Paleo 203 Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/196
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:03 AM on 12/10/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
197 Terms
1
New cards
Tetrapoda (informally, tetrapods)
Terrestrial vertebrates named for their four weight-bearing limbs. Includes all living and extinct amphibians, birds, mammals, and reptiles.
2
New cards
Amniota (informally, amniotes)
A clade of vertebrates that develop special membranes around their eggs, allowing them to cut reproductive ties with water. Includes all living and extinct birds, mammals, and reptiles.
3
New cards
Amnion
a membrane that surrounds an embryo which protects the developing young from drying out
4
New cards
Aquatic problem
The main theme of this course. Encompasses differences between air and water and the challenges terrestrial amniotes had to overcome to successfully live in the water.
5
New cards
Morphology
The shape and structure of an animal or any of the parts of its body.
6
New cards
Terrestrial
An organism that can carry out all aspects of its life on land.
7
New cards
Aquatic
An organism that can carry out all aspects of its life in water.
8
New cards
Semi-aquatic
An organism that requires both land and water environments to carry out all aspects of its life. Have long, smooth bodies, flippers, tail fluke and hind legs
9
New cards
Primarily aquatic
An organism that lives in the water, and is descended from ancestors that also lived in the water. Includes all living and extinct fishes.
10
New cards
Secondarily aquatic
An organism that lives in the water, but is descended from ancestors that live on land. Includes all living and extinct aquatic birds, mammals, and reptiles.
11
New cards
Pinniped
A member of the Pinnipedia- the group that includes seals, sea lions, and walruses.
12
New cards
Carapace
The bony shell across the back of an animal.
13
New cards
Plastron
The bony shell across the abdomen of an animal.
14
New cards
Crocodyliformes
(informally, crocodiles) A sub-group of the Crocodylomorpha containing all modern and some extinct crocodiles, alligators and gharials. Body armour, webbed toes, laterally compressed tails, Saltwater crocs use ocean currents to travel between Indonesian islands
15
New cards
Laterally compressed
When an object is flattened such that it is taller than it is wide.
16
New cards
Extant
Still in existence, currently living.
17
New cards
Extinct
No longer in existence, with no living members.
18
New cards
Thrust
The force that generates propulsion.
19
New cards
Appendicular skeleton
The bones that form the limbs and limb girdles. Includes all bones of the shoulders, arms, hips, and legs.
20
New cards
Appendicular locomotion
Motion generated by movement of the limbs. Have flippers or webbed feet to increase thrust and surface area
21
New cards
Flippers
Flatter bones, shorter radius, humerus, ulna, longer and numerous phalanges, covered in smooth flat tissue
22
New cards
Axial skeleton
The bones that form the mid-line of the body. Includes all bones of the skull, spinal column, and ribs.
23
New cards
Axial locomotion
Motion generated by movement of the spinal column. Developers caudal fluke to increase surface area
24
New cards
Flippers
Modified limbs that are adapted to manoeuvre in water.
25
New cards
Phalanges
The bones that form the individual segments of fingers or toes.
26
New cards
Caudal fluke
An expanded, soft-tissue fin supported by the last tail vertebrae. Vertical in marine reptiles, horizontal in marine mammals.
27
New cards
Collagen
A structural protein found in connective tissues of animals.
28
New cards
Caudal fin
An expanded vertical structure, completely supported by thin bones, but no vertebrae, that forms the tail of fishes.
29
New cards
Anguilliform locomotion
A form of axial locomotion in which the entire spinal column undulates, propagating waves of muscle contractions down the entire body. Low efficiency. Animals that use this form of locomotion tend to be long and skinny. Ex. Sea snakes and eels
30
New cards
Thunniform locomotion
A form of axial locomotion in which only the tail undulates. Maximum efficiency. Animals that use this form of locomotion tend to be torpedo-shaped. In high speed predatory fish, not body oscillation, crescent shaped fins and fluke. Ex. Tuna, dolphins
31
New cards
Carangiform locomotion
A form of axial locomotion in which only the back half of the spinal column undulates. Animals that use this form of locomotion tend to be spindle-shaped. ex. Seals, crocs, marine iguanas
32
New cards
Pitch
Up and down motion. One of three planes of motion in a 3D environment.
