AP Psychology: Science Practices - Set G
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Falsifiability
the principle that a theory, hypothesis, or assertion can be proven false through observation or experiment--an important characteristic of the scientific method

Placebo
a treatment that appears real, but is designed to have no therapeutic benefit (helps researchers determine the effectiveness of the actual treatment)

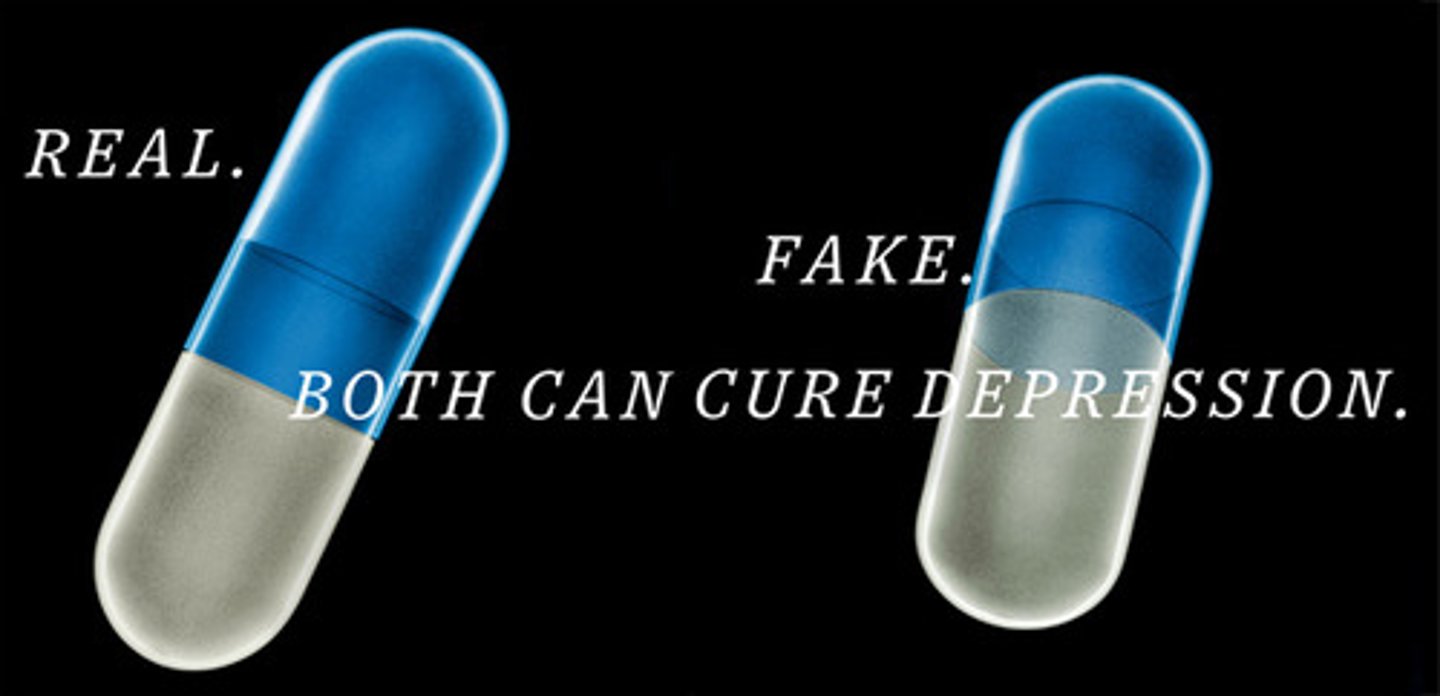
Placebo effect
when a person's physical or mental health appears to improve after taking a placebo or 'dummy' treatment (showing that a psychological effect can sometimes be as powerful as other medical treatments)
