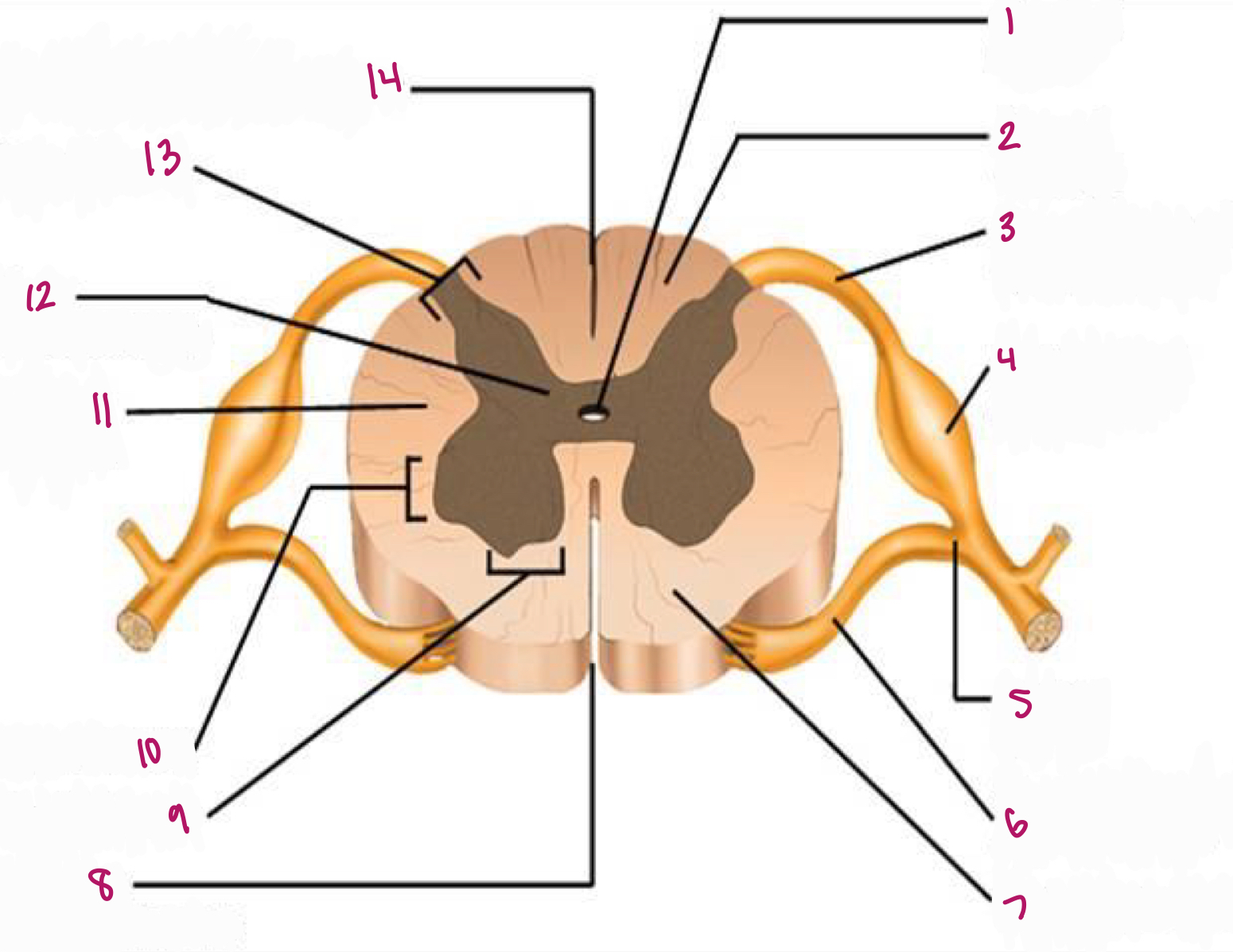
Label figure 3.
dorsal root of spinal nerve
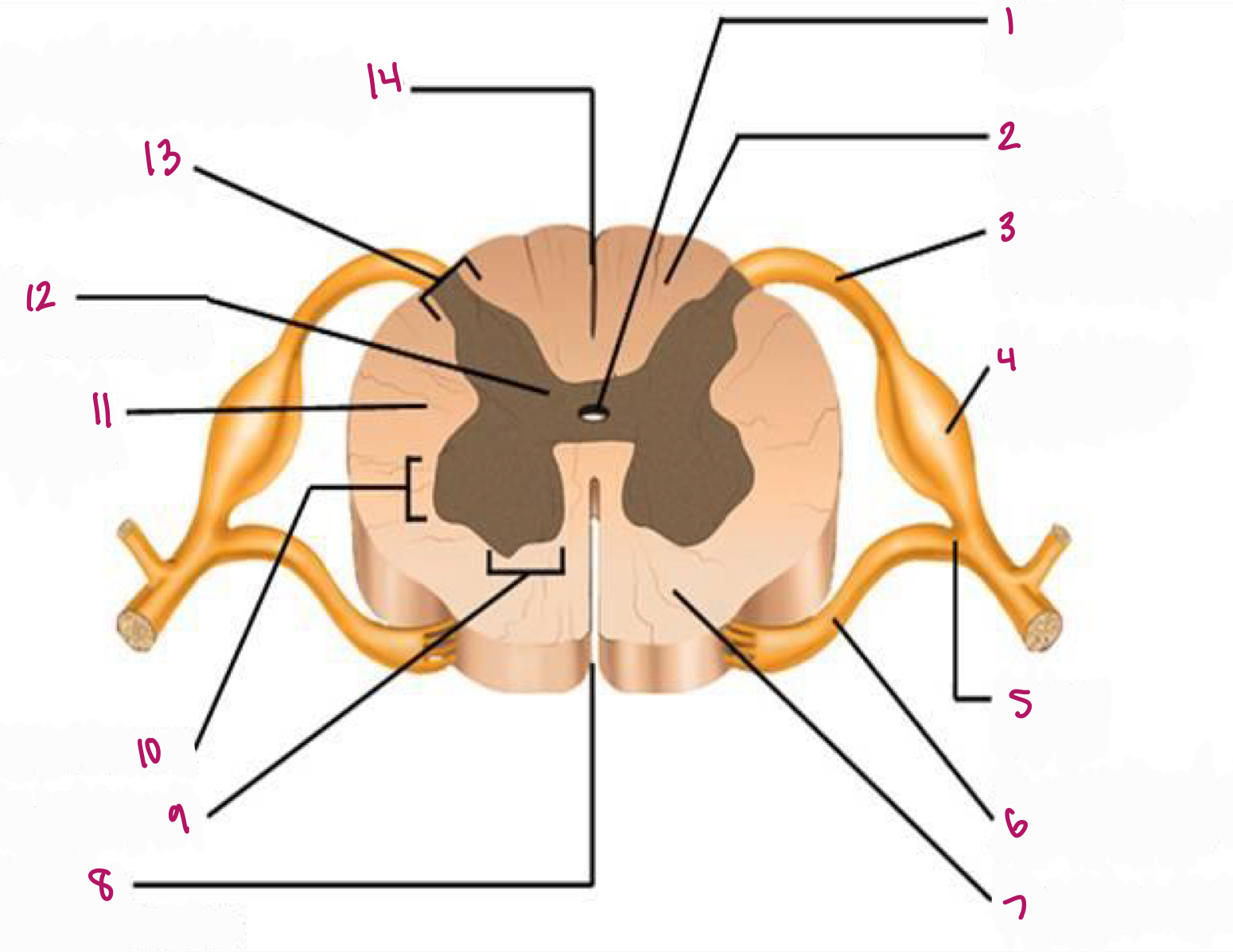
Label figure 4.
dorsal root ganglion
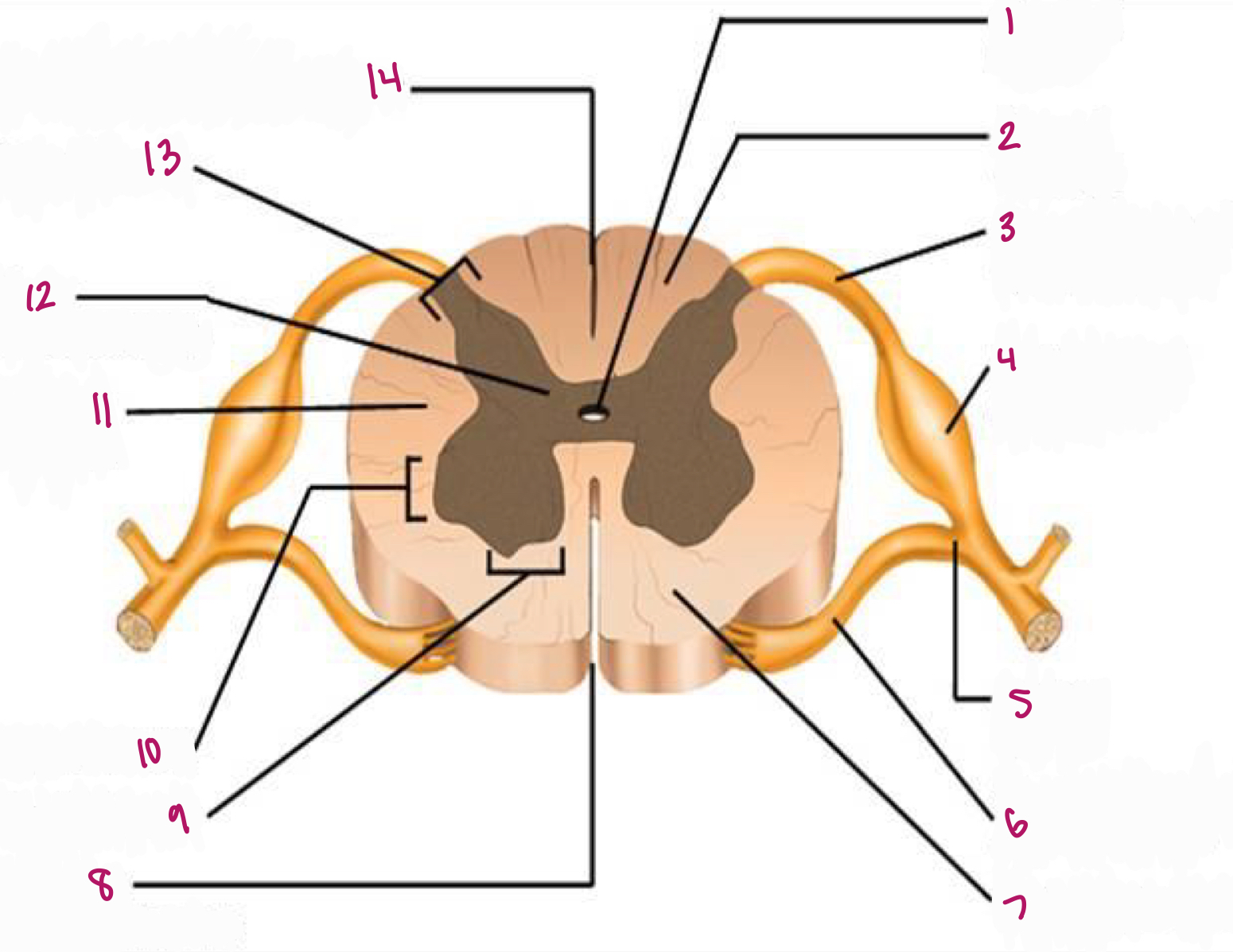
Label figure 5.
