IB DT: Topic 10.2: Lean production
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1VZyCbo1VFmkqOoWMNAPdoIN83IBaIrR_llW-0AmSOHg/present?slide=id.g1108cc1bfa6_0_275
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What does lean production aim to achieve?
Eliminate waste and maximise the value of a product based on the perspective of the consumer
What is lean production?
A production methodology focused on eliminating waste, where waste is defined as anything that does not add value for the customer. Used to streamline production processes and eliminate errors and waste.
What are the benefits of lean production?
improved on time delivery
improved quality
improved customer service and satisfaction
simpler production process (and therefore management)
reduced defects
reduced resource consumption
increased efficiency
what is a pull system?
a lean manufacturing strategy used to reduce waste in the production process. in this type of system, components used in the manufacturing process are the only replaced once they have been consumed so companies only make enough products to meet customer demand.
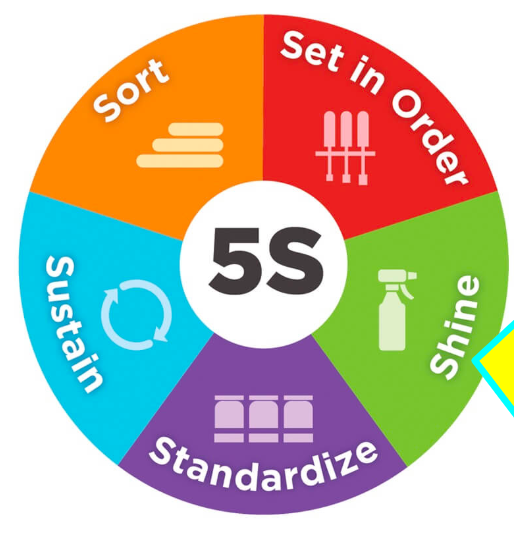
what are the 5s’s? what does implementing this system achieve?
a system to reduce waste and optimise productivity through maintaining an orderly workplace and using visual cues to achieve more consistent operational results.
implementation of this method cleans up and organises the workplace in its existing configuration - typically the first lean method which organisations implement
saves time and money, avoiding waste
what are the seven wastes?
defects: waste from a product failure to meet customer expectations
overproduction: waste from making more product than demand
waiting: waste from time spent waiting for the next process step to occur
transportation: wasted time, resources and costs when unnecessarily moving products
inventory: wastes resulting from excess products and materials that aren’t processed
motion: wasted time and effort related to unnecessary human movement
extra processing: wastes related to more work, or higher quality than is required
(extra 8th) unused talent: wastes due to underutilisation of people’s talents, skills and knowledge
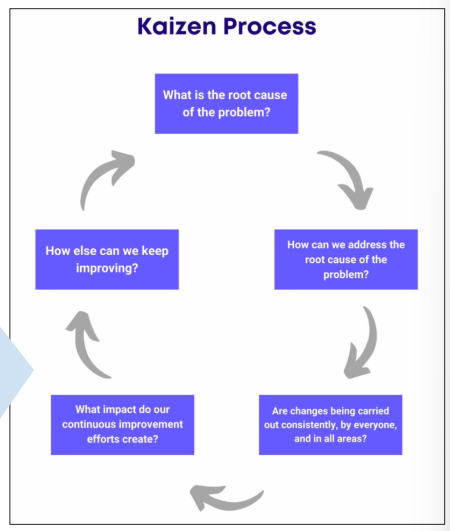
what is kaizen?
a culture of continual development/improvement
what are the principles of lean production?
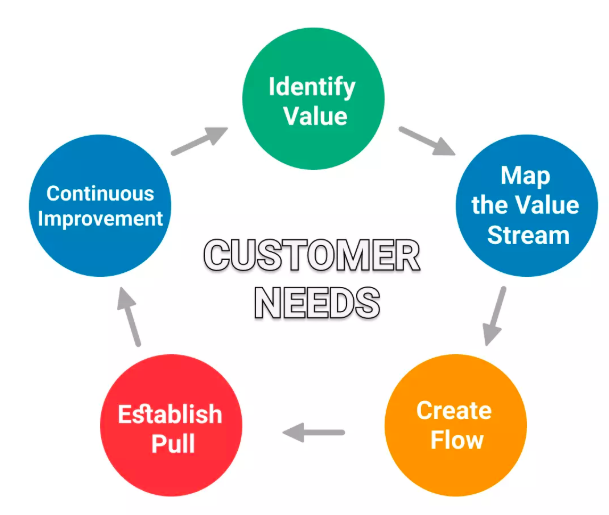
what is identify value?
value is always defined by the customer’s needs for a specific product.
what is value stream mapping?
once the value has been determined, the next step is mapping the value stream, or all the steps and processes involved in taking a specific product from raw materials and delivering the final product to the customer. the idea is to draw, on one page, a map of the flow of material through the process. the goal is to identify every step that does not create value and then find ways to eliminate those wasteful steps.
what is create flow?
after the waste has been removed from the value stream, the next step is to be sure the remaining steps flow smoothly with no interruptions and bottlenecks.
what is establish pull?
with improved flow, time to market can be dramatically improved. this makes it much easier to deliver products as needed. this means the customer can pull the product from you as needed. as a result, products don’t need to be built in advance or materials stockpiled.
what is kaizen?
making lean thinking and process improvement as part of your corporate culture. requires constant effort and vigilance to perfect. every employee should be involved in implementing lean.
what is a product family?
a group of related goods produced by the same company under the same brand. used to leverage the loyalty of existing customers towards its original brand.
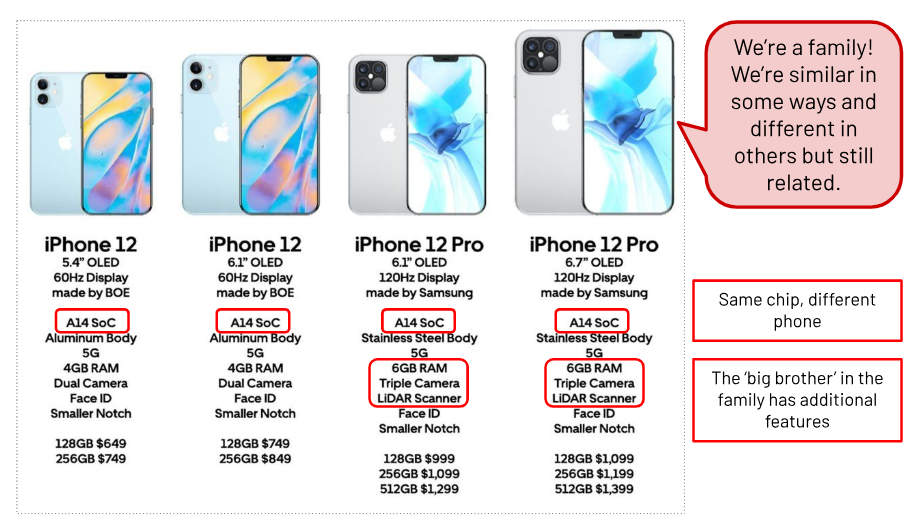
what are the advantages of having common parts across different models?
higher efficiency and reduced costs when manufacturing parts
reduced costs (staff training r&d)
parts always on hand for replacement (jic)
saves on waste when using high end parts on mid end products the next year