33
New cards
Roll
Movement where an object turns over on its forward-backward axis. One of three planes of motion in a 3D environment.
34
New cards
Yaw
Left and right motions. One of three planes of motion in a 3D environment.
35
New cards
Dorsal fin
An unpaired fin on the back of an animal which helps to stabilize them against rolling.
36
New cards
Drag
The force that resists the movement of an object through any medium. Increased by both density and viscosity of the medium.
37
New cards
Inertial drag
The force that resists the movement of an object by disturbing the flow of molecules around that object crates a space where the medium fills and pulls body backward. It is based on the density of the medium through which it moves. Needs fusiform body shape, smooth, elongate, decreased surface area, loss of hind limbs and external ears
38
New cards
Streamlined
A morphology that reduces resistance of a body moving through a medium by reducing the way it disturbs the medium. Minimizes inertial drag.
39
New cards
Fusiform
An oblong morphology that tapers at both ends. Can be described as spindle-shaped or torpedo-shaped.
40
New cards
Viscous drag
The force that resists the movement of an object based on friction generated between the object and the medium it is moving through. Caused by the viscosity of the medium through which it moves. Needs smooth, hairless body
41
New cards
Lactic acid
An organic acid produced in muscles during strenuous activity when there is little oxygen available. Causes muscle fatigue and soreness. In crocs
42
New cards
Nares
Openings in the skull that allow for the passage of air from the nostrils to the windpipe.
43
New cards
Blowhole
Nostrils that have migrated to the top of the head in a marine mammal.
44
New cards
Neutral buoyancy
When an object has the same density as the medium that surrounds it. The object with neither sink nor float.
45
New cards
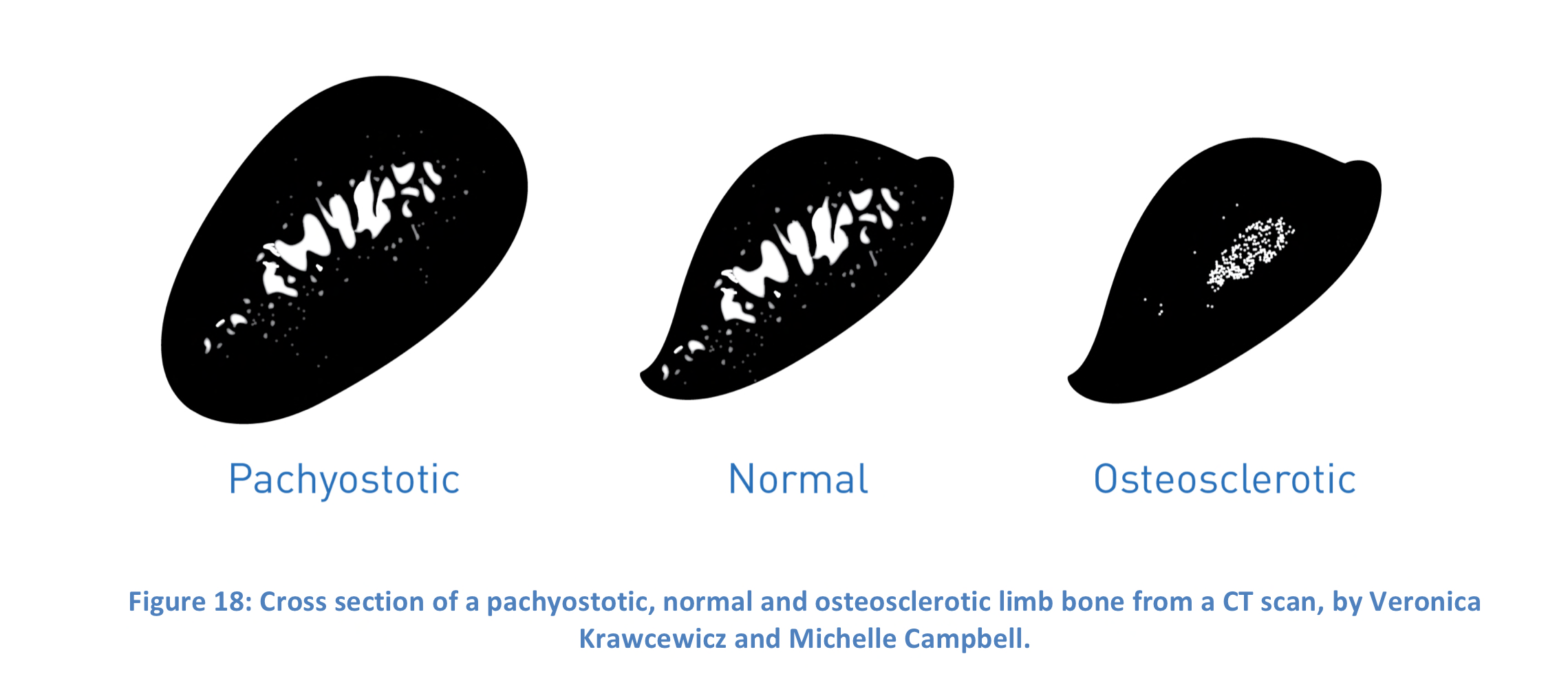
Pachyostosis
A condition in which bones become denser and larger due to increased growth of the denser outer layers of the bones. In manatees, penguins, early whale relatives
46
New cards
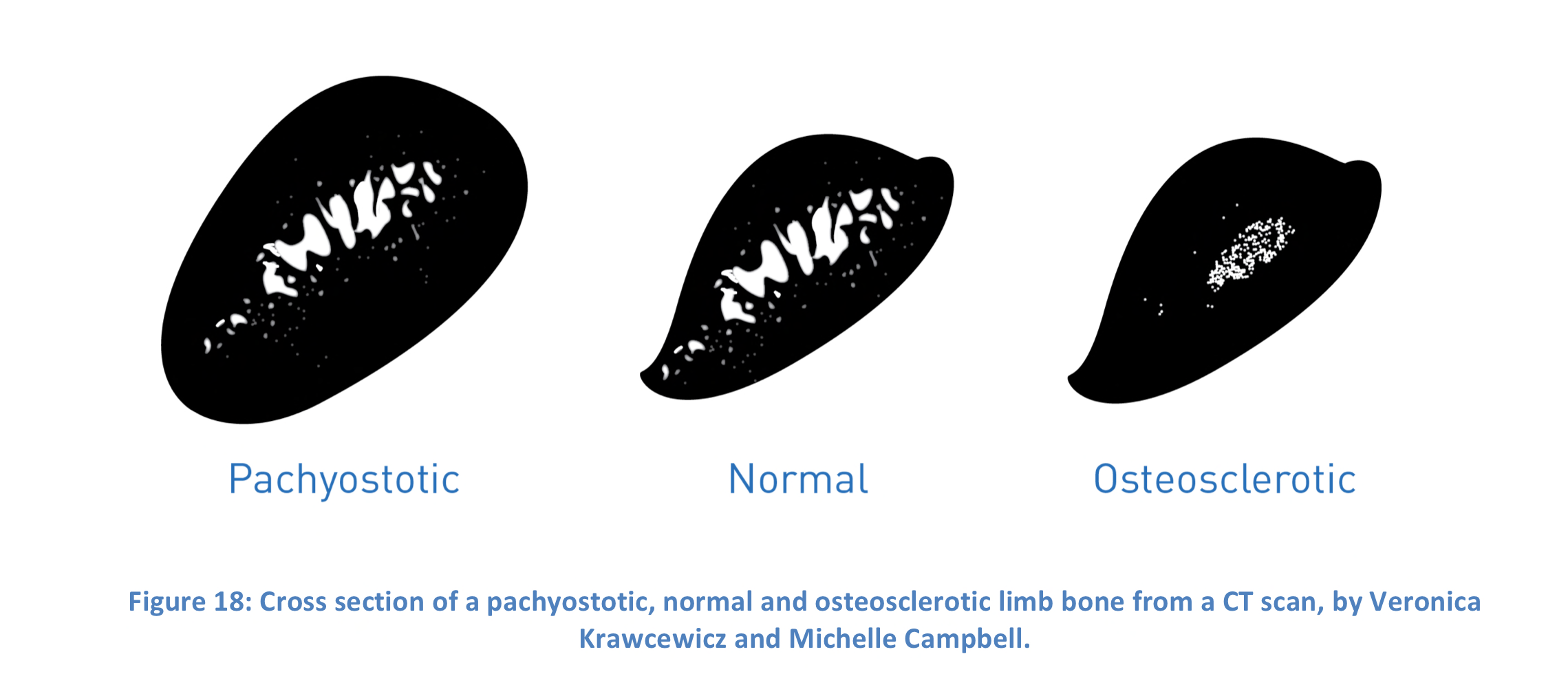
Osteosclerosis
A condition in which bones become denser, but not larger, due to increased mineralization usually in the spongy inner regions of the bones. In walrus and turtles
47
New cards
Gastroliths
A small stone swallowed by an animal to aid in digestion of tough materials and/or to contribute to neutral buoyancy. Sometimes called gizzard stones. In crocs and birds
48
New cards
Osmosis
A process in which water passes through a membrane from an area of low solvent concentration to an area of high solvent concentration. Equalizes the concentration between the two areas.