spinal nerve
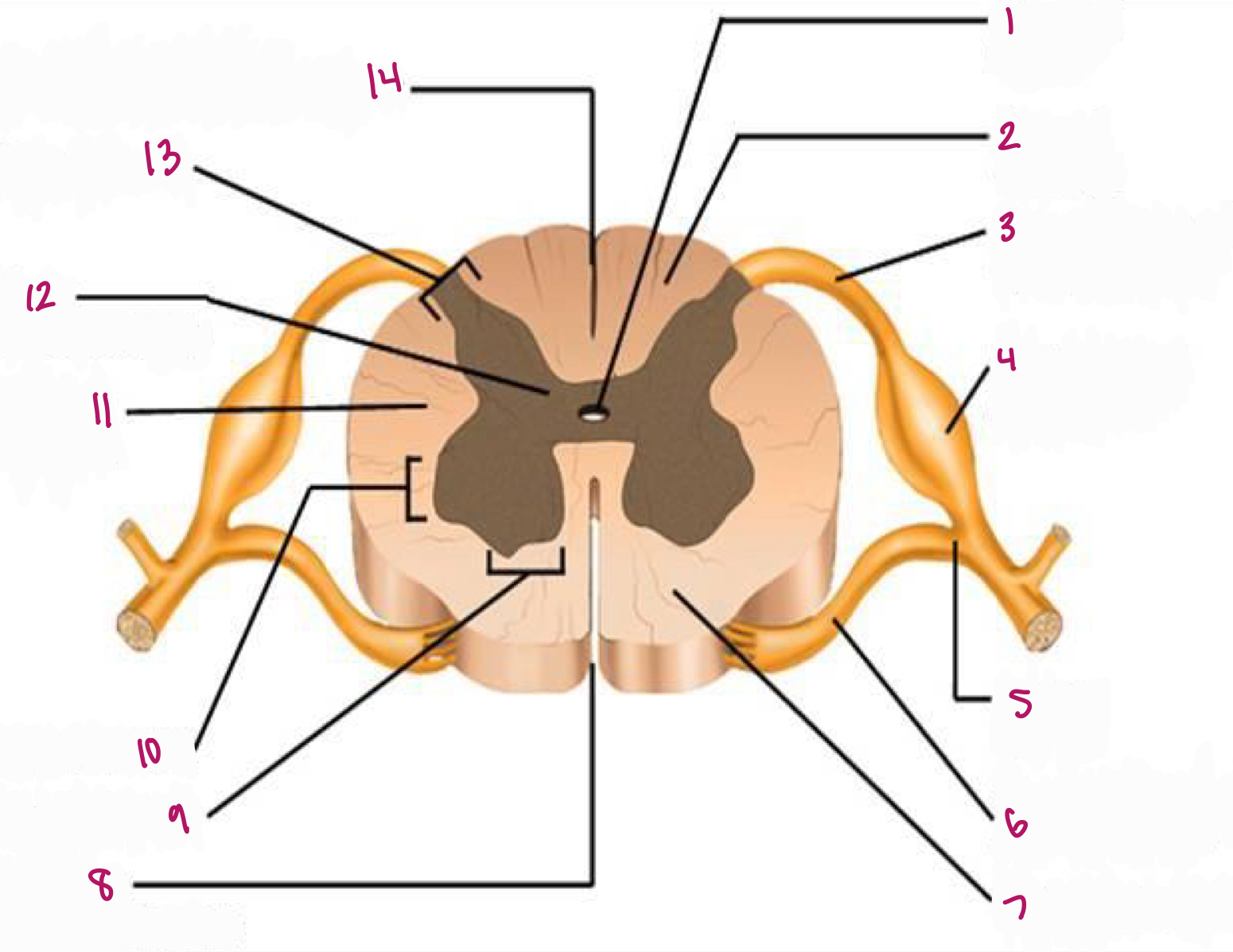
Label figure 6.
ventral root of spinal nerve
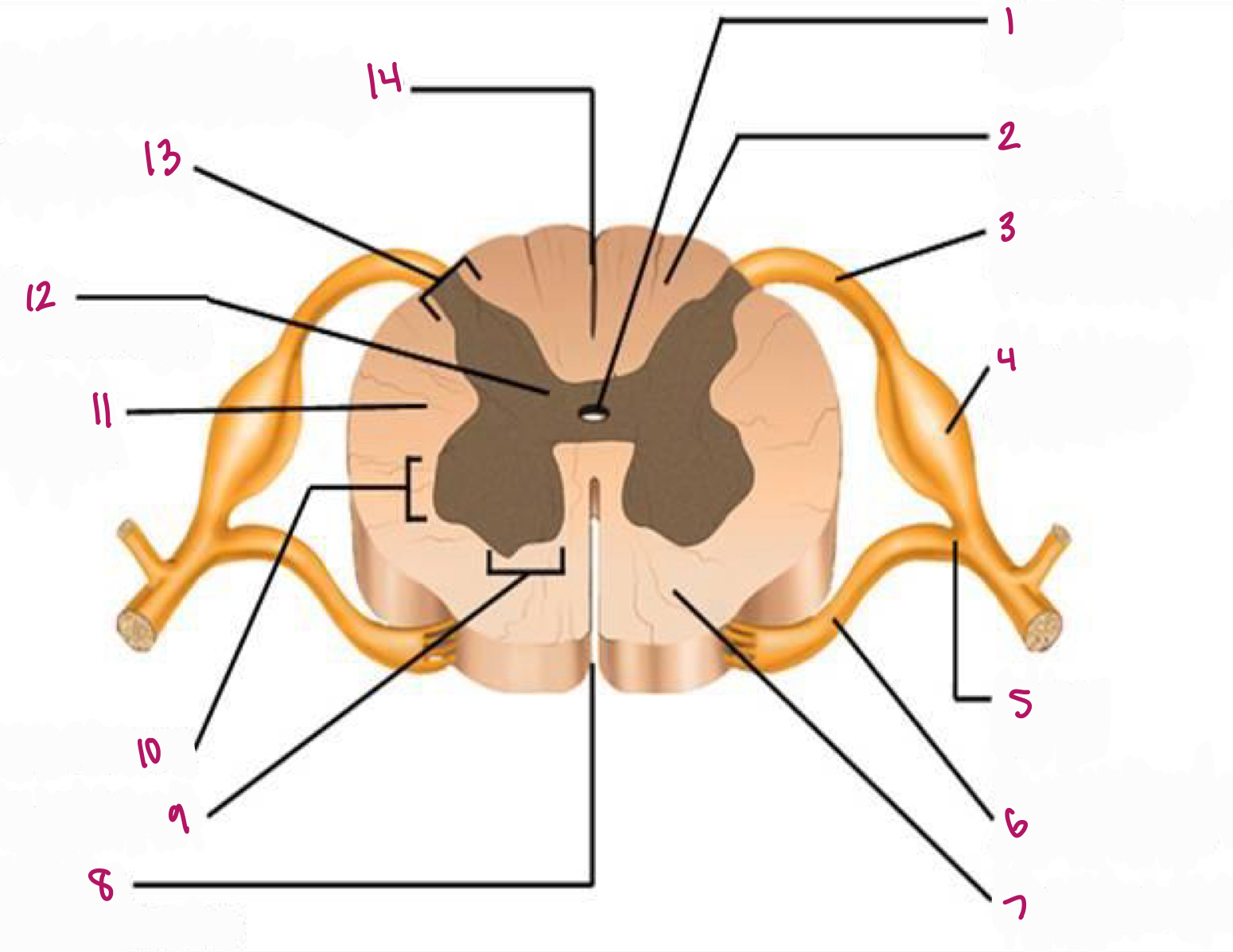
Label figure 7.
ventral column
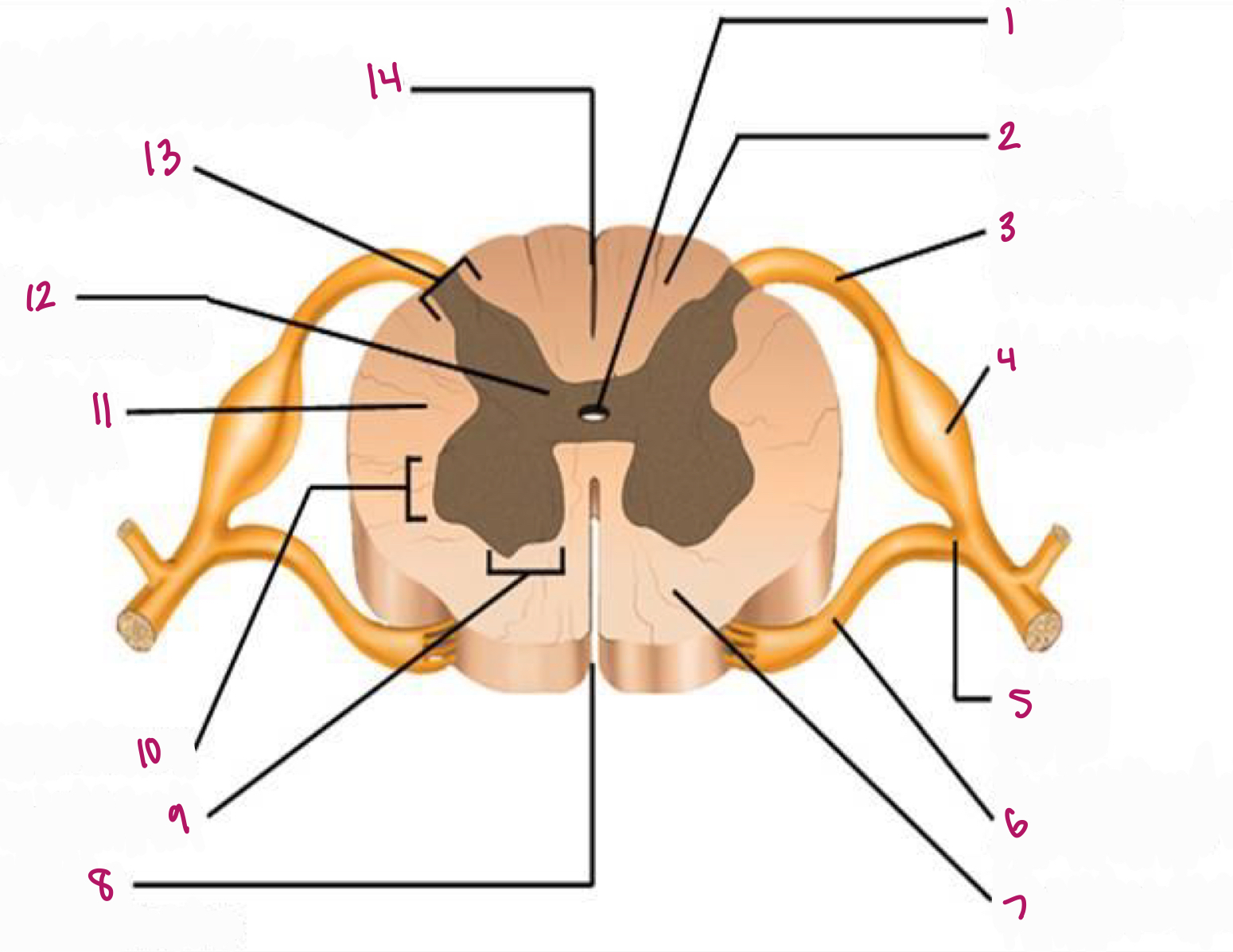
Label figure 8.
