ICM Exam 2 Hair, Skin, & Nails
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
What percentage of a person's body weight is skin?
16-20%
What are functions of the skin? (5)
1. Blood vessels help regulate body temperature and respond to hot/cold
2. Tough cushion to protect deeper organs
3. First line of defense against harmful microbes
4. Prevents outward loss of water, blood, and other essential body fluids
5. Produces vitamin D
What are the 3 layers of the skin?
Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous
What is the epidermis?
Outer layer of the skin, contains layers of keratocytes
Has a basal cell layer containing melanocytes (gives skin color)
What is the dermis?
Support layer below the epidermis, bulk of the skin
Includes appendages (blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands)
What is the subcutaneous layer of the skin?
Hypodermis, skin layer underneath the dermis
Contains fatty tissue and acts as a thermal regulator and protector of bony prominences
How many hairs does the average scalp have?
> 100,000
What is the average growth phase of scalp hair?
1000 days, average of 0.3 to 0.4 mm/day (6 in per year)
What is a unique feature of hair growth pattern?
It is mosaic -- shedding is at random
What are the 3 phases of hair growth?
Anagen (growing phase)
Catagen (transition phase)
Telegen (resting phase)
Describe the anagen phase of hair growth.
First stage, active growth
Hair contains the highest amount of melanin here, this phase lasts 3-6 years
Describe the catagen phase of hair growth.
Transition phase, hair is not growing and not shed
Lasts about 2-3 weeks
Follicle being reabsorbed here
Describe the telegen phase of hair growth.
Resting stage, follicle recedes and hair begins to fall out in anticipation of new hair
Lasts between 6-8 weeks
IS NORMAL !!
What is melanin?
Brown-ish pigment of the skin that determines the skin's normal color
Genetically determined, increased by exposure to sunlight
What is oxyhemoglobin?
Bright red pigment in the arteries and capillaries that cause reddening of the skin
Combo of hemoglobin and oxygen
What is deoxyhemoglobin?
Darker blue pigment as a result of hemoglobin releasing oxygen to the tissues
What are the 3 types of hair?
Lanugo
Vellus
Terminal
Describe lanugo hair.
Fine hairs found on body of fetus
Describe vellus hair.
Similar to lanugo but found on adults, "peach fuzz"
Describe terminal hair.
Thick, pigmented hairs, usually found on the head, axilla, pubic areas and face on males

Hairs on the head, beard, axillae, and pubic areas are influenced by:
Androgens
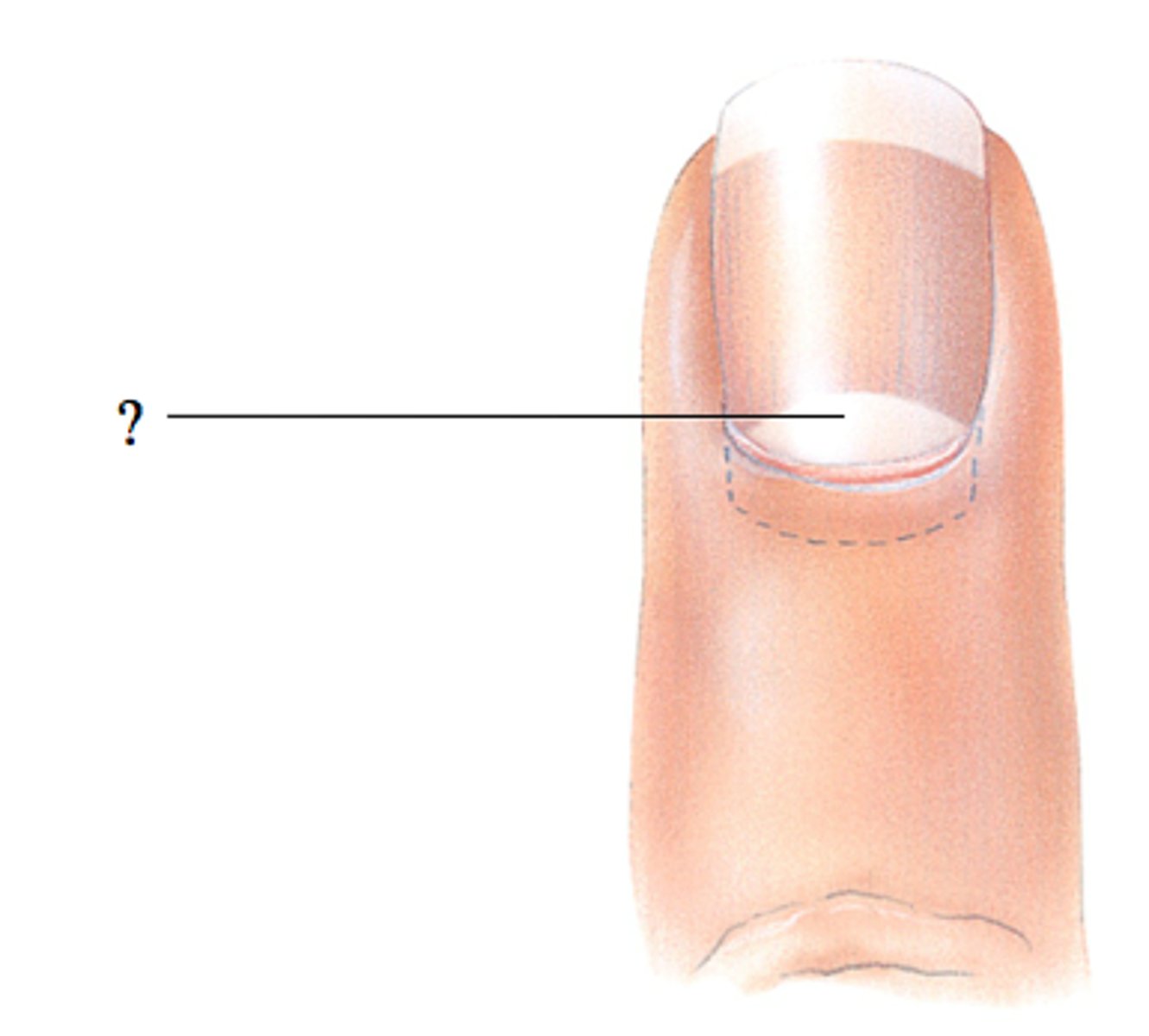
List all the parts of the nail.
- Nail plate
- Nail bed
- Nail root
- Cuticle
- Nail fold
- Lunula
- Free edge
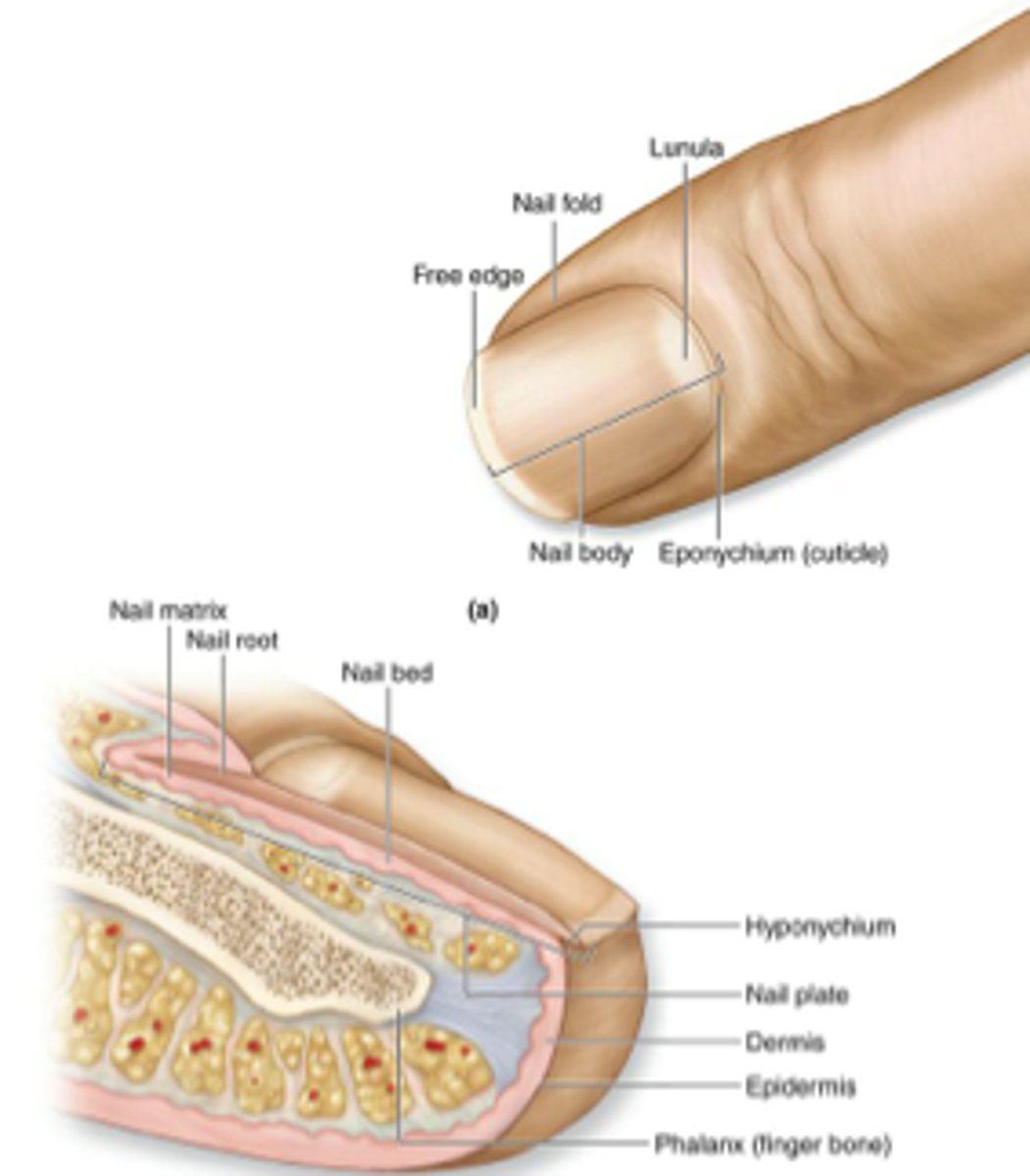
What is the nail plate?
Rectangular and pink in color
Hard part of the nail, what you think of when you think of nails
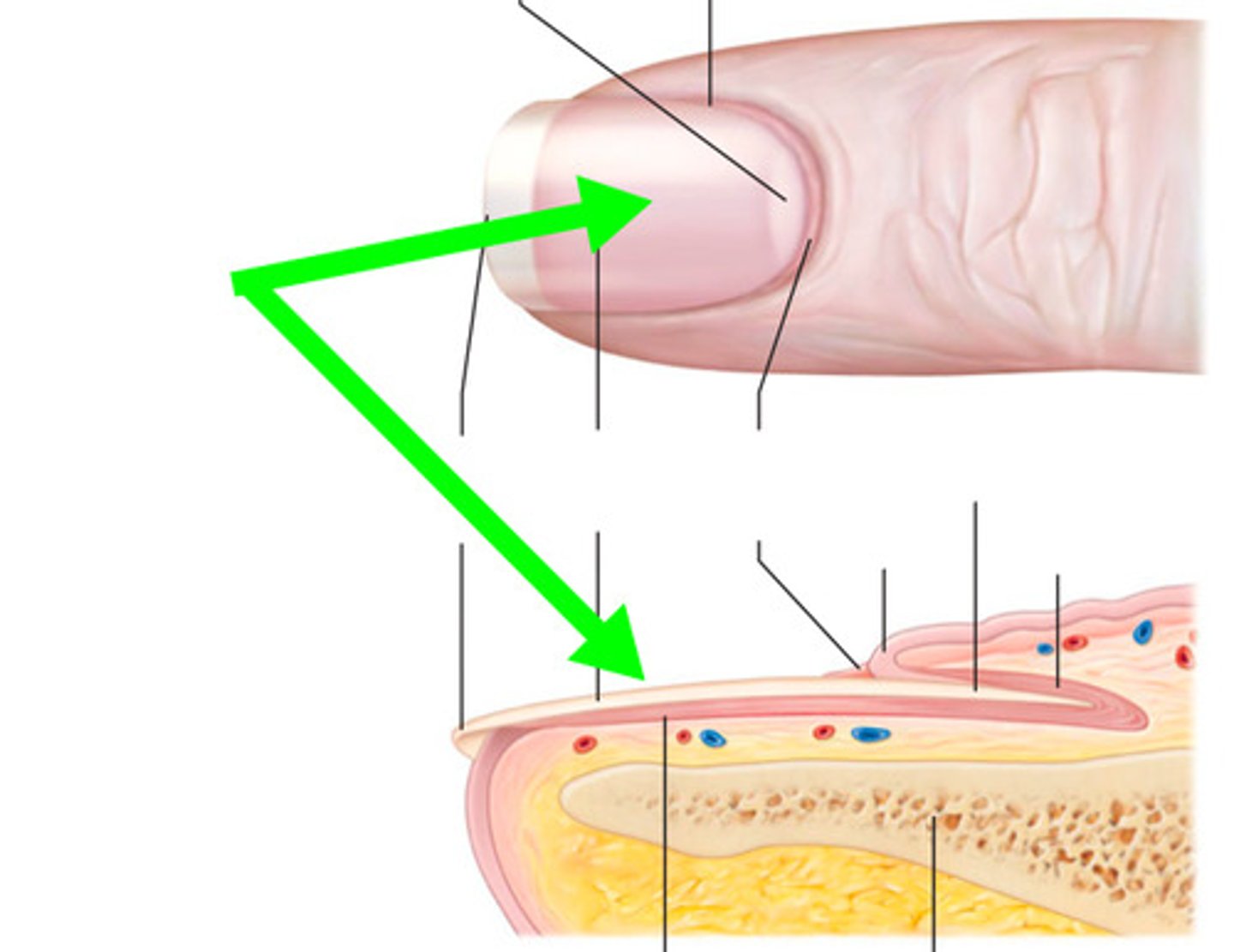
What is the nail bed?
Vascular area where the nail plate is attached

What is the lunula?
Whitish moon portion of the nail
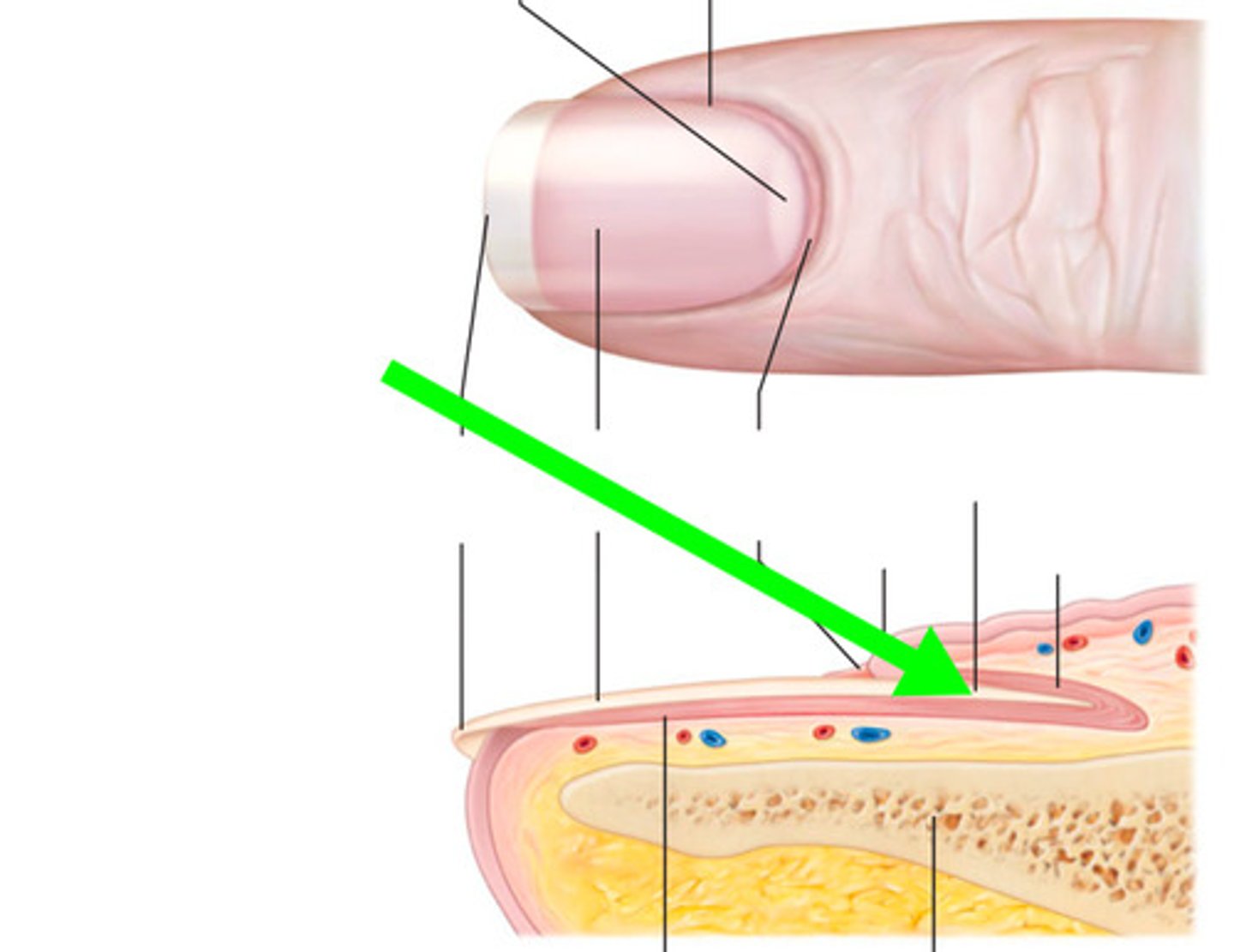
What is the nail root?
Covered by the proximal nail fold, where the nail attaches to the skin
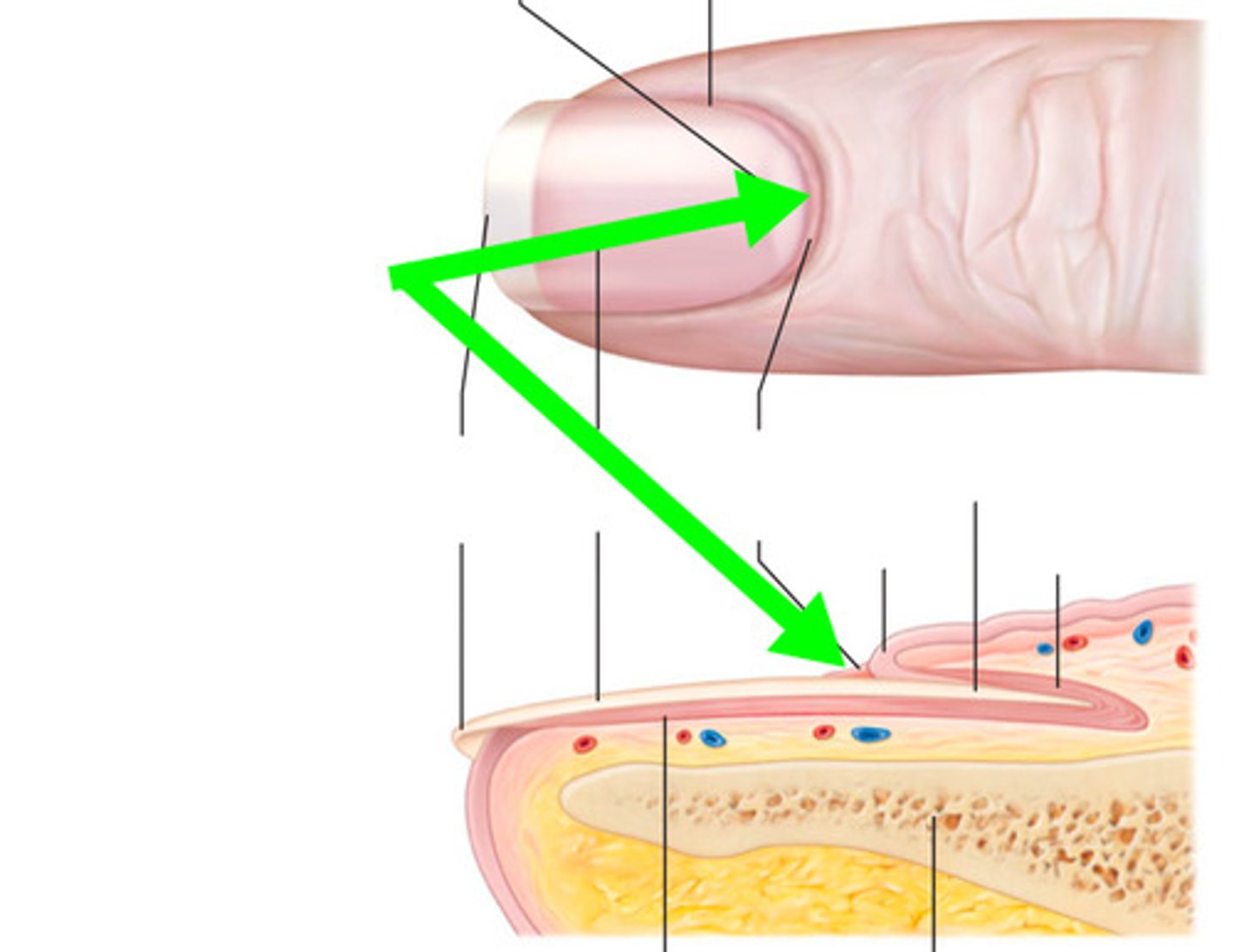
What is the cuticle?
