Biology 3.7 - homeostasis and the kidney
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is homeostasis?
The mechanism by which a constant internal environment is achieved within a living organism
Why is regulation of an internal environment vital?
maintains optimal conditions for cell function
protects cells from changes in the environment
What are some factors that are kept constant in mammals?
Core body temperature
Blood glucose concentration
Solute potential of blood
blood pH
How do the factors such as body temperature change?
They fluctuate due to body activity or environmental conditions
homeostasis prevents wild fluctuations
fluctuations are small and about a set point
The body is kept in a dynamic equilibrium, what does this mean?
Constant changes occur but corrective mechanisms bring the internal environment back towards the set point
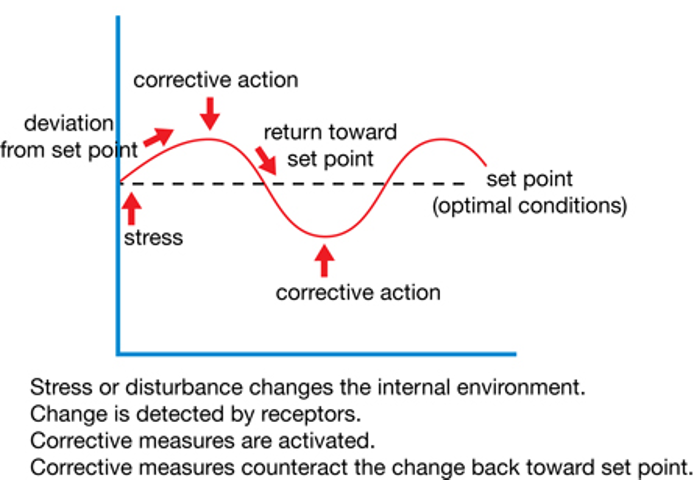
What are the stages involved in a negative feedback system?
A set point or norm at which a system operates (determined by a control centre/co-ordinator)
A receptor/detector - detects and monitors the level of a factor and its deviation from the set point and sends instructions to…
A control centre/co-ordinator - evaluates the information and communicates with one or more effectors (muscles, glands)
An effector - carries out a corrective response + factor returns to the set point
Explain negative feedback system that controls glucose concentration in the plasma
increase above normal
detected by pancreas
pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream
to target cells (liver + muscle)
take up more glucose from blood + convert it to glycogen
decrease in blood glucose
decrease below normal
detected by pancreas
pancreas releases glucagon into bloodstream
target liver cells
breakdown of glycogen into glucose
glucose moves into blood
increase in blood glucose
What is positive feedback?
When an effector increases a change i.e., movement away from the norm causes a further movement away from the norm
Example of positive feedback
Oxytocin
stimulates contraction of the uterus at the end of a pregnancy
contractions stimulate production of more oxytocin
increases the stimulus i.e. more uterine contractions
What is excretion?
the removal of waste products of metabolism from the body
What are the 4 excretory organs?
lungs
kidneys
skin
liver
Lungs…
excrete water vapour and CO2
in air
through respiration
Kidneys…
excrete urea, uric acid and creatine
in urine
through amino acid breakdown, nucleic acid breakdown, and muscle tissue breakdown
Skin…
excrete urea
in skin
through amino acid breakdown
Liver…
excrete bile pigments
in faeces
through haemoglobin breakdown
How is water removed from the body?
tears
sweat
breathing out/water vapour
urination
faeces
saliva
mucus
What are the 2 functions of the kidney?
excretion
osmoregulation
What is excretion?
The removal waste products of metabolism e.g. urea
kidneys filter the blood and remove waste as urine
What is deamination?
Removal of amine group from excess amino acids
amine group converted to urea
urea is transported to kidney and filtered out of blood
What is osmoregulation?
