5.5 gas exchange in plants
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Why do plants need gas exchange?
For respiration (uses O₂, releases CO₂) and photosynthesis (uses CO₂, releases O₂). Rates of each process vary with light.
Why is gas exchange slower in plants compared to animals?
Plants have a lower metabolic rate, so lower demand for O₂ and CO₂ than animals.
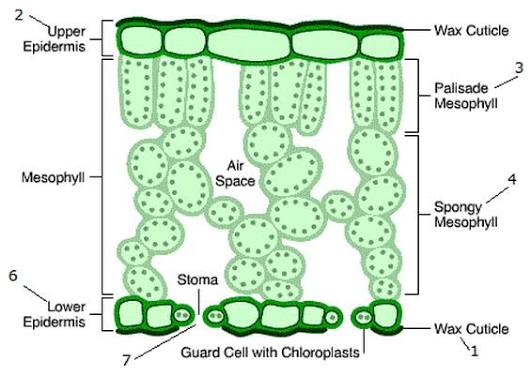
Which leaf adaptations increase the efficiency of gas exchange?
Thin leaves → short diffusion pathway
• Large surface area
• Air spaces in spongy mesophyll → diffusion of gases
• Stomata → control gas entry and exit
• Moist internal surfaces → allow gases to dissolve before diffusion
What is the role of the spongy mesophyll in gas exchange?
Contains large intercellular air spaces allowing diffusion of CO₂ and O₂ between stomata and photosynthetic cells.
What are stomata?
Pores in the epidermis (usually lower surface) that allow gas exchange and regulate water loss.
How do guard cells open the stomata?
K⁺ ions actively transported into guard cells.
Water enters by osmosis.
Guard cells become turgid, thinning the outer wall.
Pore opens.
NEED MORE INFO
How do guard cells close stomata?
K⁺ ions leave guard cells → water exits → cells become flaccid → pore closes.
What environmental factors cause stomatal opening?
Light, low CO₂ inside leaf, adequate water.
What environmental factors cause stomatal closure?
Darkness, water stress, high temperature, high wind, high leaf CO₂.
What happens to gas exchange at high light intensities?
Photosynthesis > respiration → net uptake of CO₂ and release of O₂.
What happens at night?
No photosynthesis, so only respiration occurs → net uptake of O₂ and release of CO₂.
What are xerophytes?
Plants adapted to dry habitats, reducing water loss.
Stomatal adaptations in xerophytes?
Sunken stomata
• Hairy leaves
• Stomata on underside only
• Reduced stomatal density
Structural adaptations of xerophytes to reduce water loss?
Thick cuticle
• Rolled leaves
• Small leaves/needles
• Fewer air spaces in mesophyll
How do gases move when stomata are open?
diffusion down concentration gradients, maintained by photosynthesis and respiration.
name the tissues and cells of a leaf