49
New cards
Salt gland
A special gland that concentrates salt from the blood so that it can be expelled from the body. On crocs tongue, under sea snake tongue, above sea turtle and bird eyes, connected to nostrils in marine iguanas (expel by sneeze)
50
New cards
Metabolism
The sum total of all chemical processes that occur within an organism in order to maintain life. Hard to maintain in water because water is a good heat conductor
51
New cards
Blubber
A thick layer of fat found on some marine mammals that is used as insulation.
52
New cards
Underhairs
The shorter, finer hairs close to the skin of a mammal. Function primarily as insulation. Traps heat near skin
53
New cards
Guard hairs
The outer layer of longer, coarser hairs on a mammal. Functions primarily as protection. Keeps water away from underhairs. Layer like shingles
54
New cards
Tapetum lucidum
A lining on the back of the eyes that reflects incoming light through the retina a second time, increasing the effectiveness of the eye in low light conditions. Seals, crocs, cats
55
New cards
Water properties related to sight
1. Density changes how light bends - bends less in water
2. Light doesn’t travel as far and diffracts
3. Only some spectrum of light is seen in greater depths - blue and green penetrate deeper, total darkness at 200m
56
New cards
Bone conduction
The transmission of sound waves from the surrounding environment to the inner ear through the skull bones. Uses vibrations, less distortion, secondarily aquatic adaptation
57
New cards
Hearing in water
Easier to hear in water, travel 5x faster
58
New cards
Echolocation
A type of sonar used by some animals to detect objects. The animal emits high-pitched sounds which bounce off of surrounding objects and back to the animal's ears, revealing the location of the objects.
59
New cards
Ecology
The relationship of an organism to other organisms and its physical surroundings.
60
New cards
Convergence
Where organisms facing similar ecological challenges evolve similar or indistinguishable solutions.
61
New cards
Paleoecology
(see ecology) The ecology of extinct organisms.
62
New cards

Marine Reptile clades
Ichthyoperygians, sauropterygians, mosasauroids
63
New cards
Basal
Belonging to the base of a lineage, usually with few of the specialized adaptations seen in later members of the group.
64
New cards
Derived
Belonging at or near the tip of a lineage, usually with many specialized adaptations not seen in ancestral forms.
65
New cards
When first tetrapods colonized
During Devonian
66
New cards
Temporal fenestrae
Holes in the side of a skull- the number of these holes determine major phylogenetic groupings.
67
New cards
Anapsid
Having no temporal fenestrae in the skull.
68
New cards
Synapsdid
Having one pair of temporal fenestrae in the skull.
69
New cards
Diapsid
Having two pairs of temporal fenestrae in the skull: the laterotemporal and supratemporal fenestrae.
70
New cards
2 diapsida lineages
Archosauromorpha, Lepidosauromorpha
71
New cards
Synapsida (informally, synapsids)
With the Sauropsida, is one of the two major divisions of amniotes. This group have only one temporal fenestra. Mammals are the modern representatives of this group.