Extends from the nail fold and functions as a seal to protect the space between the fold and plate from external moisture
What are the lateral nail folds?
Cover the side of the nail plate
What is the angle between the proximal nail fold and the nail plate?
Less than 180 degrees
What are sebaceous glands?
Oil glands, produce a fatty substance secreted onto the skin surface through hair follicles
What are the 2 types of sweat glands?
Eccrine and Apocrine
Describe eccrine sweat glands.
Widely distributed, open directly onto skin surface
Controls body temperature through sweat production
Describe apocrine sweat glands.
Found chiefly in axillary and genital regions and usually open into hair follicles.
Bacterial composition of these glands lead to body odor
What are some things that can lead to rashes?
1. Dietary items (gluten and dairy)
2. Cosmetics
3. Work chemicals
4. Sunlight
5. Medications
6. Foreign travel
Questions to ask about a rash
1. Does it itch?
2. If so, does it precede or follow the rash
3. Any seasonal allergies, asthma, or eczema?
4. Can the patient sleep at night or does the rash wake them up?
5. What kind of moisturizer or OTC products does the patient use?
Questions to ask about hair loss
1. Is hair thinning or shedding, and if so, where?
2. If shedding, does it come out at the roots or break along the hair shaft?
3. Frequency of shampooing?
4. Use of dyes, chemical relaxers, heating appliances
How to document/describe lesions
1. Number
2. Size (in mm or cm)
3. Shape (oval, annular, nummular, polygonal)
4. Color (if red, do they blanch)
5. Texture (smooth, fleshy, verrucous, warty, scaly)
6. Location
7. Configuration (grouped, annular, linear, any patterns)
What does annular mean in terms of a lesion?
Ring-like with central clearing
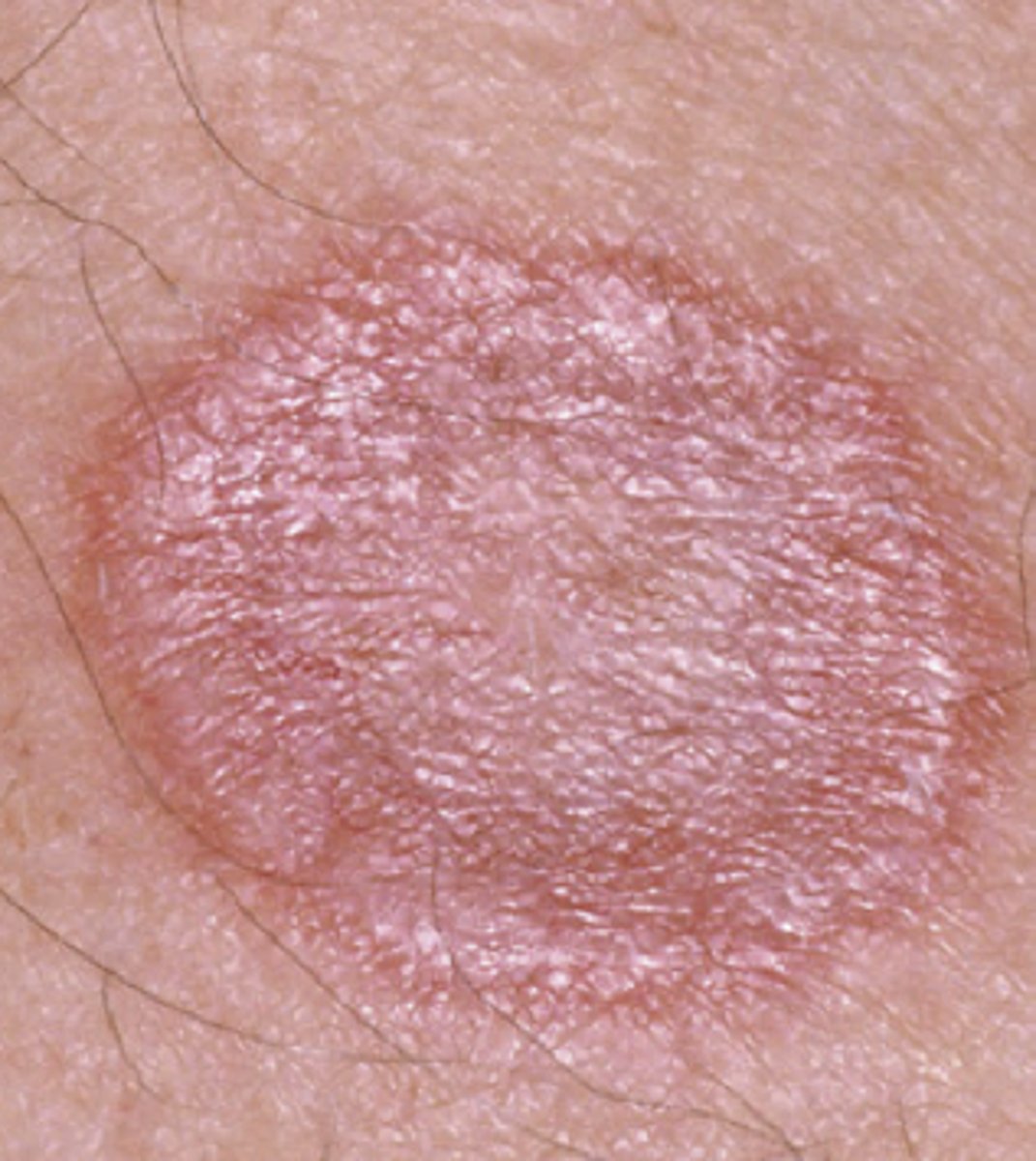
What does nummular or discoid mean in terms of a skin lesion?
Coin-shaped, no central clearing
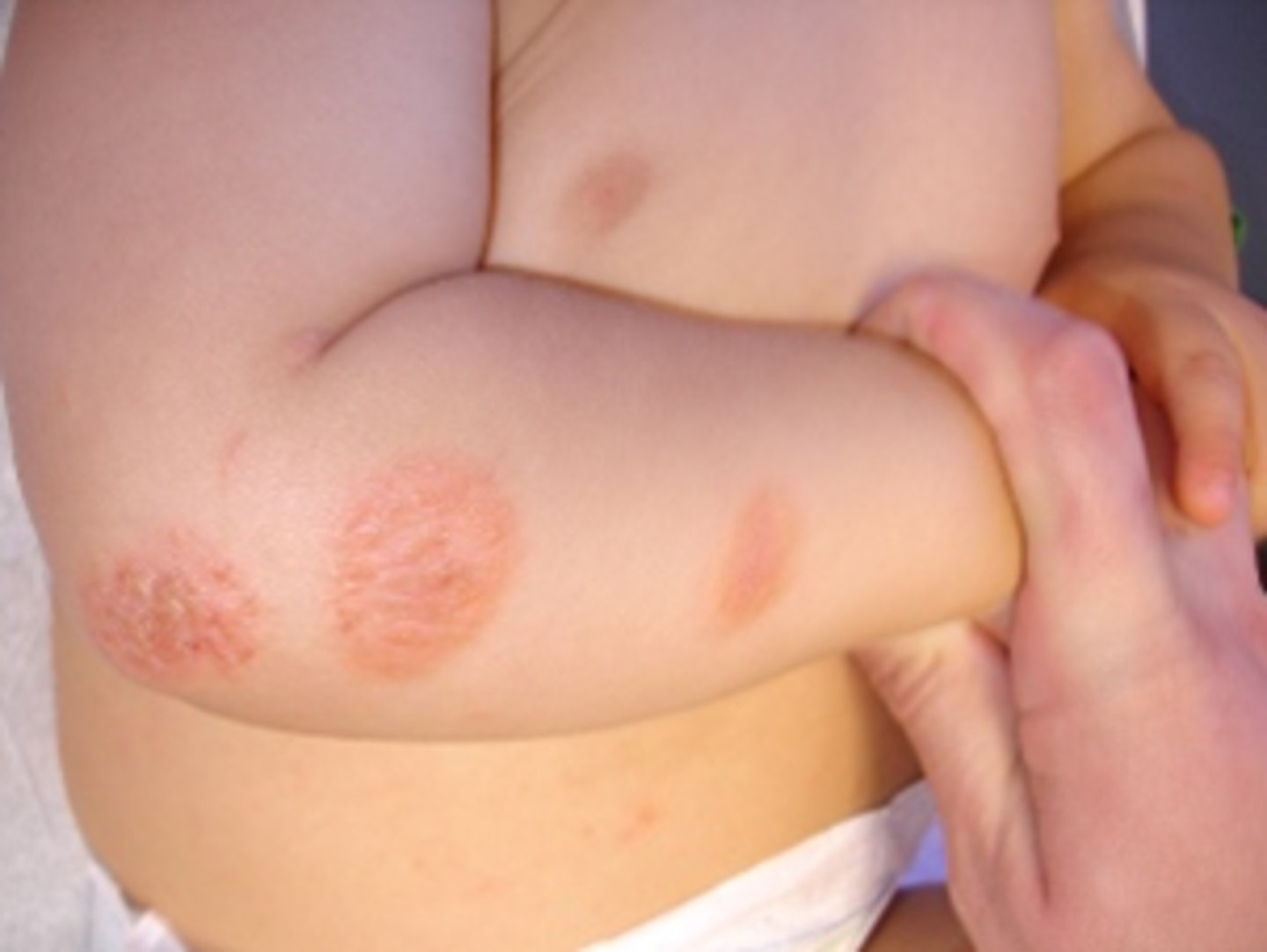
What is the ABCDEFG rule for melanoma?
A - Asymmetry of one side of the mole compared to the other
B - Border irregularity (ragged, notched, blurred)
C - Color variations (more than 2 colors, especially blue-black, white or red)
D - Diameter (greater > 6 mm)
E - Evolving and Elevation
F - Firmness to palpation
G - Growth in the past several weeks
What is a macule?
Flat, well circumscribed area with change in skin color
Usually less than or equal to 1 cm
Examples include freckles, small flat mole
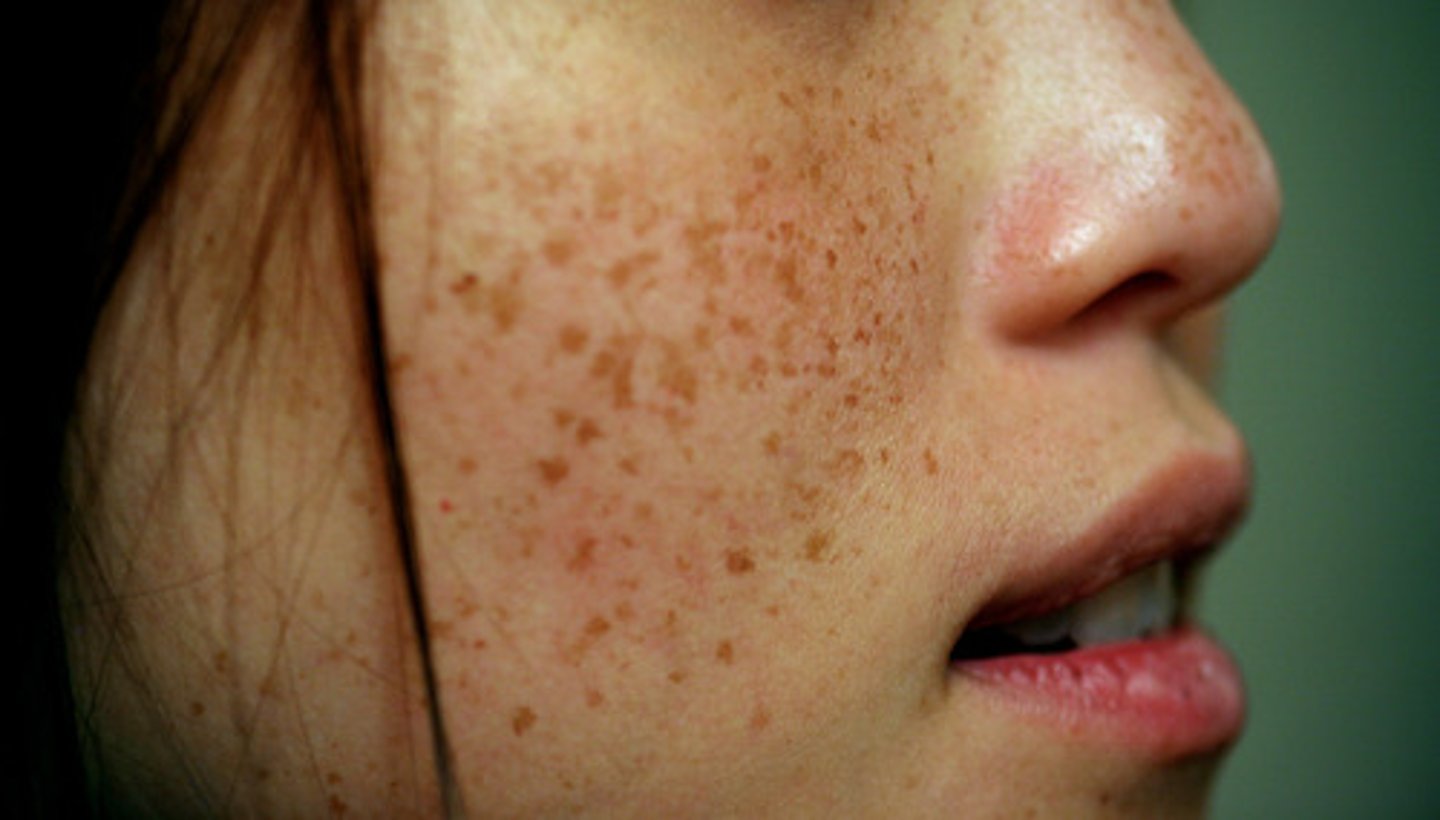
What is a macular xanthem?
Rash consisting of macules, typically seen in measles
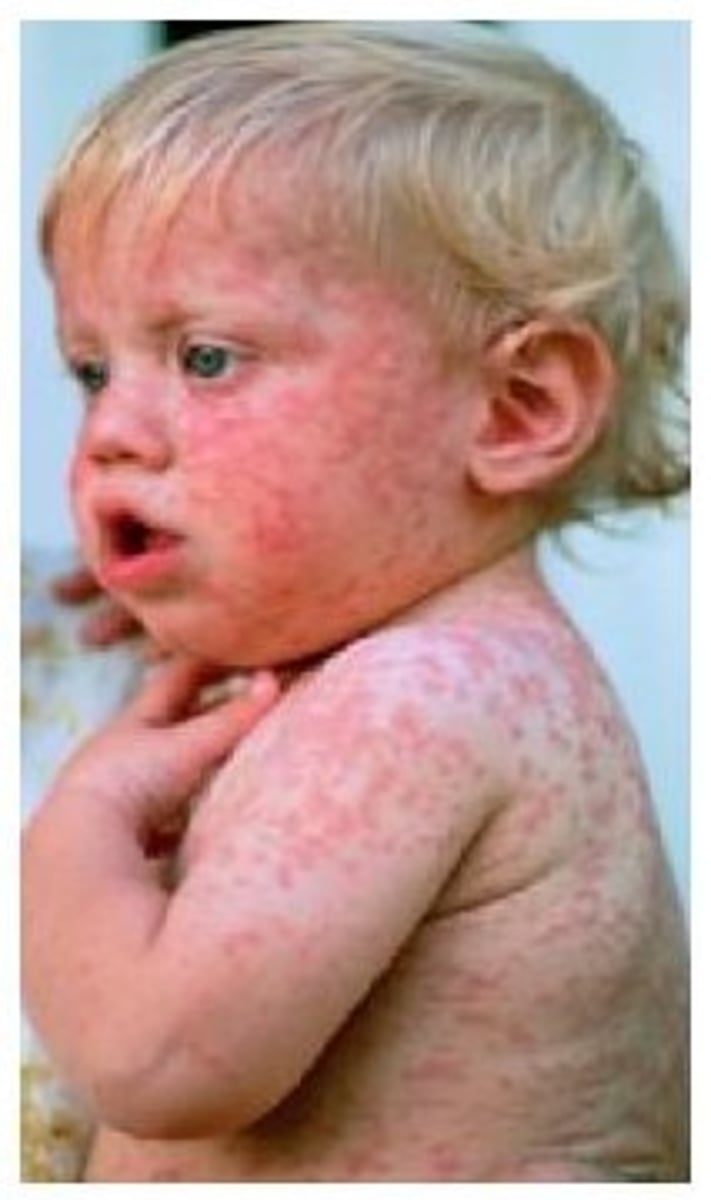
What is a patch?
Flat, nonpalpable, irregular shaped macule
Greater than or equal to 1 cm
Examples include vitiligo, port-wine stains, cafe au lait spots
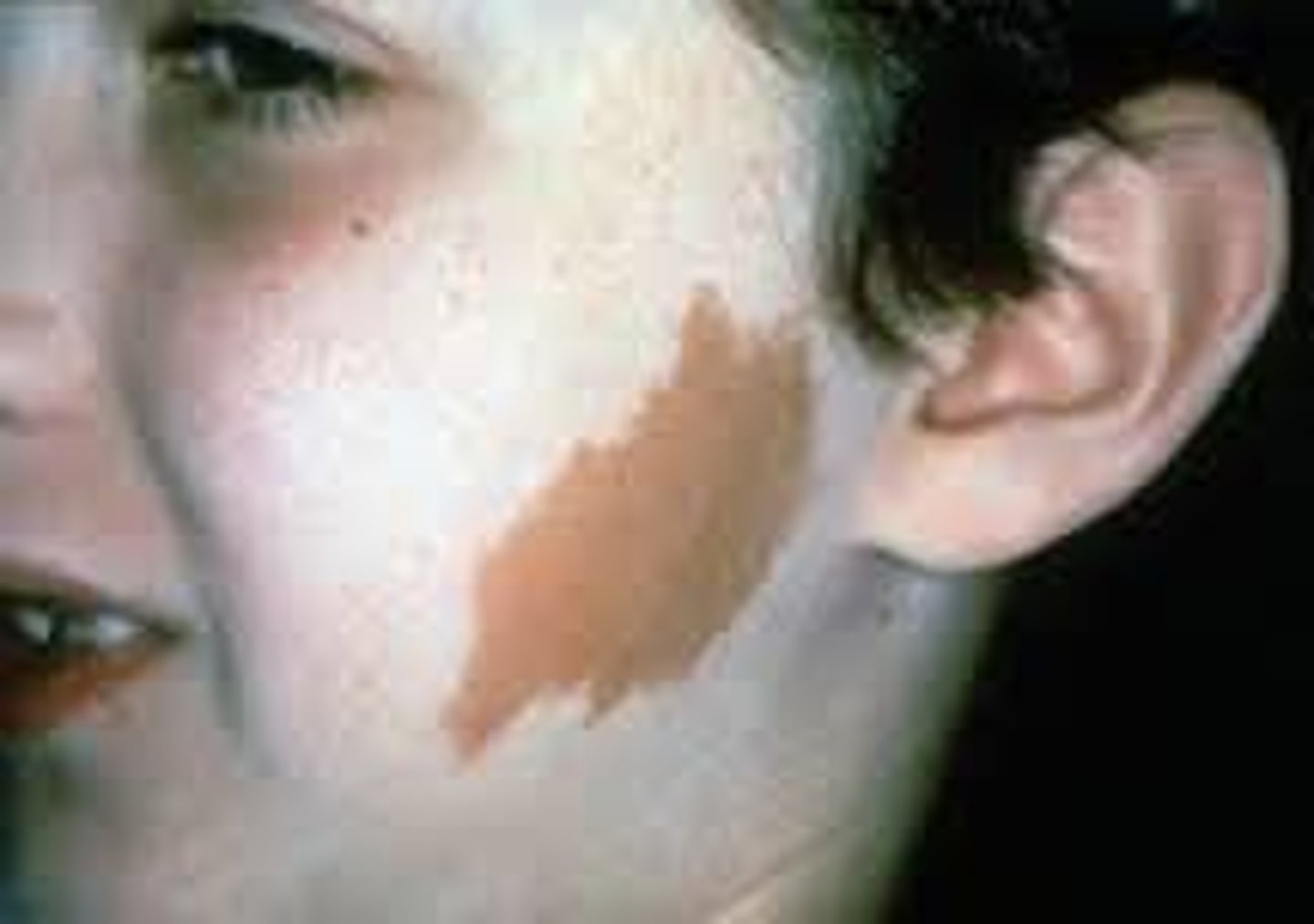
What is a papule?
