Carbohydrates (unit 2)
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What are the four major classes of carbohydrates and formula?
monosaccharides : single carbonyl group and 2/more hydroxyl groups
.
disaccharides
.
polysaccharides
.
oligosaccharide: sugars linked by glycosidic bonds
.CnH2Oy
Role of carbohydrates
-Chemical energy( glucose, starch, glycogen)
.
-supportive structures(Cellulose, crustacean shells)
.
-Essential components of nucleic acids
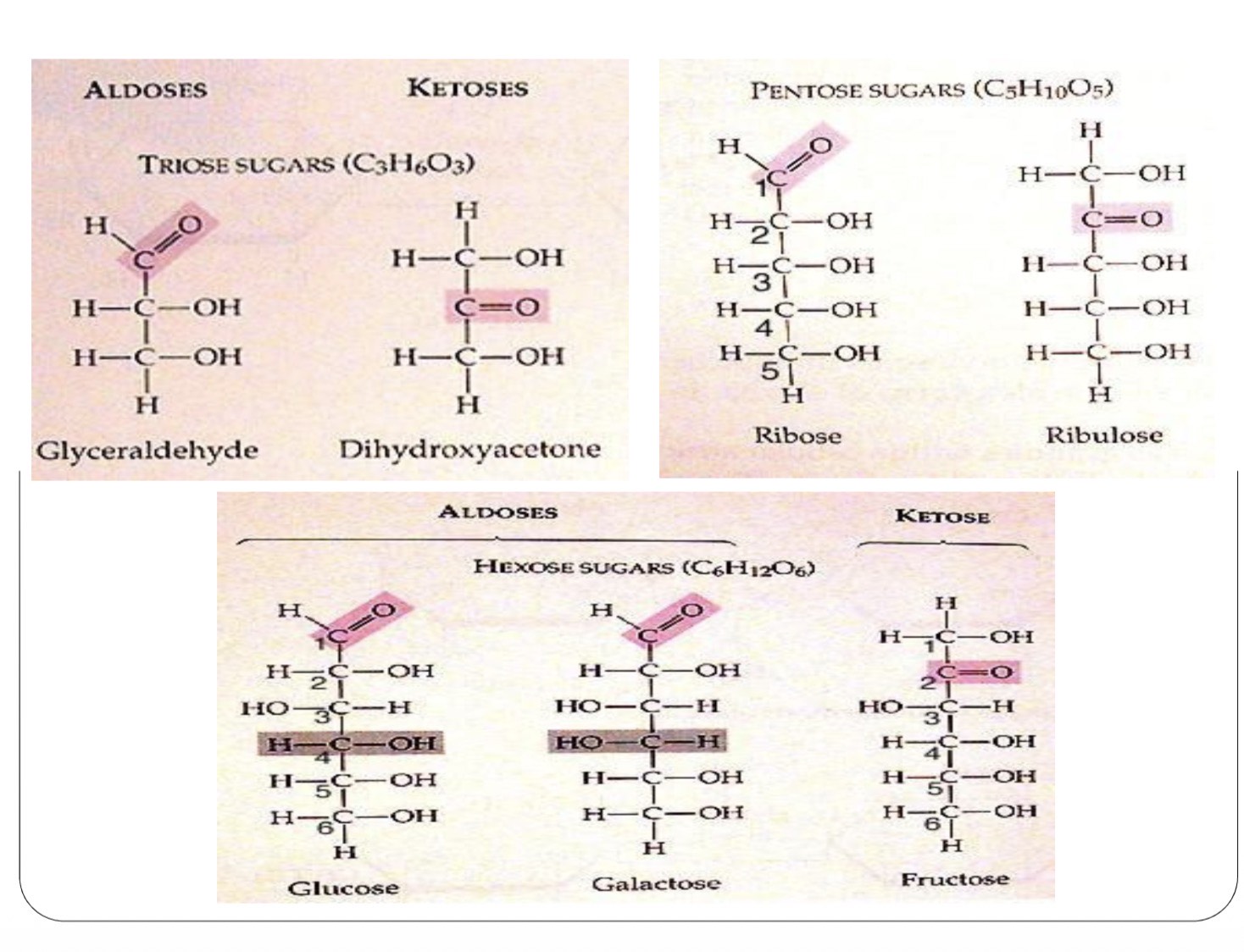
How are monosaccharides named ?