72
New cards
Sauropsida (informally, sauropsids)
With the Synapsida, is one of the two major divisions of amniotes. This group has two temporal fenestrae. Crocodiles, lizards and birds, Parareptiles and diapsida
73
New cards
Orbit
The opening in the skull where the eye is located.
74
New cards
Parareptilia (informally, parareptiles)
With the Diapsida, is one of two major divisions within the Sauropsida. Has the anapsid skull condition.
75
New cards
Diapsida (informally, diapsids)
With the Parareptilia, is one of two major divisions within the Sauropsida. Has the diapsid skull condition.
76
New cards
Laterotemporal fenestra
The lower of two temporal fenestrae in the diapsid skull condition, found below and/or behind the eye.
77
New cards
Supratemporal fenestra
The upper of two temporal fenestrae in the diapsid skull condition, found above and/or behind the eye.
78
New cards
Archosauromorpha (informally, archosaurs)
Ruling reptiles. With the Lepidosauromorpha, is one of two major divisions of the Diapsida. Have an additional fenestra in front of the eye and on the jaw. Members include birds, crocodiles, dinosaurs and pterosaurs.
79
New cards
Lepidosauromorpha (informally, lepidosaurs)
Scaly Reptiles. With the Archosauromorpha, is one of two major divisions of the Diapsida. Members include lizards and snakes. No extra temporal openings
80
New cards

Mesosauridae (informally, mesosaurs)
Group of aquatic marine parareptiles from the Permian. Earliest known group of secondarily aquatic amniotes. Includes genera such as Mesosaurus. Slender body, long neck, elongated skull, dense bone, long hind limbs, laterally compressed tail, needle like teeth, paddle in sallow water, could NOT live in open ocean
81
New cards

Tanystropheidae
Includes Tanystropheidae and Dinocephalosaurus
82
New cards
Tanystropheidae
Lacks paddles, laterally compressed tail, long and stiff neck, snatch fish at lake edge
83
New cards
Dinocephalosaurus
Long neck and paddles, lived in ocean
84
New cards
Crocodylomorpha (informally, crocodylomorphs)
A clade of archosaurs characterized by the articulation of their ankles. Includes all living and extinct alligators, caimans, thalattosuchians, and crocodiles. Webbed feet, laterally compressed tail.
85
New cards
Thalattosuchia (informally, thalattosucians)
A group of fully aquatic crocodylomorphs from the Jurassic and Cretaceous. Includes genera such as Geosaurus.
86
New cards

Geosaurus
Paddle like forelimbs, tail fluke (controls propulsion in water column), reduced dermal armour (for neutral buoyancy), salt glands in orbit, layer eggs on land, lived in water
87
New cards
Protorosauria (informally, protorosaurs)
A very basal clade of archosaurs.
88
New cards
Tanystropheidae (informally tanystropheids)
A family of protorosars with very long necks thought to be semi aquatic. Includes genera such as Tanystropheus and Dinocephalosaurus.
89
New cards
Drepanosauridae (informally, drepanosaurs)
A family of protorosaurs with convergent adaptations to chameleons, feet and hands for tree climbing, huge claws, though one species, Hypuronector, is thought to be aquatic.
