APES UNIT 3: POPULATIONS
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Density Independent Factor
A factor that has the same effect on a individual's probability of survival and reproduction at any population size
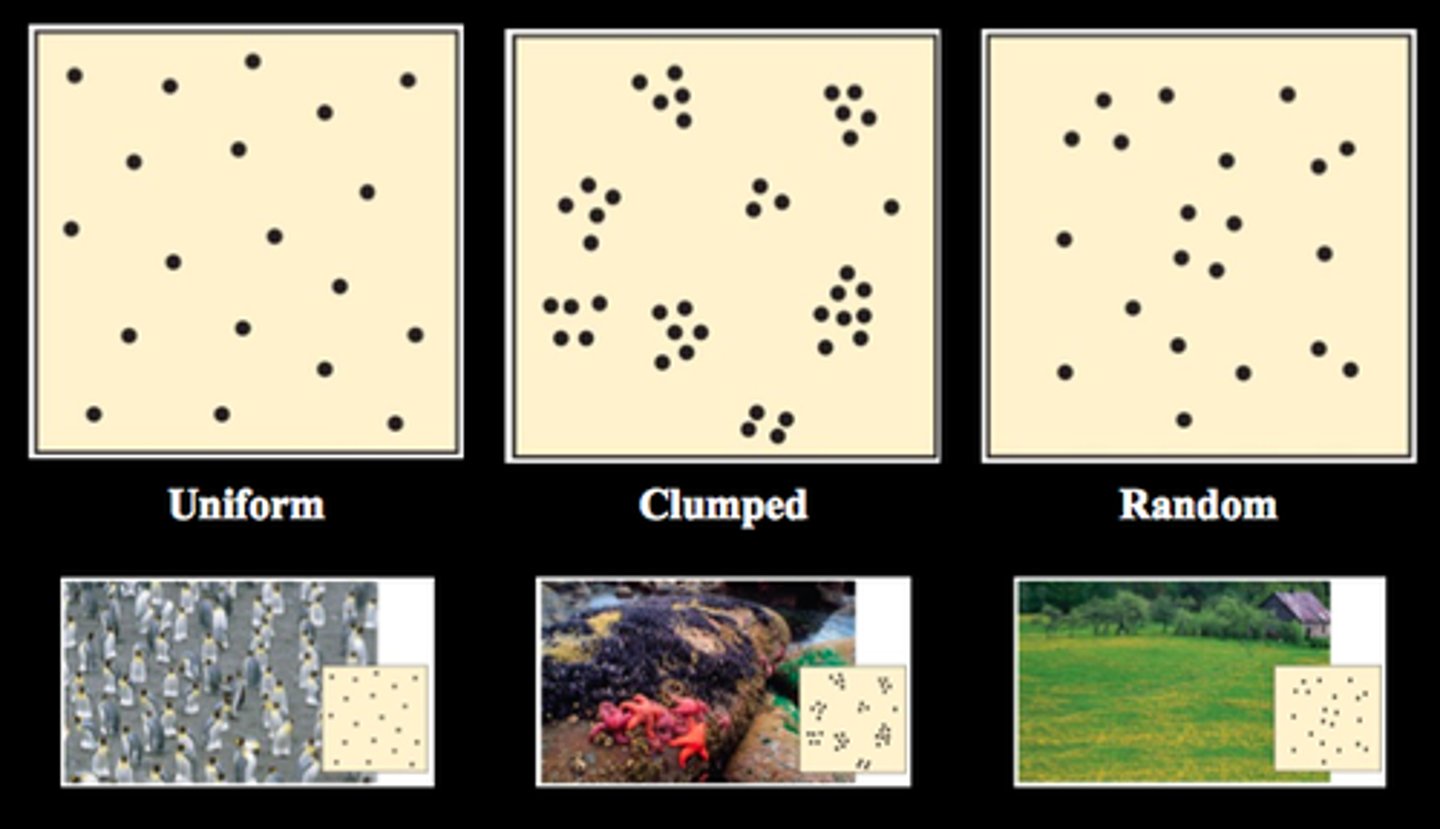
random, uniform, clumped
Three types of population distribution

Density Dependent Factor