Elevated, firm, circumscribed area
Usually less than 1 cm
Examples include warts and elevated moles
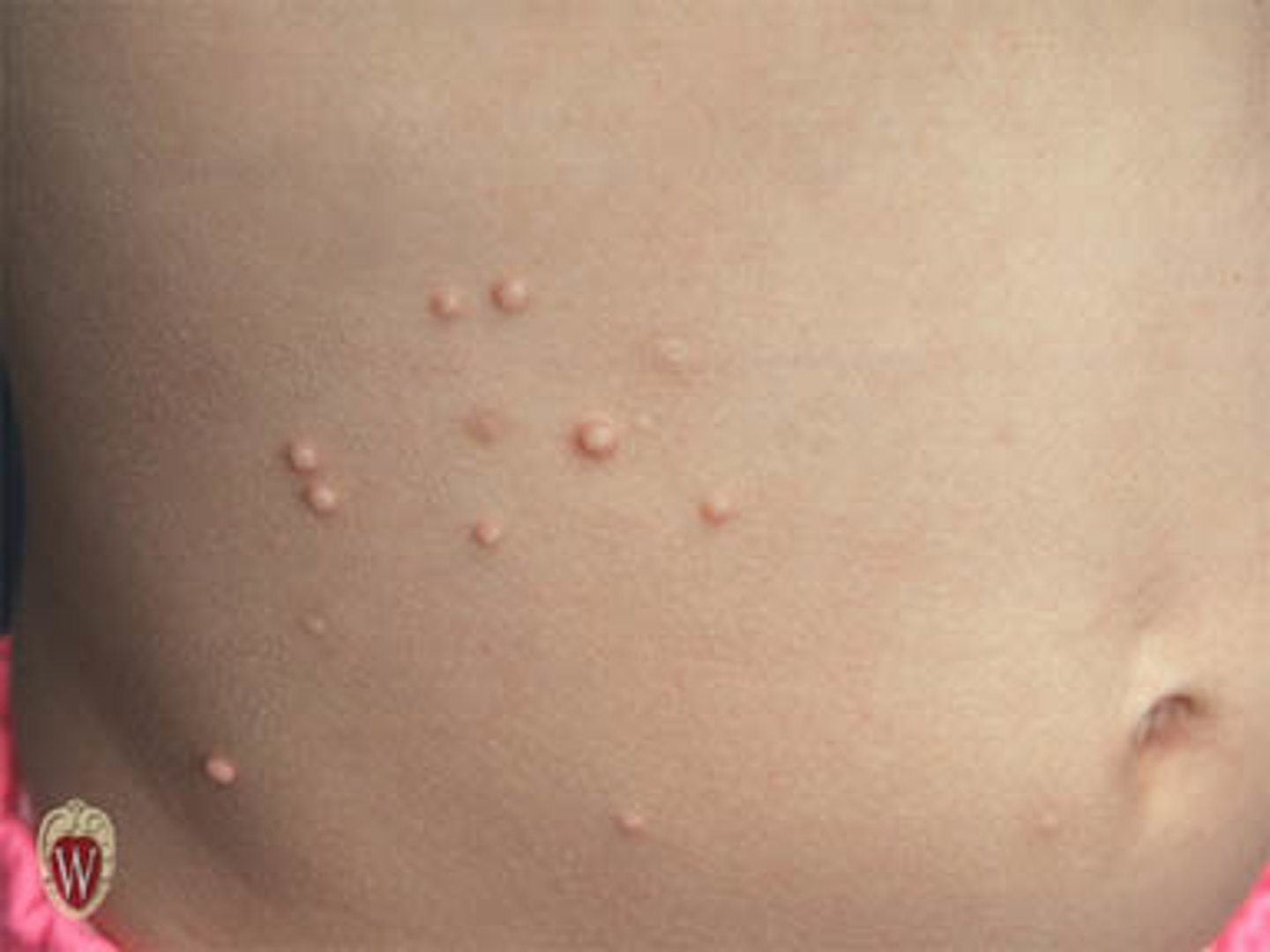
What is a plaque?
An elevated solid lesion (>1 cm in diameter)
Examples include psoriasis
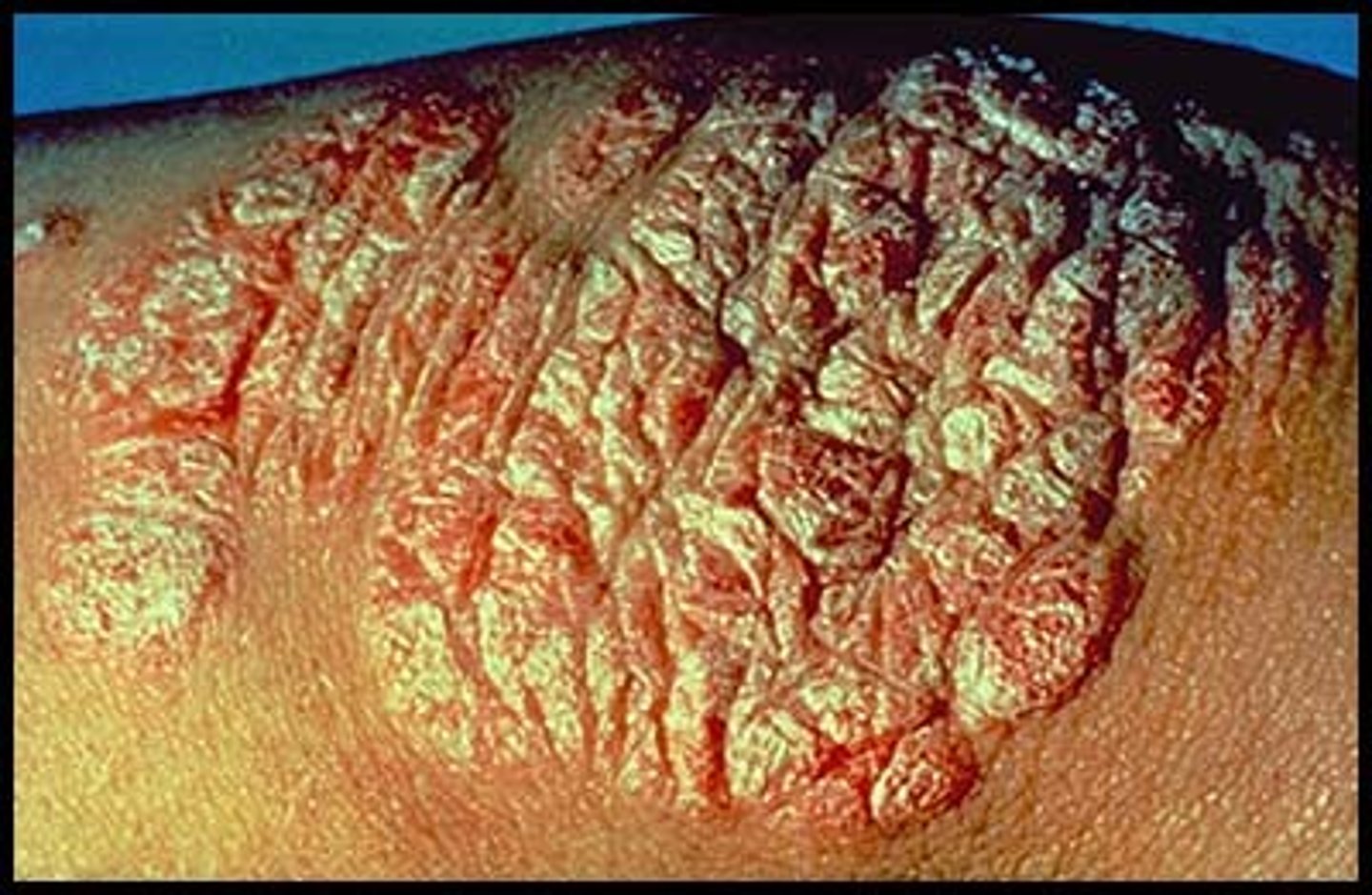
What are the 5 P's of Lichen Planus?
Pruritic (itchy)
Planar
Purple
Polygonal
Papular
What is lichen planus?
A type of inflammatory dermatosis of the skin that manifests with papules
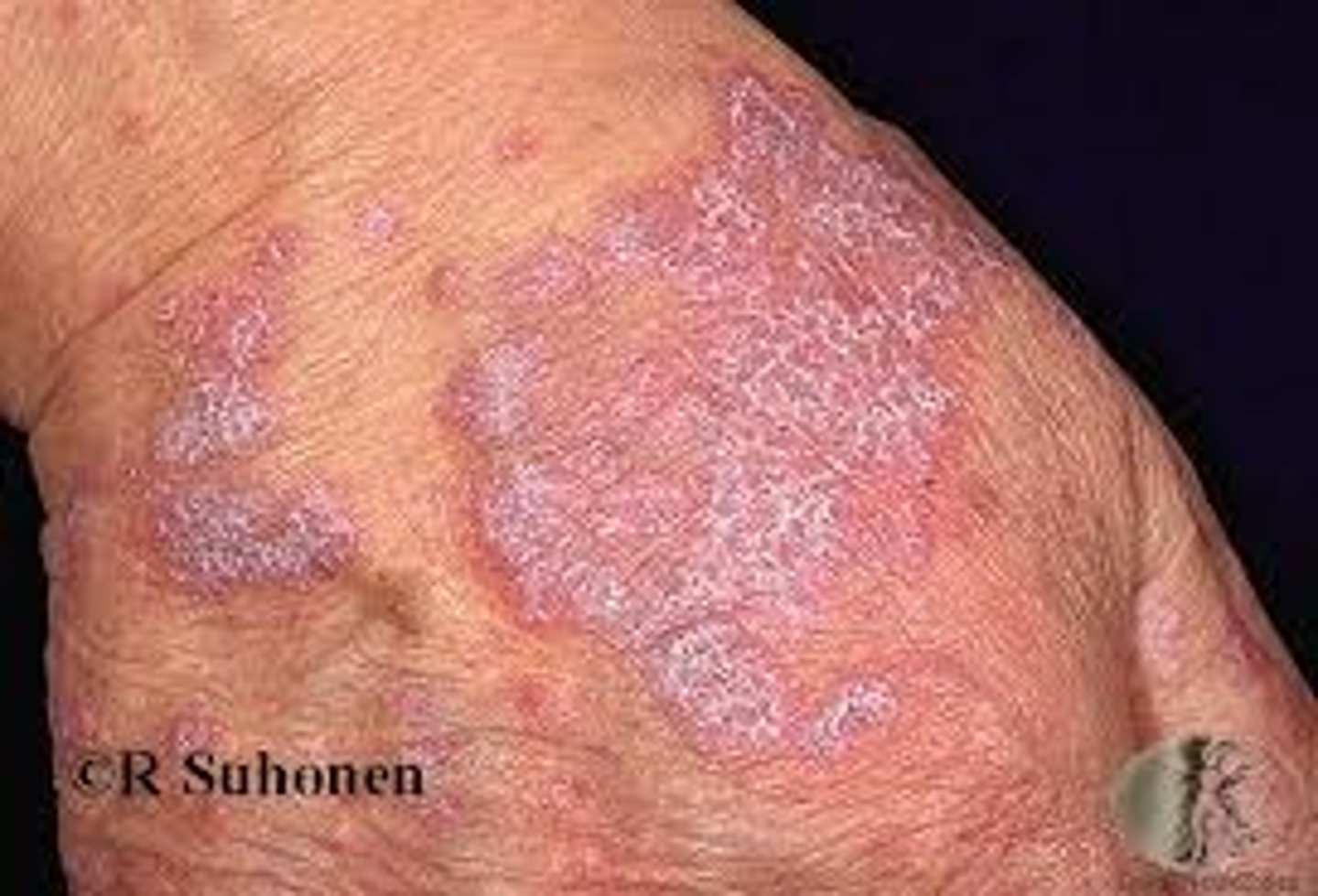
What is a pustule?
Skin lesion filled with pus
Examples can be seen in impetigo
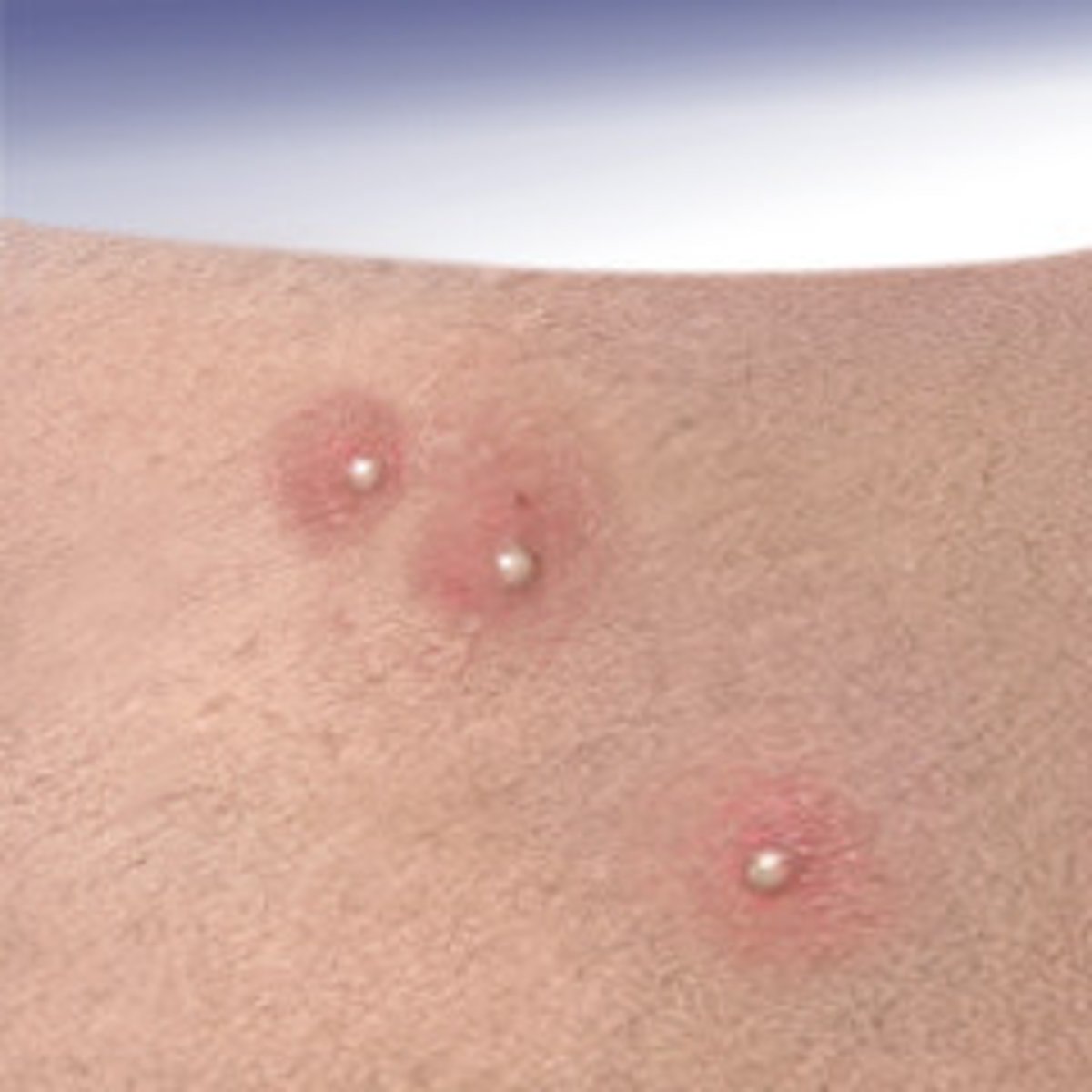
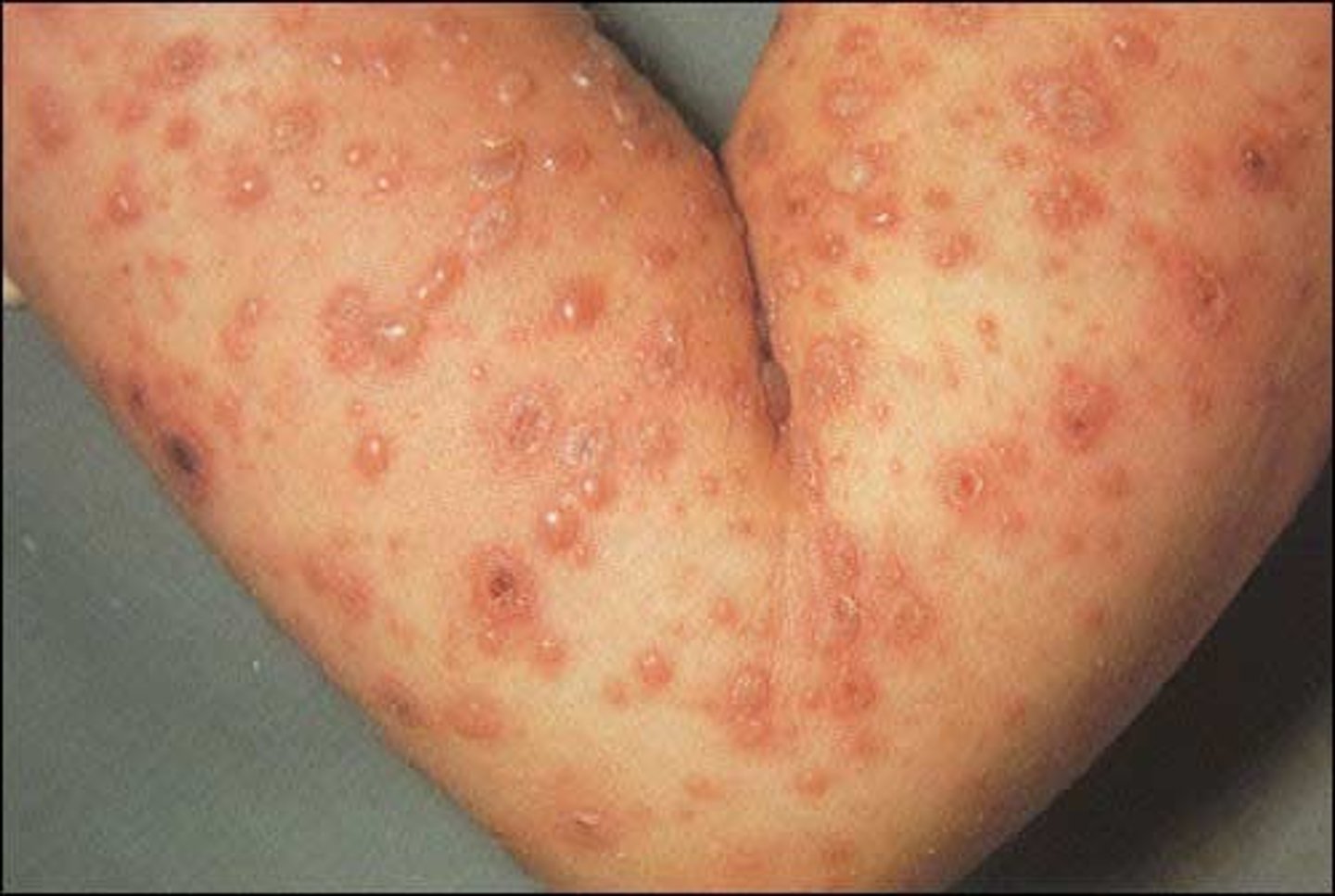
What is a vesicle lesion?
