Users Guide to Laboratory Diagnostics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Why is it necessary to identify infectious diseases?
knowledge of likely spread
epidemiology
choice of treatment
How can we diagnose infection?
grow the agent
look for immune response to the agent
look for DNA/RNA of the agent
look for pathological signs
What should you consider when growing a culture?
aerobic/anaerobic
can it cause disease or is it a contaminant?
how quickly does it grow?
can I grow it at all?
What are the pros of growing pathogen?
know you have a live organism
positive identification
no prediction necessary
can test it for antibiotic resistance
What are the cons of growing pathogen?
false negative are common for some disease
slow

What does this image show?
Dipstick tests

What does this image show?
ELISA
What does this image show?
microscopic agglutination test
How can you look for an immune response?
dipstick tests
ELISA
microscopic agglutination test (MAT)

What can you use a microscopic agglutination for?
leptospirosis
How do you look for an immune response?
look for antigen circulating in blood - use antibody to capture this
can look for antibody - IgG or IgM using antigen to capture this
Antigens and antibodies binding makes complexes that are either:
MAT - visible
detected by using a second antibody against the antibody or antigen once it has been captured
What are ELISA tests?
coated plates used to analyse fluid samples
What are ELISA plates coated with?
known antigen
antibody
Why can you get false positives from ELISAs?
vaccination
maternal transfer
historic infection
What do ELISAs detect?
antibody level in samples (if coated with known antigen)
antigen (if coated with antibody)
What do you look for in an ELISA when coated with antibody to detect circulating antigen?
unique parts of viruses, fungi, bacteria
What causes a colour change in a substrate in ELISA?
second antibody attached to an enzyme
What are the pros of dipsticks?
fast
can be done while patient is in the room
What are the cons of dipsticks?
you need to suspect something to test for it
cross reactivity can be a problem
What are the pros of looking for an immune response to diagnose?
fast
indicates recent (IgM) or historical (IgG) exposure OR presence - antigen
What are the cons of looking for an immune response to diagnose?
you have to predict what you are looking for
you can miss new infections - antigen variation confuses the test
How can you look at DNA to diagnose?
PCR
What are the pros of PCR?
sensitive
good for viruses
relatively fast
What are the cons of PCR?
need to predict what you are looking for
doesn’t indicate amount (so has to be used for obligate pathogens)
What is real time PCR?
like PCR but based on the incorporation of dye into the growing amount of PCR product and monitoring this
or based on the release of fluorescent tags from the DNA products as they are made
What are the pros of real time PCR?
fast
specific
quantifies the agents so can be used for infections that are opportunistic
What are the cons of real time PCR?
need to know what you are looking for (panels)
internal controls needed - do you even have DNA
What test is quickest?
antibody
What test is most specific?
real time PCR
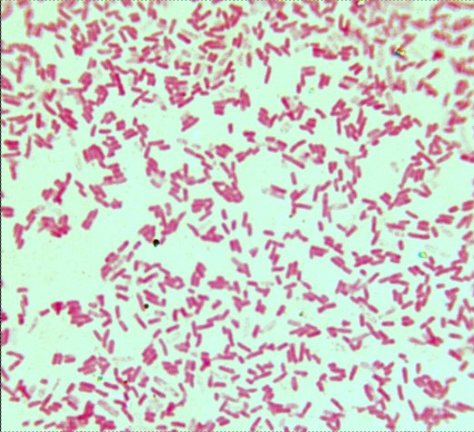
Gram?
negative - pink

What sort of atmosphere does this like growing in?
anaerobic - spore former
Are hopanoids, peptidoglycan layers or lipopolysaccharide gram positive?
peptidoglycan layers
Are hopanoids, peptidoglycan layers or lipopolysaccharide gram negative?
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Are hopanoids, peptidoglycan layers or lipopolysaccharide gram positive and gram negative?
hopanoids
Name somewhere a biofilm can form in a patient
heart valve
urinary catheter
Under what conditions can a facultative anaerobe grow?
atmospheric oxygen
no oxygen
low oxygen
all of them
ALL - facultative means it’s adaptable
Your feet smell of cheese because bacteria there produce:
ethanol
methane
lactic acid
formic acid
butyric acid
lactic acid
How do the bacteria on your feet produce lactic acid?
fermentation
What are methane, hydrogen and sulphide produced by?
fermentation
aerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
What does an ELISA measure?
DNA or RNA
antigen or antibody
prokaryotic DNA or antigen
IgG or IgM
antigen or antibody

What is this?
snap/dipstick test

What does this snap/dipstick test measure?
lateral flow device

If you use this and got a positive result for IgM against SARS-CoV2 in a 3yr old cat, are they likely to have the infection?
IgM indicates current infection, so unless it is vaccinated, YES

If you use this and got a positive result for IgM against SARS-CoV2 in a 3 week kitten, are they likely to have the infection?
not clear, could be maternal transfer, not a good test

If it was IgG and positive, would this be a better test for disease? why?
NO IgG indicates historical infection
If you do a PCR for SARS-CoV2 and it’s positive does this indicate infection?
better than dipstick - tells you that nucleic acid and so live virus is there
If you do a swab from your nose and it’s positive for Staphylococcus aureus, should you visit your GP?
NO - staph is a normal commensal here
If you do a swab from a cut on your leg and it’s positive for Staphylococcus aureus, should you visit your GP?
probably not - you don’t know whether there’s lots of bacteria or just a few - it’s a qualitative test - look for signs of infection too