anterior median fissure
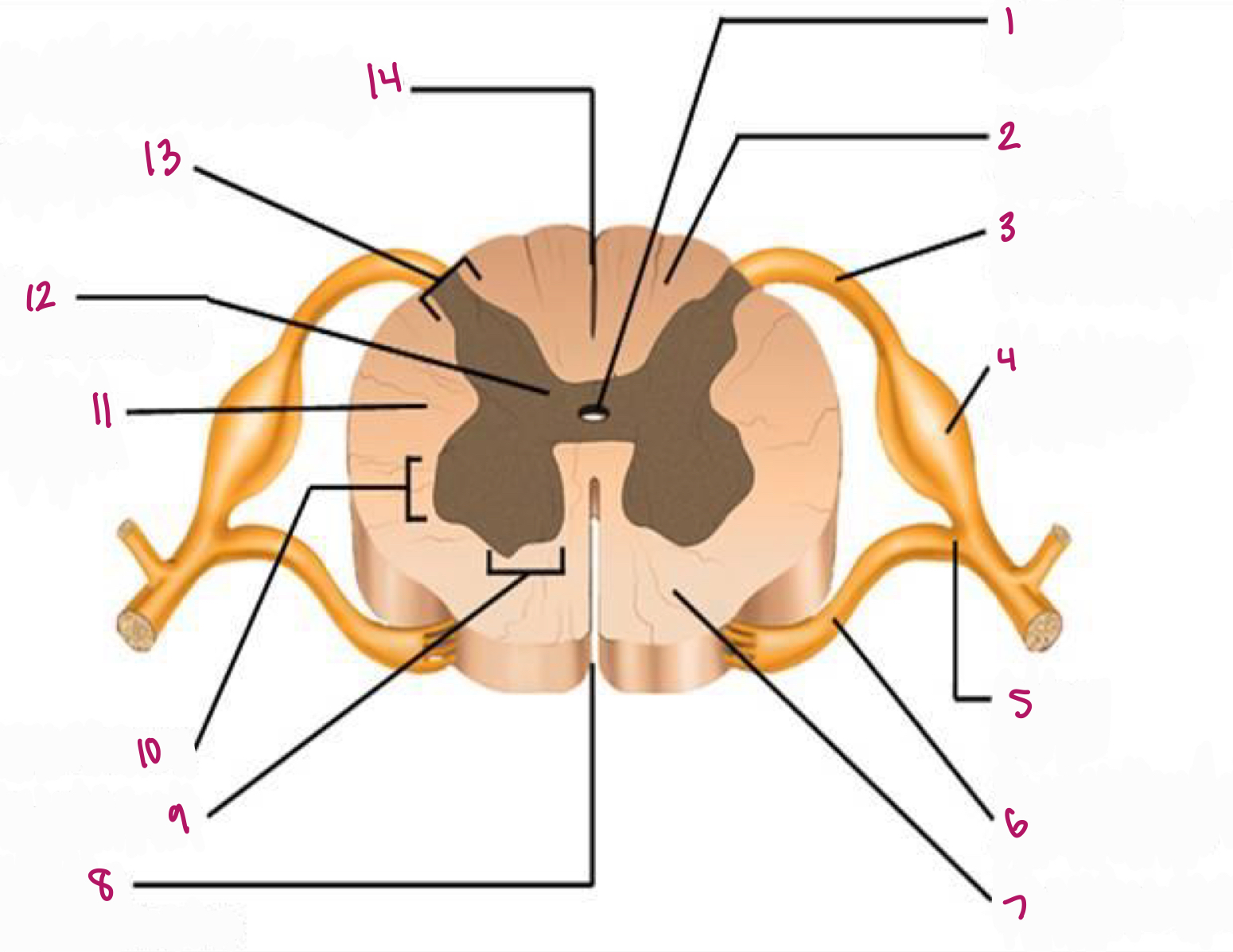
Label figure 9.
ventral horn
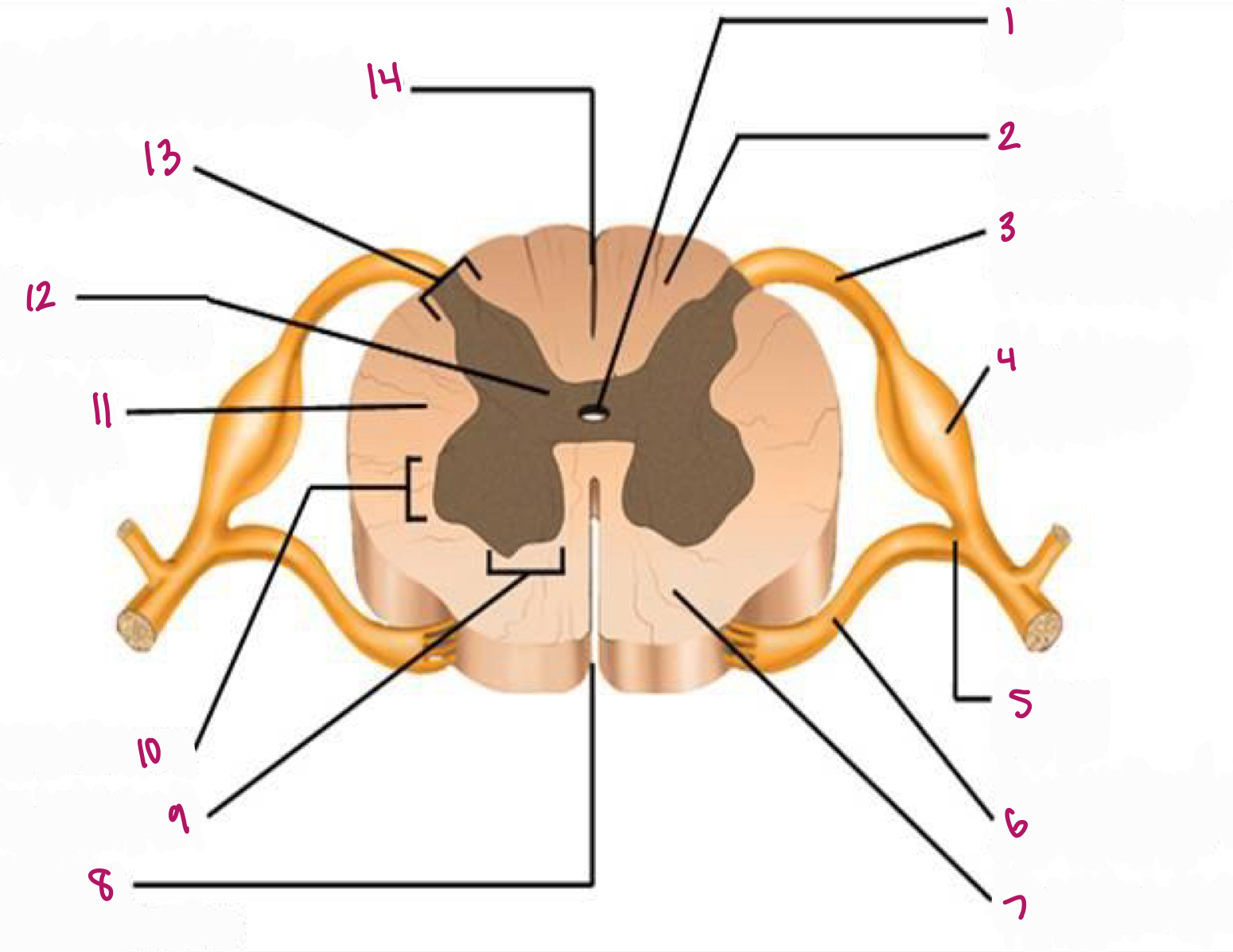
Label figure 10.
lateral horn
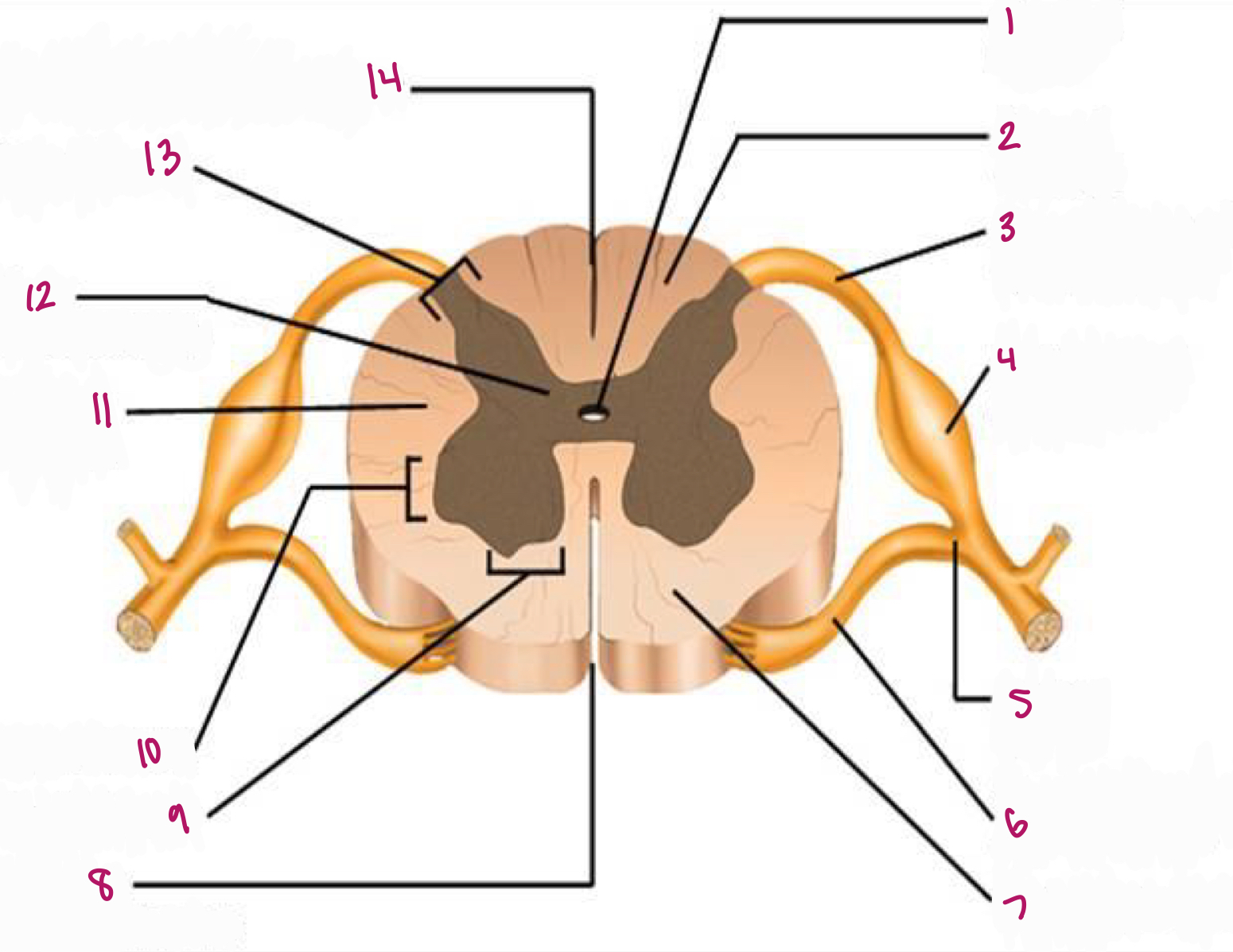
Label figure 11.
