Solid Mensuration Definition of terms
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Plane
a surface that a straight line joining two points in it lies wholly in the surface.
Plane Geometry
about flat shapes like lines, circles, triangles, etc. shapes that can be drawn on a
piece of paper.
plane figures
Figures which lie on a plane are called
Solid Geometry
is about three-dimensional objects like cubes, prisms, cylinders, spheres, etc.
solid figures
Figures which occupy a three dimensional space are called
two-dimensional shape
can be defined as a plane figure that can be drawn on a flat surface.
It has only two dimensions (length and width), with no thickness or depth.
three-dimensional shape
is any solid object that has three dimensions (length, width and
thickness).
Area
the number of space occupied by a two-dimensional figure.
Perpendicular
one straight line cuts another so as to make any two adjacent angles equal, each
line is perpendicular to the other.
Tangent
a straight line which, however far it may be produced, has only one
point in common with the circle.
Perimeter
of a shape is defined as the total distance around the shape.
Square
four sides are equal
Rectangle
two parallel sides are equal and four angles are 90°
Triangle
portion of a plane bounded by three straight lines.
Right Triangle
one angle measures 90°
Altitude of a Triangle
is a perpendicular from any vertex to the
side opposite, produced if necessary.
Hypotenuse
is the side opposite the right angle.
Parallelogram
opposite sides are parallel
Trapezoid
one pair of opposite sides are parallel
Circumference
distance around the circle
Radius
line segment that joins center to the boundary of a circle or sphere
Diameter
any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose
endpoints lie on the circle
Similar polygons
polygons that have their homologous angles equal and their homologous sides
proportional.
Similar polygons
have the same ratio as the squares of any two corresponding lines
Solid
any limited portion of space, bounded by surfaces
Section of a solid
plane figure cut from the solid by passing a plane through it.
Polyhedron
solid bounded by planes
edges of a polyhedron
are the intersections of the bounding planes
faces
are the portions of the bounding planes included y the edges.
vertices
intersections of the edges
cube
polyhedron whose six faces are all squares
equal
The three dimensions of a cube are ___to each other.
congruent
All the faces of a cube are ___ squares
rectangular parallelepiped
polyhedron whose all faces are rectangle.
equal
The parallel edges of a rectangular parallelepiped are ___.
opposite lateral faces
The_____ of a rectangular parallelepiped are equal and parallel.
base
Any two opposite faces of a rectangular parallelepiped may be taken as the ___.
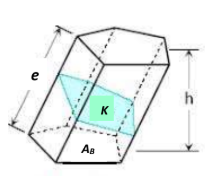
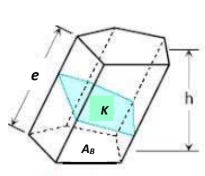
Prism
a polyhedron of which two faces are equal polygons in parallel planes, and the other faces are
parallelograms.
bases
AB, the equal polygons;
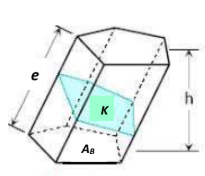
lateral edges
e, intersections of lateral faces, are equal and
parallel.
lateral area
the sum of the areas of the remaining faces. (prism)
altitude
h, the perpendicular distance between the planes of its bases.
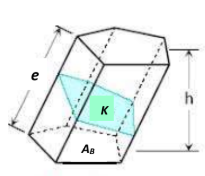
right section
K=Area of ___section perpendicular to the lateral edges.
right prism
prism whose lateral edges are perpendicular to its bases; its lateral faces are
rectangles.
equal
sections of a prism made by parallel planes cutting all the lateral edges are ___ polygons.
lateral area
___of a prism is equal to the product of lateral edge and the perimeter of the right section.
volume
___of a prism is equal either to the product of area of the base and the altitude, or to the product of
a right section and a lateral edge.
cylindrical surface
a surface generated by a moving straight line (generator) which is always parallel to
a fixed line, and which always intersects a fixed plane curve (directrix) not in the plane with the fixed line.
cylinder
solid bounded by a closed cylindrical surface and two parallel planes.
lateral surface
The bounding cylindrical surface of a cylinder
equal
The bases of a cylinder are __.
altitude
The __ of a cylinder is the perpendicular distance between the bases.
right section
of a cylinder is a section perpendicular to all elements of the cylinder.
lateral area
of a cylinder is equal to the product of an element and the perimeter of the right section.
volume
of a cylinder is equal either to the product of a base and the altitude, or to the product of a right
section and an element.