Intro to EKG
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Electrocardiography
recording of the cardiac signals the myocardial cells are producing, AKA their electrical activity
Electrocardiogram
result of the recording of cardiac cells
smaller, action potential, SA, AV, heart rate
Conducting Cells
Myocardial Conducting Cells:
1% of all myocardial cells
________ in size
Fewer myofibrils/filaments
Can create or pass an _______ ________
Specialized Conducting Cells
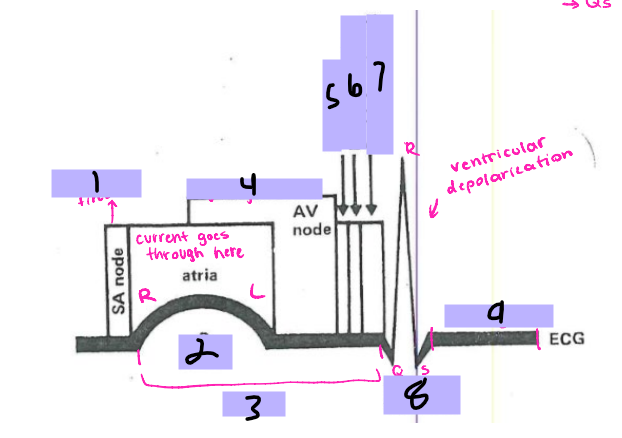
__ and __ nodes are bands of specialized cells that can speed up or slow down the _____ _____
The AV node has a delayed signal because it helps prevent backflow and gives the heart time to pump out the blood
SA node
#1, __ ____ fires
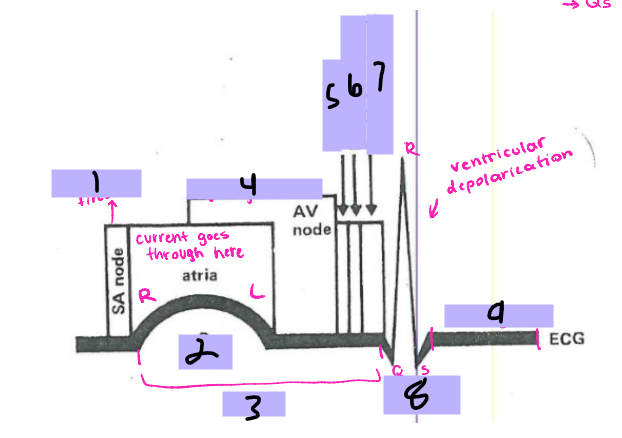
P wave