lateral column
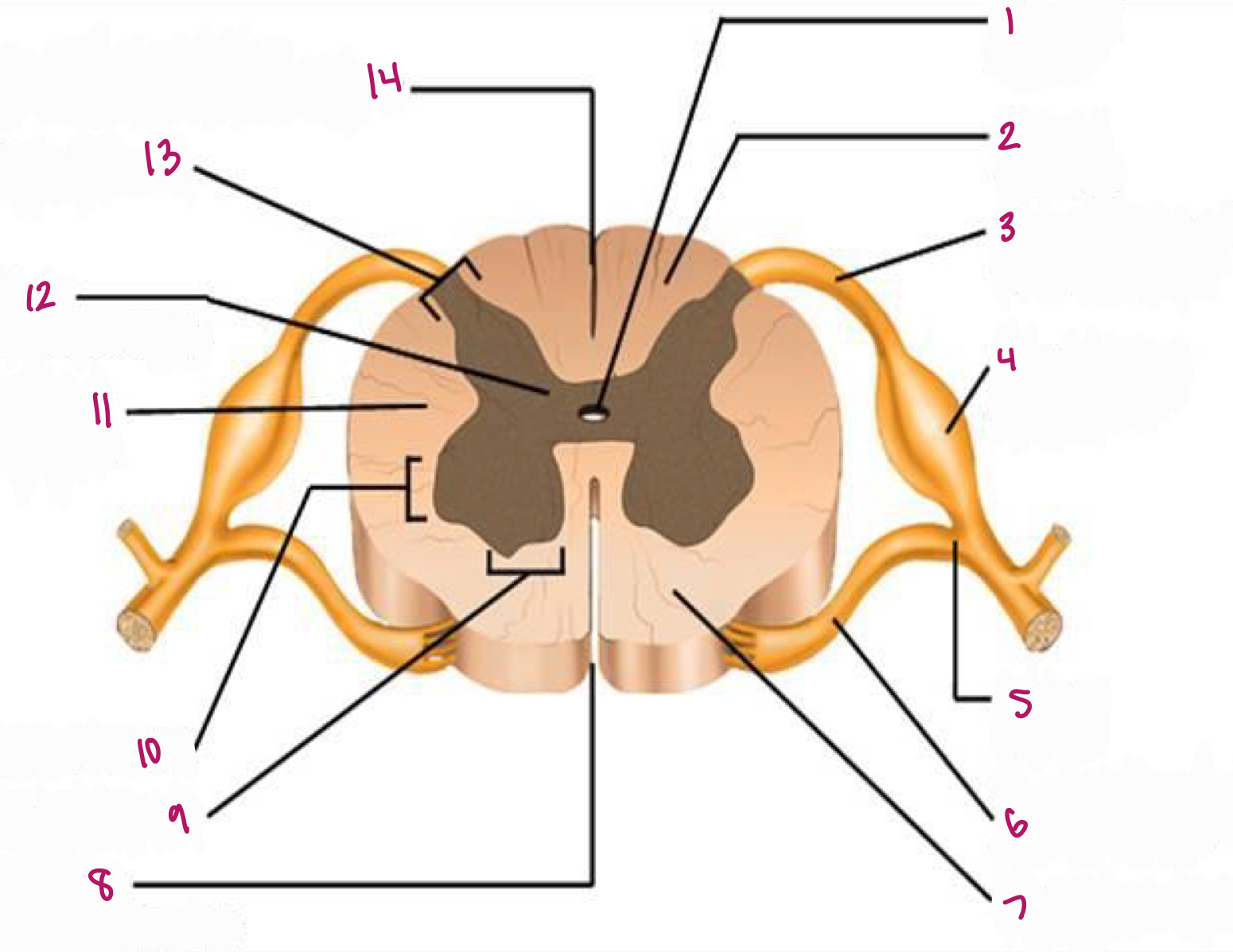
Label figure 12.
gray commissure
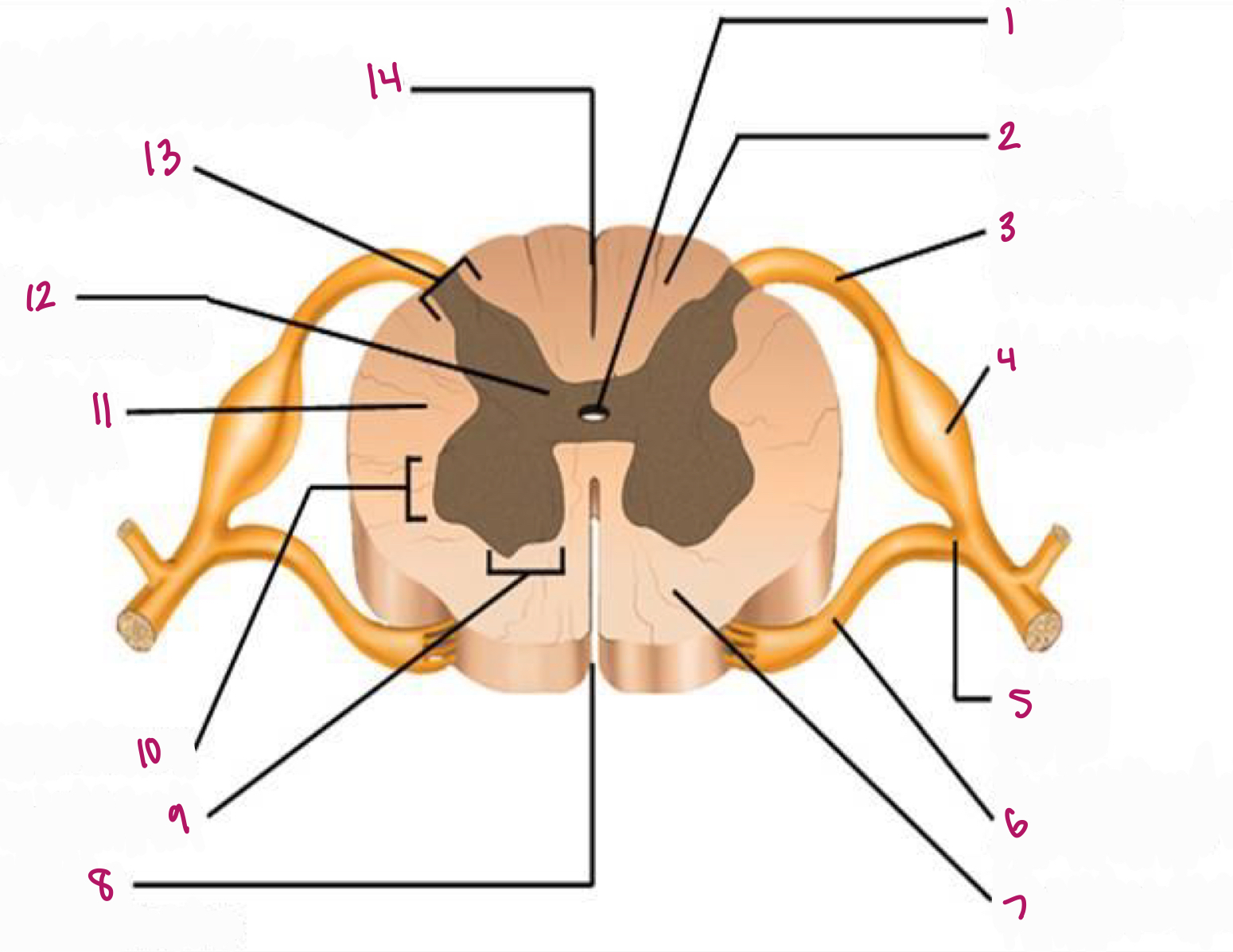
Label figure 13.
dorsal horn
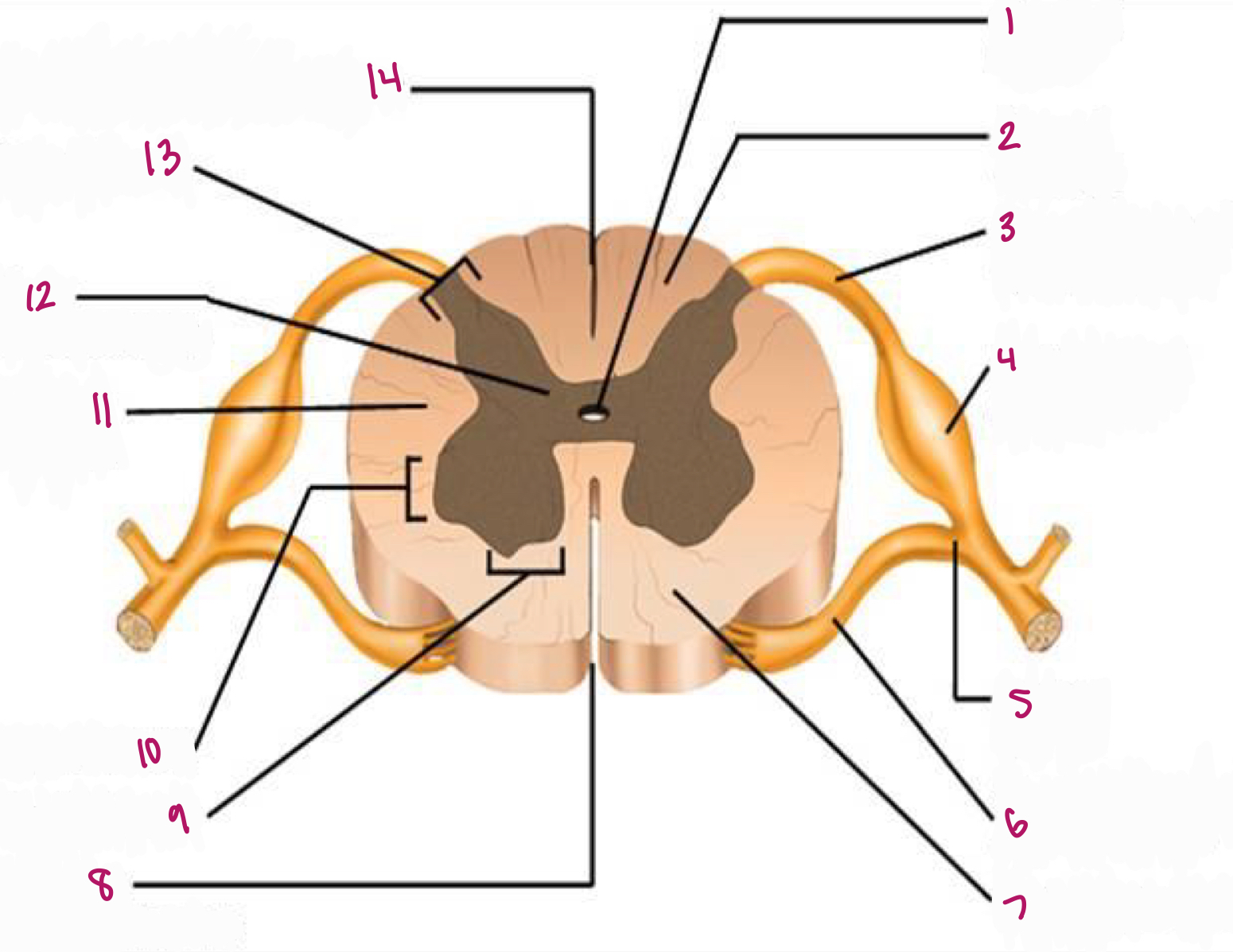
Label figure 14.
posterior median sulcus
What is the posterior root of the spinal cord?
where sensory (afferent) fibers enter
What is the anterior root of the spinal cord?
where efferent (motor) fibers exit
What is the tube in the middle of the gray matter that contains cerebrospinal fluid called?
central canal
What is the enlarged area; location of the cell body of sensory neurons called?
dorsal root ganglion
Rapid, automatic, subconscious response to a stimulus causing an ____________________
involuntary reaction
Reflexes are?
“built in” or learned
What kind of pathway does a reflex have?
simple; including a few neurons
What are examples of reflexes?
patellar reflex (posture)
withdrawl reflex (protection)
What is the function/importance of reflexes?
protection
detects disease or injury (pupil)
maintaining homeostasis
check for infant development
What is step one of reflex arc pathway?
stimulus
What is step two of reflex arc pathway?
afferent/sensory neurons carry impulse towards the CNS
What is step three of reflex arc pathway?
enter the dorsal root of spinal cord
What is step four of reflex arc pathway?
enter the dorsal horns of gray matter
What is step five of reflex arc pathway?
exit ventral horn of gray matter
What is step six of reflex arc pathway?
exit ventral root of spinal cord
What is step seven of reflex arc pathway?
response travels via spinal efferent/motor neurons
What is step eight of reflex arc pathway?
effector- reaction of muscle or gland
What are the three parts of the ear?
external, middle and inner
How do organs for hearing work?
sound waves are produced from vibrating objects
The inner ear provides sense of?
equilibrium
What structures are part of the external ear?
auricle (pinna)
external auditory canal
What structure is outer, funnel-like; directs sound waves into ear; locating direction of sound ?
auricle (pinna)
What structure is a “tube” in temporal bone that carries sound waves inward to the eardrum located in middle ear?
external auditory canal
What structures are part of the middle ear?
eardrum/tympanic membrane
auditory ossicles
eustachian tube
What structure is a semitransparent membrane that vibrates from sound waves; attached to the malleus?
eardrum/tympanic membrane
What is known as the three small bones in the ear that connect vibrations from eardrum to oval window (inner ear); increases (amplifies) the force of vibration?
auditory ossicles
What are the auditory ossicles (list largest to smallest)?
malleus
incus
stapes
What structure connects the middle ear to the throat; helps maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum; helps drain fluid from middle ear?
eustachian tube
What are the three main parts of the inner ear?
cochlea
vestibule
semicircular canals
What is also known as the “snail shell” organ of hearing?
cochlea
How many chambers does the cochlea have?