A factor that influences an individuals probability of survival and reproduction in a manner that depends on the size of the population (i.e. predation, disease, food supply)
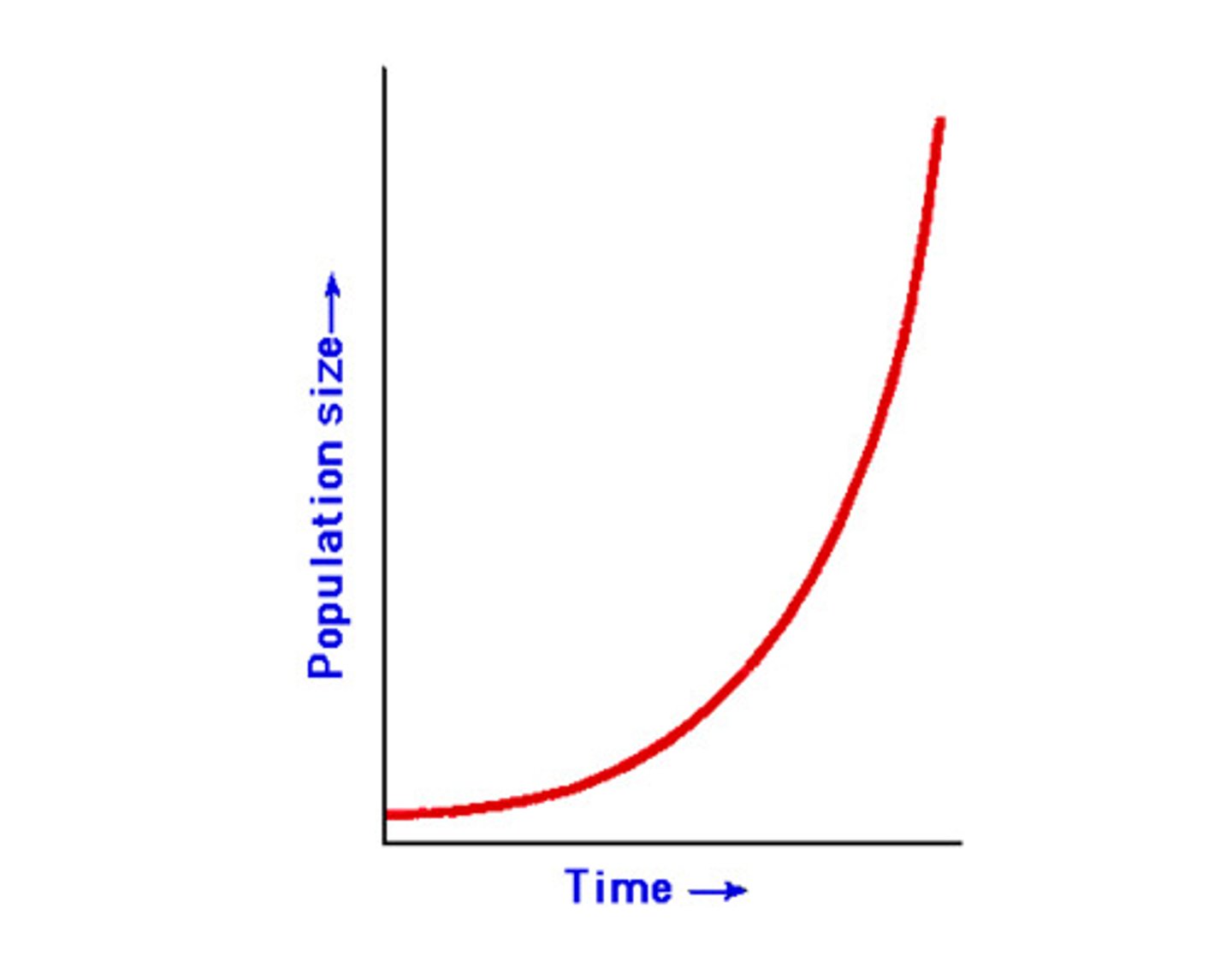
exponential growth models
occurs when populations are not limited by resources. (J-curve)
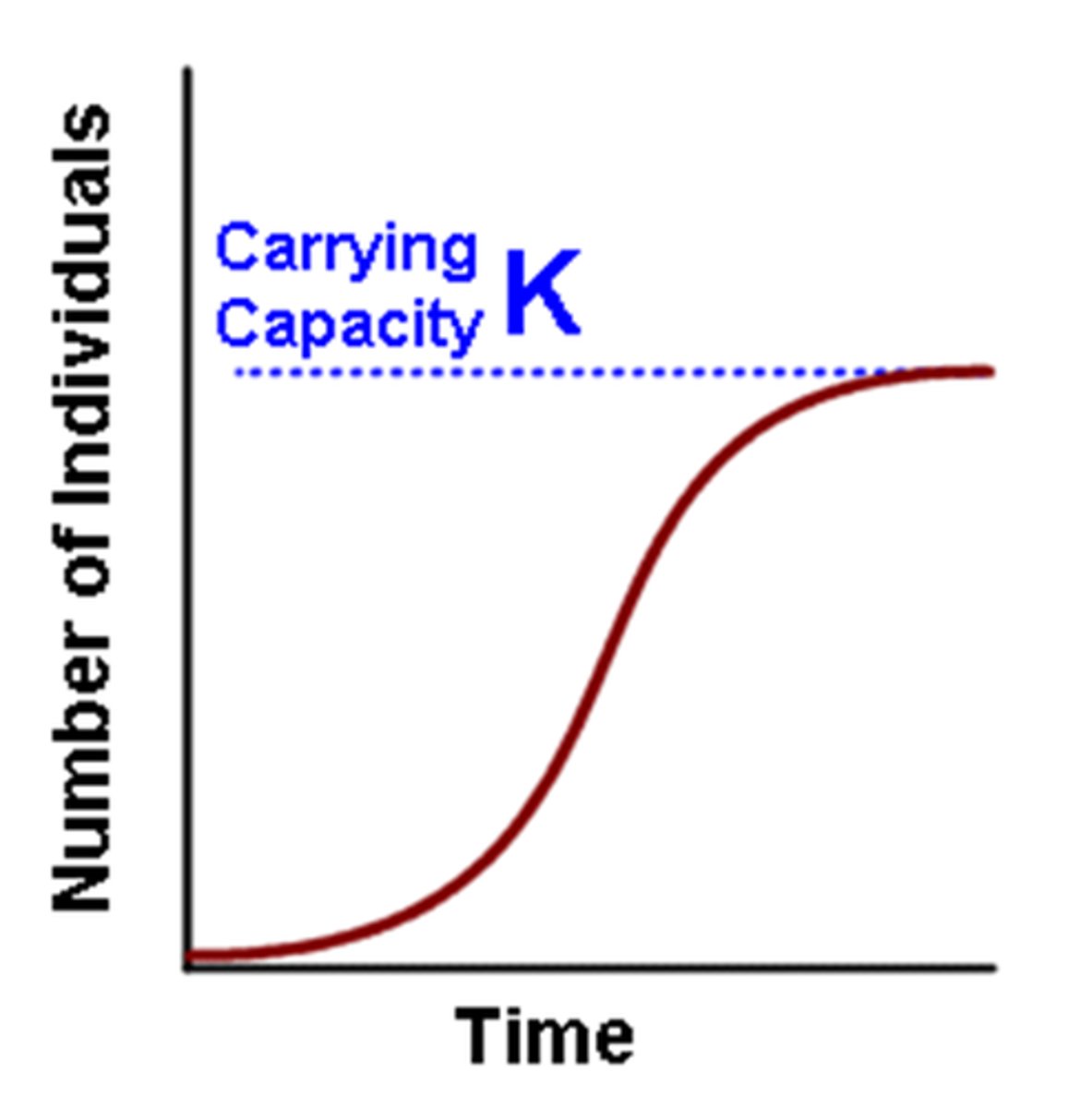
logistical growth model
occurs when populations fluctuate at a carrying capacity established by a limiting resource and initially experience large growth but then level off at K
survivorship curve
survival patterns of different species. Type I (K-selective) care for their young, Type II constant death rate throughout life, and type III (r-selective) low survival of the young.