-based on number of C present
.
-the first part of the name represents the number of carbon atoms present and the suffix –ose then added
-Number of carbon atoms
.
-position of carbonyl group
.
-chirality of molecule

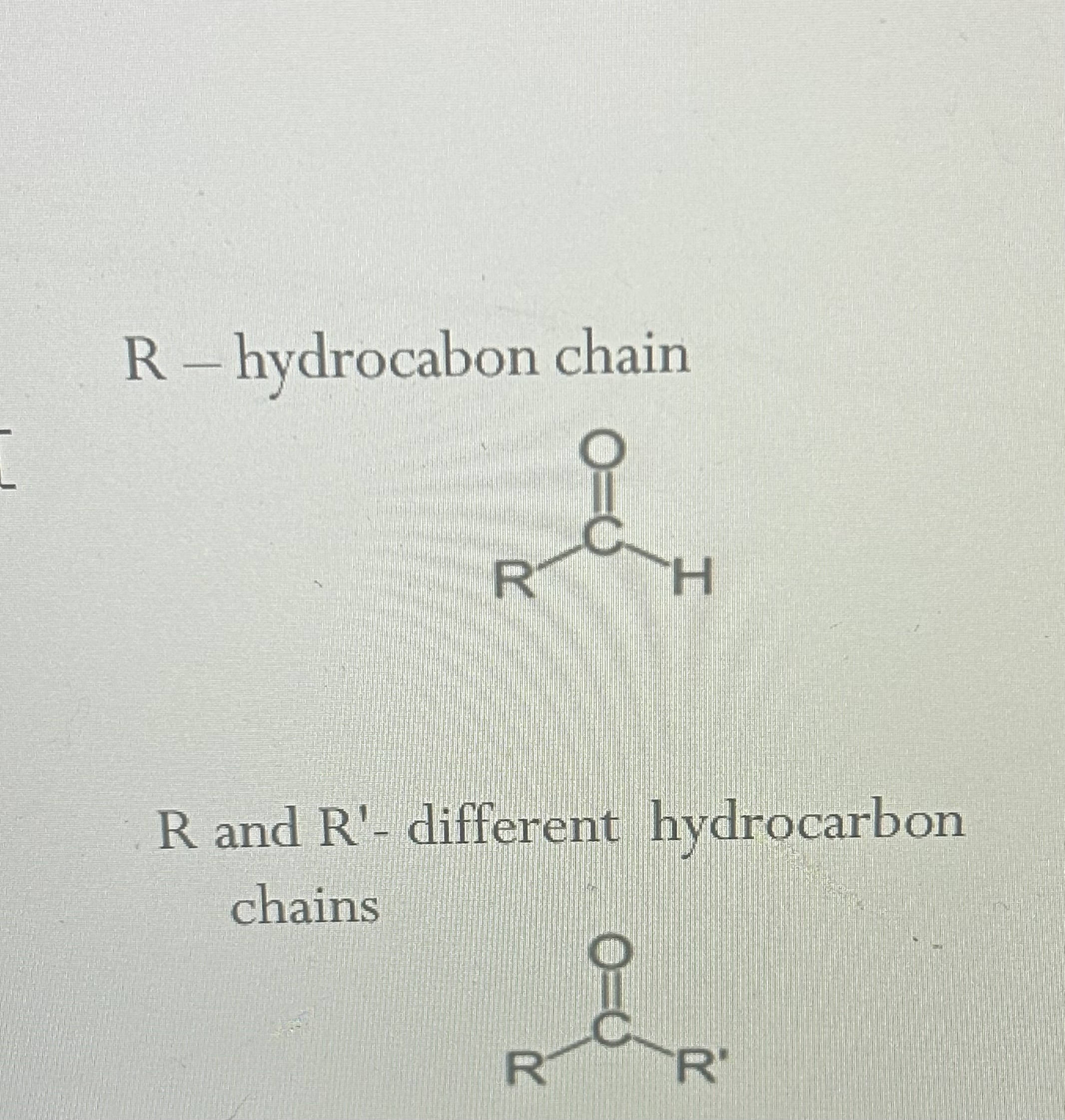
Terminal carbonyl forms an aldose; molecule aldehyde
.