3 chambers
What are the chambers of the cochlea?
cochlear duct (middle)
scala vestibule (above cochlear duct)
scala tympani (below cochlear duct)
Where is the organ of corti located?
cochlea → cochlear duct
What occurs in cochlear duct?
vibrations from stapes cause fluid to vibrate
hair cells connected to nerves bend causing action potential sent to brain
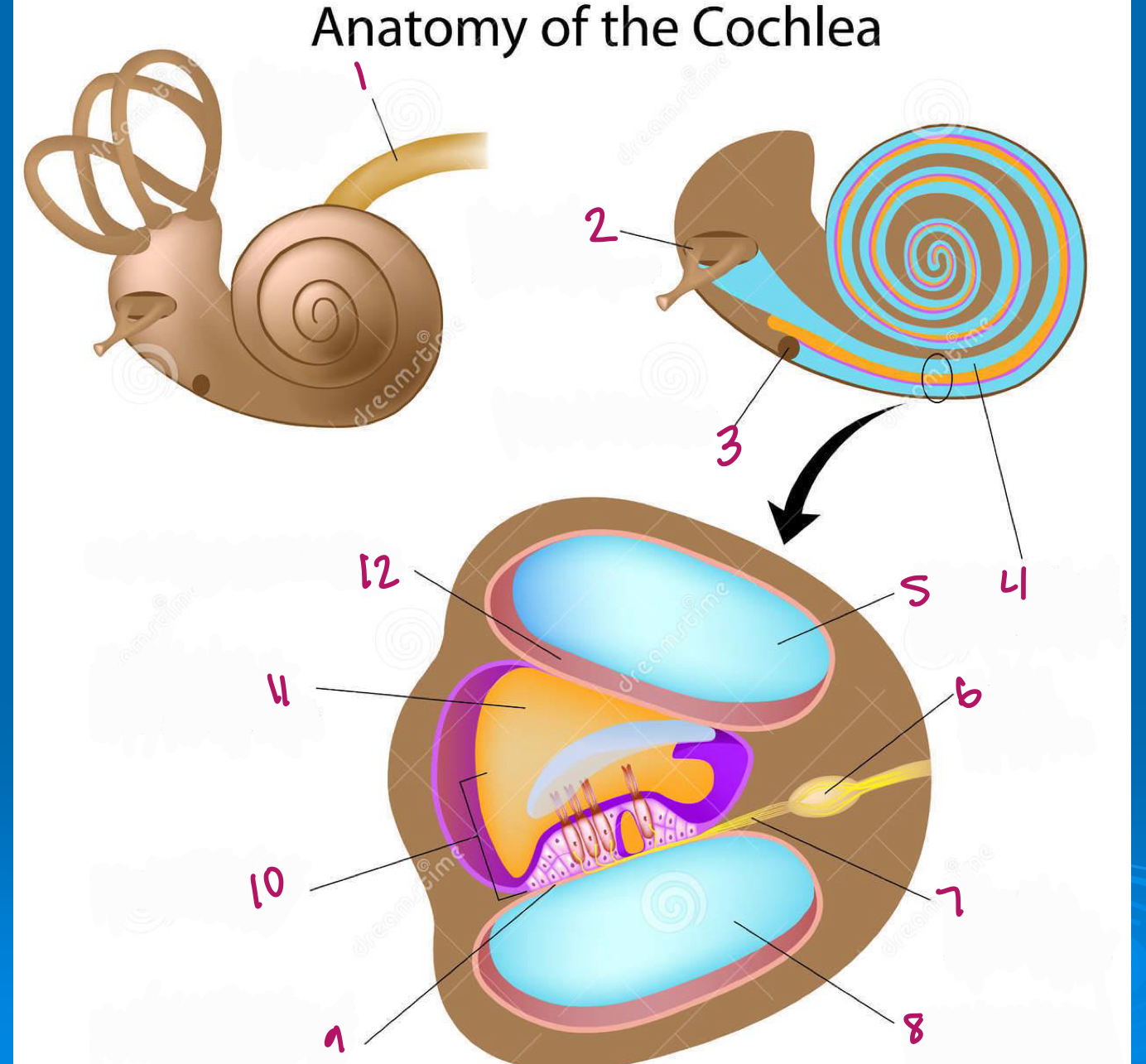
Label figure 1.
cochlear nerve
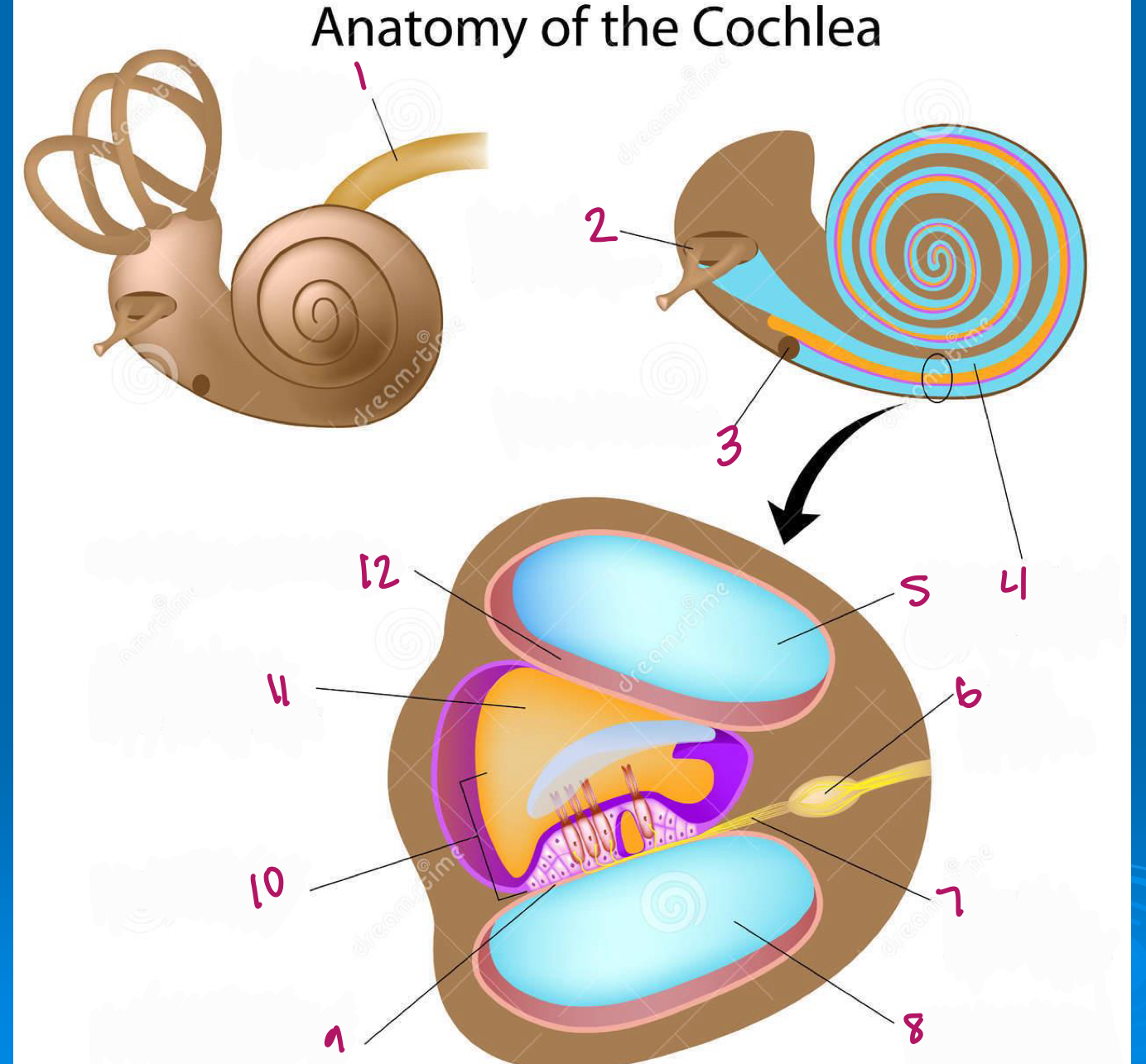
Label figure 2.
stapes in oval window
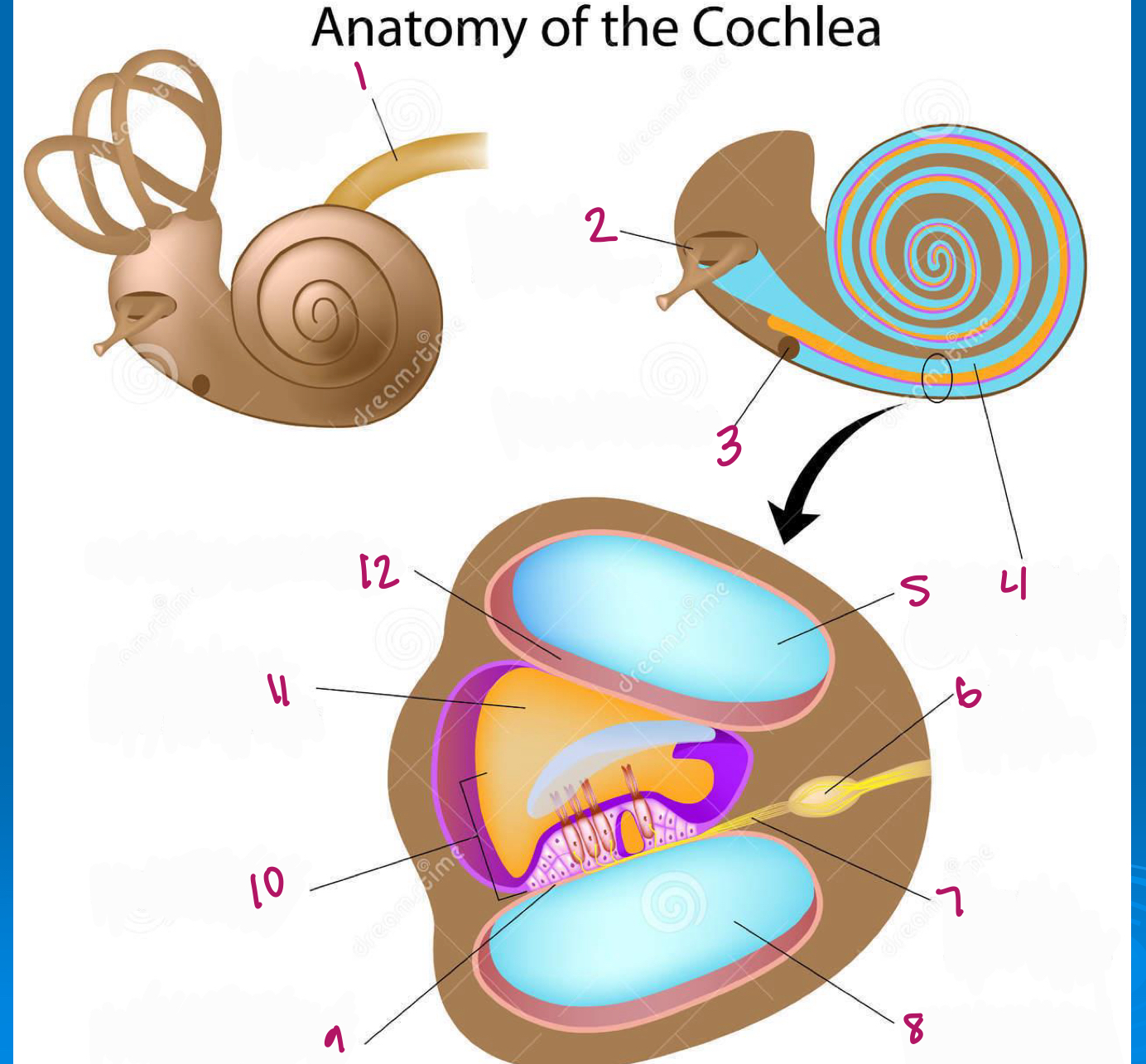
Label figure 3.