Elevated, circumscribed and superficial lesion filled with serous (clear) fluid
Less than or equal to 1 cm in diameter
Examples include chicken pox
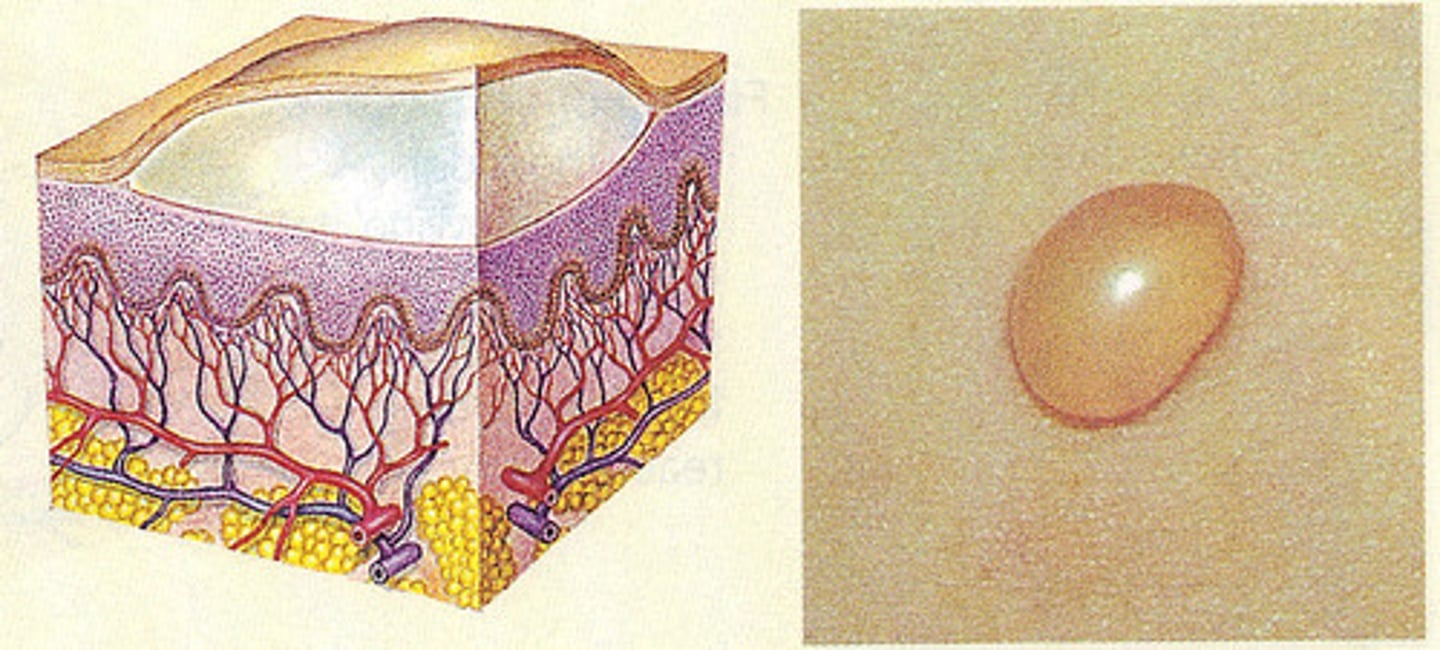
What is a bulla lesion?
Similar to a vesicle but larger, greater than 1 cm
Filled with serous fluid
Examples include blisters, second degree burns, and insect bites
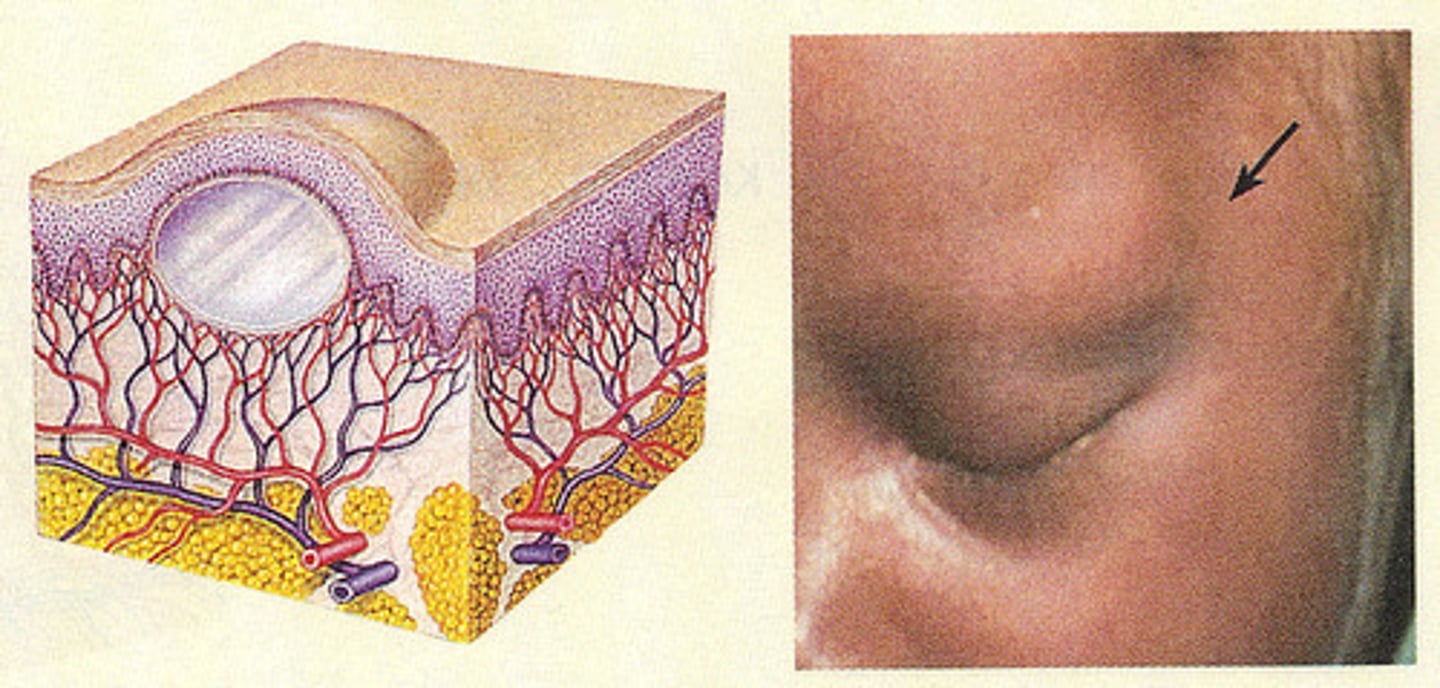
What is a cyst?
Nodule filled with expressible material, usually either liquid or semi solid
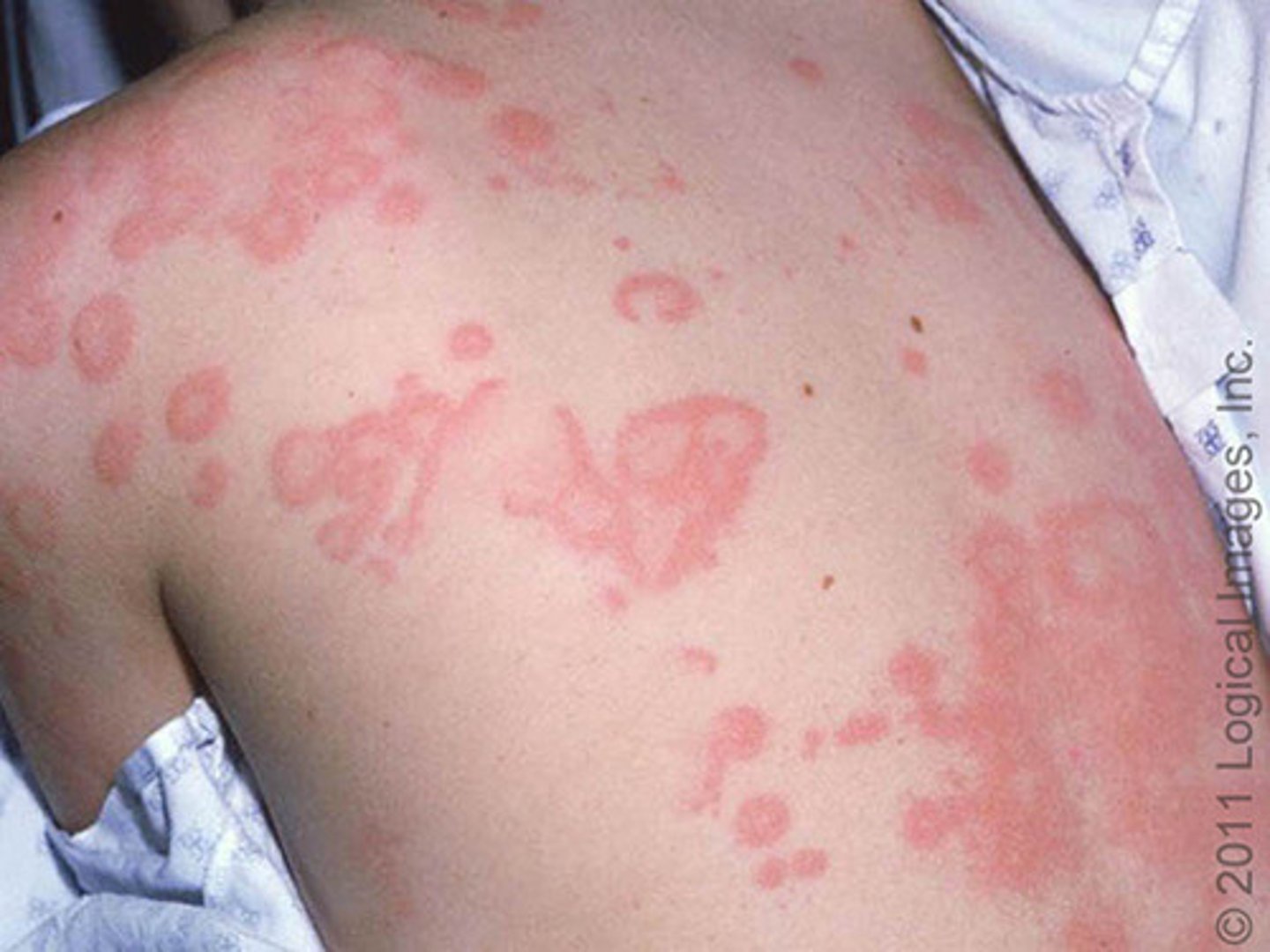
What is a wheal?
Hives
Elevated, irregular superficial area of localized edema
Solid, transient, variable diameter
Examples include insect bites, urticaria, and allergic reactions
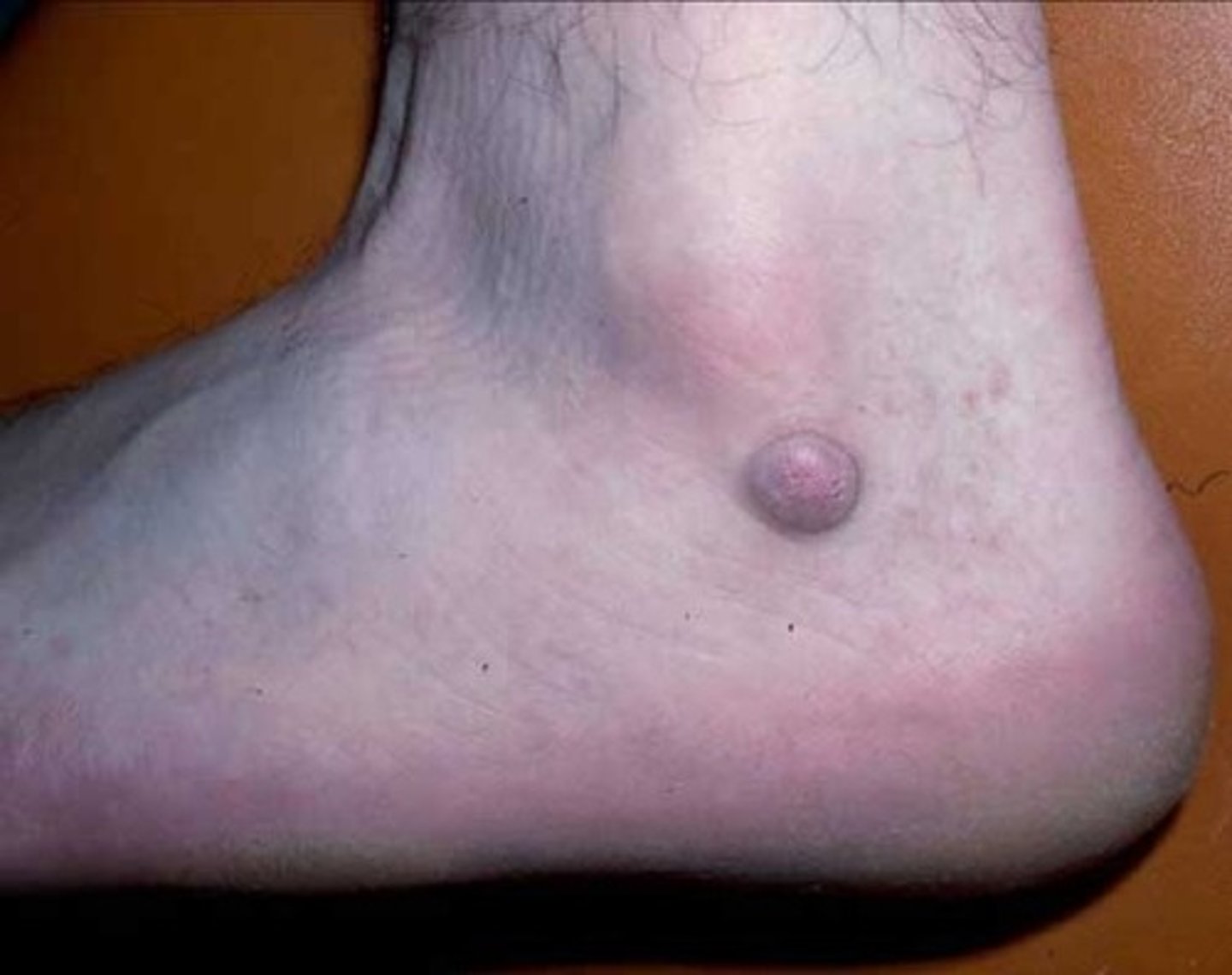
What is a nodule?
Elevated, firm, circumscribed lesion that is marble-like
Deeper and firmer than papule, larger than 0.5 cm, usually about 1-2 cm
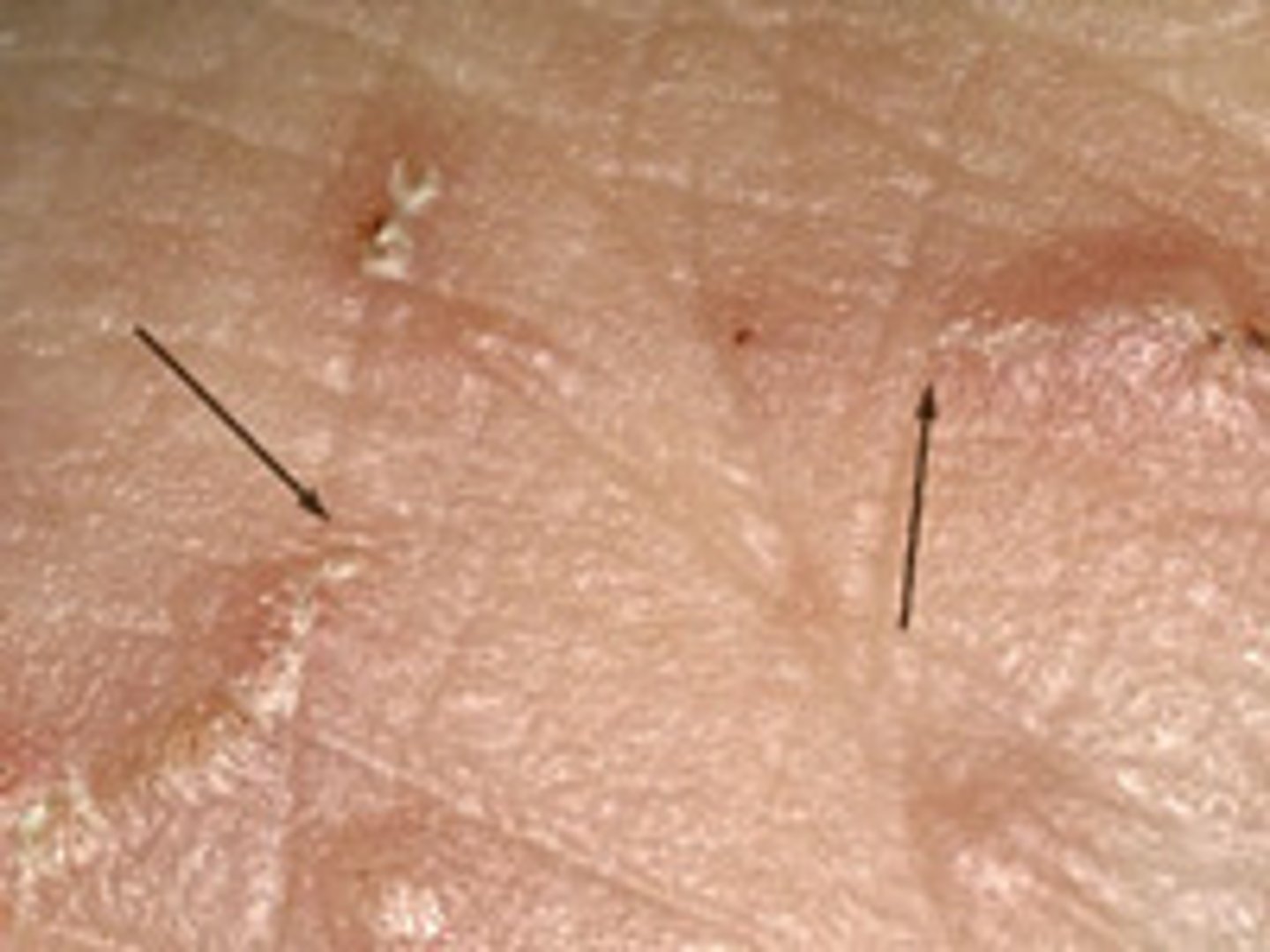
What is a burrow?
Small linear or serpiginous pathways in the epidermis created by the scabies mite
What are examples of secondary lesions?
Scales
Crust
Scars
Keloids
Lichenification
Erosions
Excoriations
Fissures
Ulcers
What is a scale?
Thin flake of dead exfoliated epidermis

What is Lichenification?
Rough, thickened epidermis secondary to rubbing, itching, or skin irritation

What is a keloid?
Irregularly shaped, elevated and enlarging scar that grows beyond the boundaries of the wound
Usually due to excessive collagen formation during healing
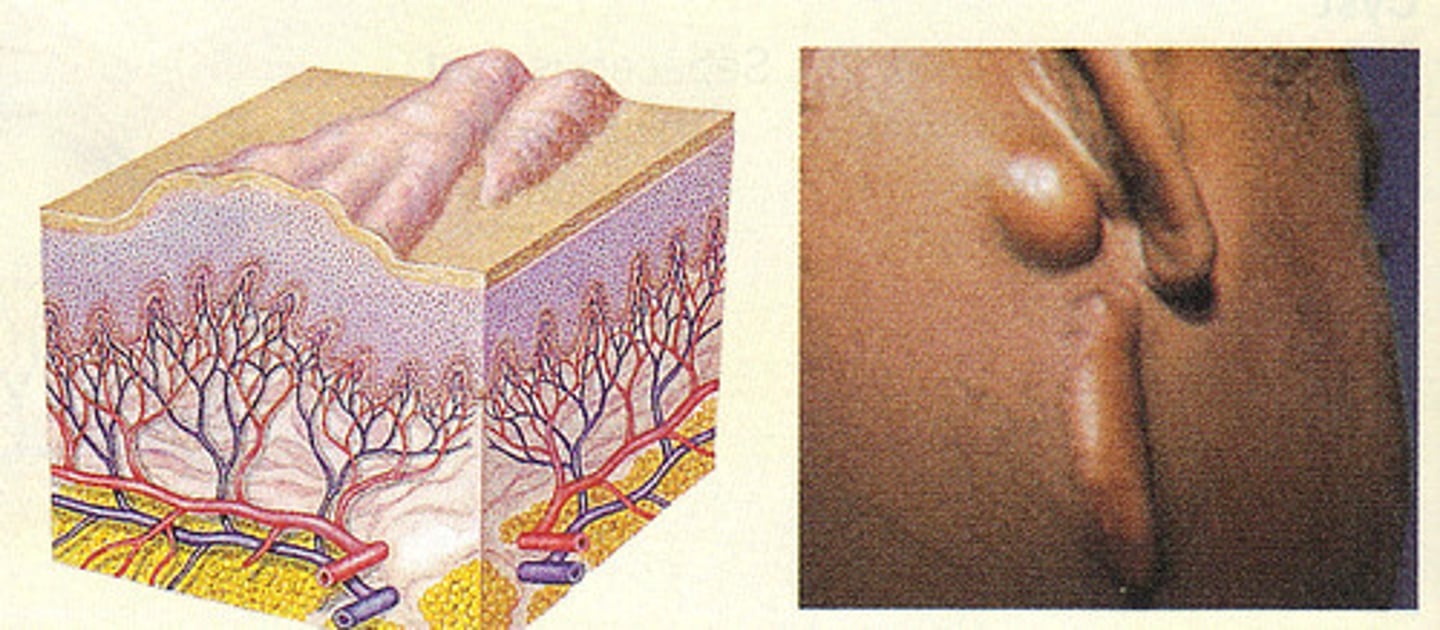
What is excoriation?
