T1 - DT in Our World
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Mass Production
Hundreds or thousands of the same product are produced (typically on production lines)
Assembly lines
Line of workers and equipment in a factory. Gradually assembled as it moves through each stage of the line
Automated production
Use of automatically controlled equipment or machinery to manufacture products
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Industry and Enterprise
Electricity allowed mass production of products of assembly lines, so products could be produced more quickly and economically
Developments allow automated production, and use of robots for repetitive tasks
Market Pull
A new product is produced in response to demand from the market
Technology Push
Development in materials, components or manufacturing methods leads to development of new products
Life Cycle
Stages a product goes through from initial idea to disposal
Market Pull in Detail
Development of new products of new products in response to demands from users
Designers produce new or revitalised products driven by the needs and wants of the users
Mobile Phones - Result of people wanting a way to contact eachother
Technology Push
Development in materials, components, or manufacturing methods lead to new products being developed
Tables and Smartphones - Development in smaller, more efficient and quicker electronics
Development of New Materials
Example of Technology Push
Graphite - Strength, Lightweight, Flexibility, Transparency, Conduction
Consumer Choice
Designers and manufacturers aim to ensure that people want or need the product they design
Technologies can influence consumer choice
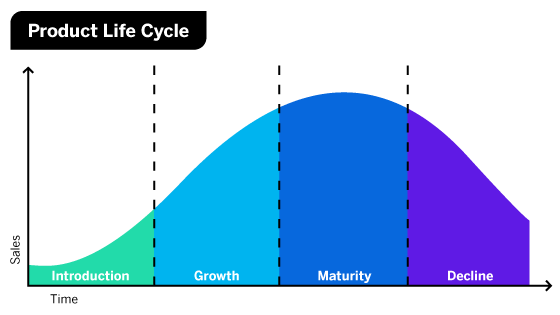
Product Life Cycle Analysis (LCA)
4 Stages a product goes through from it’s initial introduction to the market until it's replaced or withdrawn
4 Stages of Life Cycle Analysis
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
Introduction (LCA)
New products are launched and are heavily publicised so consumers are aware of the product.
Could be a revision of a product, or a new one
Growth
Once products are available, sales grow as more people become aware of it, and buy it to replace previous products or older models
Maturity
Sales of products reach their peak.
Companies want this stage to last for as long as possible to maximise sales
Decline
Interested consumers have already bought the product, or a new model will be available
Sales will begin to fall