#2
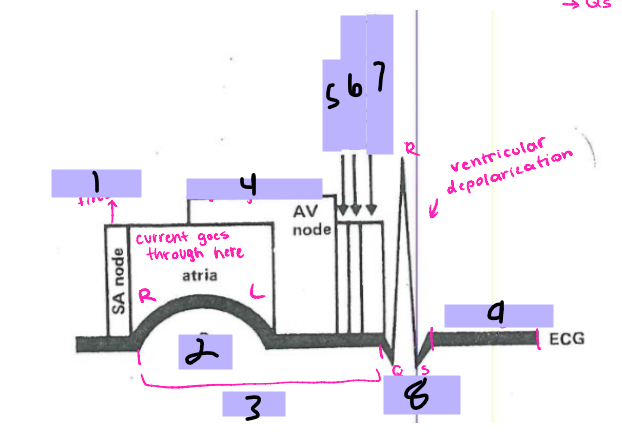
PRI
#3
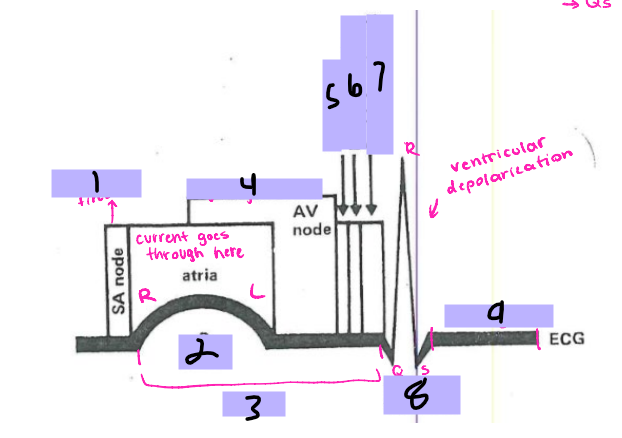
AV node
#4, signal goes to the __ ____
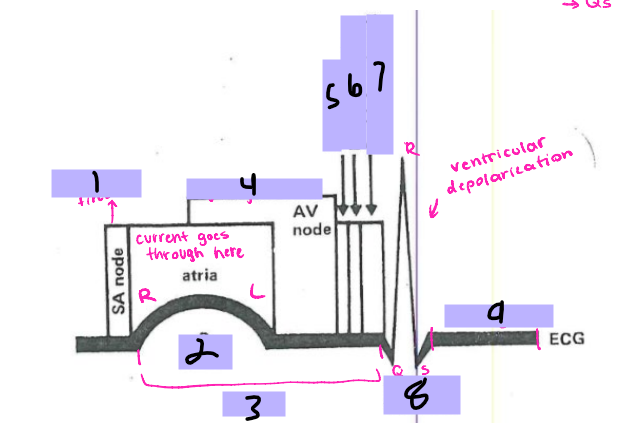
Bundle of His
#5, the signal goes to the ______ __ ___ after the AV node
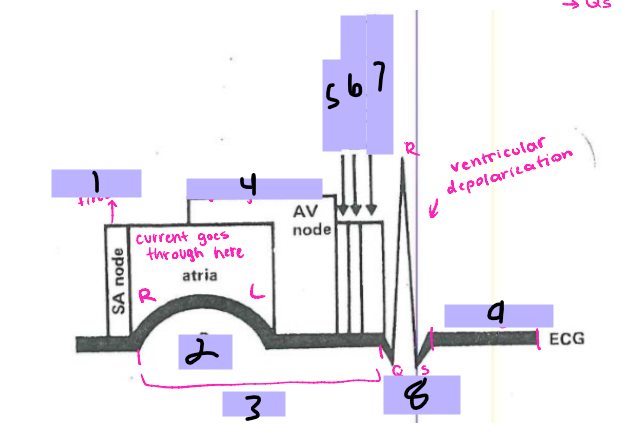
Bundle branches
#6, the signal travels from the Bundle of His to the _______ _______
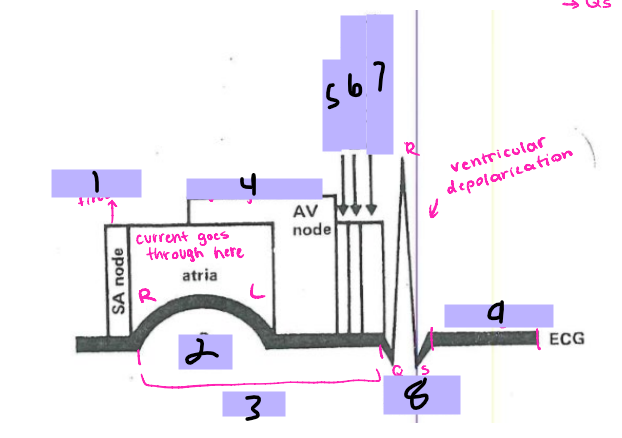
Purkinje Fibers
#7, the signal travels from the bundle branches to the _______ ______
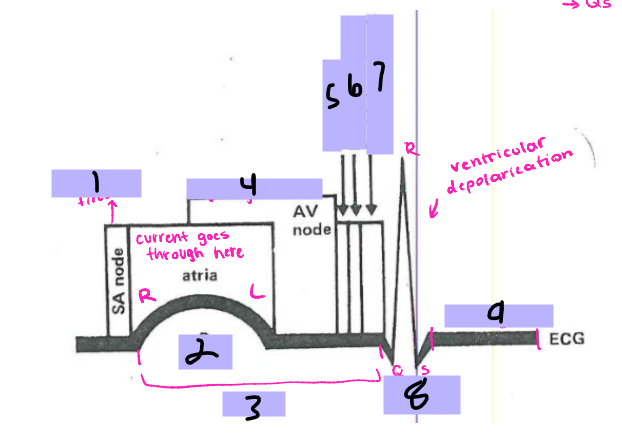
QRS Complex
#8, the ventricles then depolarize and form the ___ ______
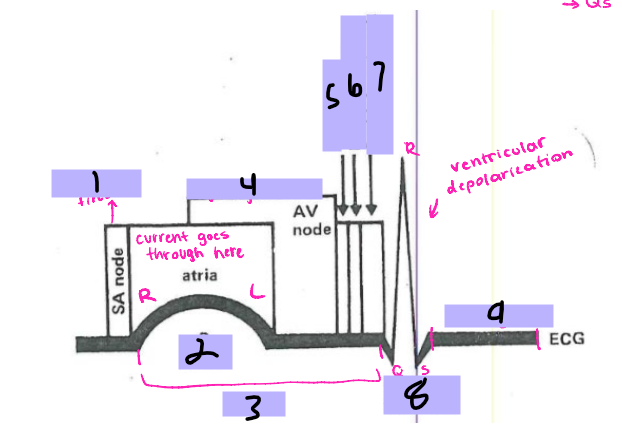
ST segment
#9, after ventricular depolarization comes the __ _________
Lead I
Which lead takes an “image” from the right arm to the left arm?