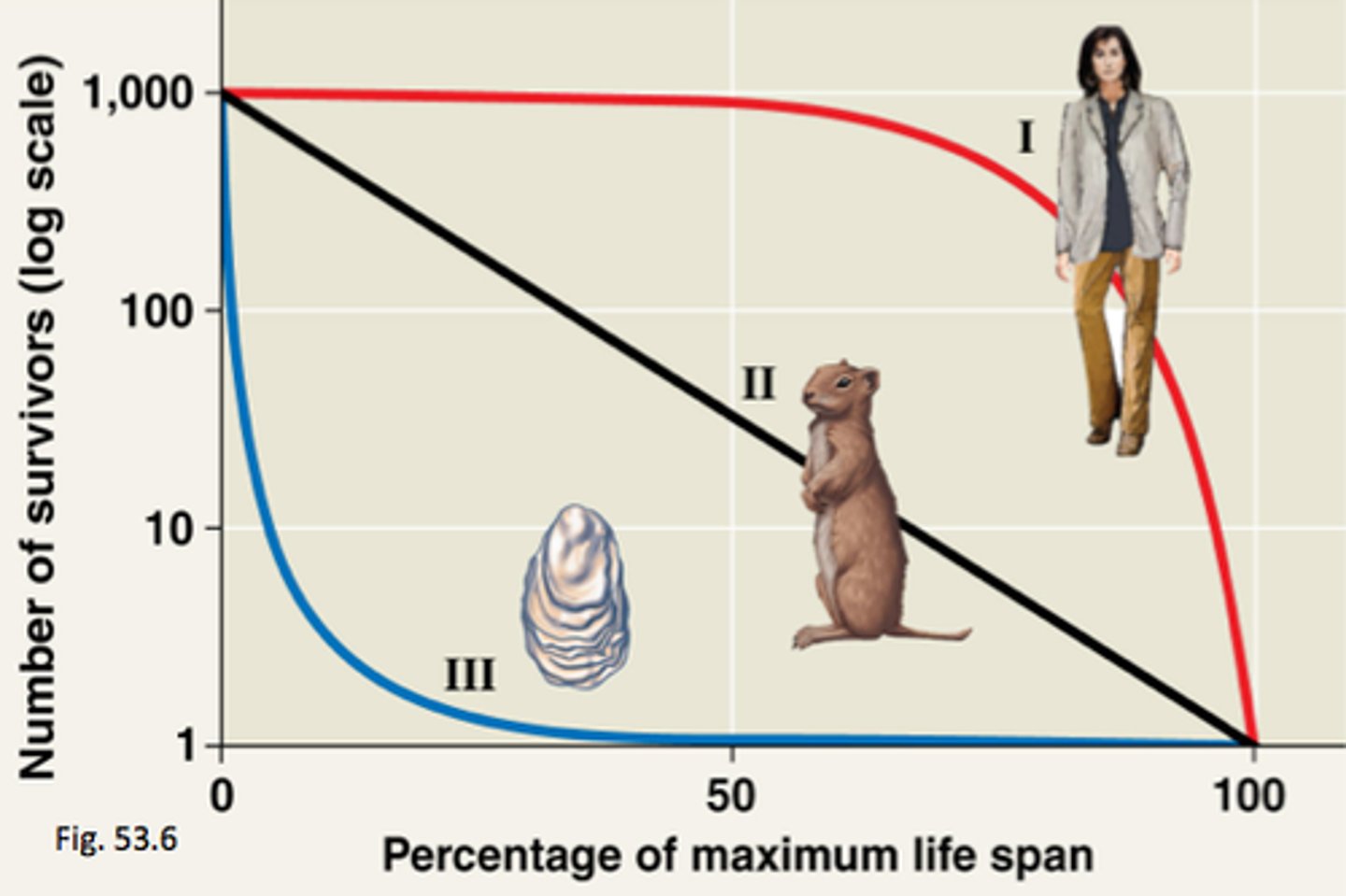
K-selected species
A species with a low intrinsic growth rate that causes the population to increase slowly until it reaches carrying capacity (TYPE I)
r-selected species
A species with a high intrinsic growth rate that causes the population to overshoot and quickly die off (TYPE III)
Population size
The total number of individuals of one species within a defined area at a given time
Population density
The number of individuals per unit area at a given time
Population distribution
How individuals are distributed with respect to one another
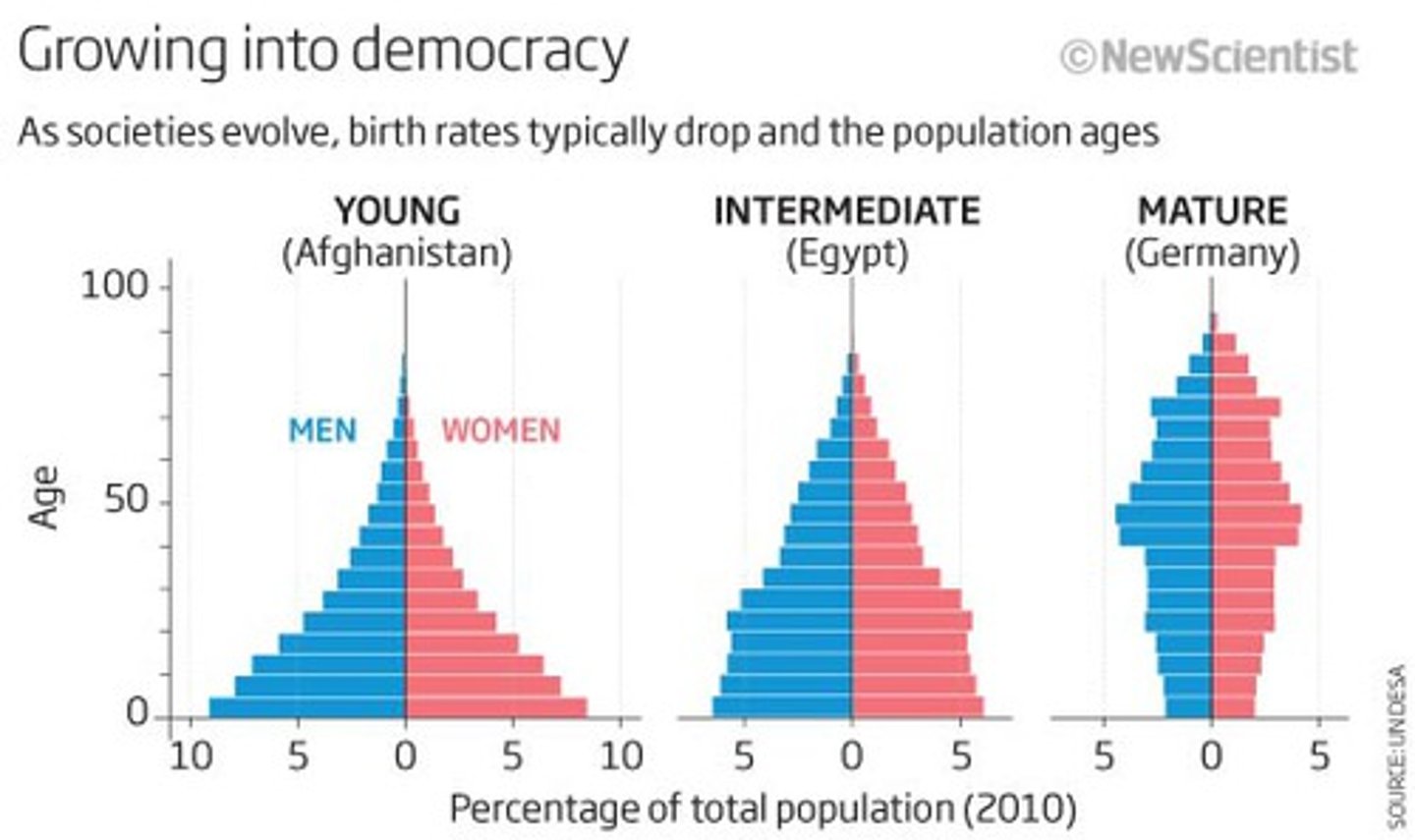
age structure diagram
how many individuals fit into age categories. (in a model)
Growth Rate
The number of offspring an individual can produce in a given period of time, minus the deaths of the individual or offspring during the same period
Metapopulations
A group of spatially distinct populations that are connected by occasional movements of individuals between the populations
Competition
The struggle of individuals to obtain a limiting resource
Resource partitioning
Where species divide up a resource based on difference in the species behavior or morphology-this can reduce competition
Predation
The use of one species as a resource by another species
Parasites
Type of predation when species live on or in the organism they consume
Parasitoids
Type of predation when species lay eggs inside other organisms
Mutualism
A type of interspecific interaction where both species benefit
Commensalism
A type of relationship in which one species benefits but the other is neither helped nor hurt
Keystone Species