the control of water content and solute composition of body fluids such as the blood, tissue fluid and lymph
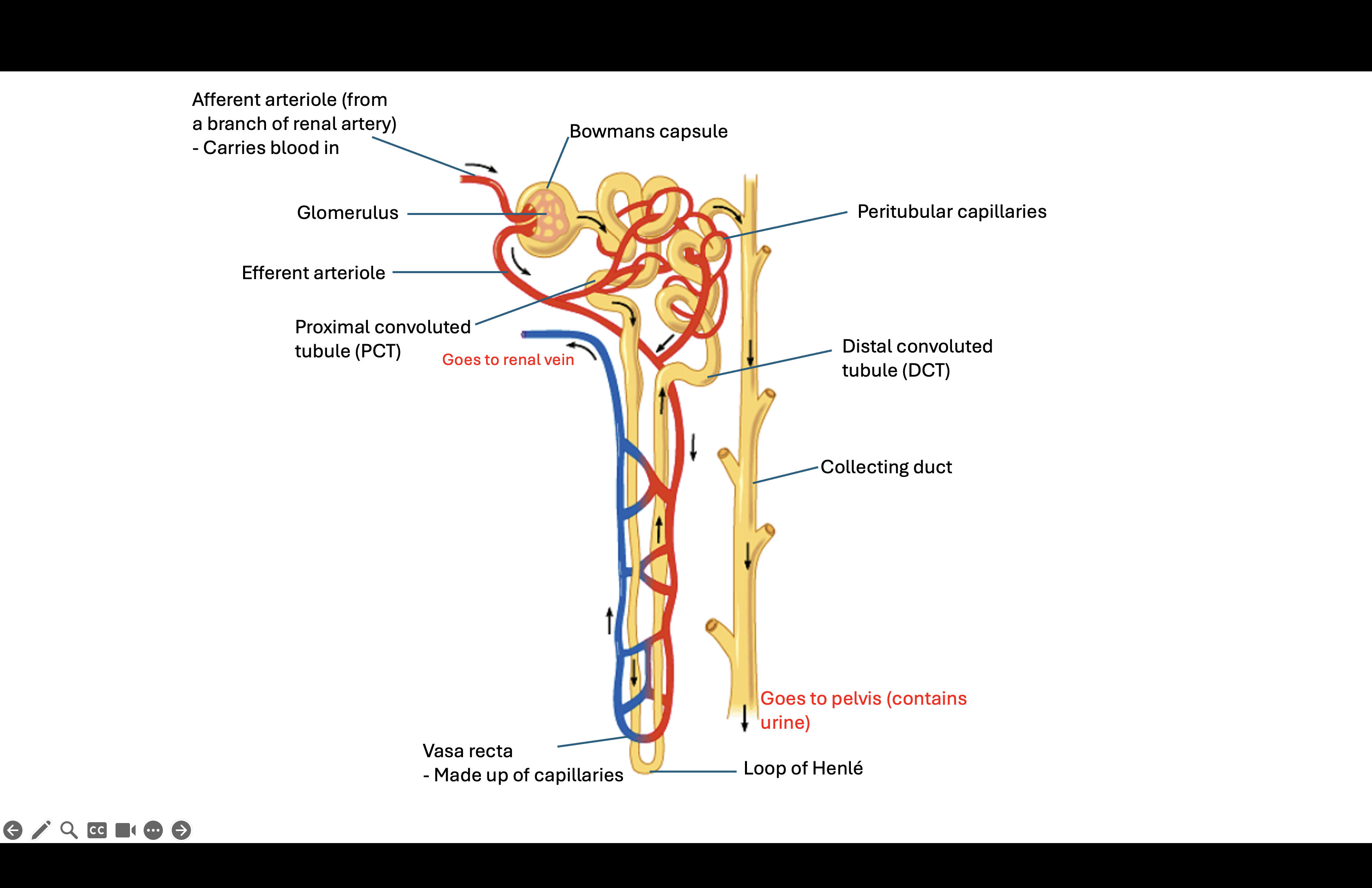
