11- Cranial Nerves
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
CN I
Olfactory - smell or olfaction
• Receptors in the nasal mucosa
• Travel through the cribriform plate (sense of smell)
• Synapse in the olfactory bulb
CN I sensory or motor?
Sensory
Testing CN I (Olfactory)
- Use non-noxious scents (coffee, lemon, garlic)
- Try to use "universally" recognized scents
- Test each nostril separately
- Rarely done in the clinic but useful to assess in head trauma
CN II
Optic - vision, visual acuity, visual field, pupillary response
CN II sensory or motor?
Sensory
CN II can be impacted by:
Stroke, tumor, injury, etc.
CN II: images seen in the L visual field goes?
L visual field goes to R retina and continues along to the R side of the brain (vice versa for R visual field)
Testing CN II - 3 ways
• Visual Acuity: Snellen Chart (Test corrective lenses if Pt. uses them; test one eye at a time, 14-18 in away)
• Visual Field: finger in each quadrant, where do you see my finger to test symmetry
• Pupillary Light Reflex's: CN II and III, Edinger Westphal Nucleus
*CN II: pupillary light reflex testing - normal response
Shining light in one eye, CN II gets info and constricts BOTH eyes (of opposite eye does not constrict = red flag)
CN 3
Oculomotor - intimately involve with the pupillary light and accommodation reflexes (finger zoom)
CN 4
Trochlear
CN 5
Trigeminal
CN 6
Abducens
CN 3, 4, 6 are tested as a group. T/F?
True. Controls movement of the extraocular eye muscles. Involved with smooth pursuit, saccades
CN 3 muscles?
Superior rectus, Medial rectus, Inferior rectus, Inferior oblique
CN 4 (trochlear) muscle and function?
Superior oblique: looking down and in
CN 6 muscle and function?
Lateral rectus: looking laterally (ABD eyes)
How do you test CN 3, 4, and 6?
Pt follows your finger as you move in an H and X pattern