90
New cards
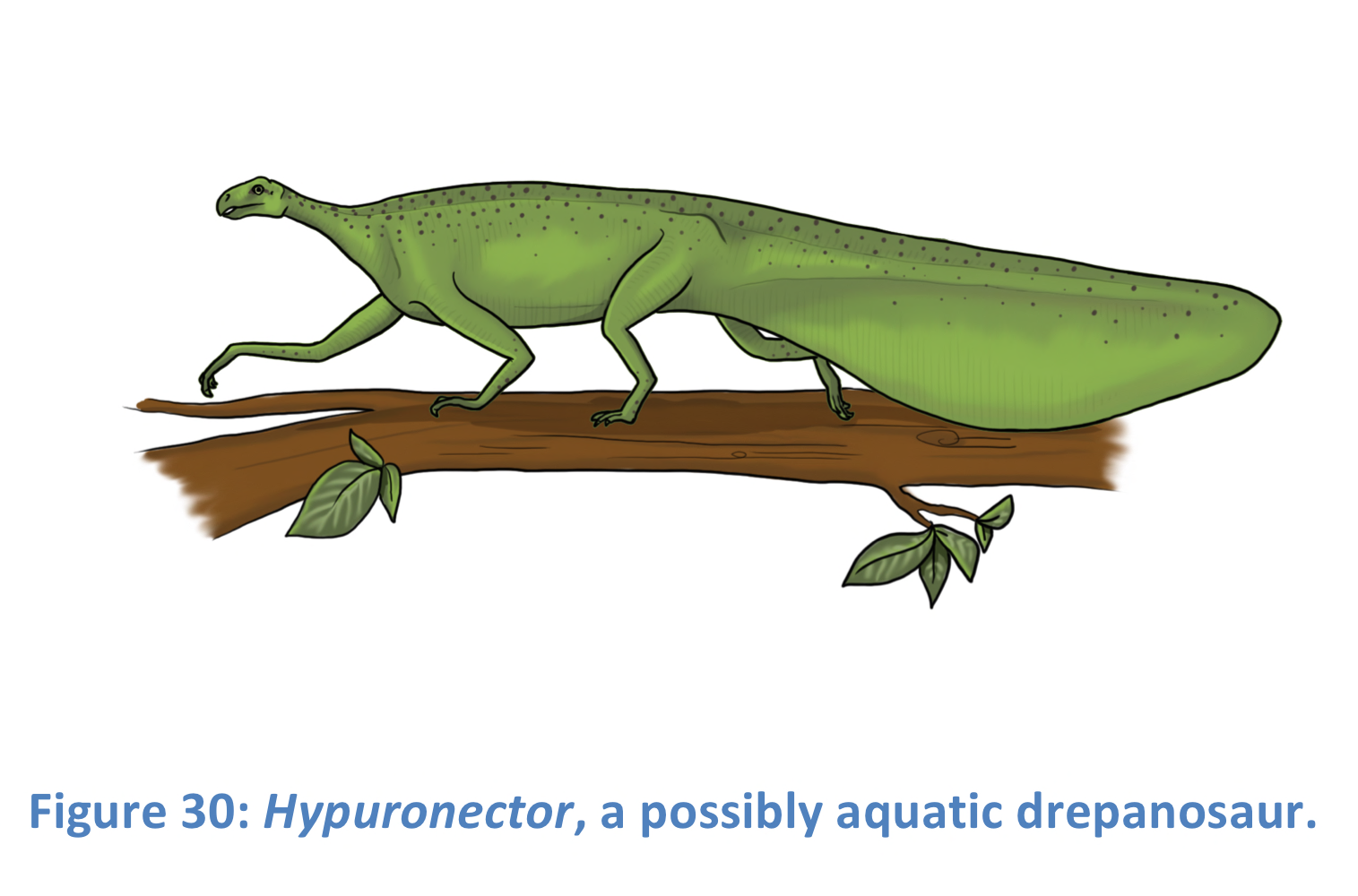
Hypuronector
Laterally compressed tail, like a newt, tail not good for trees but good for water propulsion, in lake deposits part of Drepanosauridae
91
New cards
Choristodera (informally, choristoderes)
A clade of aquatic diapsid archosauromorphs with uncertain phylogenetic relationsips. Convergent body plan to crocodylomorphs. Includes genera such as Champsosaurus. Lived in waterways in the mesozic, survived end-Cretaceous mass extinction, unknown extinction in Miocene epoch
92
New cards

Champsosaurus
Long narrow snout with conical teeth for fish, distant realities of crocodiles, pachyostotic ribs for neural buoyancy
93
New cards