a species that plays a role in its community that is far more important that its relative abundance might suggest
Primary Succession
Replacement of species, one after another, which occurs on surfaces that are initially devoid of soil. Starts with moss and lichens on the exposed rock and it it progresses to shrubs and plants and eventually restores ecosystem.
Secondary Succession
Replacement of species, one after another, occurs in areas that have been disturbed but have not lost their soil
Community Ecology
The study of the interactions between species in a habitat
Competitive exclusion principle
two species competing for the same limited resource cannot coexist. This explains why resource partitioning takes place so that both can survive
Interspecific Competition
When two species compete over one limited resource
Intraspecific Competition
When two individuals within the same species compete over one limited resource
Factors that determine species richness
Latitude (distance from equator), Time (older the habitat, the higher SR), Habitat size (larger=greater)
Theory of Island Biogeography
Explains that both habitat size and distance from coloring species determine species richness; larger habitats contain more species, as do habitats which are closer to colonizers
innovation and technology
How does the human population not have a food deficit?
growth rate equation
CBR-CDR/10
doubling time for a population equation
70/growth rate
Demography
The study of human populations and population trends
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
estimate of the average number of children each woman will bear in her lifetime
Replacement level fertility (RLF)
the total fertility rate required to offset the average number of deaths in a population and for the current population size to remain stable
Developed Countries
Countries with high levels of industrialization and income
Developing Countries
Countries with relatively low levels of industrialization and income
Life Expectancy
The average number of years that an infant born in a particular year in a particular country can be expected to live, given the current average life span and death rate of that country
Infant Mortality Rate
Number of deaths of children under the age of one per 1000 births
Child Mortality Rate
Number of deaths of children under the age of five per 1000 births
Demographic Transition
The theory that as a country moves from a subsistence economy to and industrialized one, it undergoes a predictable shift in population growth
Family Planning
Regulating the number or spacing of children through the use of birth control
IPAT equation
environmental Impact=Population x Affluence x Technology
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The sum total of the value of all the goods and services produced in a nation
population momentum
The propensity for a growing population to continue growing even through fertility is declining because of their young age distribution
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
limiting resource
a resource that a population cannot live without and which occurs in quantities lower than the population would require to increase in size
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area
symbiotic
mutually beneficial; supporting one another's life
pioneer species
first species to populate an area during succession
Pathogens
organisms that cause disease