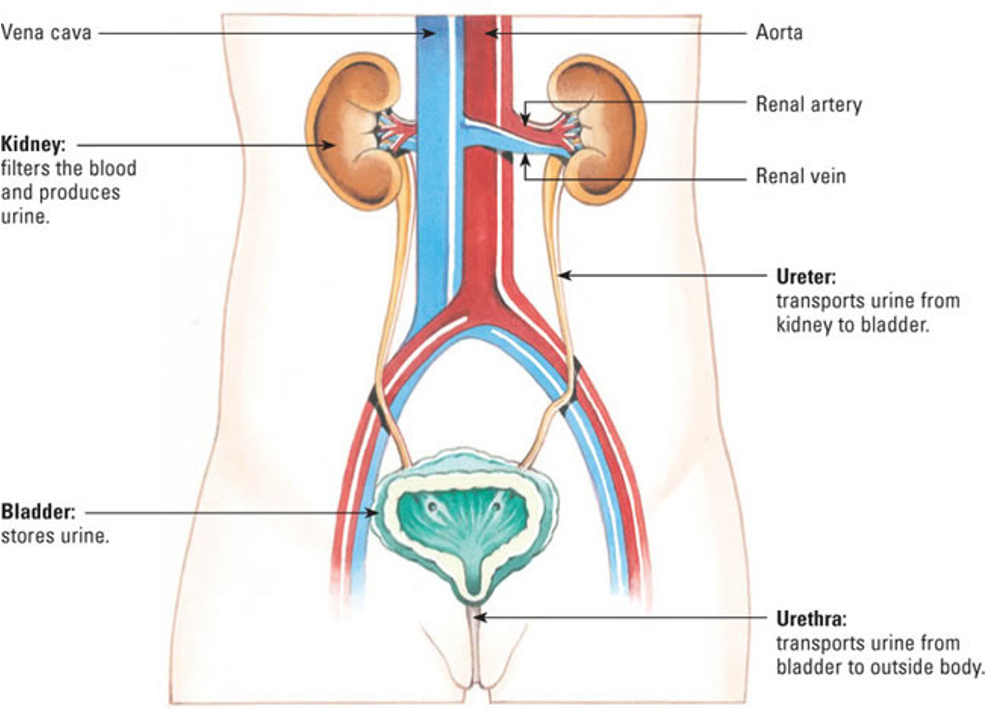
urinary system
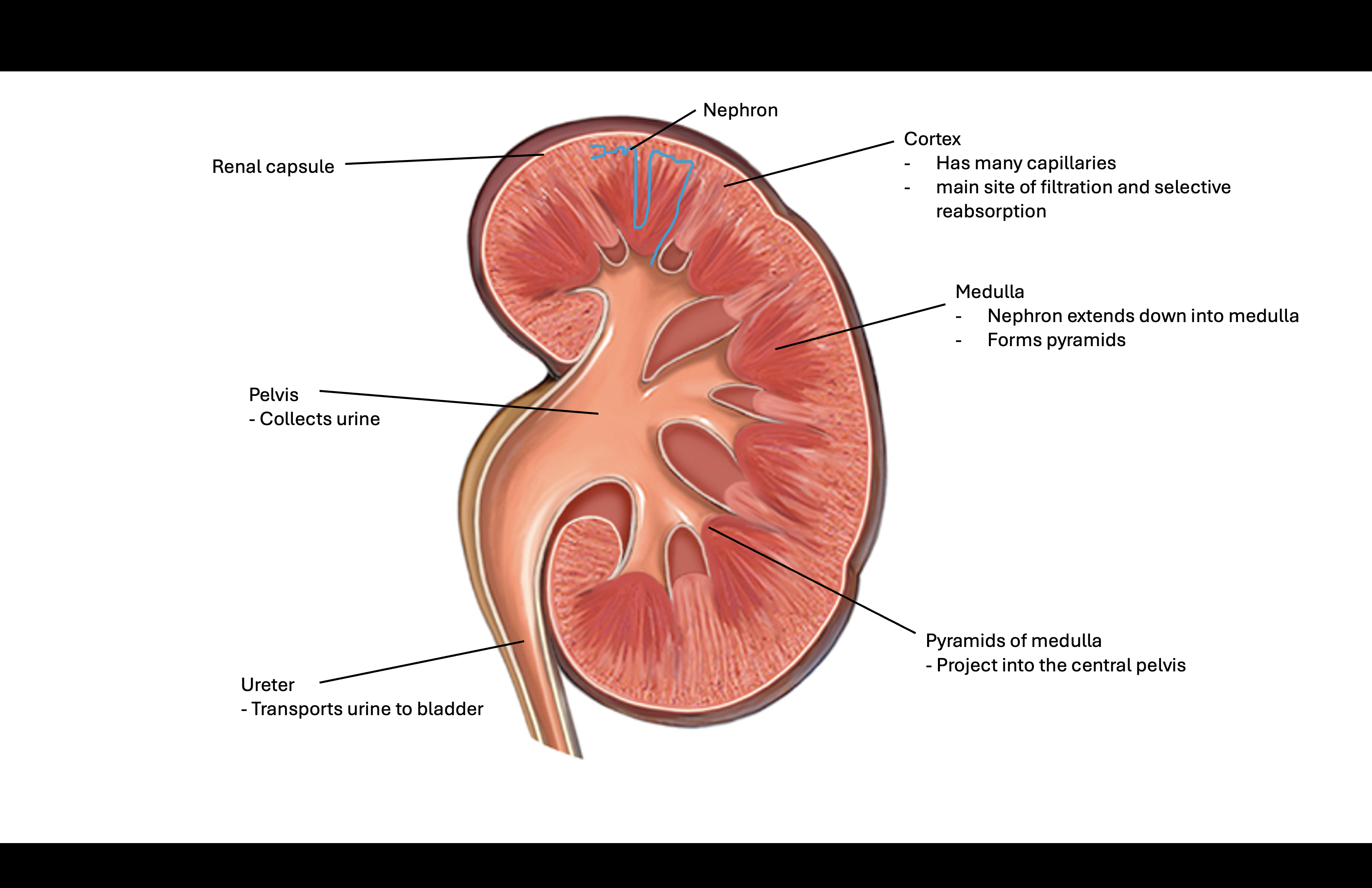
LS of kidney
single nephron