Your patient has a head injury from a hockey fight, now they can no longer smell. What cranial nerve do you want to test?
CN 1
Information on the R side of the retina comes from what visual hemisphere?
Left
Information on the L side of the retina leaves the optic nerve and goes to which optic track?
Left
What cranial nerve controls the superior oblique?
SO4
What cranial nerve controls the lateral rectus?
LR6
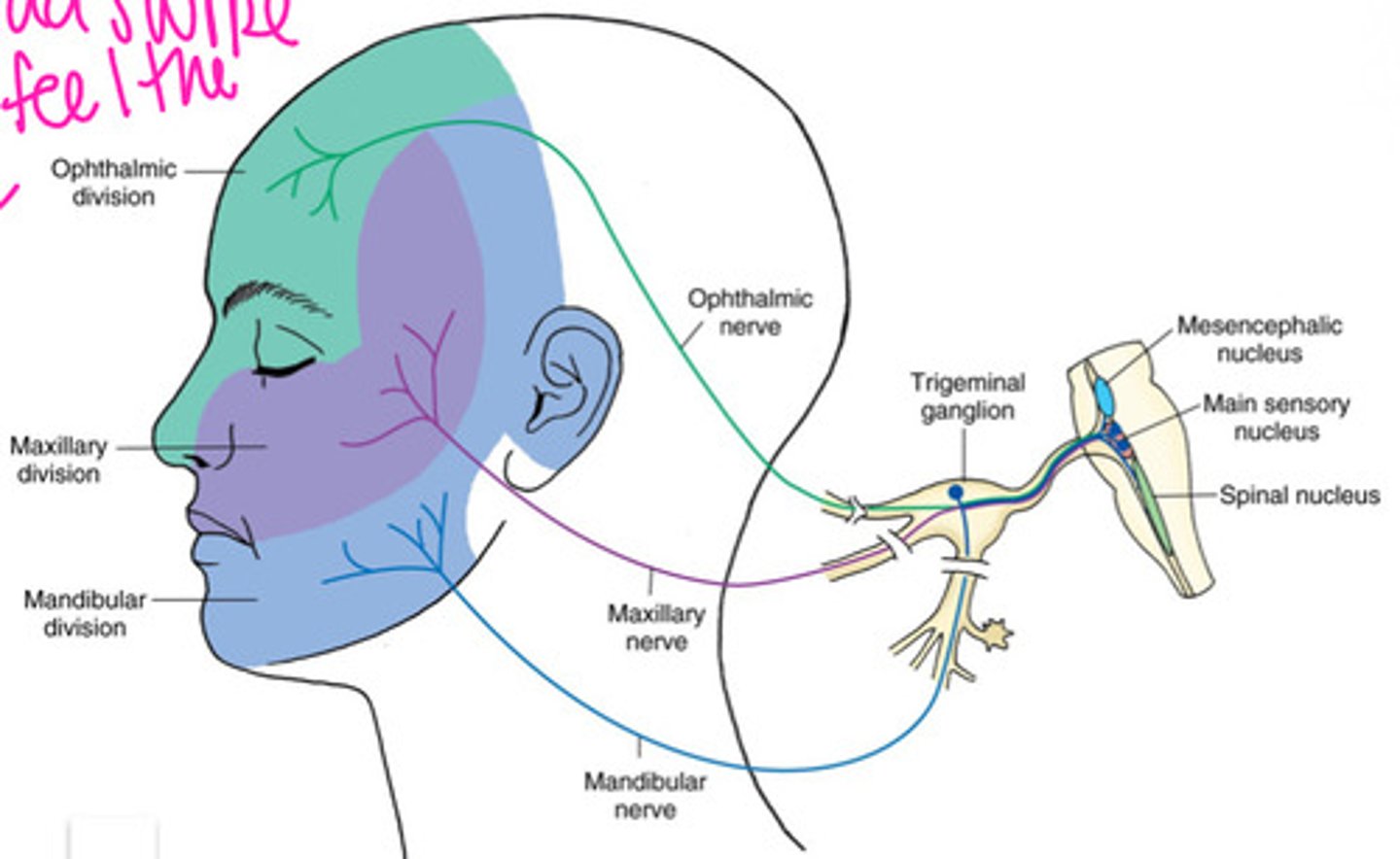
function of CN 5 - trigeminal nerve?
- Muscles of mastication: temporalis, masseter, pterygoid
- Sensation of the face: pain, light touch, proprioception
How to test CN 5
- palpate muscles, resist movement
- sensation: pain, light, touch, proprioception - pt closes eyes to feel forehead swipe
What are the sensory divisions of Trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
V1: Ophthalmic
V2: Maxillary
V3: Mandibular
CN 3 oculomotor, sensory or motor?
Motor
CN 4 Trochlear, sensory or motor?
Motor
CN 5 Trigeminal, sensory or motor?
Both
CN 6 Abducens, sensory or motor?
Motor
CN 7
Facial nerve
CN 7 - facial nerve, sensory or motor?
Both
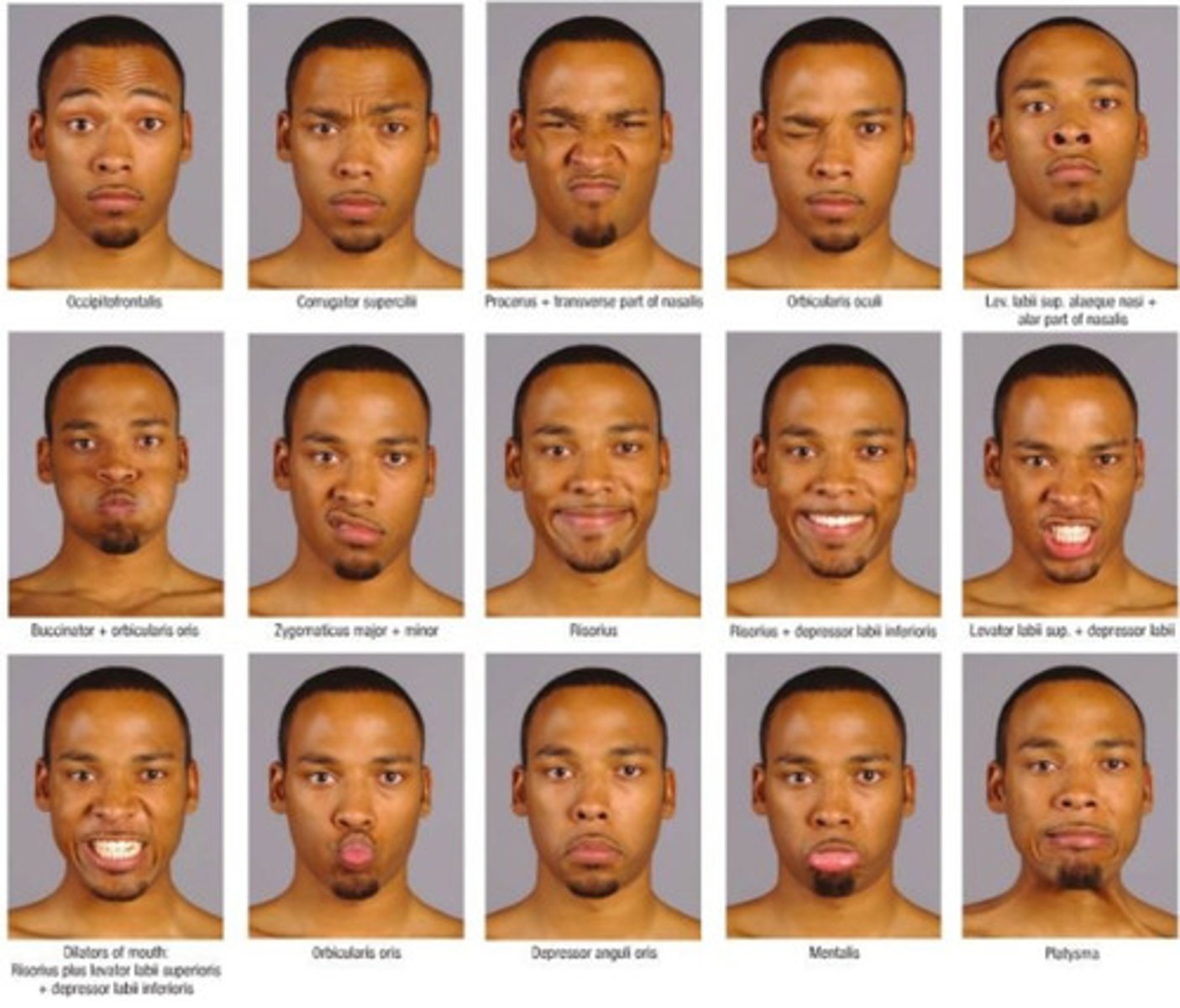
CN 7 function?
Muscles of facial expression
TASTE - anterior 2/3 of tongue
CN 7 testing
Ask patient to make facial expressions can offer mild resistance
What are the 5 divisions of the facial nerve?
temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical (to Zanzibar by motor car)
Facial nerve innervates the same side (R-R, L-L), T/F?
True
Other aspect of facial nerve
• Requires cortical drive
• Reinforced drive present to upper 1/3 of facial muscles
• Brain injuries (stroke) result in facial palsy on opposite side
but only in lower 2/3 of face
During a stroke, a pt can retain the ability to move eyebrows with paralysis of face. T/F?
True
CN 8
Vestibulocochlear
CN 8, sensory or motor?