Loss of epidermis, linear hollowed out and crusted area
Examples can include cat scratches
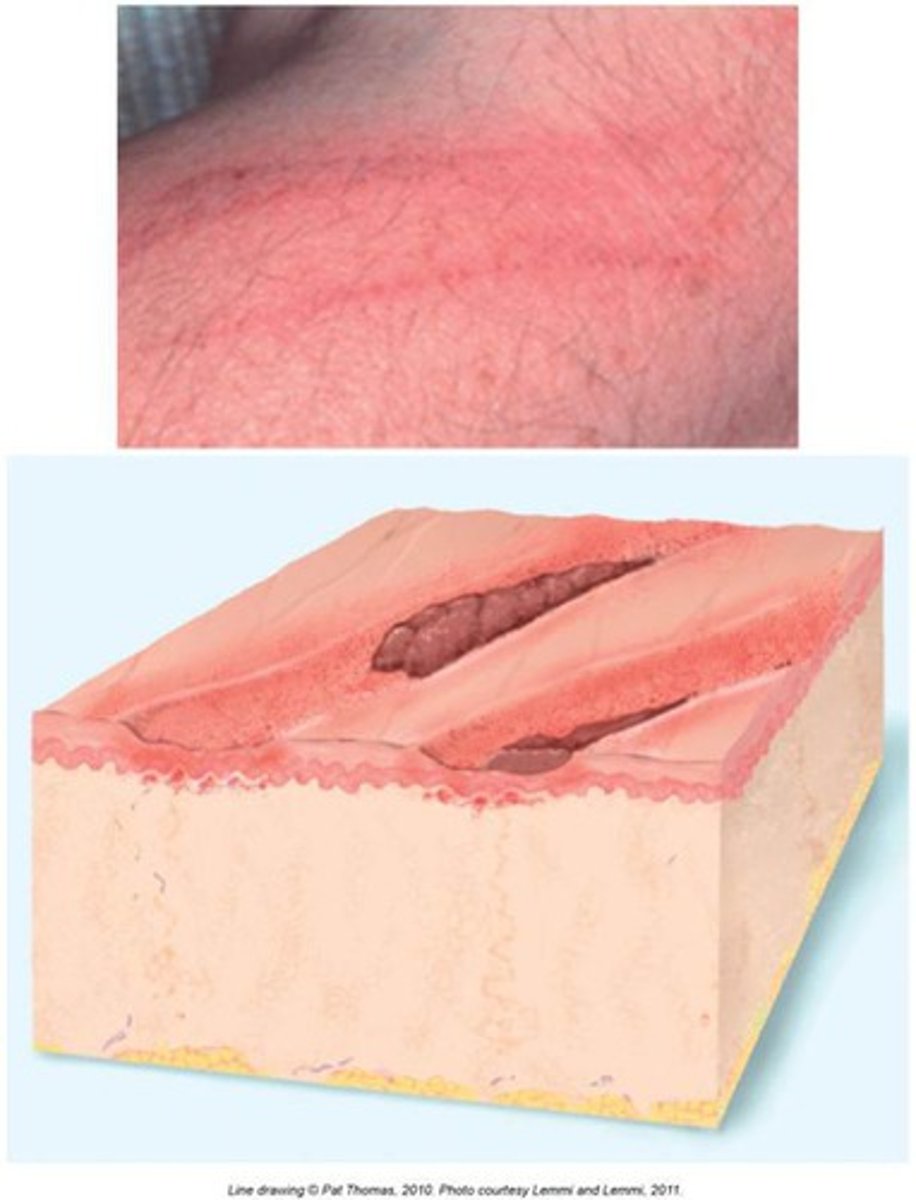
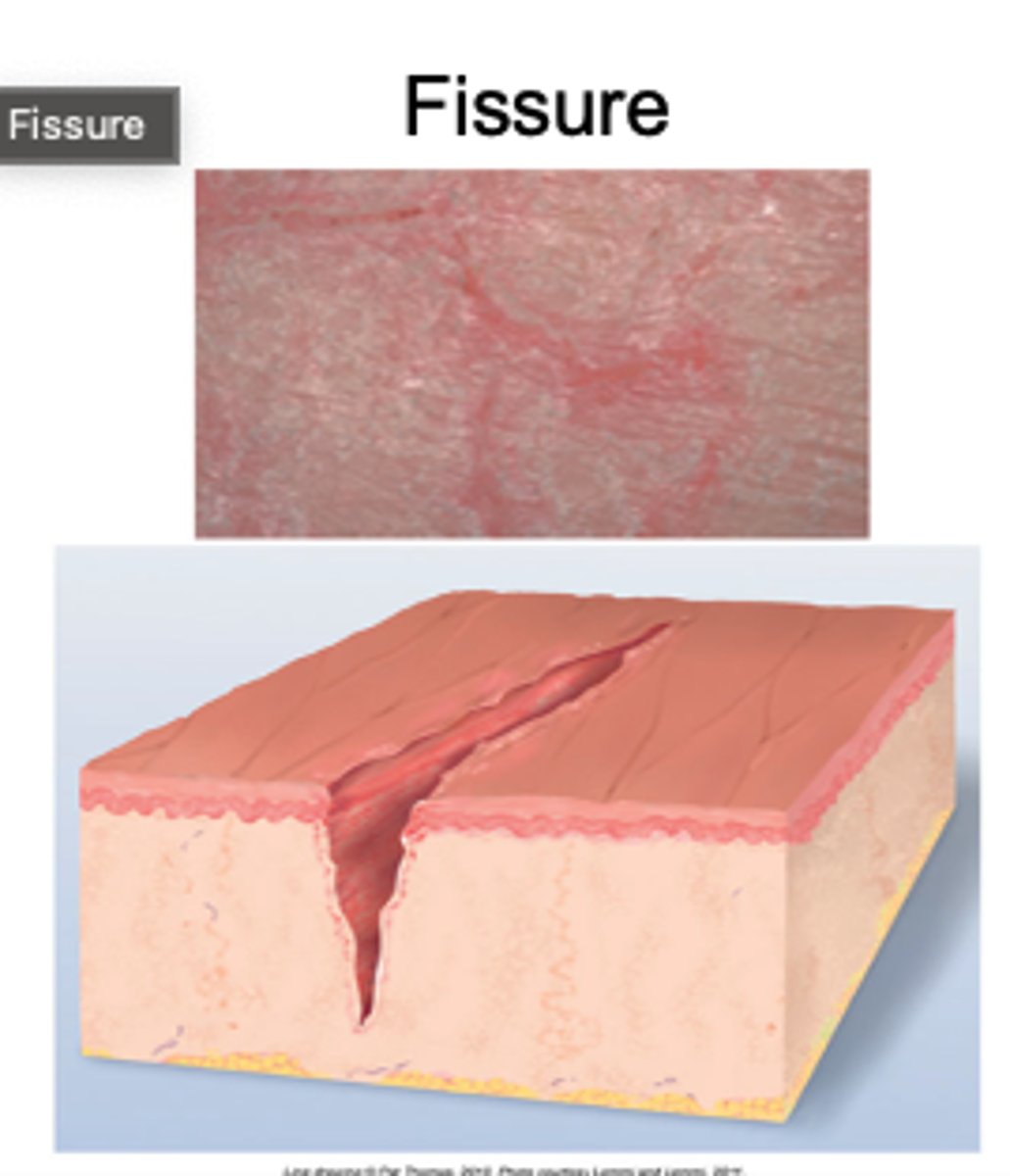
What is a fissure skin lesion?
Linear crack or break from epidermis to dermis
Seen in tinea pidus (athlete's foot)
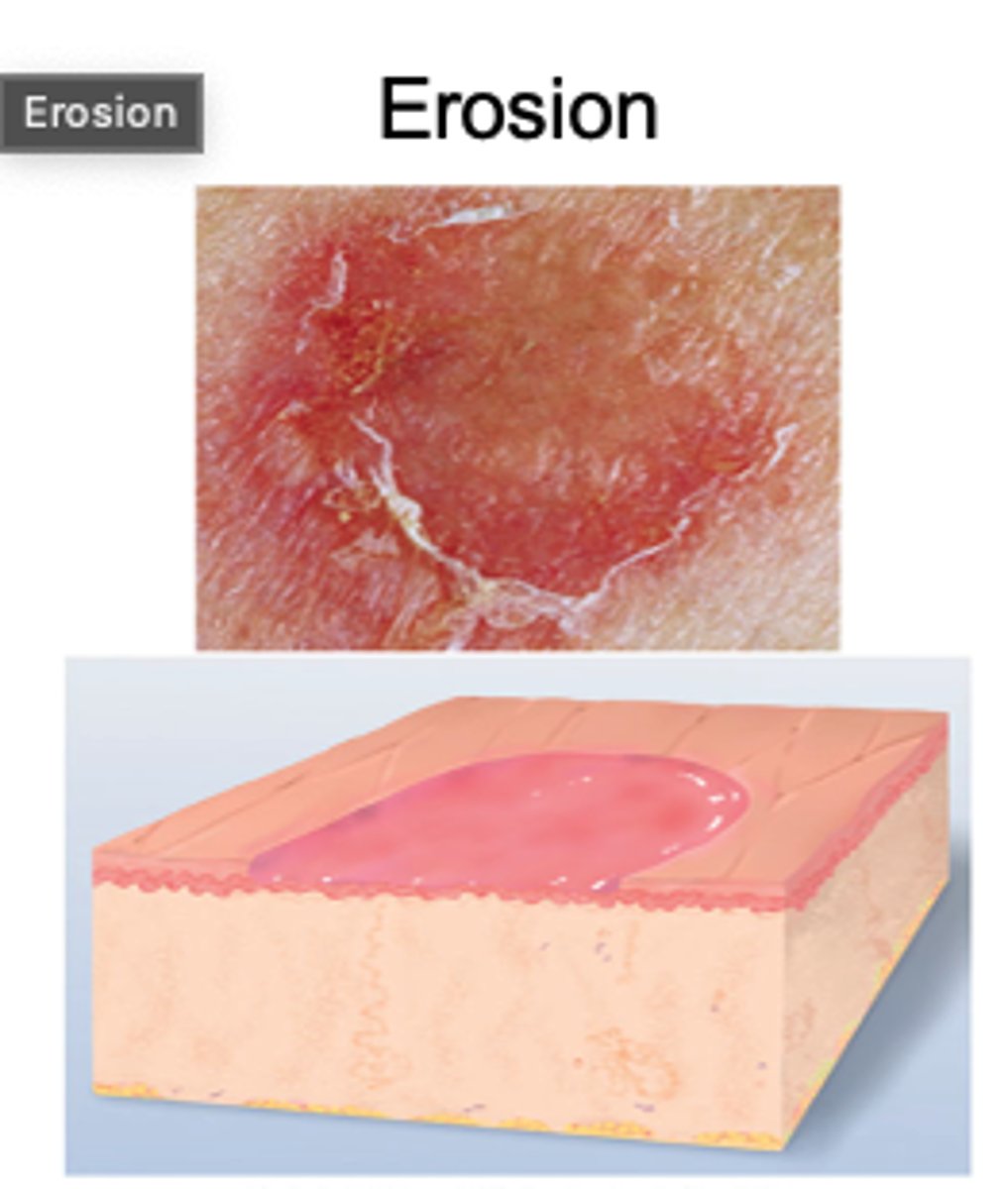
What is an erosion skin lesion?
Loss of part of the epidermis
Presents as depressed and moist area, follows a ruptured vesicle or bulla
What is an ulcer?
Loss of epidermis and dermis
Presents itself as concave lesion
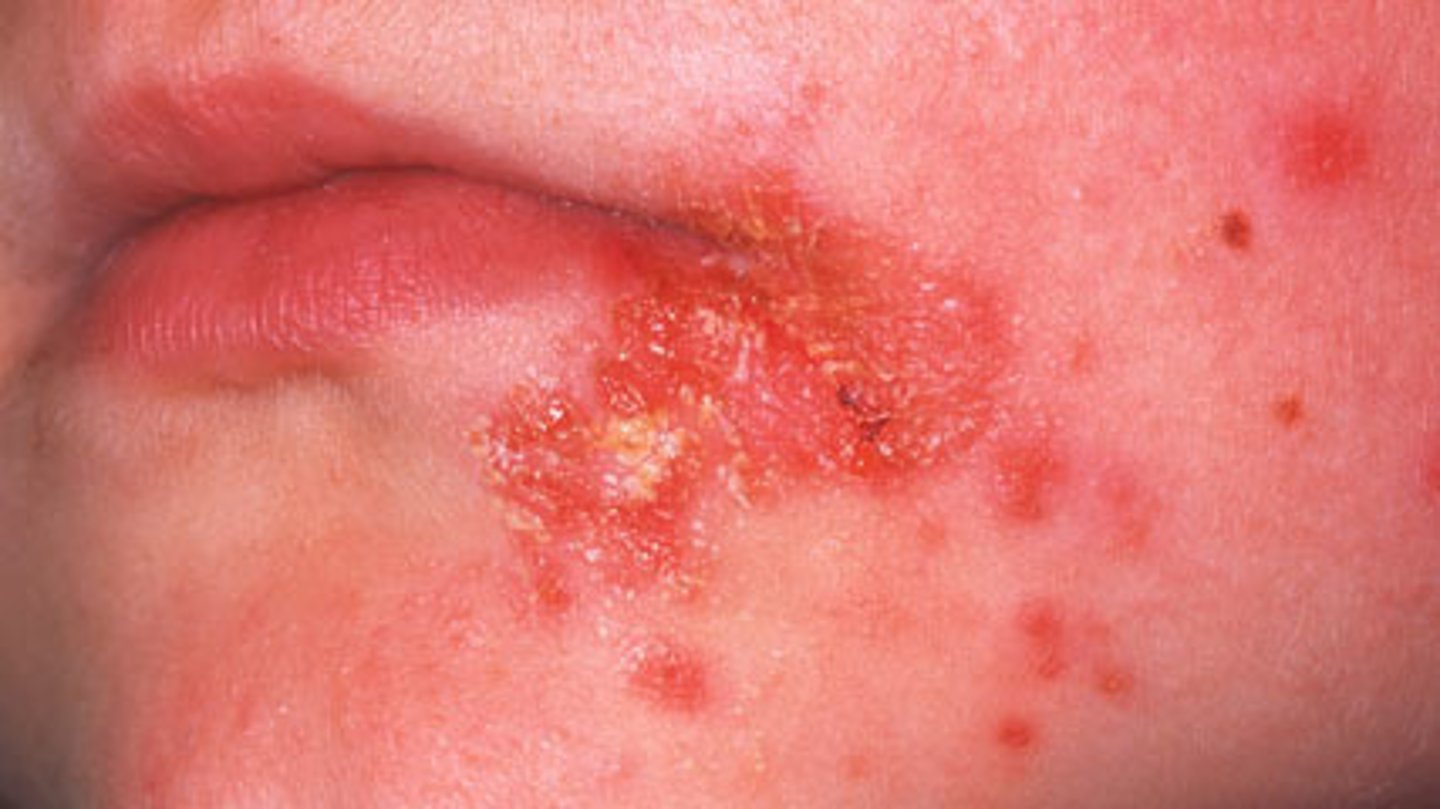
What is crust skin lesion?
Dried residue of skin exudates such as serum, pus or blood
Examples include crust from impetigo
A well circumscribed lesion that measures less than 1 cm and is filled with serous fluid is known as a:
Vesicle!!
Bulla and vesicles both have serous fluid but a vesicle is smaller (< 1 cm)
What is a cherry angioma?
Papular, round red/purple lesion found on the body

What is petechiae?
Small dot like pinpoint hemorrhages on the skin
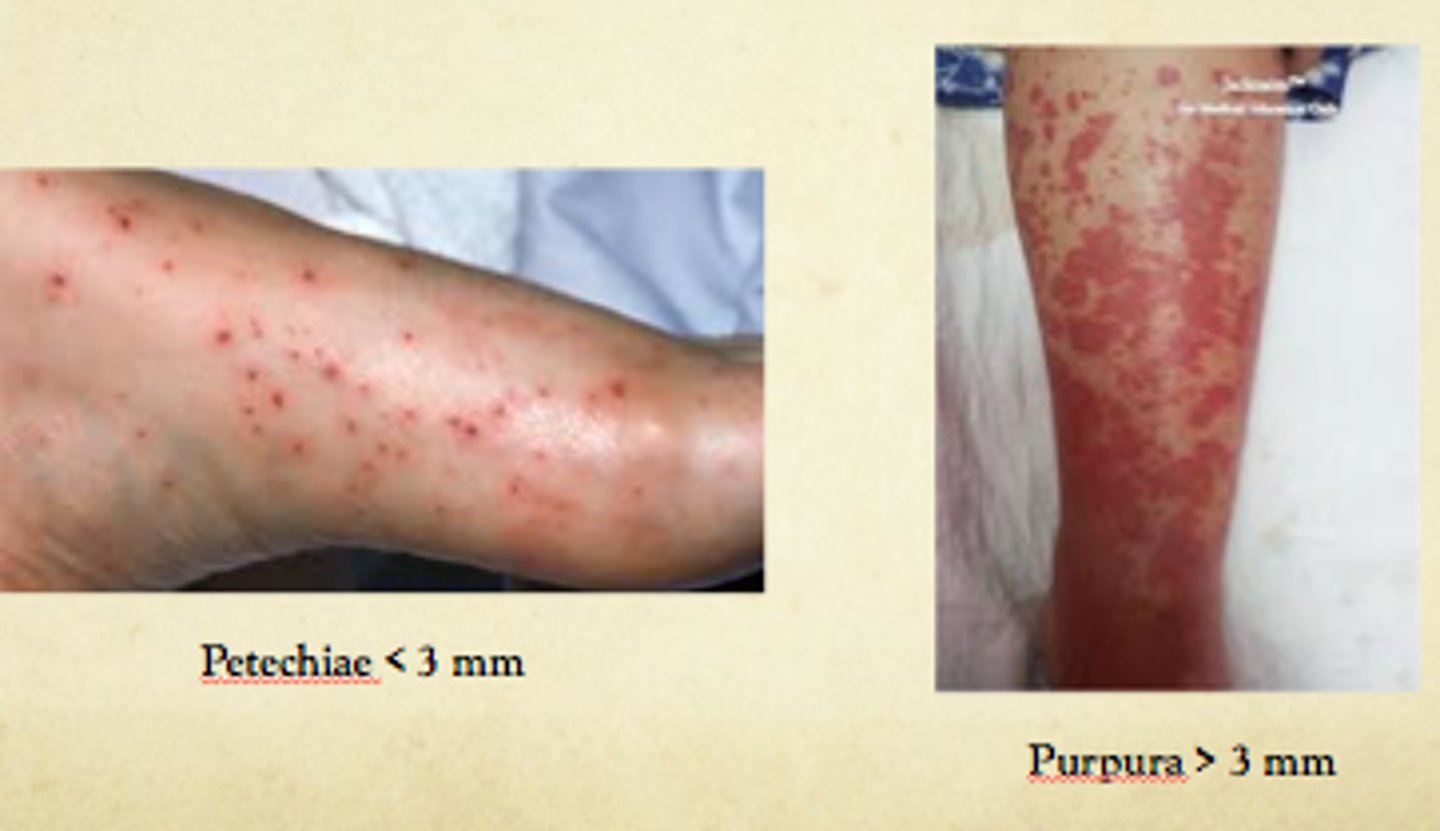
During the skin exam, what part do you examine last?
Breasts and genitalia
Always ensure there is a chaperone and consider patient modesty
What are the most common causes of hair thinning in males and females, respectively?
Male pattern baldness
Female pattern baldness
What is the hair pull test?
Grab 50-60 hairs with thumb and index finger and pull firmly away from the scalp
Observe where the hair is shedding from
If the hair has telegen bulb attached, it is a normal shedding of the hair indicative of telegenic effluvian
What is the hair tug test (hair fragility test)?
Grabbing hairs from the center and ends and tugging to see if there is breakage along the shaft
If hair breaks along the shaft during the hair tug test, what could this indicate?
Damage from hair care or tinea capitis
How much of hair loss is non-scarring?