Tangasauridae (informally, tangasaurids)
Lizard-like basal diapsids from the Permian of Madagascar. Includes genera such as Hovasaurus. 2 temporal openings but not archosauromorph of lepidosauromorph, long flattened tail
94
New cards
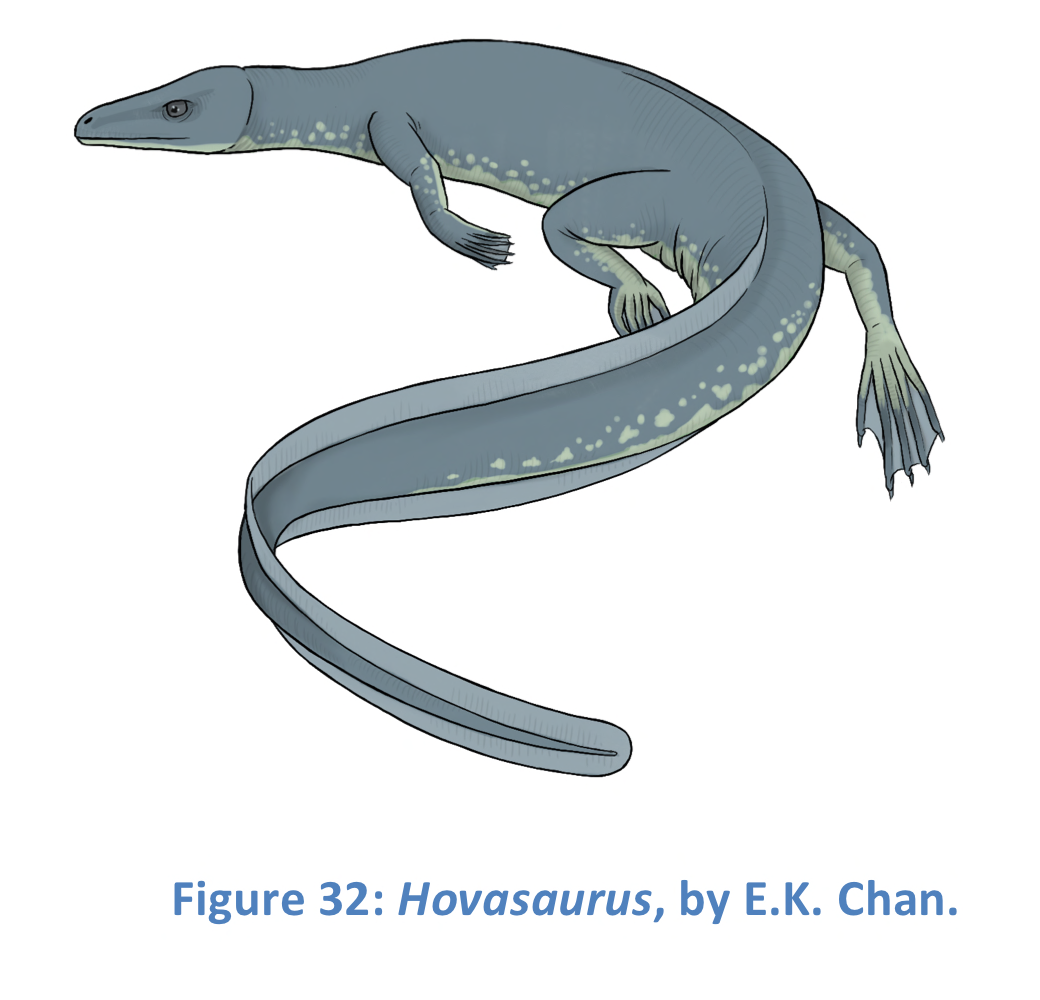
Hovasaurus
Found with gastroliths, dense bones, semi aquatic, unclear ecology, part of Tangasauridae
95
New cards

Atopodentatus
An unusual genus of semi-aquatic reptiles of unknown relationships (probably related to sauropterygians, with a zipper-like split up the front of its face that was filled with needle like teeth, possibly for filter feeding and sieve in mud. Long bodies, short limbs but strong enough for terrestrial.