Lead II
Which lead takes an “image” from the right arm to the left leg?
-It’s the most specific to look at, for it traces the path that the signal uses to move through the heart
Lead III
Which lead takes an “image” from the left arm to the left leg?
aVR
Which augmented lead takes an image of the right side of the body?
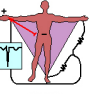
aVL
Which augmented lead takes an image of the left side of the body?
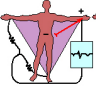
aVF
Which augmented lead takes an image from below?
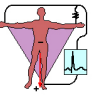
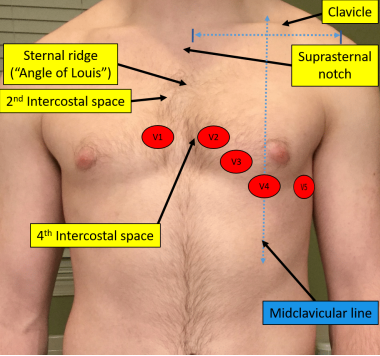
Precordial Leads
type of leads that take “images” straight through the torso to monitor the electrical current
-placed in the same place for every patient
6
An EKG typically represents _ seconds of heart activity
0.04
How many seconds does each small box represent on the EKG?
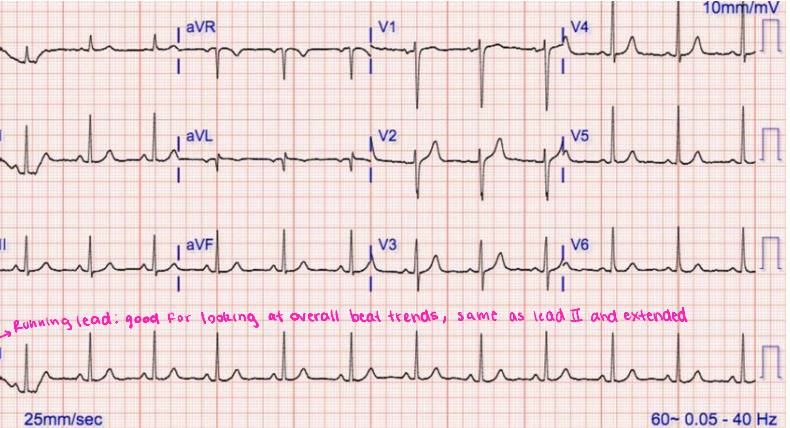
Running Lead
The __________ ____ is a continuous recording of one lead (typically Lead II) over a longer period, which provides a longer view of cardiac rhythm to help assess the heart’s rate and rhythm more clearly
shave, palpate, abrade
Skin Prep for EKGs
_______, if needed, to help prevent artifact and adhere the electrodes
__________ to find the correct placement
Alcohol swab the skin to remove any residue
______ the skin to remove all dead skin cells or dirt
Place electrodes
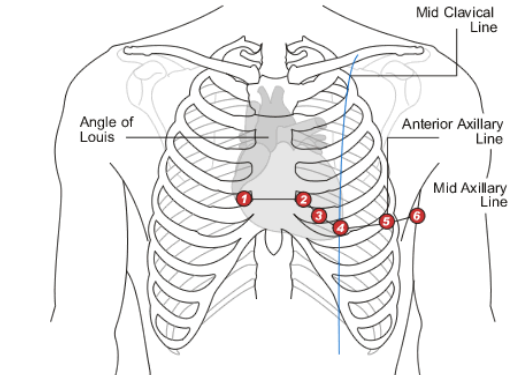
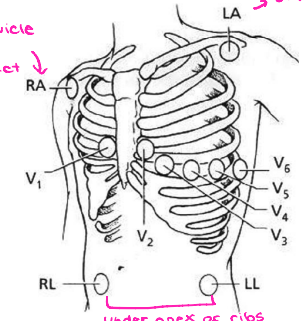
V1
Which precordial lead is placed on the RIGHT sternal border in the 4th intercostal space?