97%
Non-scarring means it produces shiny spots without any hair follicles
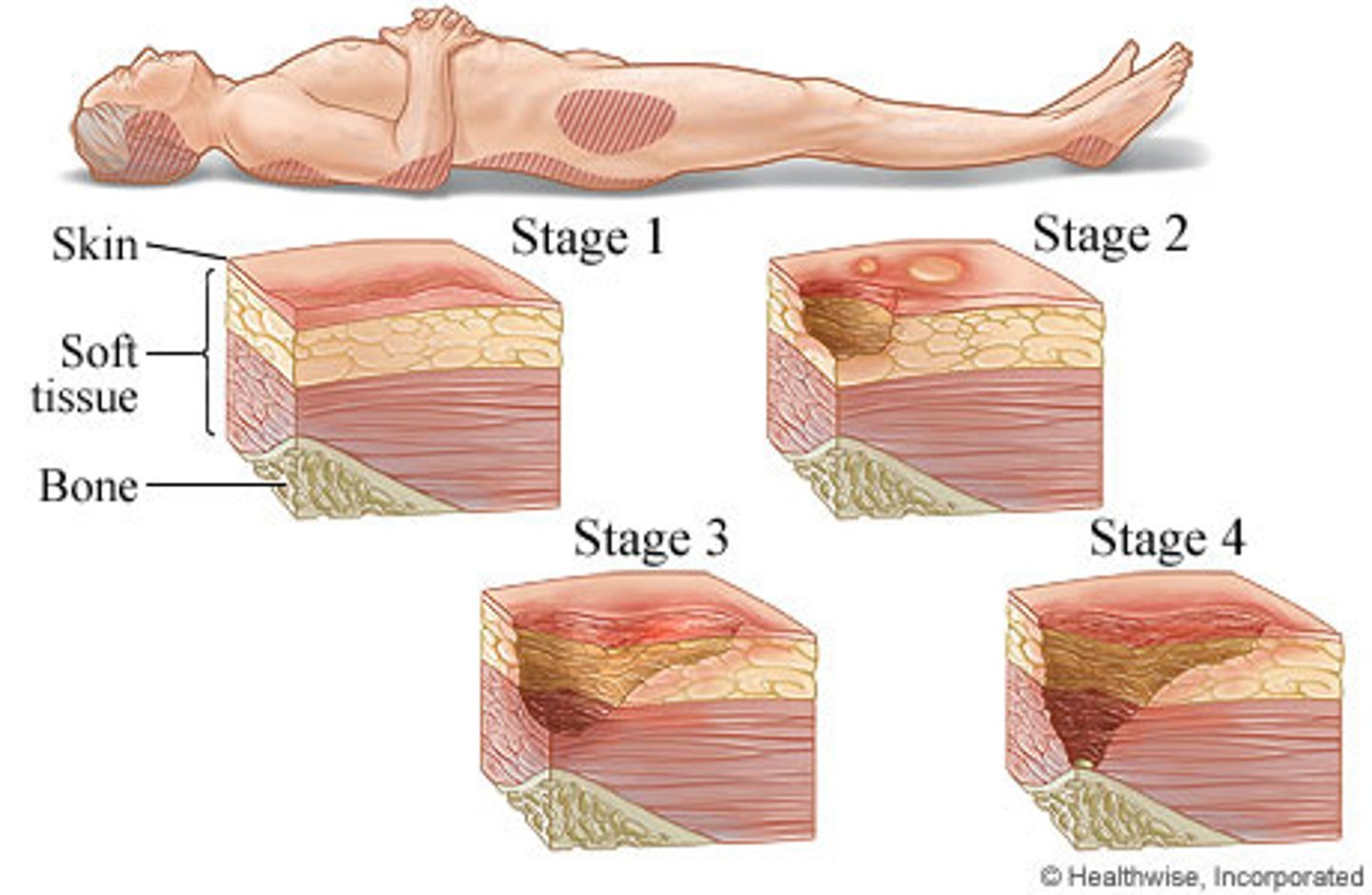
What is a stage 1 pressure injury?
Intact skin with localized area of nonblanchable erythema
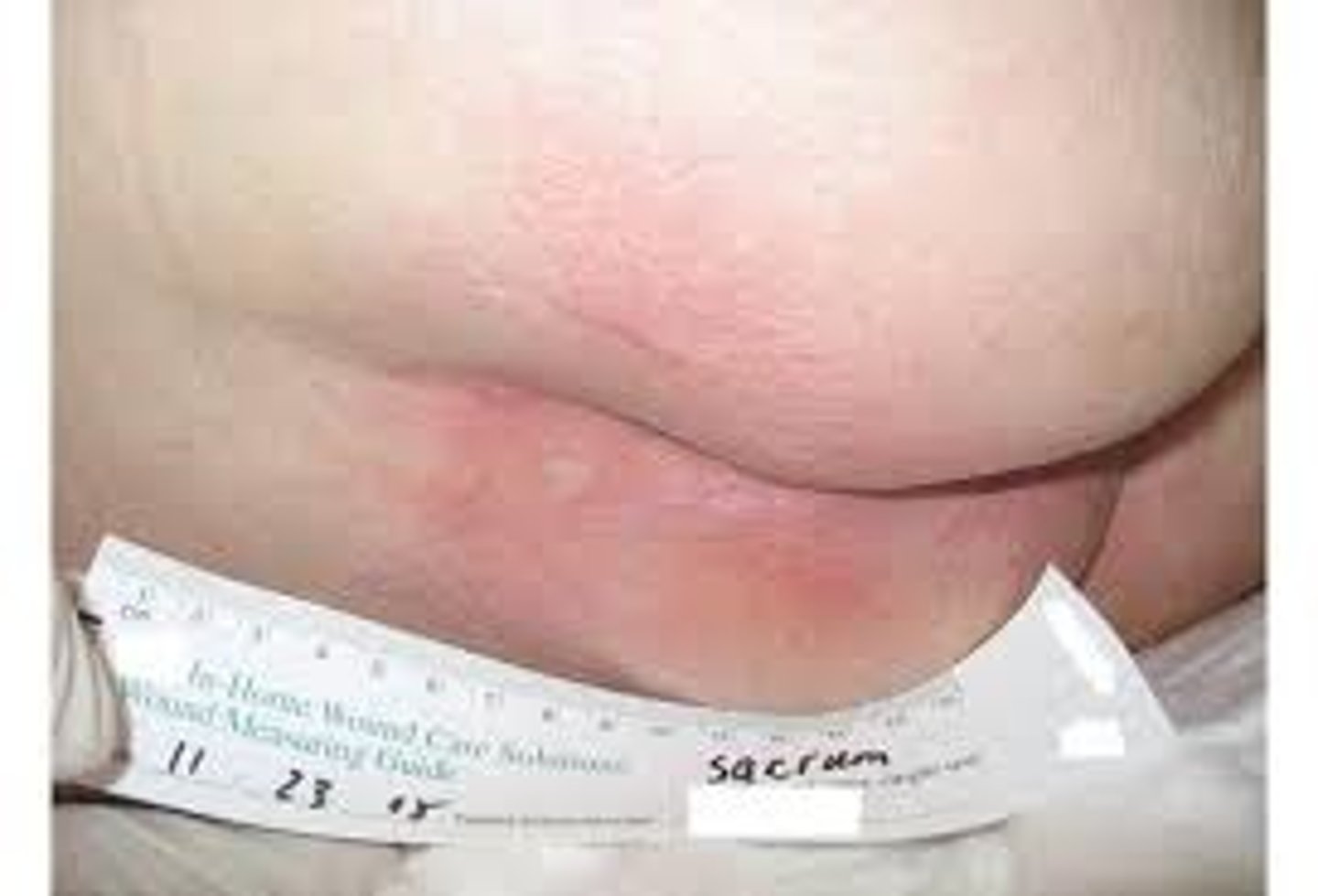
What is a stage 2 pressure injury?
Partial-thickness loss of skin with exposed dermis
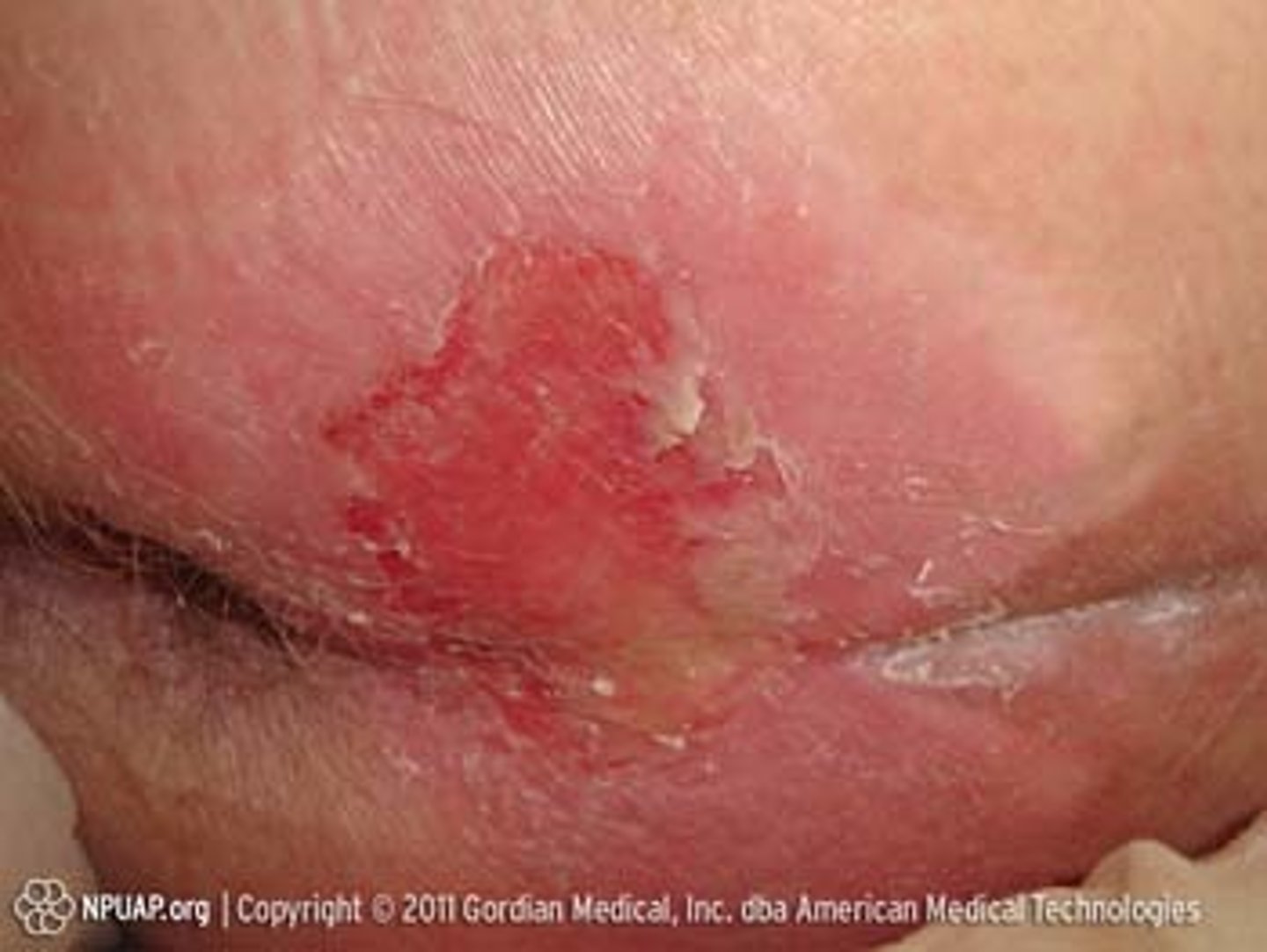
What is a stage 3 pressure injury?
Full-thickness skin loss, in which fat is visible in the ulcer and granulation tissue and rolled wound edges are often present
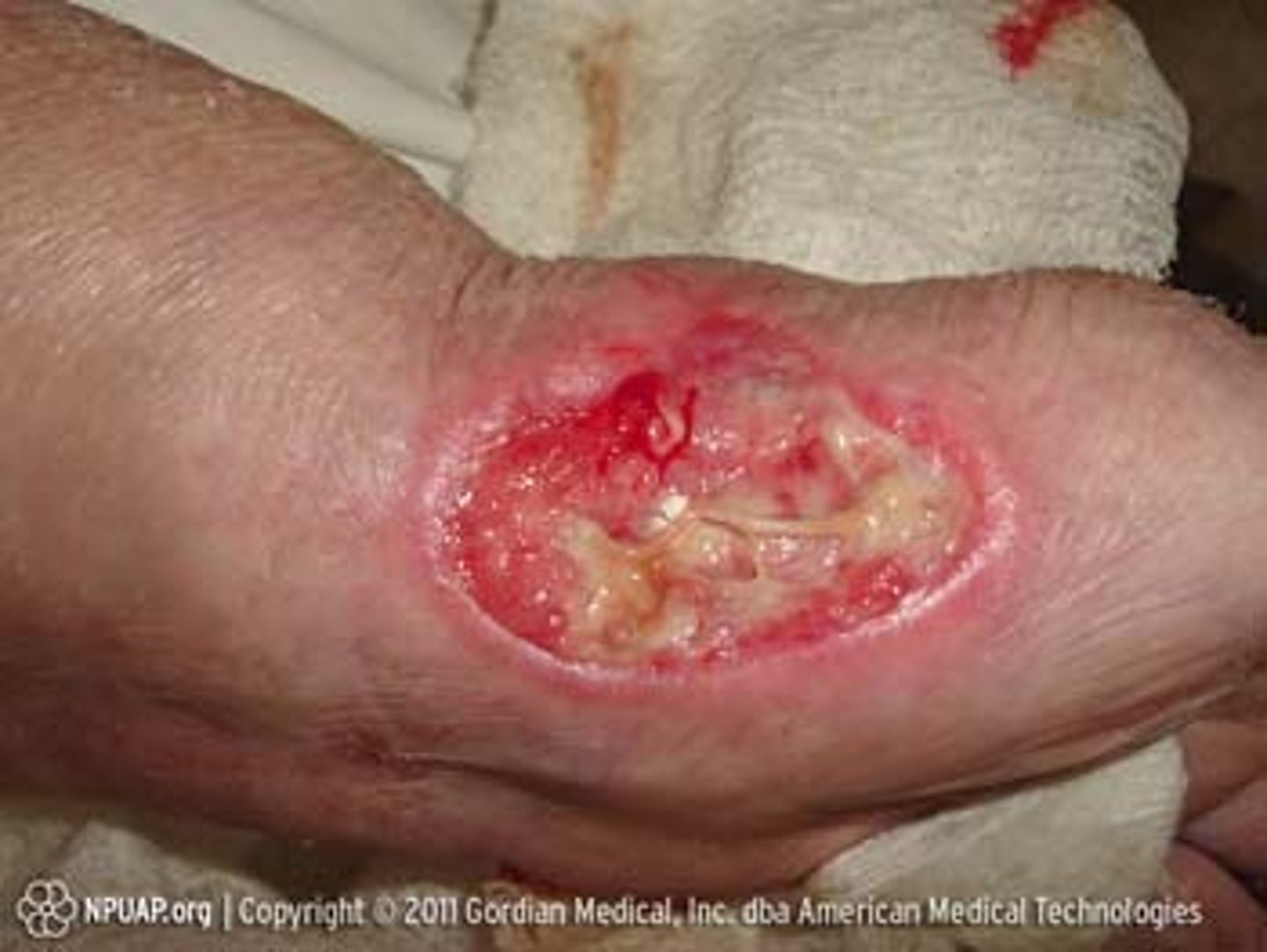
What is a stage 4 pressure injury?
Full-thickness skin and tissue loss with exposed or directly palpable fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage, or bone in the ulcer
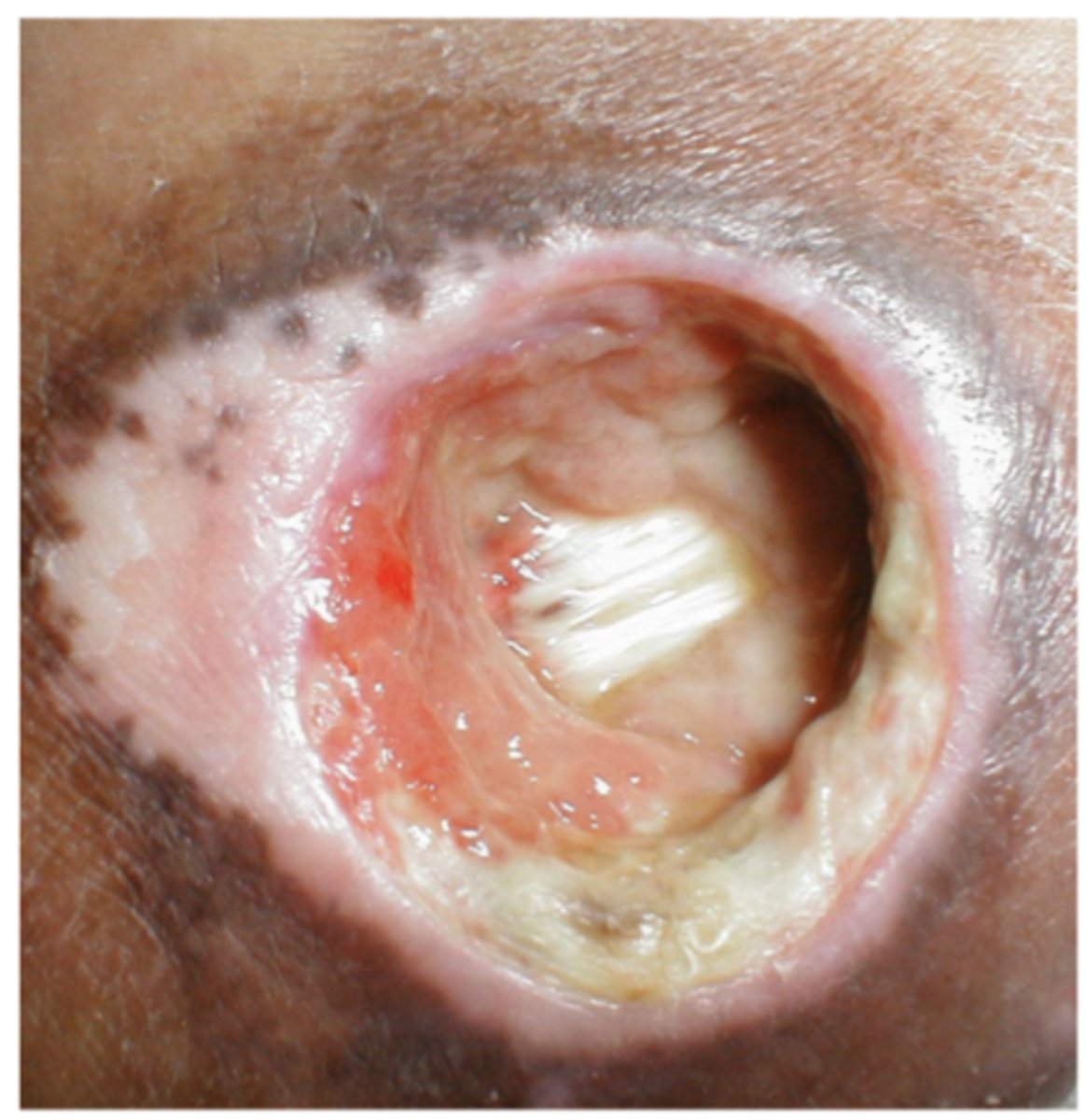
What is a deep tissue pressure injury?
Persistent non-blanchable deep red, maroon, or purple discoloration
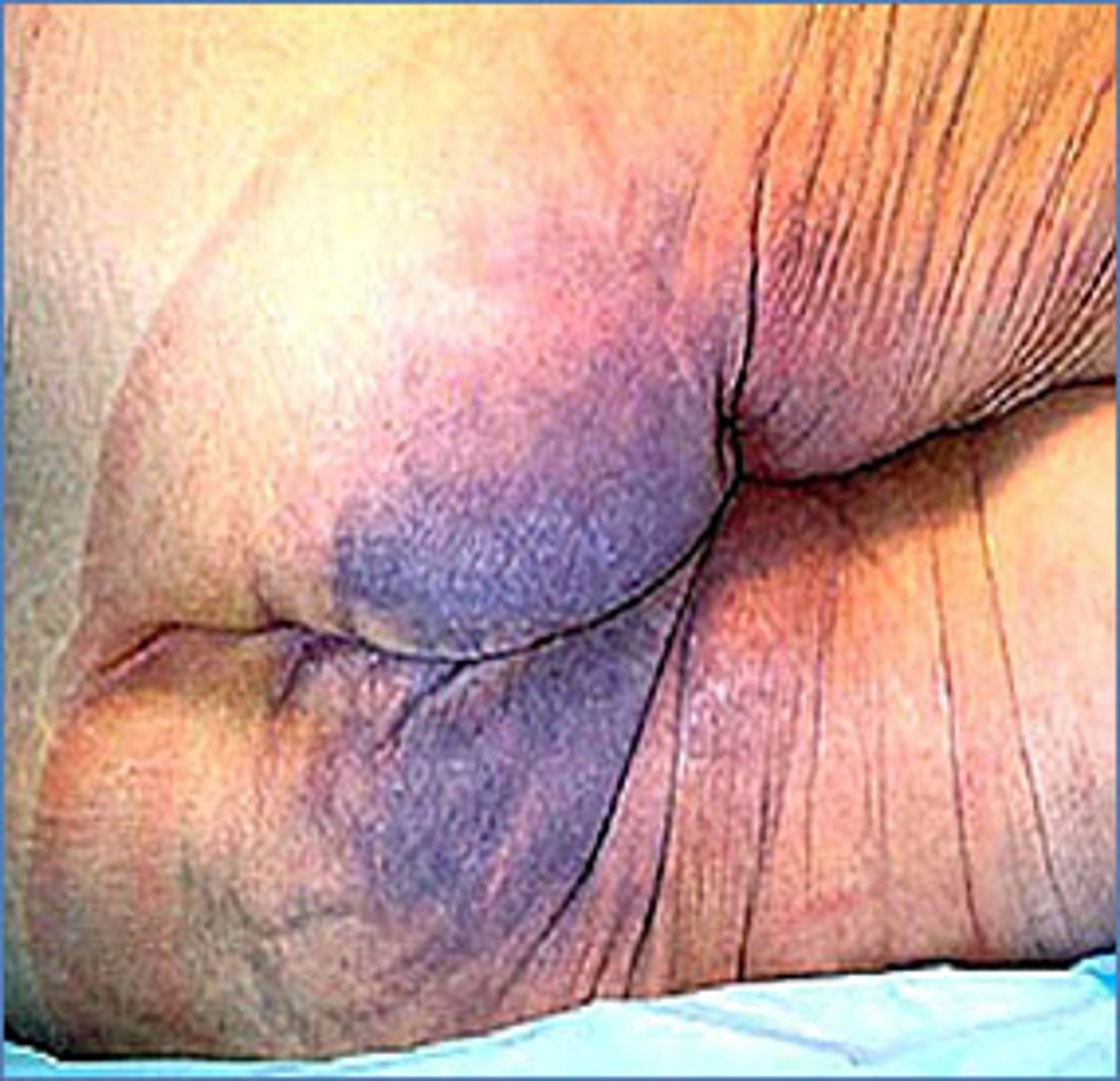
What are the 3 types of skin cancer, in order from most to least common?
