apbio unit 2 concept 7 continues
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
in__________ _______(move along), transport proteins speed the movement of molecules across the plasma membrane
facilitated diffusion (passive bc solutes move down the concentration gradient, requiring no energy)
transport proteins include channel and carrier, basically if a molecules is too big then it has to go through a protein
some transport proteins can move against concentration gradients
_________ _________provide tunnels that allow specific molecules/ions to cross the plasma membrne
__________ facilitate the diffusion of water
____ _________ facilitate the diffusion of ions
Channel proteins (hydrophillic tunnel, transports large molecules, goes down from high to low, is passive)
Aquaporins
ion channels
some ion channels called gated channels open or close in response to a stimulus like nerve cells
_________ _____ undergo a change in shape that transports the solute-binding site across the membrane
this can be triggered by the binding and release of the transported molecule
carrier proteins (can go up(would need atp) and down, goes high to low, is passive)
________ _______ requires energy, usually in ATP, to move substances against their concentration gradient
all proteins involved in this are carrier proteins (clamp and release ones)
active transport (low to high)
allows cells to maintain concentration gradients that differ from their surroundings as the inside of the cell is negative bc of the pumo
ex. an animal cell has higher potassium (K+) and lower sodium (Na+) concentrations compared to its surroundings
controlled by the sodium-potassium pump, a transport protein that is energized by the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP (3 phosphates)
goes against the concentration(Chemical) and electrical gradient
3 Na+ going up and 2 K+ going down (potassium in, sodium out)
passive transport, facilitated diffusion, and active transport differences
passive=simple diffusion, high to low, passive(no energy)
facilitated=high to low w/transport proteins, passive
active=low to high, (like in the sodium-potassium pump)
________ _________ is the voltage (charge diff.) across a plasma membrane
membrane potential
voltage is created by differences in the distribution of pos. and neg. ions across a membrane
ion pumps maintain membrane potential
the cytoplasm side of the membrane is negative in charge compared to the extracellular side