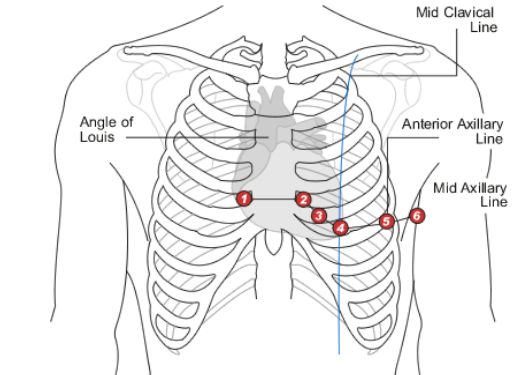
V2
Which precordial lead is placed on the LEFT sternal border in the 4th intercostal space?
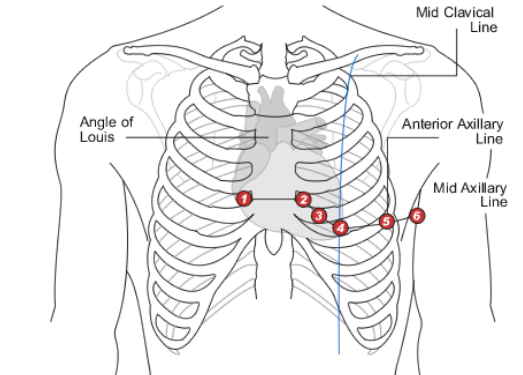
V3
Which precordial lead is found on the 5th rib, in the middle of V2 and V4?
V4
Which precordial lead is found in the 5th intercostal space aligned with the midclavicular line?
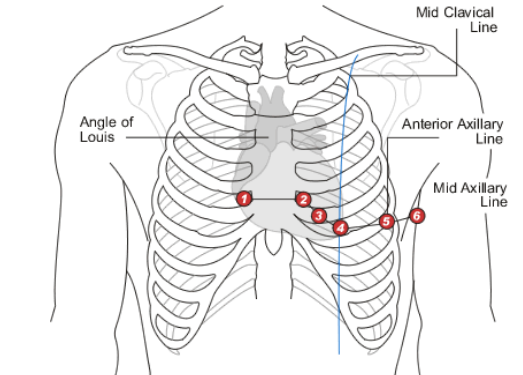
V5
Which precordial lead is found in the anterior axillary line on the 6th rib?
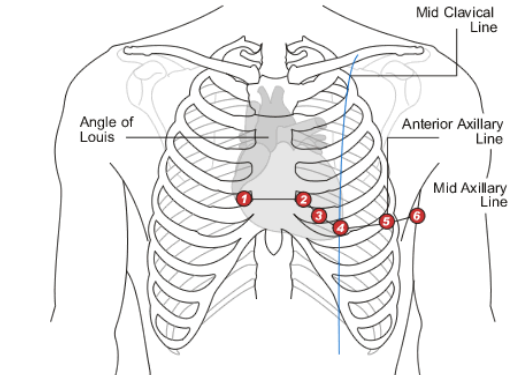
V6
Which precordial lead is placed in the midaxillary line on the 6th rib?
stress, deltoid, clavicle, apex, hips
Mason-Likar Limb Leads
-Use this if the patient is moving around or doing a ______ test
-The right arm lead should be placed off the _______, below the clavicle
-The left arm lead should be placed off the deltoid, below the ________
-The right leg and left leg leads should either be placed below the ___ of the ribs on their respective sides or on the _____ if the patient has abdominal fat
wrists, ankles, quads, biceps
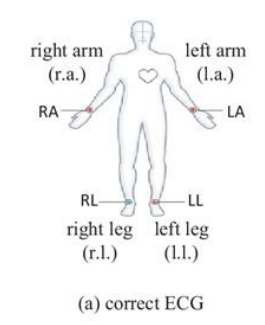
Resting Limb Leads
-If the patient is at rest, you can place the electrodes on the _______ and ______ OR the _____ and ______. These pairs have to remain together.
V1
When placing a holter monitor, the patient only needs which precordial lead?