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Melanoma
Which of the 3 types of skin cancers is most deadly?
Melanoma, causes over 70% of skin cancer-related deaths each year
What are risk factors for skin cancer?
- UV radiation
- Immunosuppression
- Genetic predisposition and susceptibility to DNA damage
- Fair skin, blond/red hair, blue eyes
- Chronic inflammation
What are some measures patients can take to prevent skin cancer?
- SPF over 30
- Avoid tanning booths
- Sun protective clothing
- Avoidance of the sun at peak hours of the day
How often should SPF be reapplied?
Every 2 hours during the day and after being in water
Describe the difference between UVA and UVB rays.
UVA cause wrinkles, leathery skin
UVB causes sun burns and skin cancers
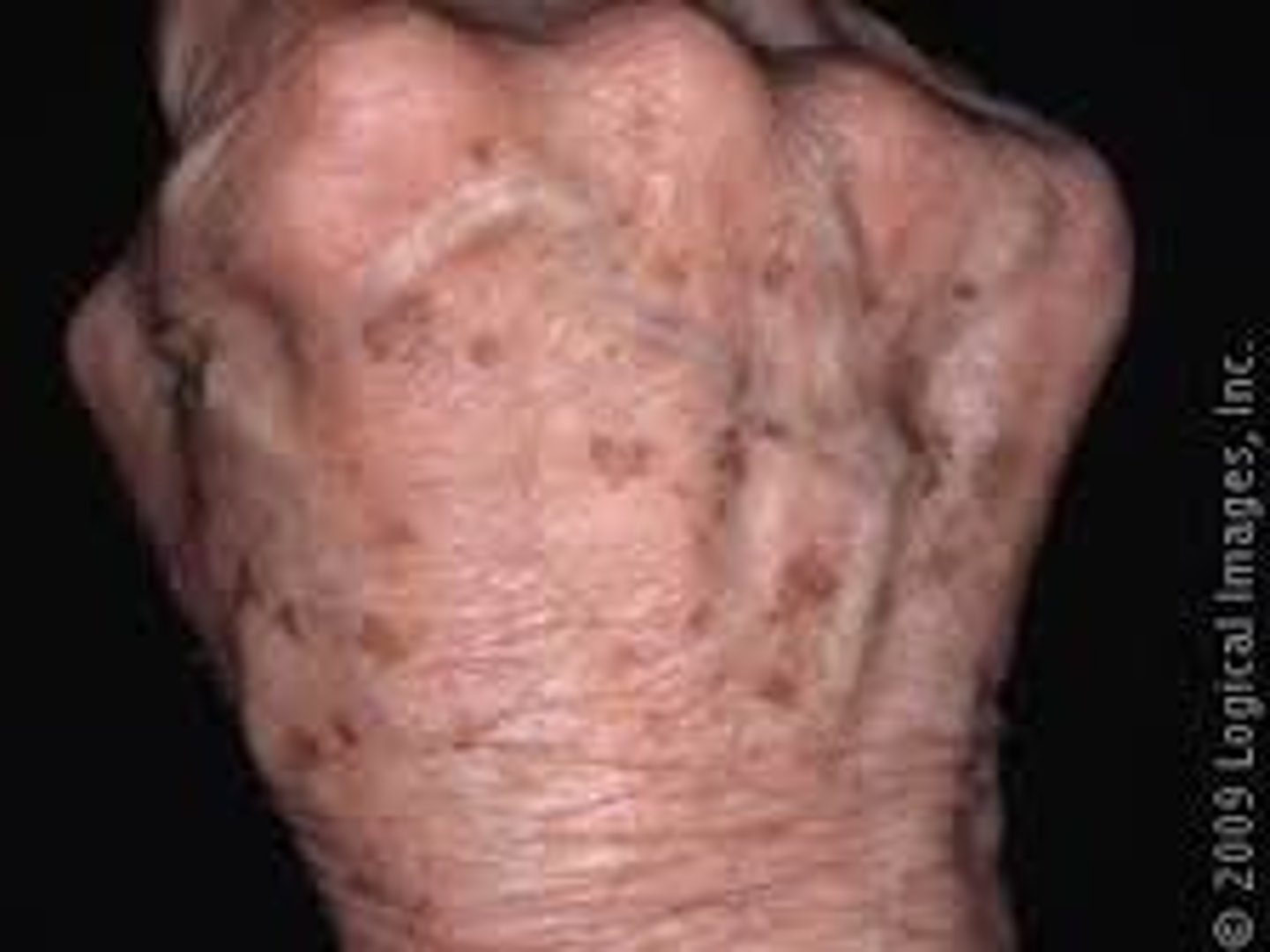
What is solar lentigo?
Bilateral symmetric brown macules located on sun-exposed areas of the skin including the face, shoulders, arms and hands
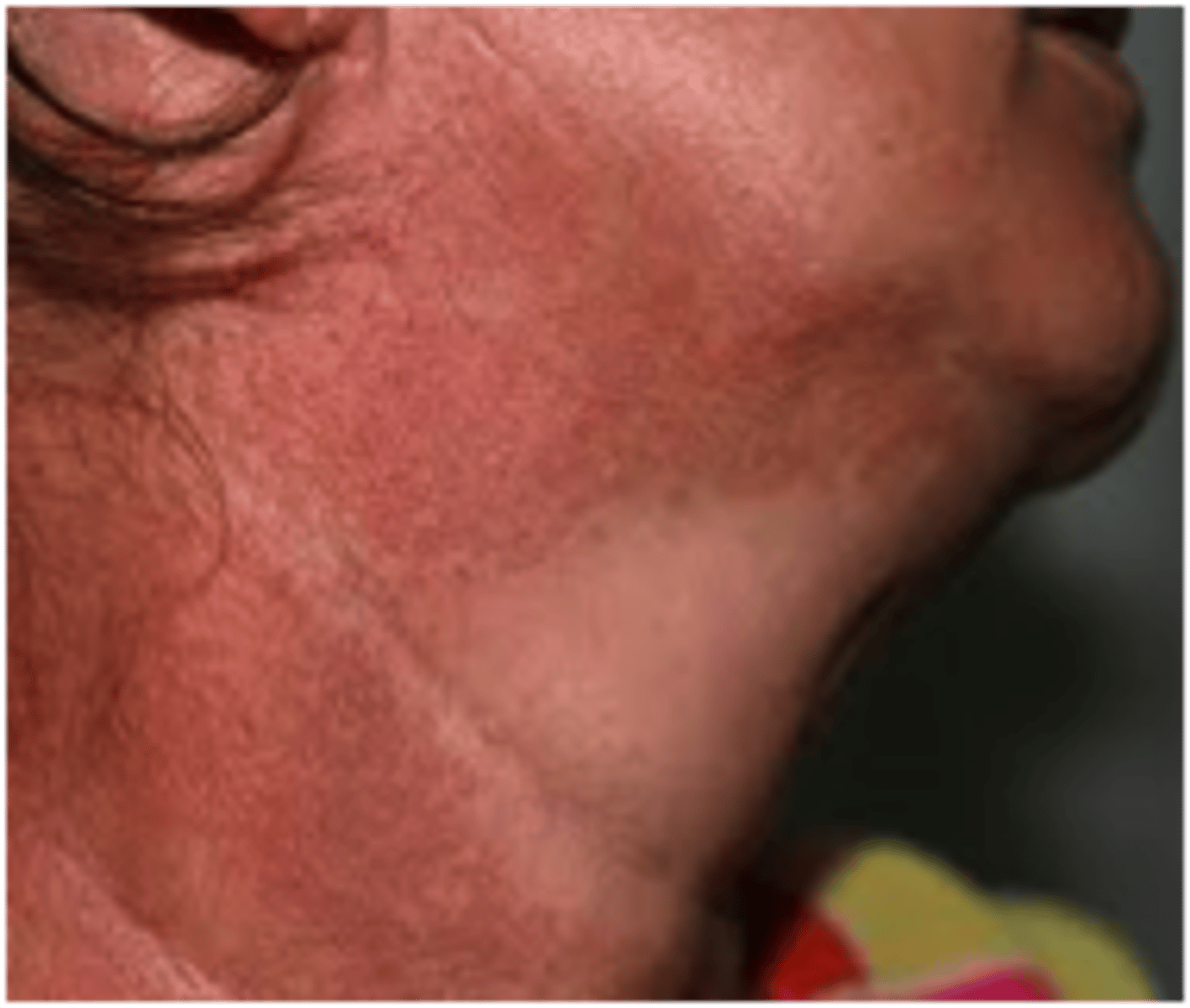
What is poikiloderma?
Red patches of skin in sun-damaged areas, especially the V of the neck and lateral neck
Often presents with fine telangectasias and hypo and hyperpigmentation
What is solar elastosis?
Yellowish white macules or papules on sun exposed skin, especially the forehead
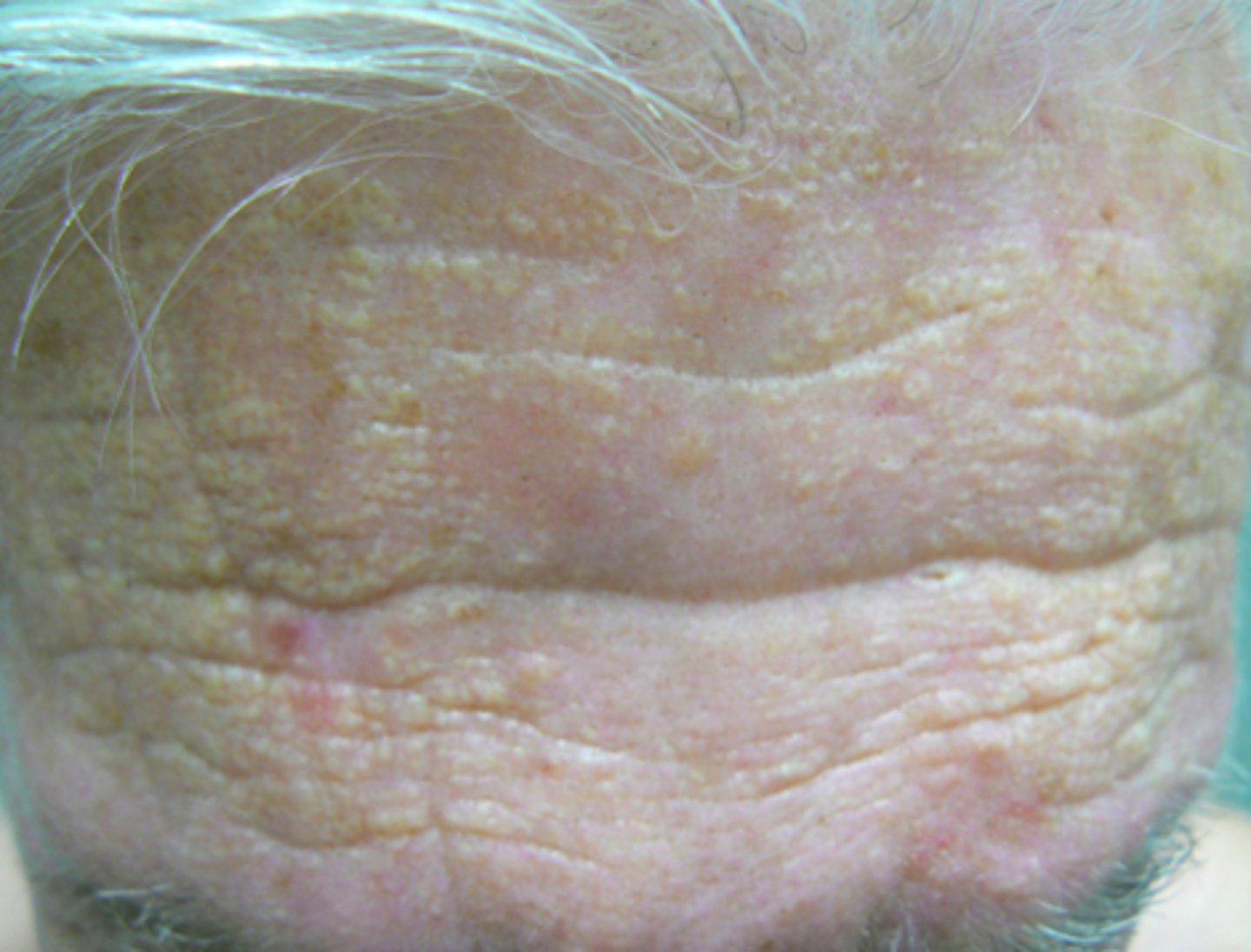
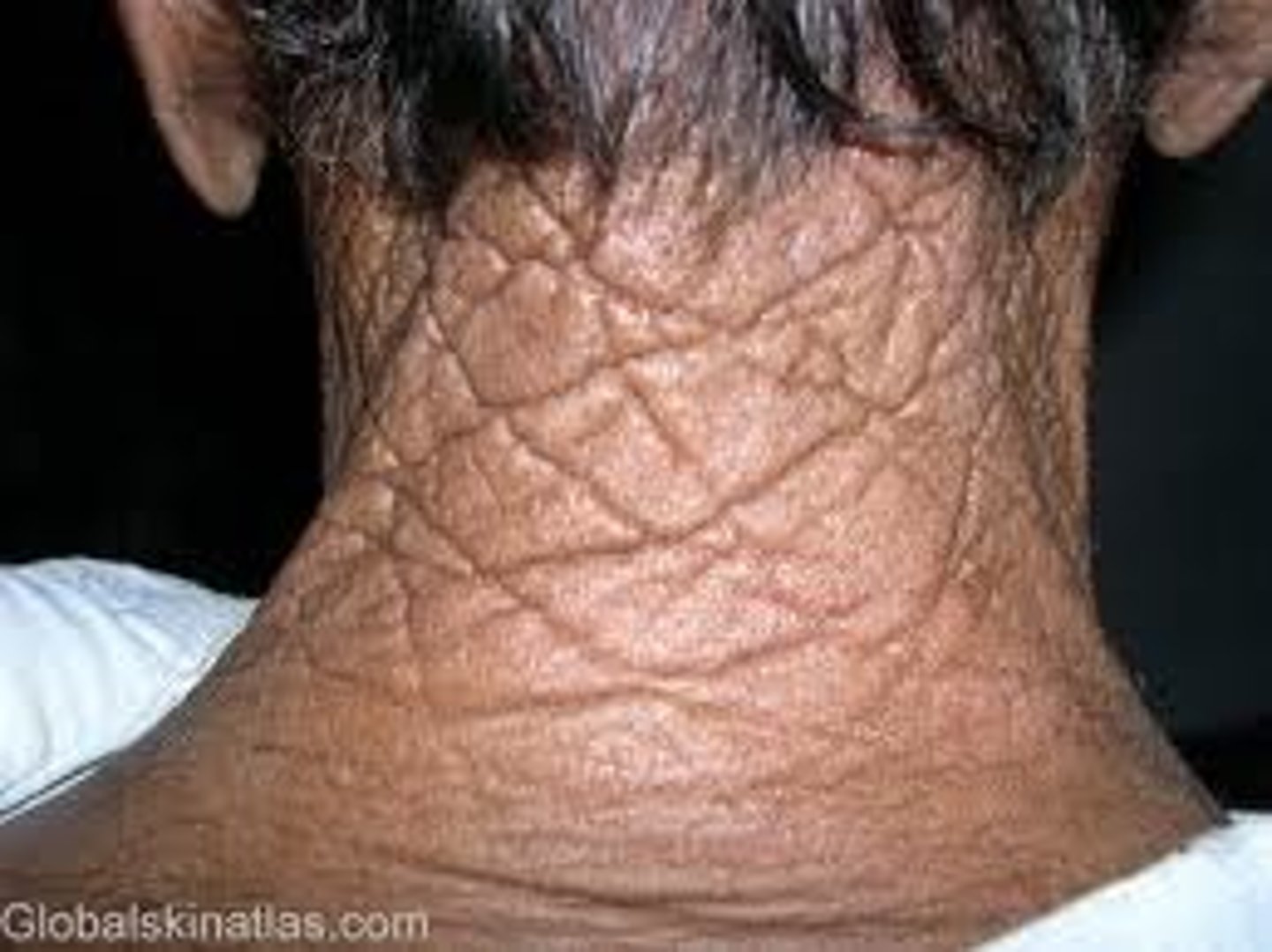
What is cutis rhomboidalis nuchae?
Worn leathery look to the posterior neck from frequent sun exposure
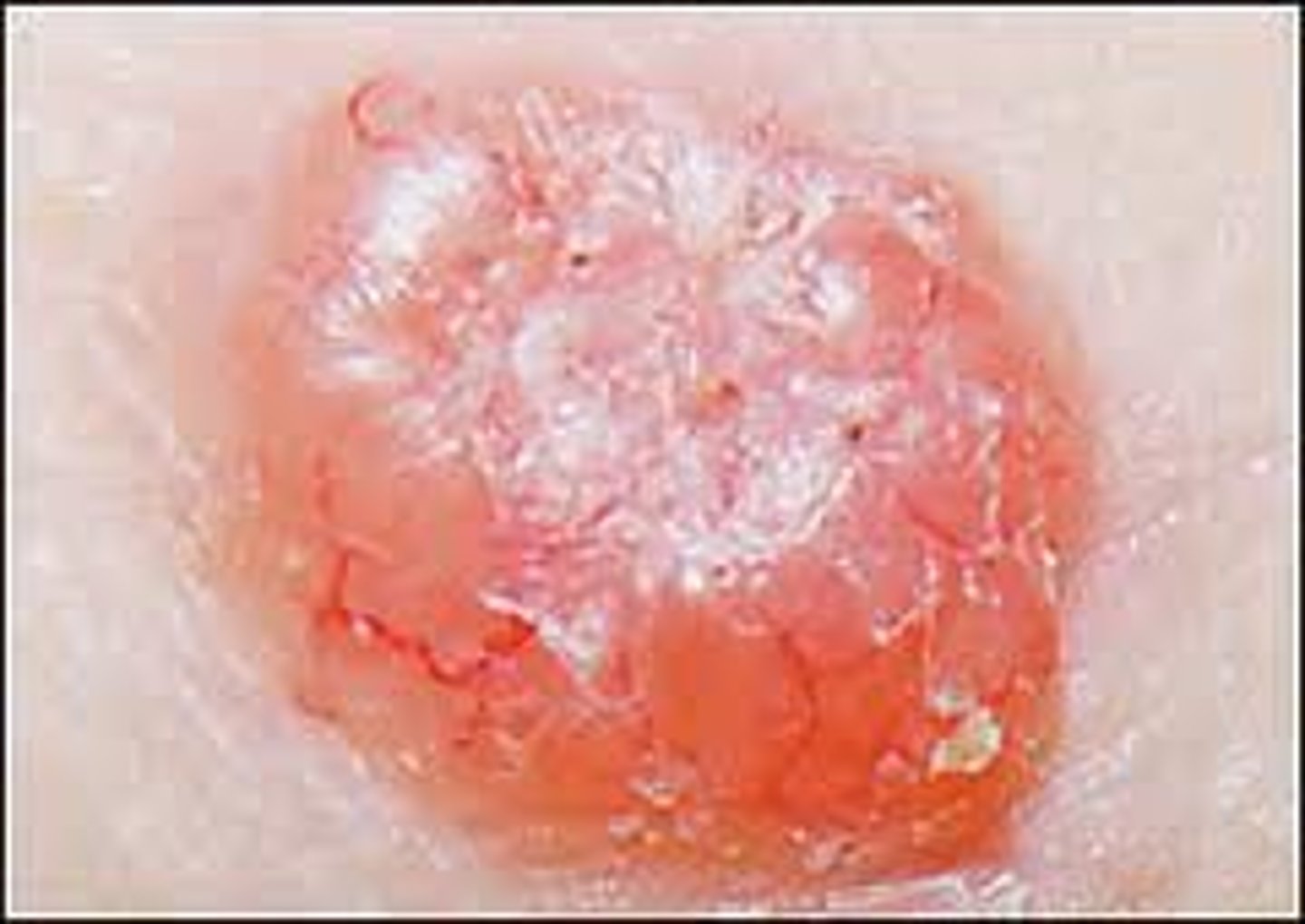
Describe basal cell carcinoma.
