2.8 - Histamine
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Histamine
- an autocoid (“self-remedy”)
- mediator of anaphylaxis and inflammation, and gastric acid secretion
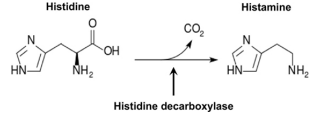
Histamine synthesis
decarboxylation of histidine catalyzed by L-histidine decarboxylase
histamine storage/distribution
- rich at sites of potential injury (bound in mast cells and basophils)
- cells of stomach release histamine to ↑ stomach acid from parietal cells
- found in brain
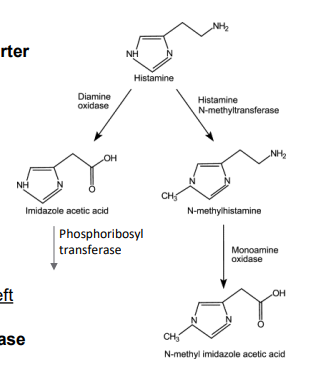
Histamine metabolism
- 2 pathways: Histamine-N-methyltransferase → MAO (terminates signaling at synaptic cleft) or Diamine oxidase → phosphoribosyl transferase
histamine receptors
- 4 metabotropic 7 TM GPC receptors
- both excitatory and inhibitory, depending on signal transduction
H1 (Histamine receptor)
- excitatory Gq found in smooth muscle, PNS SN, and CNS
- increased cotrical activity, arousal, and wakefulness
H2 (Histamine receptor)
- Gs located on smooth muscle and pariental cells
- activation causes release of stomach acid
H3 (Histamine receptor)
inhibitory Gi/o autoreceptor found in the CNS cortex and subcortex
H4 (Histamine receptor)
- Gi receptor located peripherally on immune cells
- strong promotor of pruritus (itching sensation) and burning feelings
functions of Histamine
inflammatory response, sexual f(x)/libido, gastric acid secretion
inflammatory response
- Mast cell + basophil granules release histamine ↑swelling, vasodilation, other autacoids → Causes hypersensitivity to pain
- ↑ bronchoconstriction; mediates allergy responses.
sexual f(x) and libido
- H2R antagonists produce ED
- direct histamine injection reverses
gastric acid secretion
Enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells in the stomach release histamine → stimulating H2 receptors → release of stomach acid
pH
Histamine release decreases with _____.
Tuberomammillary pathway
- H1 receptors + histamine as NT
- Histamine from the hypothalamus affects brain areas linked to arousal, cognition, and neuroendocrine functions.
- Cognition and Sedation: H₁ agonists boost cognition; antihistamines cause sedation and regulate pain sensitivity.
- Pain and Body Regulation: Histamine impacts pain sensitivity, appetite, body temperature, and cardiovascular activity.
neuromodulation of Histamine
- Presynaptic H3 receptors in brain act as autoreceptors: reducing their own release
- decrease release of ACh, NE, DA and serotonin to modulate nociception + signal satiety