96
New cards
Odontochelys
A basal turtle genera, oldest fossil with a plastron, teeth and no carapace. Had teeth, Triassic of china, marine sediments
97
New cards
Turtles
Anapsid skull, derived diapsids, debated Parareptiles, related to crocodylomorpha, originated as aquatic amniotes, later returned to freshwater and terrestrial
98
New cards
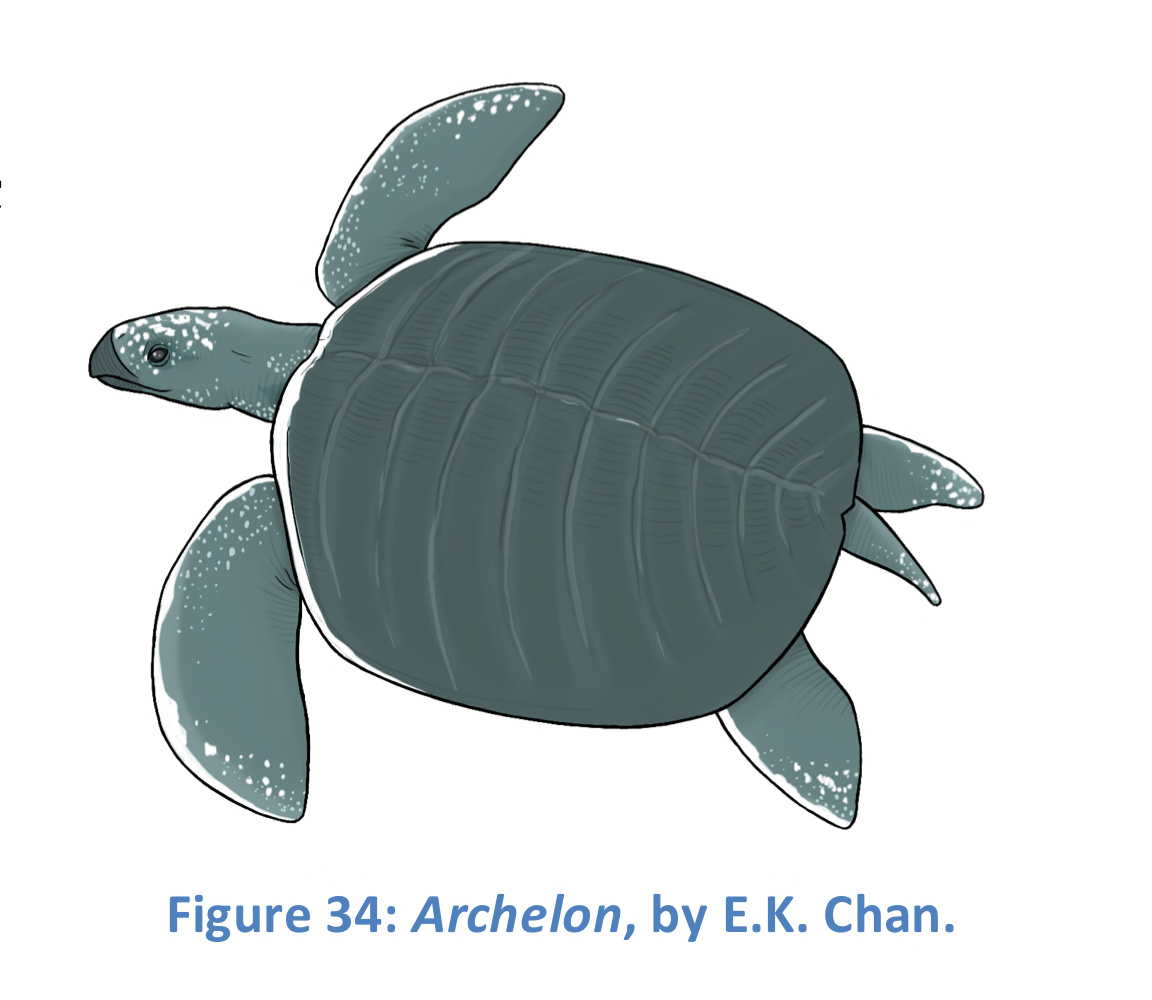
Archelon
The largest marine turtle that ever lived, growing to lengths of more than four metres.
99
New cards
Cephalopoda (informally, cephalopods)
A class of molluscs characterized by their tentacles. Includes extant members such as octopus, squid and nautilis; and extinct members such as ammonites and belemnites.
100
New cards
Ammonites
A sub group of extinct cephalopods very common in the Mesozoic oceans that typically had spiral shells with ridges. Eat small prey in water column, like nautilus