- Most common skin cancer (about 80%)
- Rarely spreads to other parts of the body
- Can invade and destroy local tissues
- Consists of immature cells similar to those in the basal layer of the epidermis
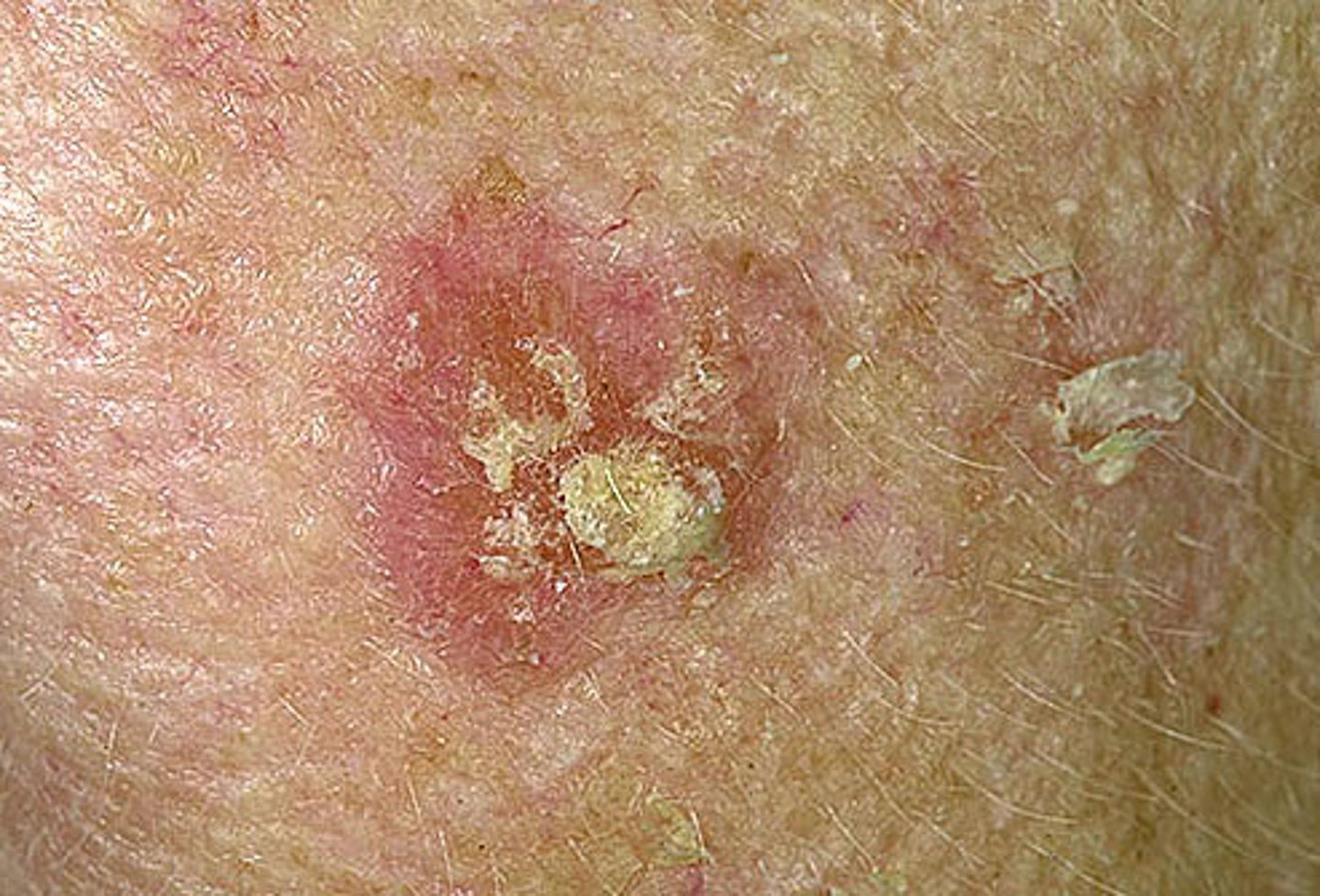
What is actinic keratosis?
A pre-cancerous lesion that is usually associated with SCC and occurs in sun-exposed areas of the skin
What is keratocanthoma?
A pre-cancerous lesion that is a fast growing nodule that develops within weeks to 1-2 months
Associated with SCC
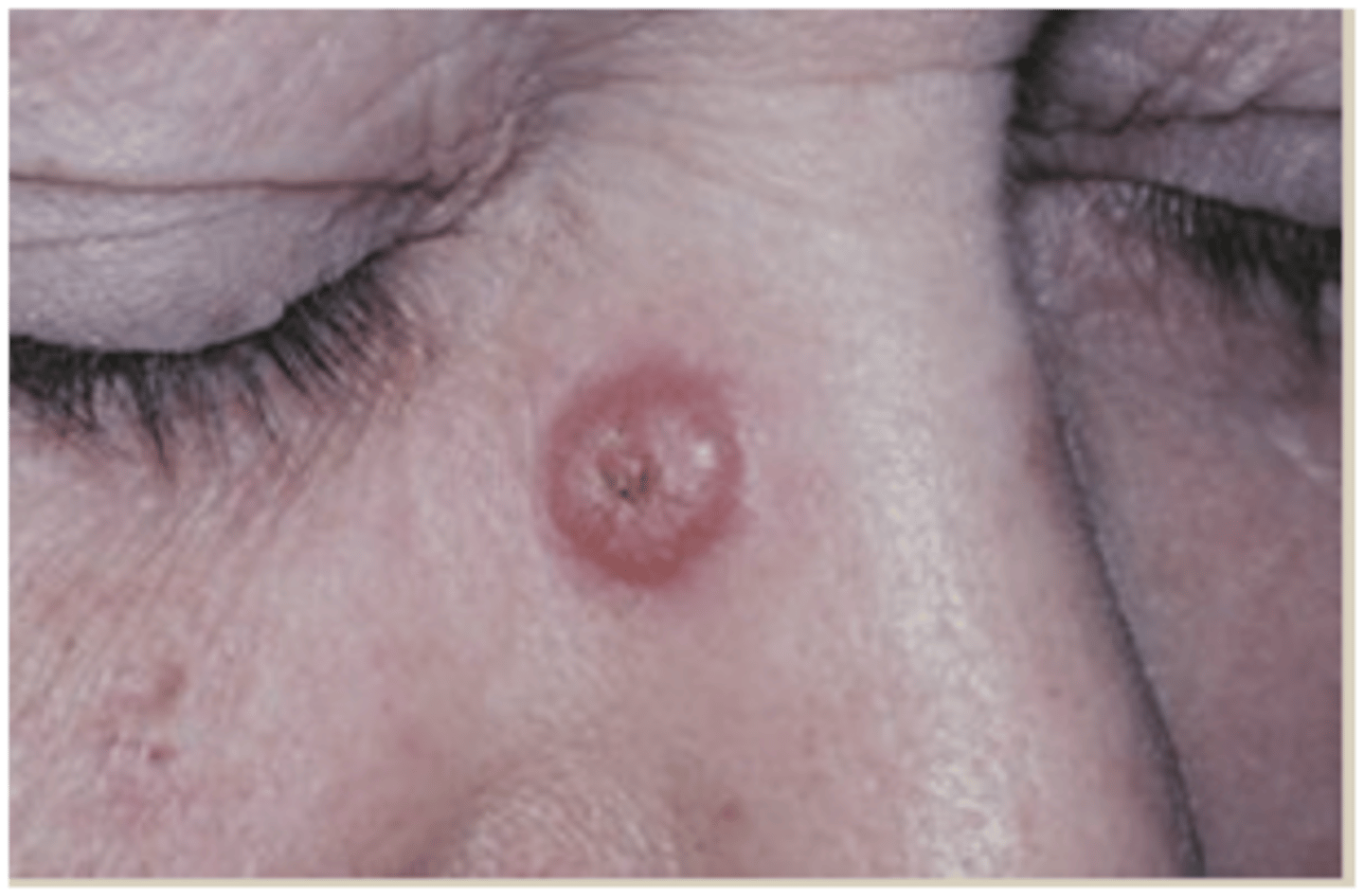
What are the precursors to squamous cell carcinoma?
- Actinic keratosis
- Keratocanthoma
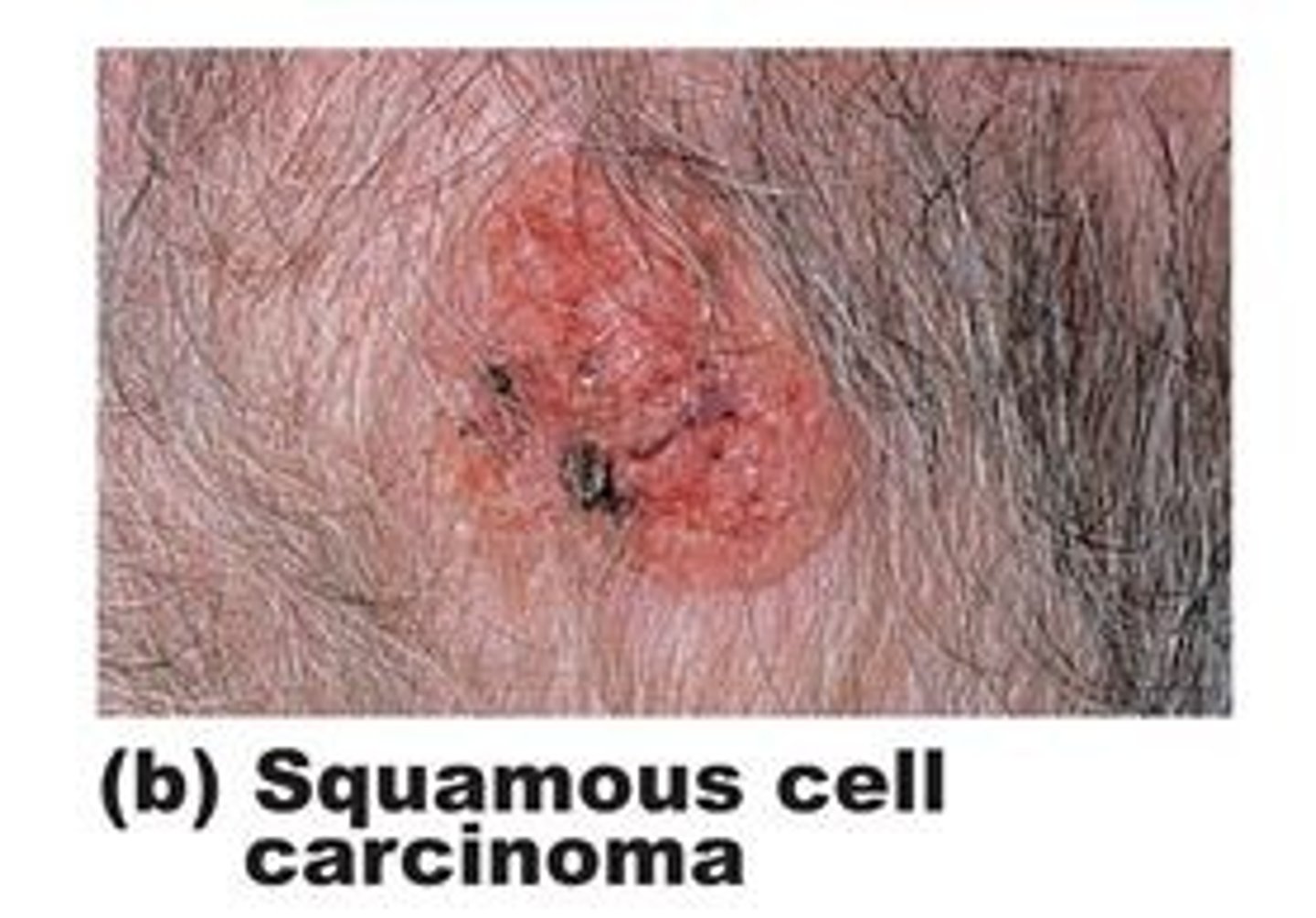
Describe squamous cell carcinoma.
Arises from the epithelium of the skin and presents as a nonhealing ulcer in a sun exposed area
More aggressive than BCC
Common on face, scalp, lower lip, ears, back of hands
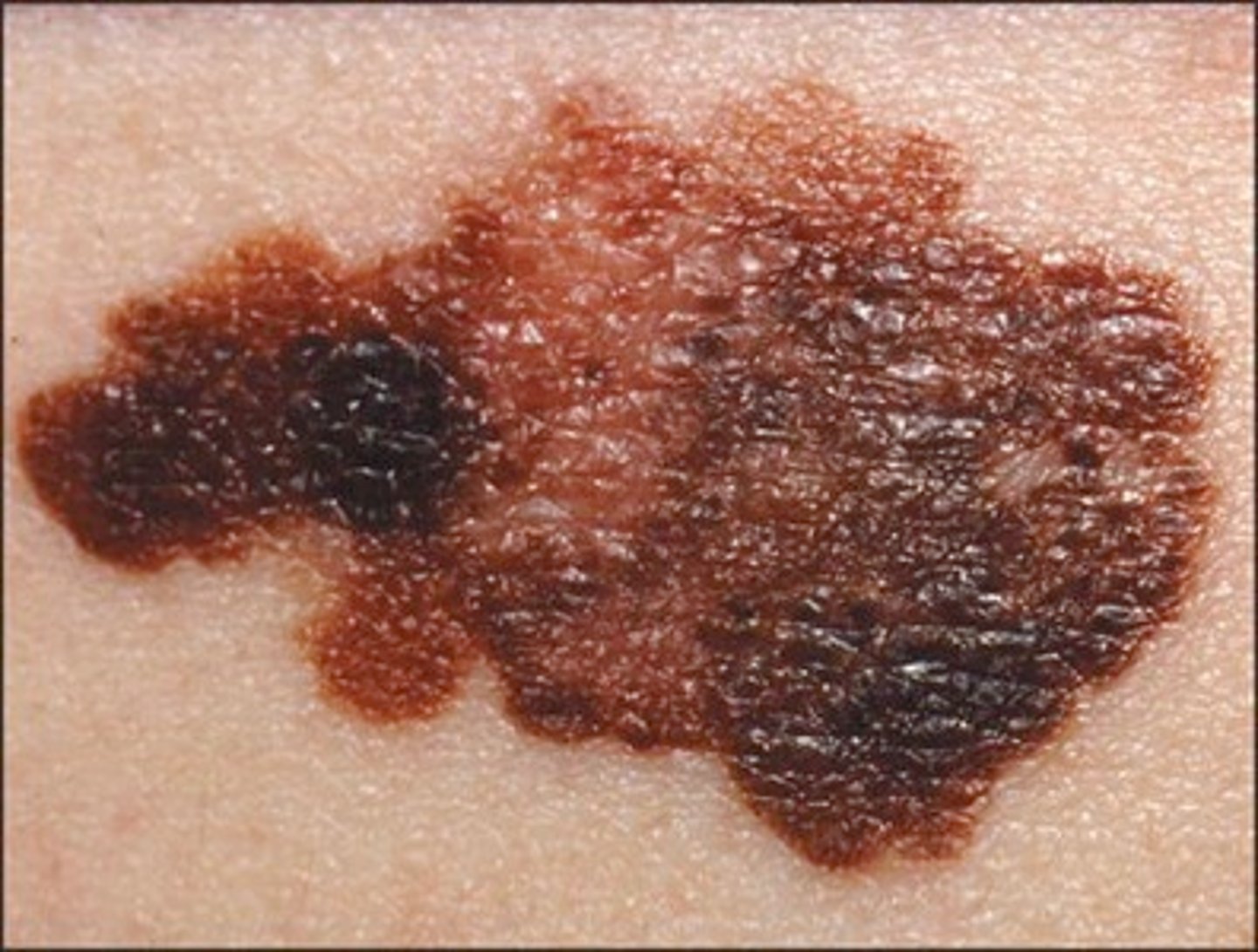
What is melanoma?
Malignancy of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes)
Most aggressive and deadly form of skin cancer as it has high metastization
Least common - only 4% of all skin cancers
What are some risk factors for melanoma?
- Family or personal history of previous melanoma
- More than 50 common moles
- Atypical or large moles
- Red/light hair
- Solar lentigines
- Freckles
- UV radiation from heavy sun exposure, sunlamps, or tanning booths
- Light eye/skin color
- Severe blistering sunburns from childhood
- Immunosuppression from HIV or chemotherapy
What is the prevalence of melanoma?
More common in white individuals
What is the prevalence of melanoma in African Americans?
1/20th as frequently as white persons
What is the prevalence of melanoma in Hispanics?
1/6 as frequently as white persons
Are mortality rates of melanoma higher in white persons or African Americans/Hispanics?
African Americans and Hispanics
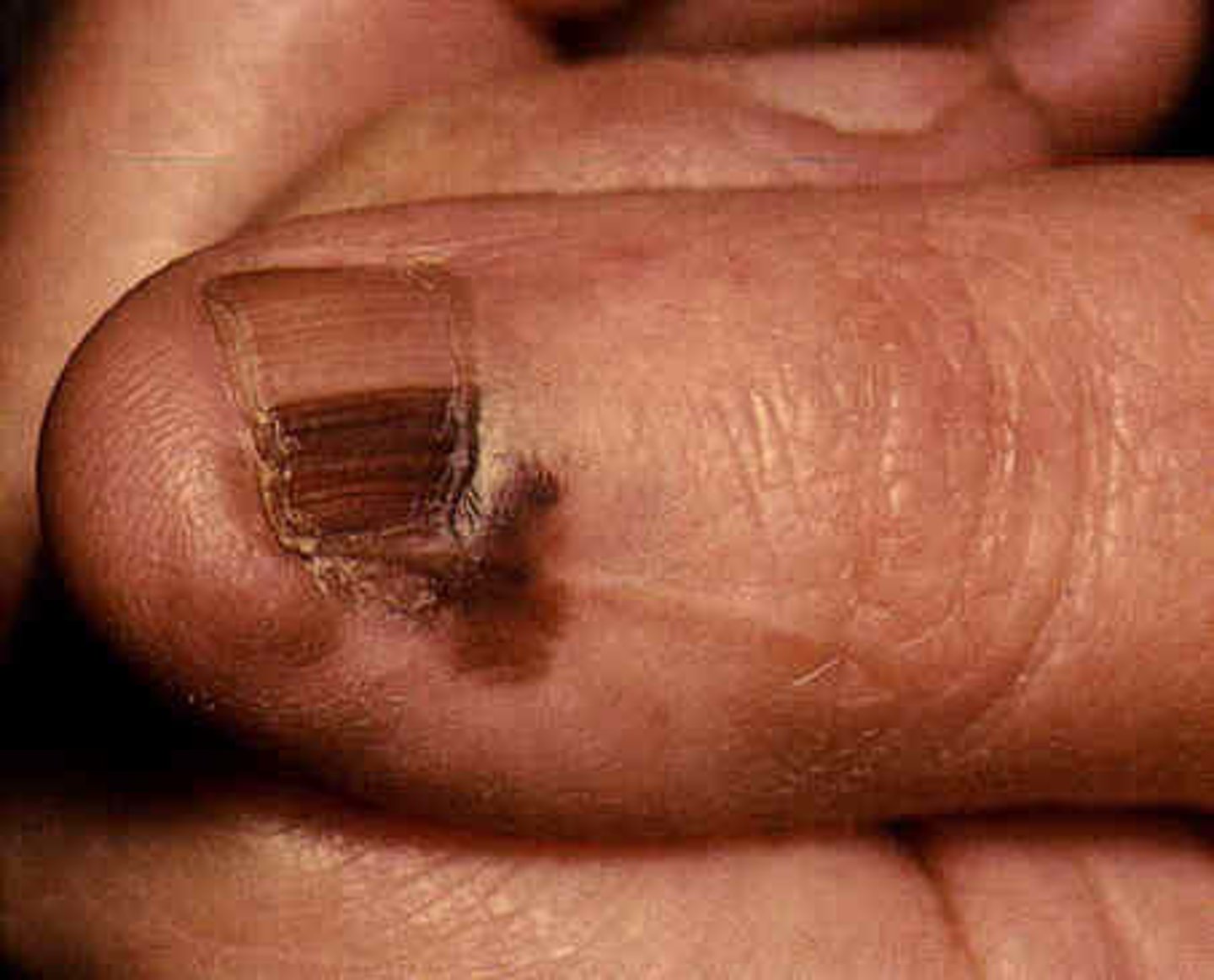
What is acral lentiginous melanoma?
Melanoma of palms/soles or distal fingers/toes or mucous membranes. Often nail beds
What is the median age of melanoma diagnosis?
53 years