Early Childhood Cognitive Development: Piaget, Vygotsky & Information Processing
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the first stage of Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
Sensorimotor stage (0-2 years)
What is the second stage of Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
Preoperational stage (2-7 years)
What is the third stage of Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
Concrete Operational stage (7-11 years)
What is the fourth stage of Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
Formal Operational stage (11+ years)
What is the most obvious feature of the preoperational stage?
Representations, but not yet operations
How does make-believe play change during the preoperational stage?
It becomes increasingly detached from real life and less self-centered.
What are the benefits of make-believe play?
It enhances cognitive, social, and emotional skills.
What is dual representation in the context of cognitive development?
The ability to understand that one object can represent another, which is a challenge for young children.
What is egocentrism in preoperational thought?
The inability to distinguish others' symbolic viewpoints from one's own.
What is conservation in cognitive development?
Understanding that certain physical characteristics of objects remain the same, even when their outward appearance changes.
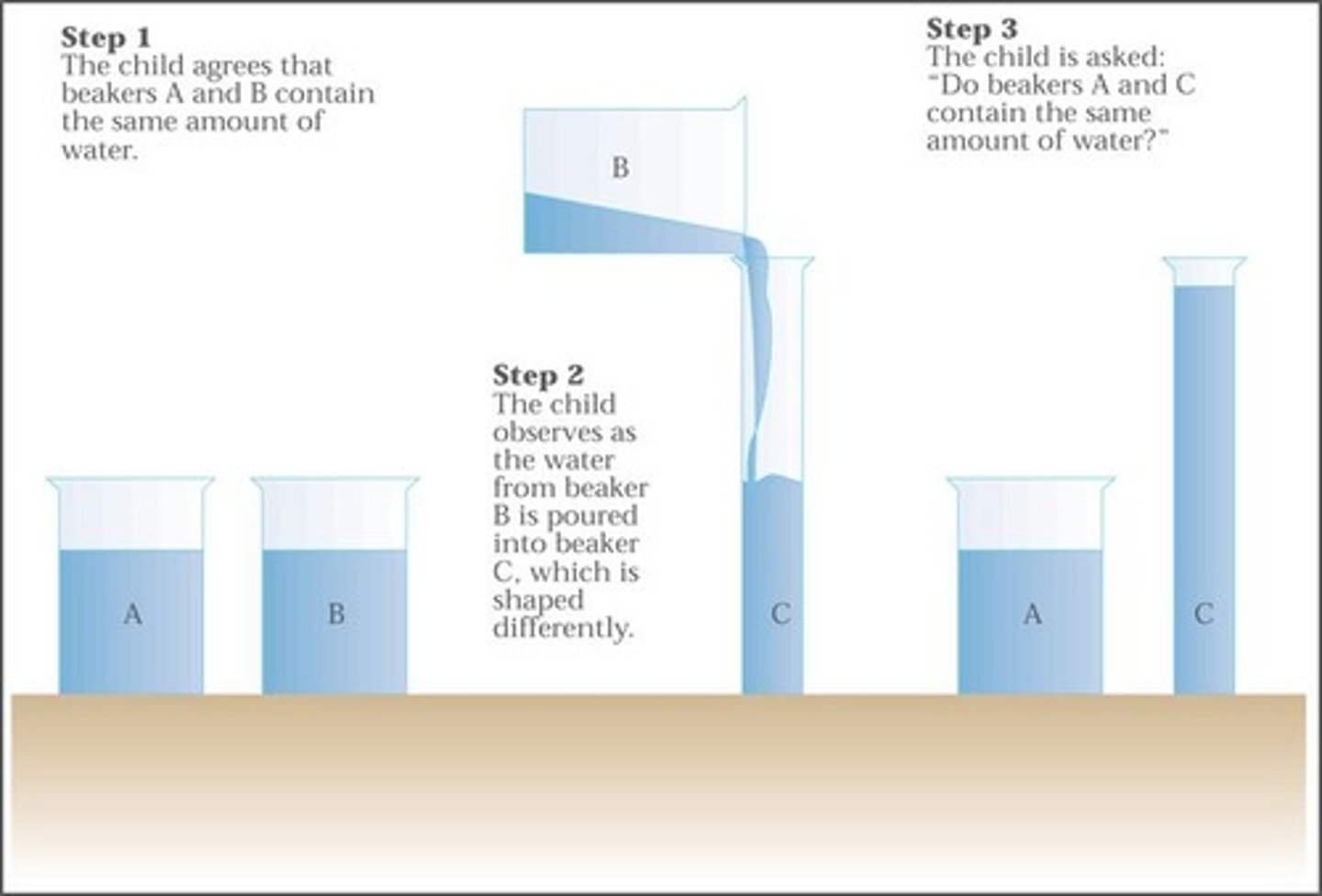
What are the limitations of preoperational thought?
Egocentrism, inability to conserve, and lack of hierarchical classification.
What is Vygotsky's sociocultural theory focused on?
The importance of social interaction and cultural context in cognitive development.
What is the zone of proximal development according to Vygotsky?
The difference between what a learner can do without help and what they can do with help.

What is scaffolding in Vygotsky's theory?
Support given to a learner that is tailored to their needs, helping them achieve a higher level of understanding.
What is executive function?
A set of mental skills that help manage everyday tasks and achieve goals.
What are the components of executive function?
Inhibitory control, flexible shifting, and working memory.
What is theory of mind?
The understanding of mental life, including beliefs, desires, and intentions of oneself and others.
At what age do children begin to understand false beliefs?
By age 4.
What is the difference between recognition and recall in memory?
Recognition involves identifying previously learned information, while recall involves retrieving it without cues.
What is fast-mapping in language development?
The ability to quickly learn a new word after only a brief encounter with it.
What is overregularization in language development?
The application of regular grammatical rules to irregular cases, such as saying 'braked' instead of 'broke.'
What role do adults play in language development?
They provide support through recasts and expansions of children's speech.