______________ ________ drive the diffusion of ions across a membrane
electrochemical gradient
a combination of a chemical force(the ion’s concentration gradient), and an electrical force(the effect of the membrane potential on the ion’s movement) (charge diff)
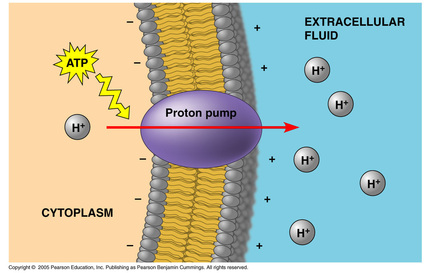
an _________ _____ is a transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane
electrogenic pump
the sodium-potassium pump is the major electrogenic pump of animal cells
in plants, fungi, and bacteria, is a proton pump, which actively transports hydrogen ion (H+) out of the cell, low to high (takes ATP) and goes against the concentration gradient
electrogenic pumps help store energy that can be used for cellular work
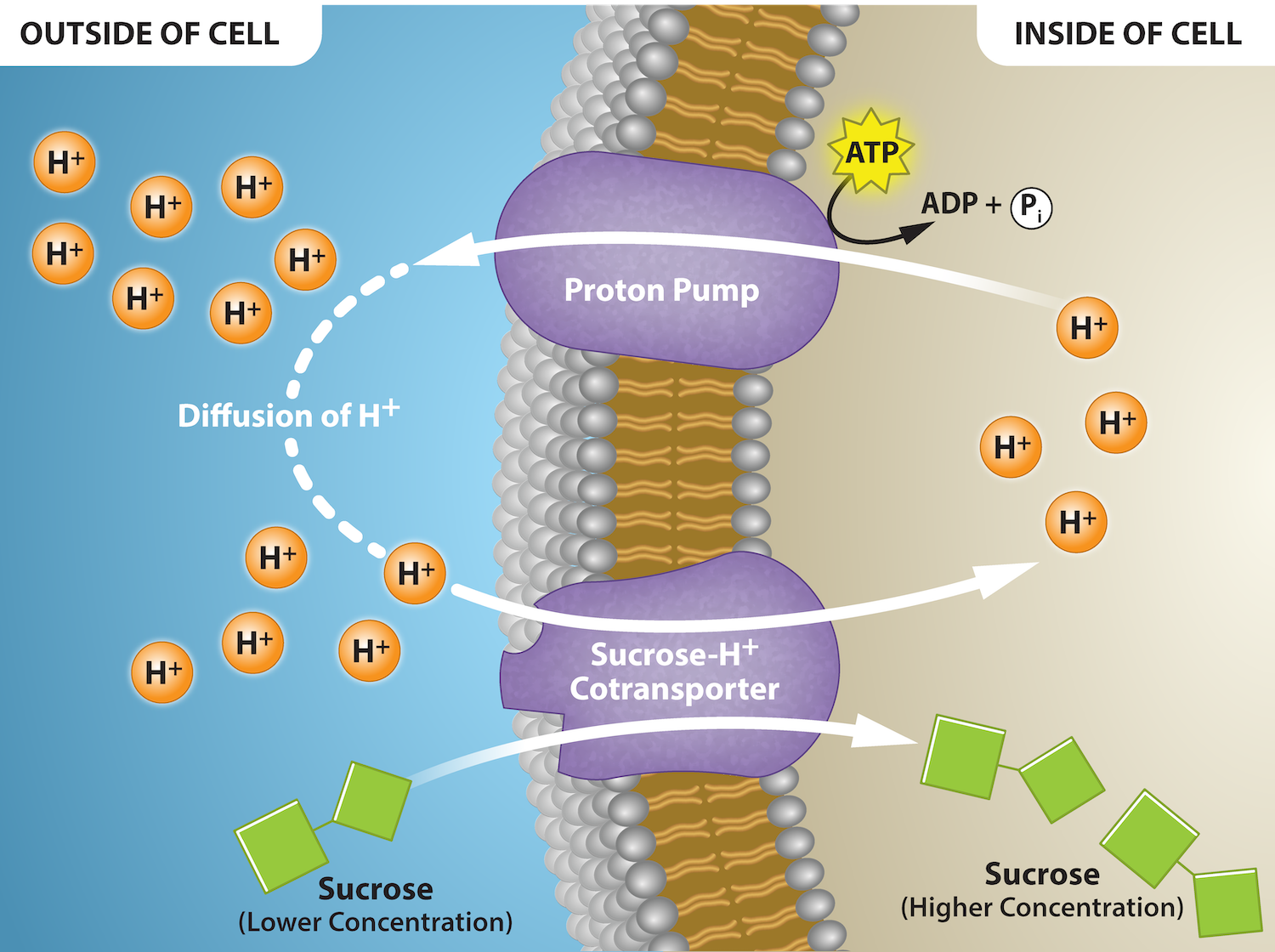
__________ occurs when active transport of a solute indirectly drives transport of other substances
coupled transport by a membrane protein
cotransport
the diffusion of an actively transported solute down its concentration gradient is coupled with the transport of a second substance against its own concentration gradient
the h/sucrose cotransporter must diffuse H+ to transport sucrose together at the same time so it doesn’t take ATP
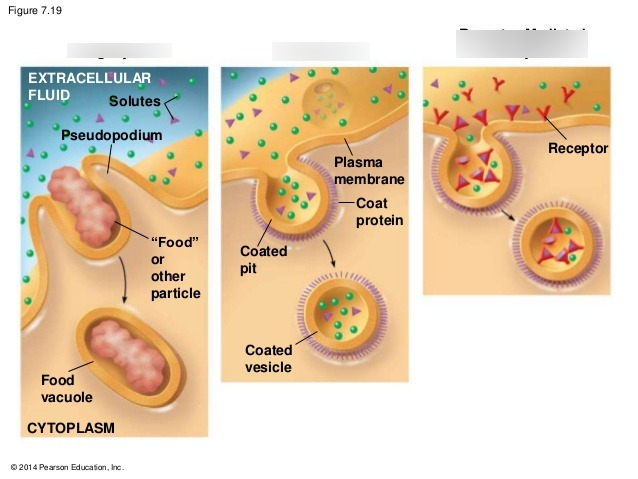
_______ ________ across the plasma membrane occurs by exo and endocytosis
bulk transport (substances are so big it cant fit through the membrane) (requires energy)
small molecules and water enter/leave the cell through the lipid bilayer or via transport proteins
large molecules like polysaccharides and proteins cross the membrane in bulk via vesicles
in ___cytosis, transport vesicles migrate to the membrane, fuse with it, and release their contents outside the cell (large molecules)
in ___cytosis, the cell takes in macromolecules (large molecules) by forming vesicles from the plasma membrane
exocytosis (many secretory cells use it to export their products)
endocytosis, reversal of exocytosis, involving three different proteins:
phagocytosis: cell engulfs a particle in a vacuole, then fuses with a lysosome to digest
pinocytosis: cell drinking, extracellular fluid is gulped into tiny vesicles
receptor-mediated endocytosis: binding of solutes to receptors, but is highly selective
humans use it to take in cholesterol, which is carried in low density lipoproteins (LDLs)
people w/ the disease hypercholesterolmia have missing/defective LDL receptor proteins, so no cholesterol binds to it, leading it to go to the blood and not the cell