internal carbonyl forms a ketose molecule ketone
Egs of aldoses and ketose
How are D- and L- monosaccharides distinguished? bk
diagram bk
bk
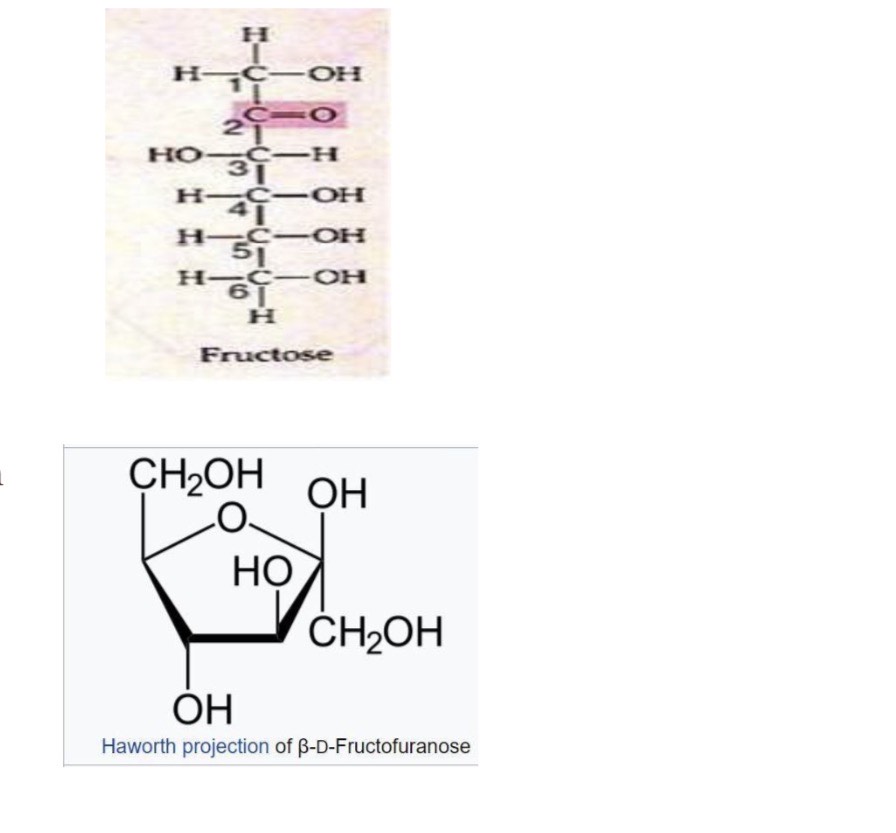
-Pyranose is a 6-membered ring (glucose and galactose)
.