Overconfidence
a cognitive bias that can lead researchers to overestimate the accuracy of their predictions
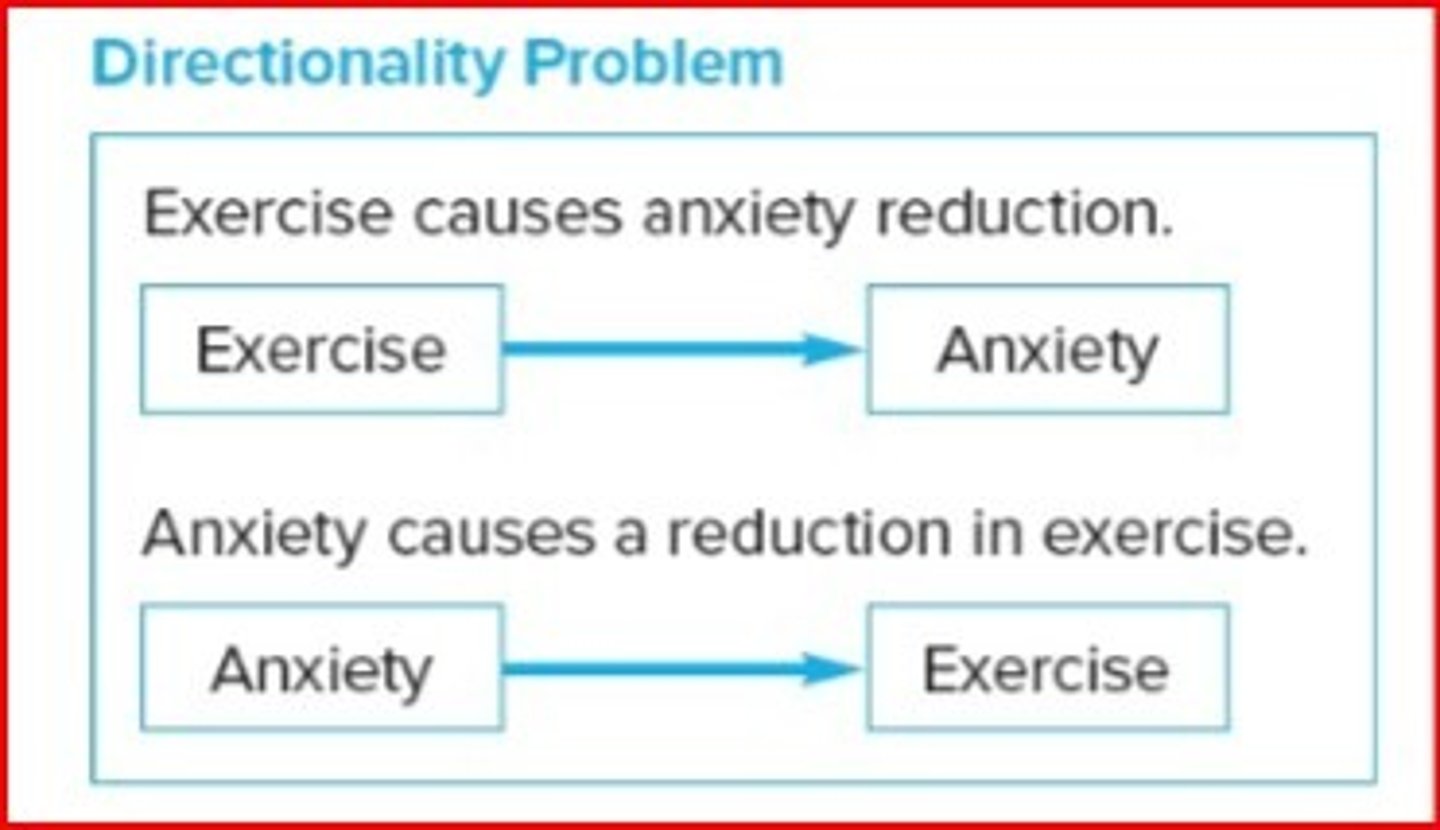
Directionality problem
a problem encountered in correlational studies when researchers cannot determine which variable may have caused changes in another variable
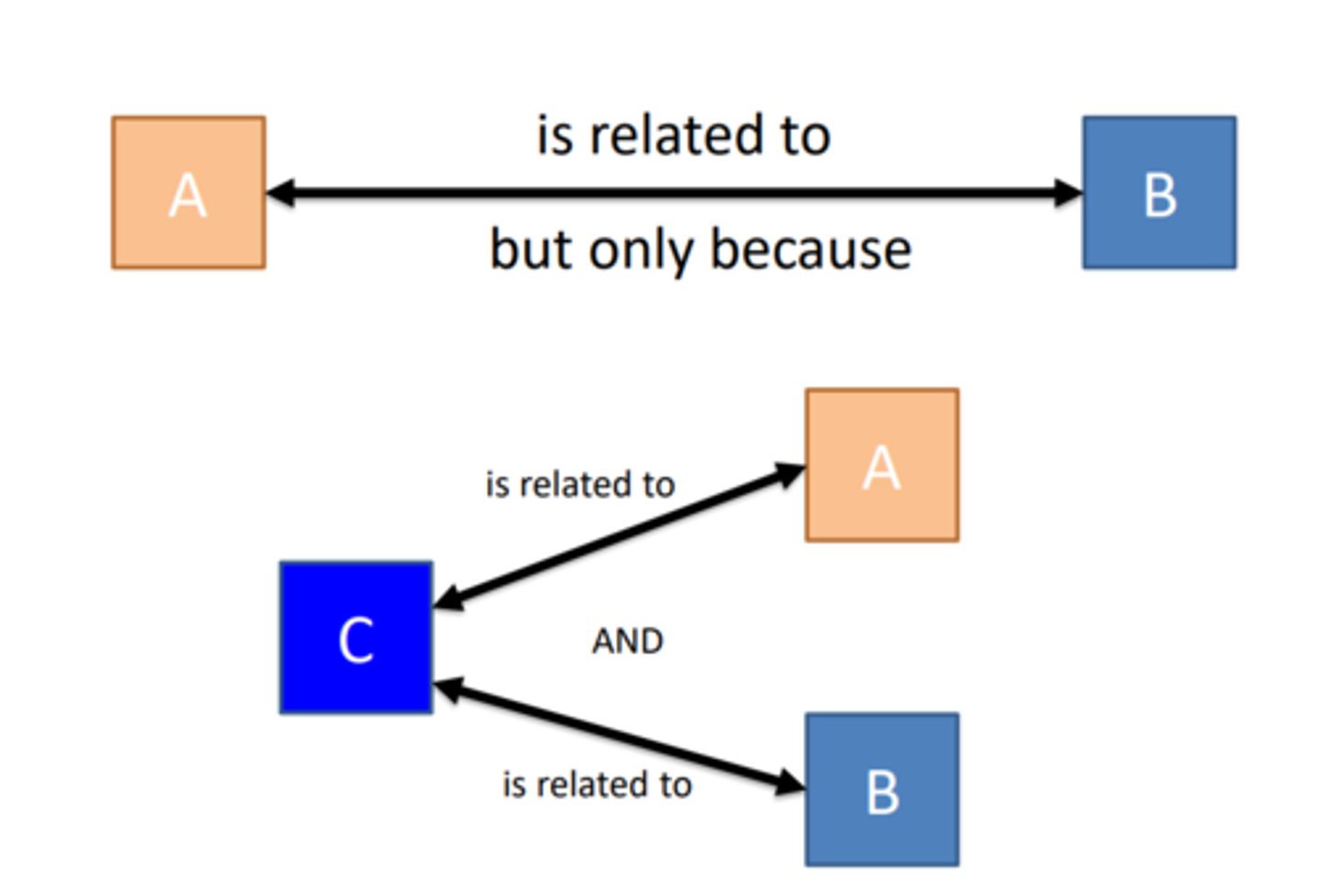
Third variable problem
occurs when a correlation between two variables is influenced by an unseen third variable (confounding variable), leading to flawed interpretations
Experimenter bias
when results, data, or participants are impacted because the researcher unknowingly involves their own expectations about the outcome of the study

Social desirability bias
occurs when people answer survey questions according to society's expectations, rather than their own beliefs or experiences

Cultural norms
the shared beliefs, values, and behaviors that are typical for a social group

Confirmation bias
the tendency of individuals to support or search for information that aligns with their beliefs or expectations and ignore information that doesn't

Hindsight bias
when a person convinces themselves that they accurately predicted an event or outcome