Sensory
CN 8 function
Hearing and vestibular responses/ balance
Testing CN 8
- Test for symmetry! - close eyes, rub fingers far to close, one side at a time
- Test Vestibular Ocular Reflex
(There’s also Webers and Rinne test)
What are the steps for testing Vestibular Ocular Reflex?
Pt focuses on PT nose, PT tilt head at different speeds going L to R. Start off with slow motion then one quick jerk. pt will be able to look at your nose at all times
*Air conduction is louder than bone conduction. T/F?
True
CN 9
Glossopharyngeal
CN 9, sensory or motor?
Both
CN 10
Vagus
CN 10, sensory or motor?
Both
CN 9 and 10 function
Gag reflex, swallowing, control of vocal muscles, taste on posterior 1/3 of the tongue
Testing CN 9 and 10
CN 9: gag reflex: use swab to touch back of tongue, check both sides to look for symmetry, have pt swallow with palpation
CN 10: Evaluate speech/voice quality
CN 9 and 10 innervates the:
tongue, pharynx, glands of tongue and parotid salivary glands with sensory and motor components.
CN 11
spinal accessory
CN 11, sensory or motor?
Motor
CN 11 provides innervation to:
Trapezius and SCM
Testing CN 11
Assess activation of the traps (shoulder shrug w resistance) and SCM
CN 12
Hypoglossal
CN 12, sensory or motor?
Motor
CN 12 innervates muscles of the
Tongue
Testing CN 12
Observe tongue (resting) and with movement
- tongue goes to R if R side doesn’t work (deviate toward side of lesions)
Your patient was hit in the face with a foul ball at a recent baseball game. The patient now reports altered sensation across their cheek bone. What cranial nerve and division is impaired?
Trigeminal nerve (CN 5) V2
When CN 12 is impaired, what way will the tongue deviate?
Towards impaired side
When CN 9 and 10 are impaired, what way will the uvula pull to?
Pull to intact/good side. Uvula will go down if normal