round window
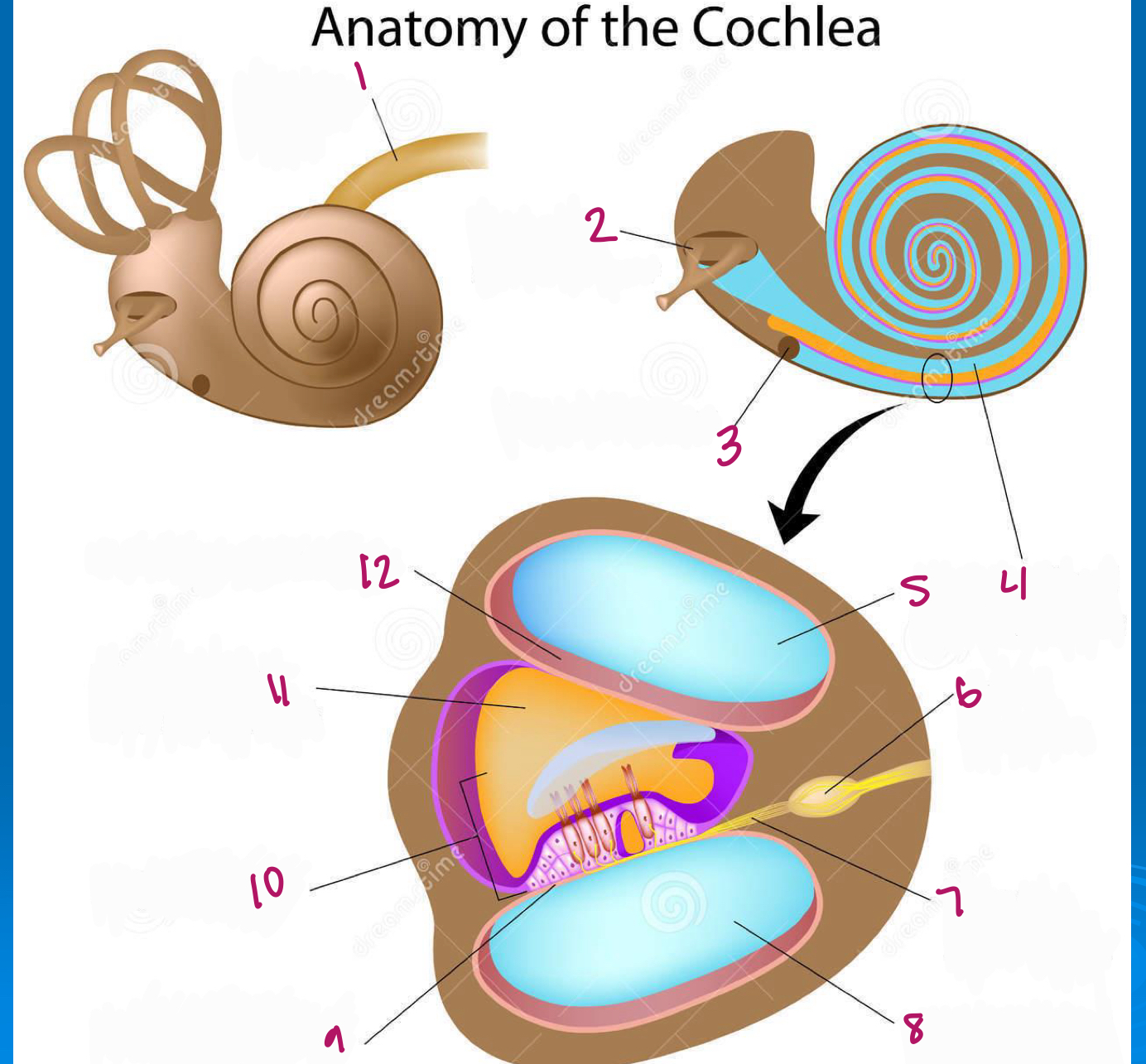
Label figure 4.
scala vestibuli
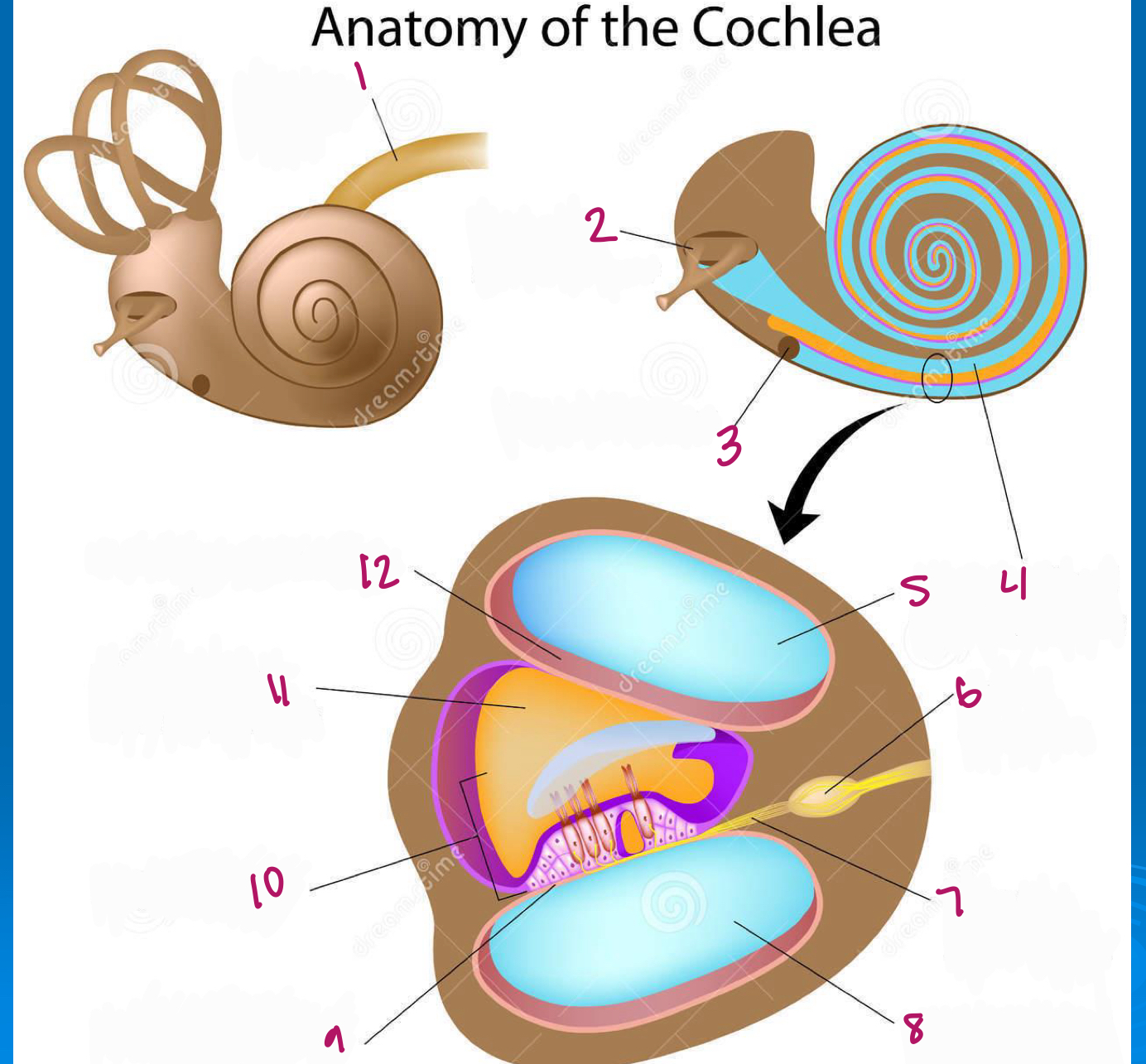
Label figure 5.
scala vestibuli
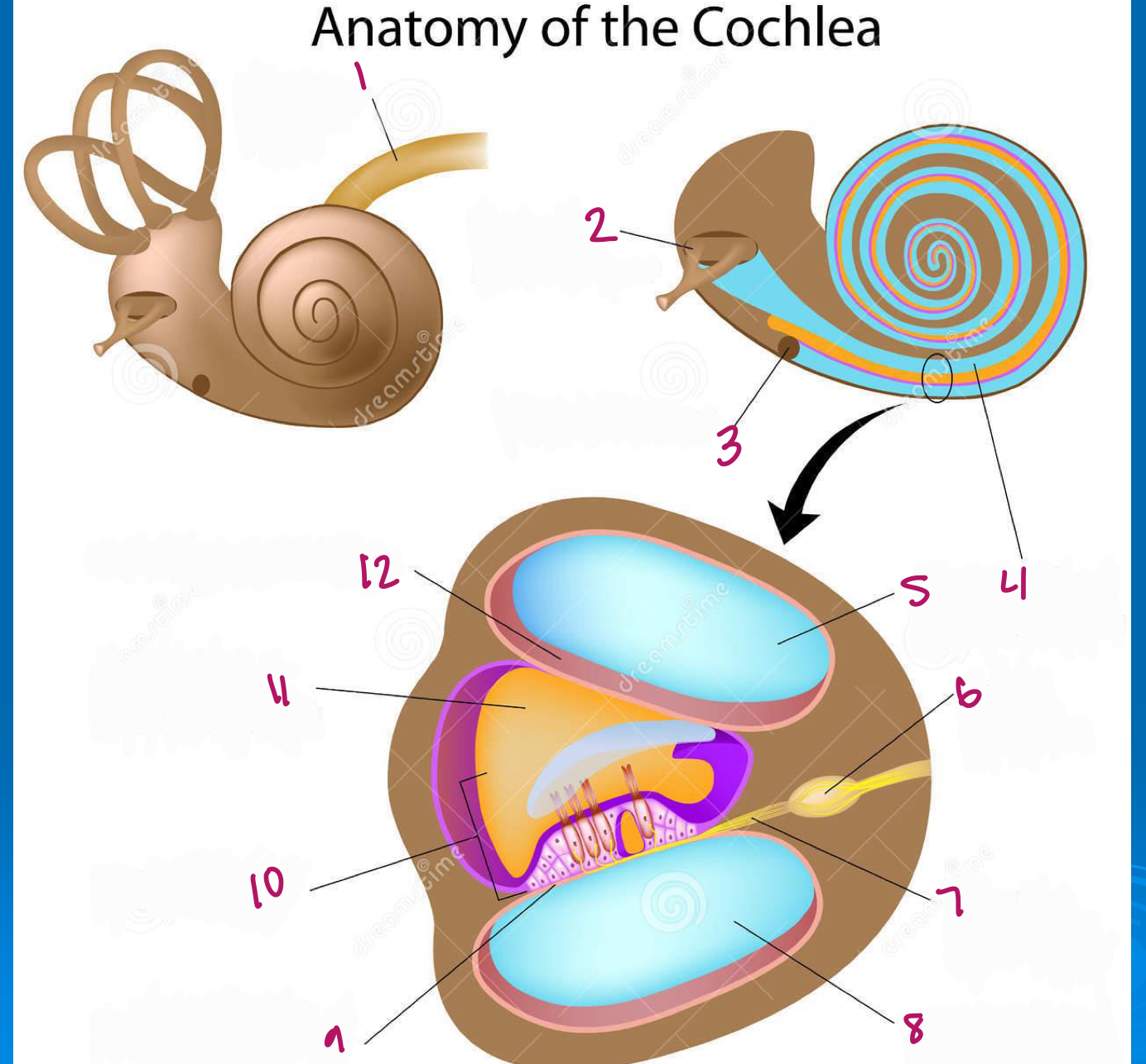
Label figure 6.
