atomic structure and bonding
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Orbital
Region within an atom where an electron is most likely to be found
Ground state
Lowest energy arrangement of electrons into subshells for a given element
Types of d orbitals
xy, xz, yz, x2 - y2, z2
Chromium and copper electron configurations
Unpaired electron in 4s and 5/10 electrons in 3d
Ionic electronic configuration
4s removed before 3d because 4s has more shielding when both subshells are filled
Factors affecting ionisation energy
Distance from nucleus, shielding, nuclear charge, spin-pair repulsion?
Polar bond
Covalent bond in which there is a separation of charge between one end and the other
Types of ionic lattices
Face-centred (co-ordination number 6) and body-centred (co-ordination number 8) when one ion is bigger than the other
Carbon covalent bonding exception
Promotes an electron from 2s to 2p so it can form four covalent bonds. Energy required for this compensated by energetic stability gained from having four covalent bonds
Inert pair
s electrons not used for bonding
Phosphorous exception
Promotes from 3s into 3d so it has five unpaired electrons to form five covalent bonds
Sulphur exception
Promotes one from 3s and one from 3p into 3d to get six unpaired electrons
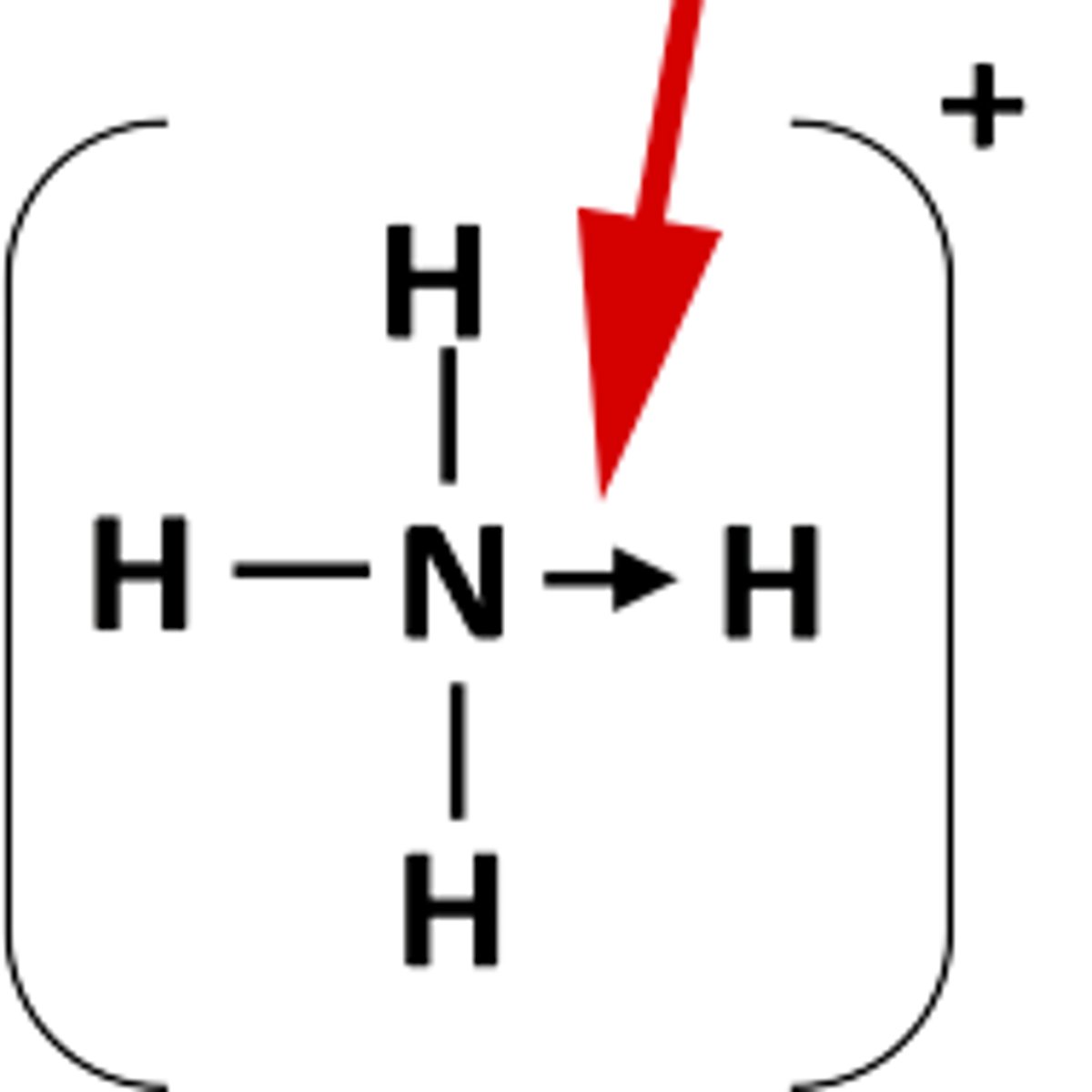
Dative covalent bonding
When one atom has a lone pair, this can be donated to another to fill its outer shell
Hybridisation trends
Size difference in lobes decreases from sp to sp3
Sigma vs pi bonds
Sigma formed from head on overlap, pi bonds formed from sideways overlap
Double and triple bonds
One sigma and one or more pi bond, pi bond restricts movement so not "freely rotating"
Factors affecting bond strength
Higher for smaller atomic radius, single < double < triple but pi bond generally weaker than sigma bond
Fluorine exception
Short bond length means more repulsion between electrons and between nuclei so weaker bond
Polarity unit
Debyes (D) - amount of charge separation multiplied by distance between centres of charge
Overall dipole?
Dipoles with equal size and opposite directions cancel out (use top to tail vectors)
van der Waals forces
intermolecular forces of attraction
Pd-pd
(Permanent dipole-permanent dipole), Strongest, two molecules which both have dipoles will attract each other with opposite dipoles neighbouring
Id-id
(Instantaneous dipole-induced dipole, London dispersion forces), 2nd strongest, oscillating electron cloud produces a temporary dipole in one molecule which induces a dipole in a neighbouring molecule
Factors affecting strength of id-id
Stronger with more electrons, unbranched molecules have more points of contact so stronger
Hydrogen bonding
Only H-F, O-H, N-H, nucleus of hydrogen atom left exposed when bonding pair attracted to very electronegative element so H then attracts lone pair of electrons from other atom
Properties of water
Due to hydrogen bonding, ice less dense than water, high melting and boiling point, high surface tension
Ideal gas assumptions
Molecules behave as rigid spheres, no intermolecular interactions, collisions perfectly elastic (no loss of KE), individual molecules have no volume, temperature of gas is proportional to average KE of particles
Most likely to behave as ideal gases at...
High temperature, low pressure
Gas equations
pV = nRT, pV = constant, V/T = constant