-A five-membered ring is called a Furanose e.g. fructose
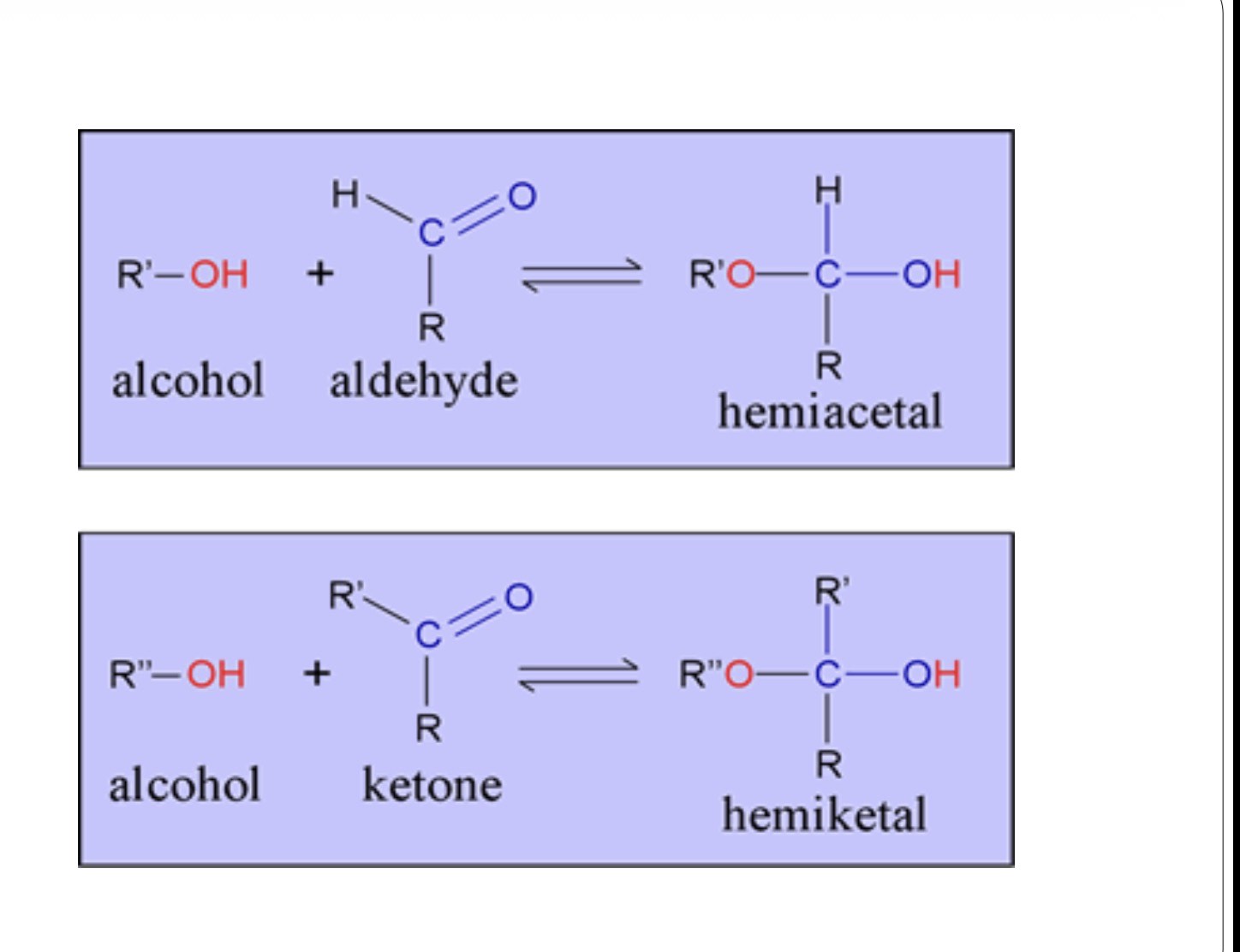
Why are Hemiacetals/hemiketals are usually unstable molecules and in an equilibrium mixture
Since the reaction is reversible they can easily break back down into a carbonyl compound and alcohol as the reaction is reversible
When the hydroxyl is apart of the same molecule with the carbonyl group what occurs
-A 5 or 6 membered ring can be formed
.
-The tendency for this reaction to occur in a six-carbon aldose is greater because the hydroxyl and aldehyde functional groups are contained within the same molecule, and the intramolecular reaction can produce a relatively stable 6-membered ring
What are α and β anomers and how do they differ?
Isomers differing in OH orientation at the anomeric carbon (Carbon to the right of O2)
What are the rules for converting a Fischer projection to a Haworth projection?bk
bk
What is mutarotation and in which sugars does it occur?
-The gradual change in specific rotation
.