spiral ganglion
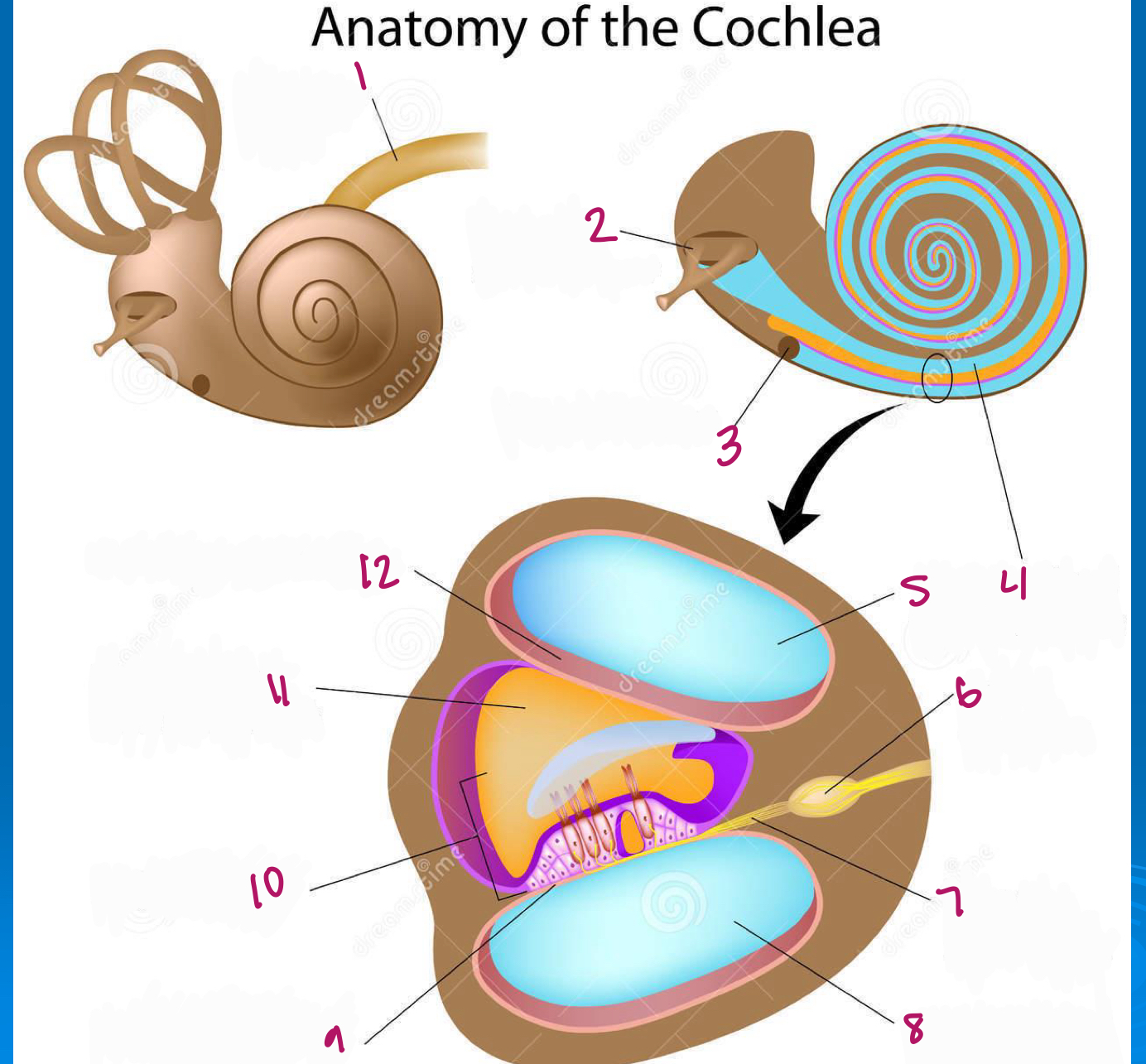
Label figure 7.
cochlear nerve fibers
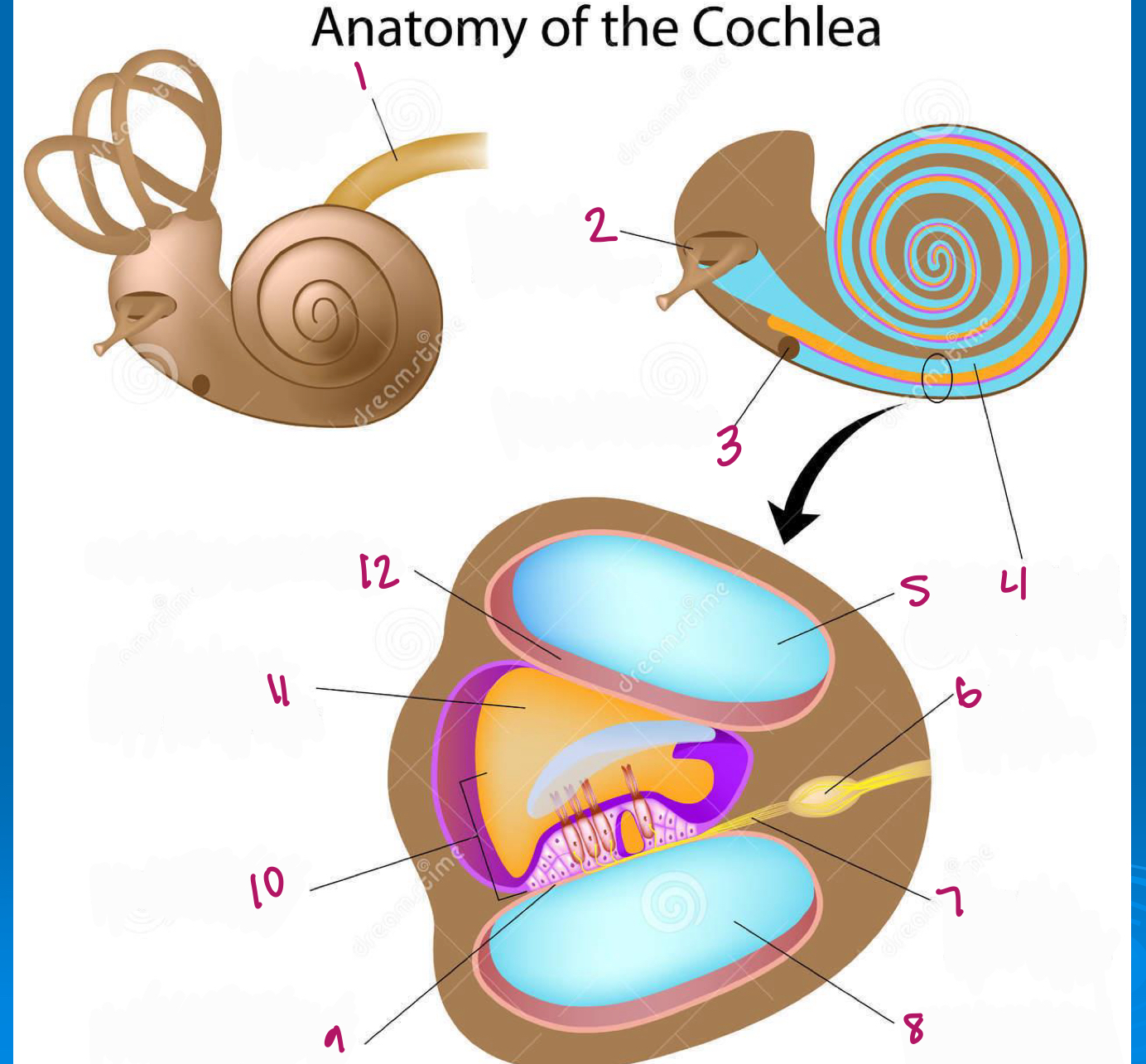
Label figure 8.
scala tympani
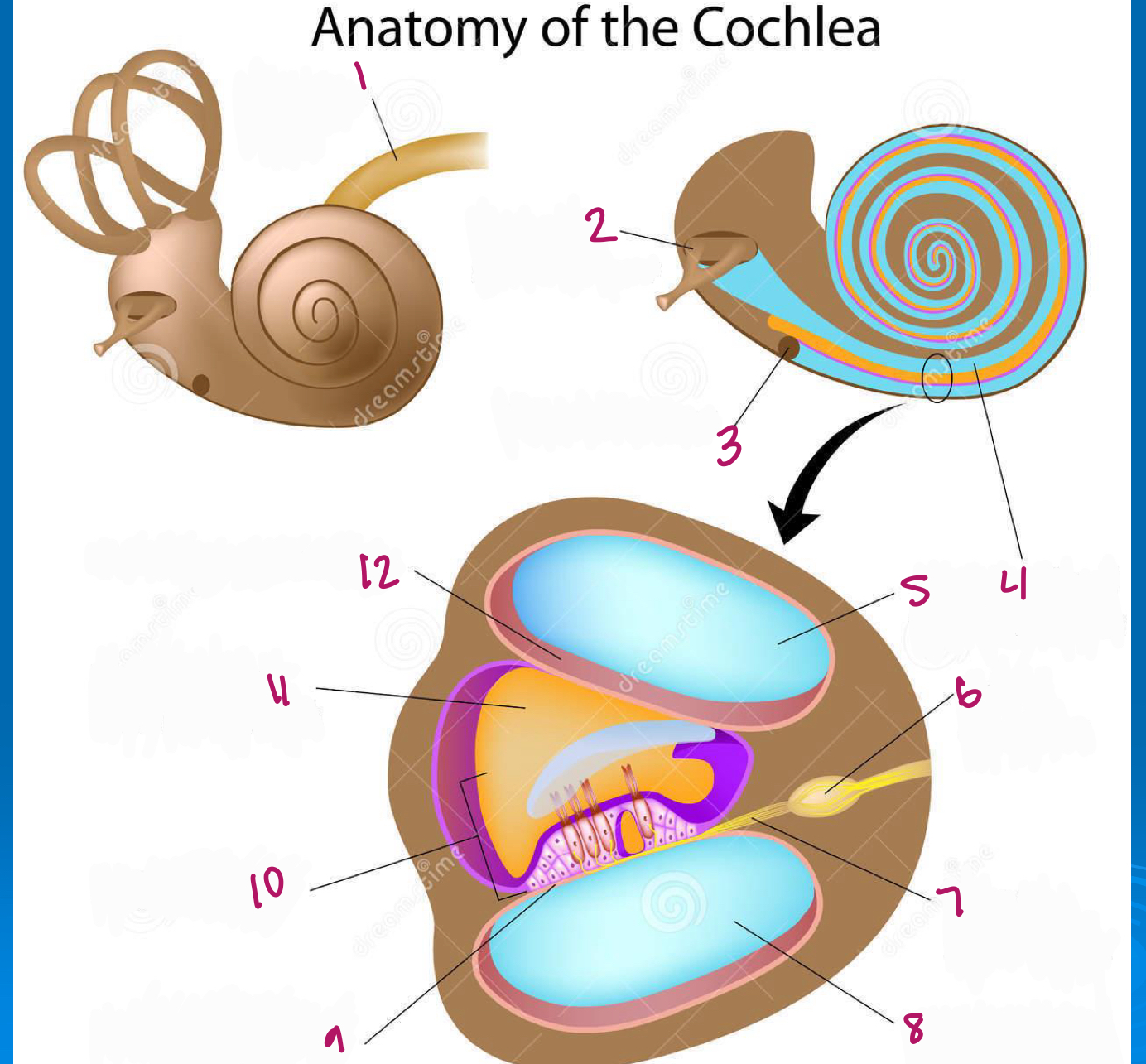
Label figure 9.
