x ray crystal structures
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
amorphous material properties (3)
broad meltin point
globular
no order
crystalline material properties (4)
narrow melting point
regular faces and edges
regular pattern and order
diffract light
what are the three crystallisation steps
supersaturation
formation of nuclei
crystal growth
why do crystals diffract
because molecules are arranged in an ordered fashion
what happens when an x ray beam strikes a crystal surface at theta
part of the beam is scattered by the layer of atoms at the surface
why do x rays scatter
the electron clouds of the atoms in the crystal
why are x rays scattered in an identical way
as a crystal has atoms in identical position
what is visible light between
400 - 700 nm
how do you calculate constructive interference
using braggs law

what is a unit cell
smallest repeating internal unit that has the symmetry characteristic of the solid
what are the seven basic crystal systems
cubic
tetragonal
orthorhombic
rhombohedral
hexagonal
monoclinic
triclinic
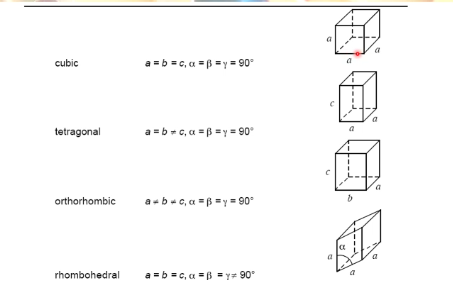
cubic unit cells properties
all sides equal
all sides equal 90
whats a primitive cubic cell (PC)
atom in each corner of a cube
whats a body centered cube (BCC)
atom in each corner and the centre
whats a face centred cube (FCC)
atom in every corner and on each face
what causes diffraction spots
x rays striking a single crystal