-Interconversion of α and β anomers in reducing sugars
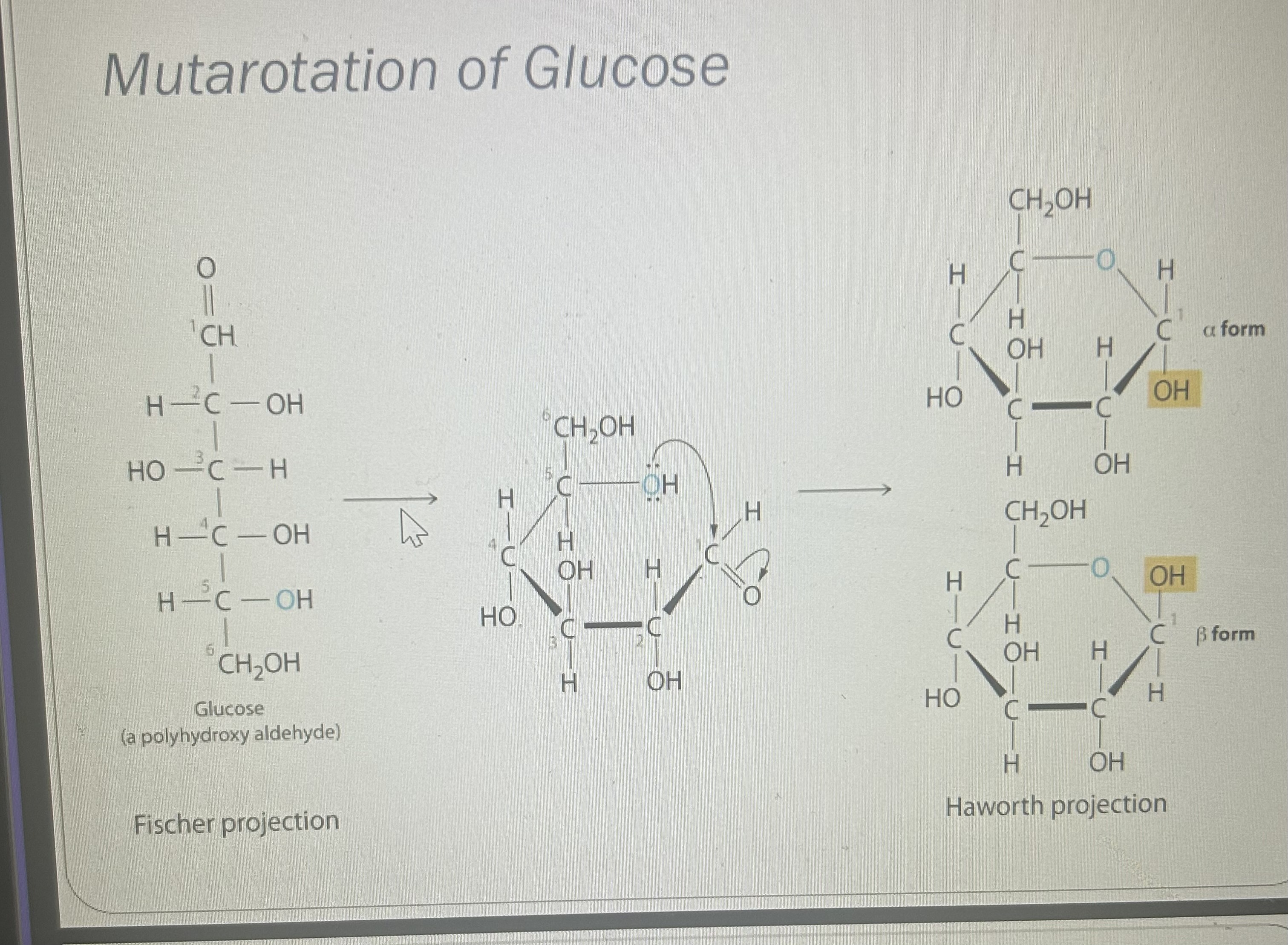
What is the equilibrium ratio of glucose anomers in solution?
Approximately 36% α-glucose and 64% β-glucose(more stable as two OH groups allow electron repulsion allowing more space
How are glycosides formed and what bond is created?
Hemiacetal reacts with alcohol to form acetal or ketal ;
.
- O-glycosidic bond (from anomeric carbon to the OR- group)
.
-This bond links sugars together to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
Another name for glycosides and show acetal reaction bk
acetal (bk)
Why do glycosides not undergo mutarotation and how are they hydrolyzed?
Acetal form is locked
an acetal unlike the hemiacetal is no longer in equilibrium with the open-chain carbonyly containing compound
; hydrolyzed in aqueous acid to yield an alcohol and monosaccharide