basilar membrane
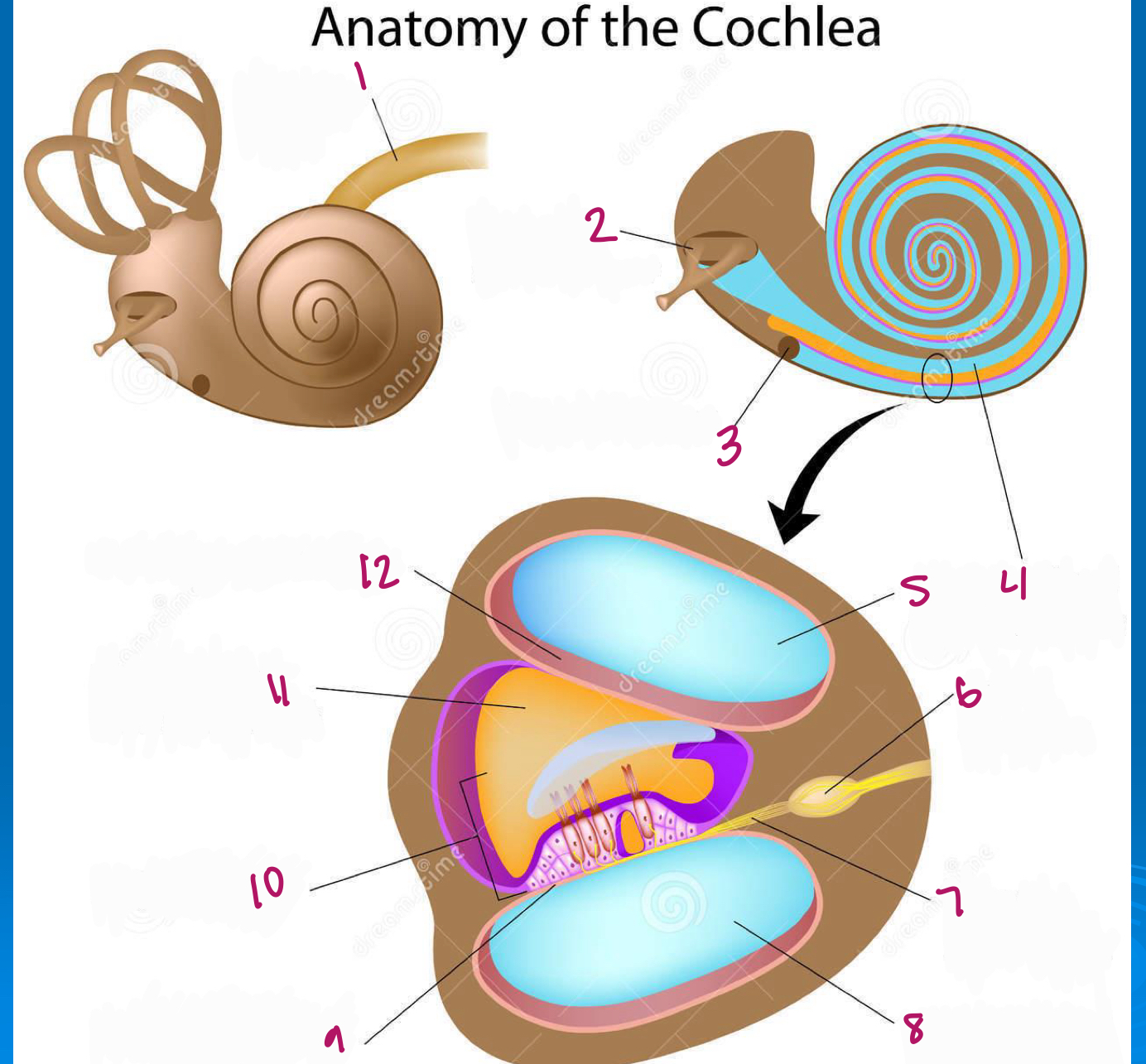
Label figure 10.
organ of corti
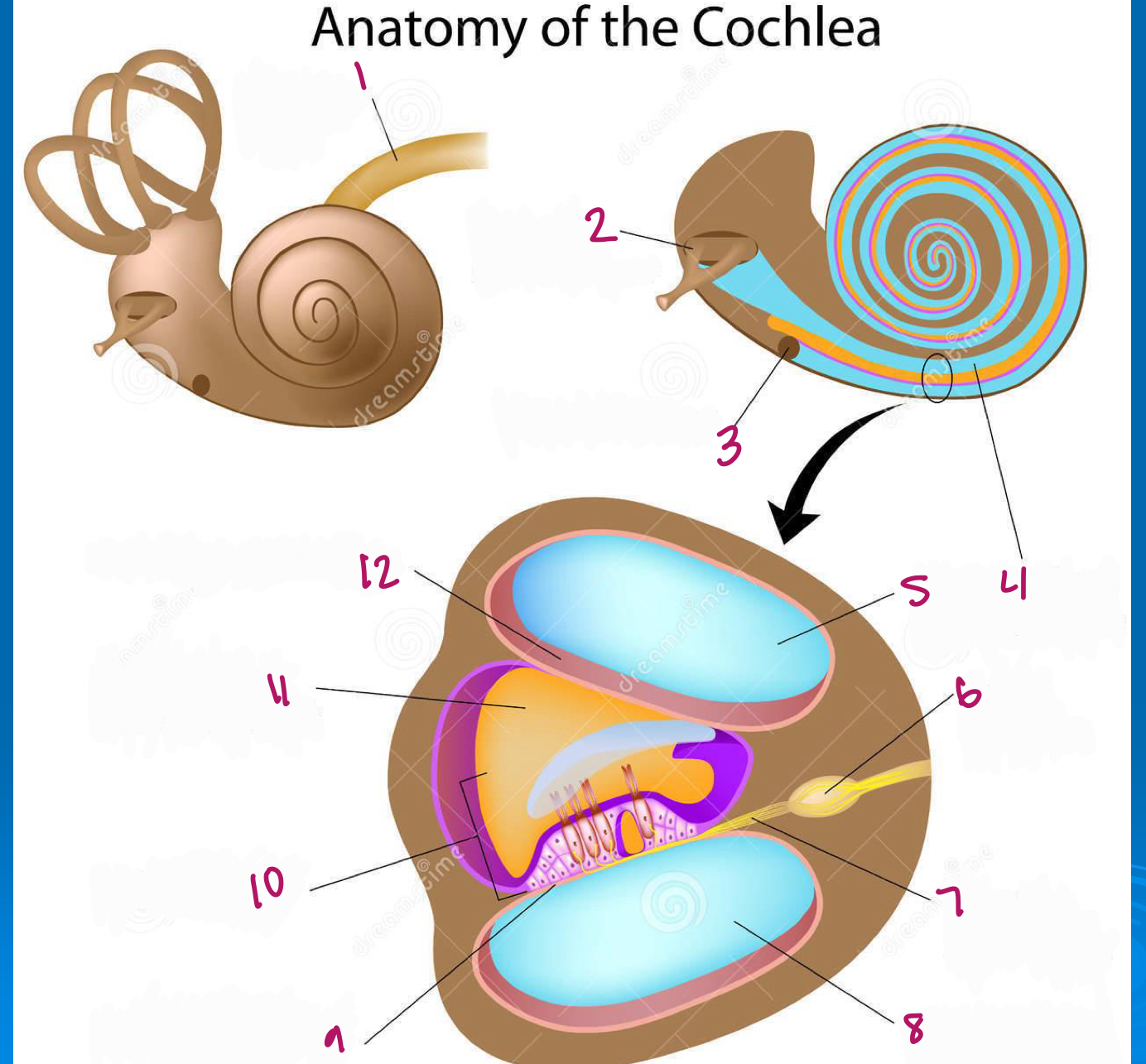
Label figure 11.
cochlear duct
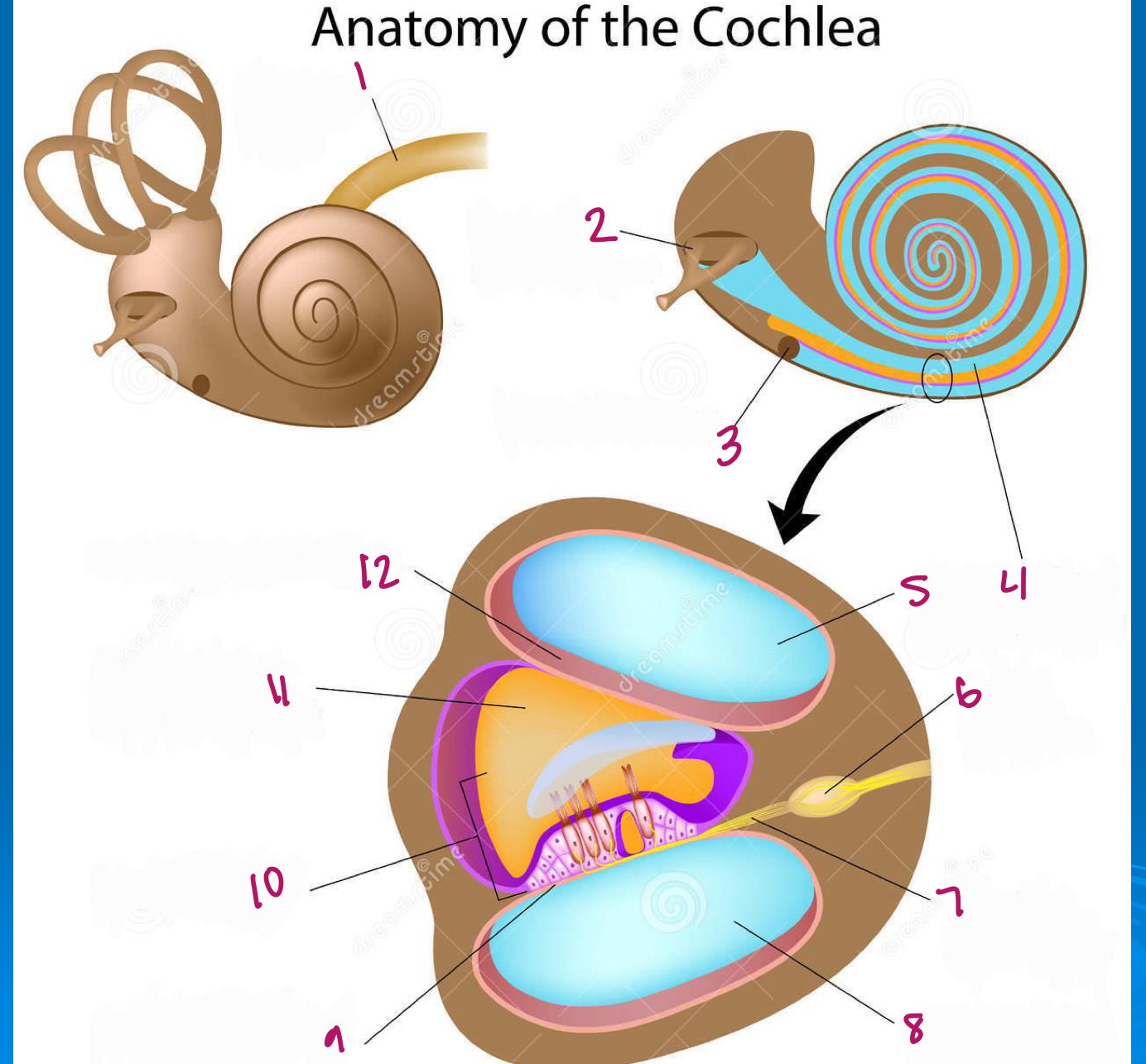
Label figure 12.
vestibular membrane
What structures work together to maintain balance and equilibrium in ear?
vestibule
semicircular canals
What structures are part of vestibule for balance?
utricle
saccule
What do the vestibule and semicircular canals have?
fluid and hair cells that move and bend in response to motion
What are the two states of equilibrium?
static equilibrium
dynamic equilibrium
Which type of equilibrium is associated with sense of position of the head when body isnt moving; maintaining balance relative to the force of gravity?
static equilibrium
The vestibule is associated with which type of equilibrium?
static equilibrium
Which type of equilibrium maintains balance when head and body are in motion; rotational acceleration?
dynamic equilibrium
The semicircular canals are associated with what kind of equilibrium?
dynamic equilibrium