IB Biology: Carbohydrates Structure, Function, and Polysaccharides
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the basic structure of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, typically in the ratio (CH2O)n.
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are simple sugars that contain between 3 and 7 carbon atoms.
Give examples of monosaccharides.
Examples include glucose, ribose, and fructose.
What are disaccharides?
Disaccharides are carbohydrates formed from two monosaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose.
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made up of long chains of monosaccharides.
What is the function of monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are used for immediate energy and as building blocks for polysaccharides.
What are examples of polysaccharides and their functions?
Examples include starch and glycogen for energy storage, and cellulose and chitin for structural support.
What is the difference between an aldose and a ketose?
An aldose has a carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, while a ketose has it in the middle.
What is the significance of carbon's tetravalence?
Carbon can form four covalent bonds, allowing for a variety of complex organic molecules.
What are the four most common elements found in living organisms?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen (CHON).
What are the two types of metabolic pathways?
Anabolic pathways synthesize molecules, while catabolic pathways break down molecules.
What is the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways?
Enzymes catalyze the reactions in both anabolic and catabolic pathways.
What is the process of dehydration synthesis?
Dehydration synthesis is the removal of water to form bonds between monomers, creating polymers.
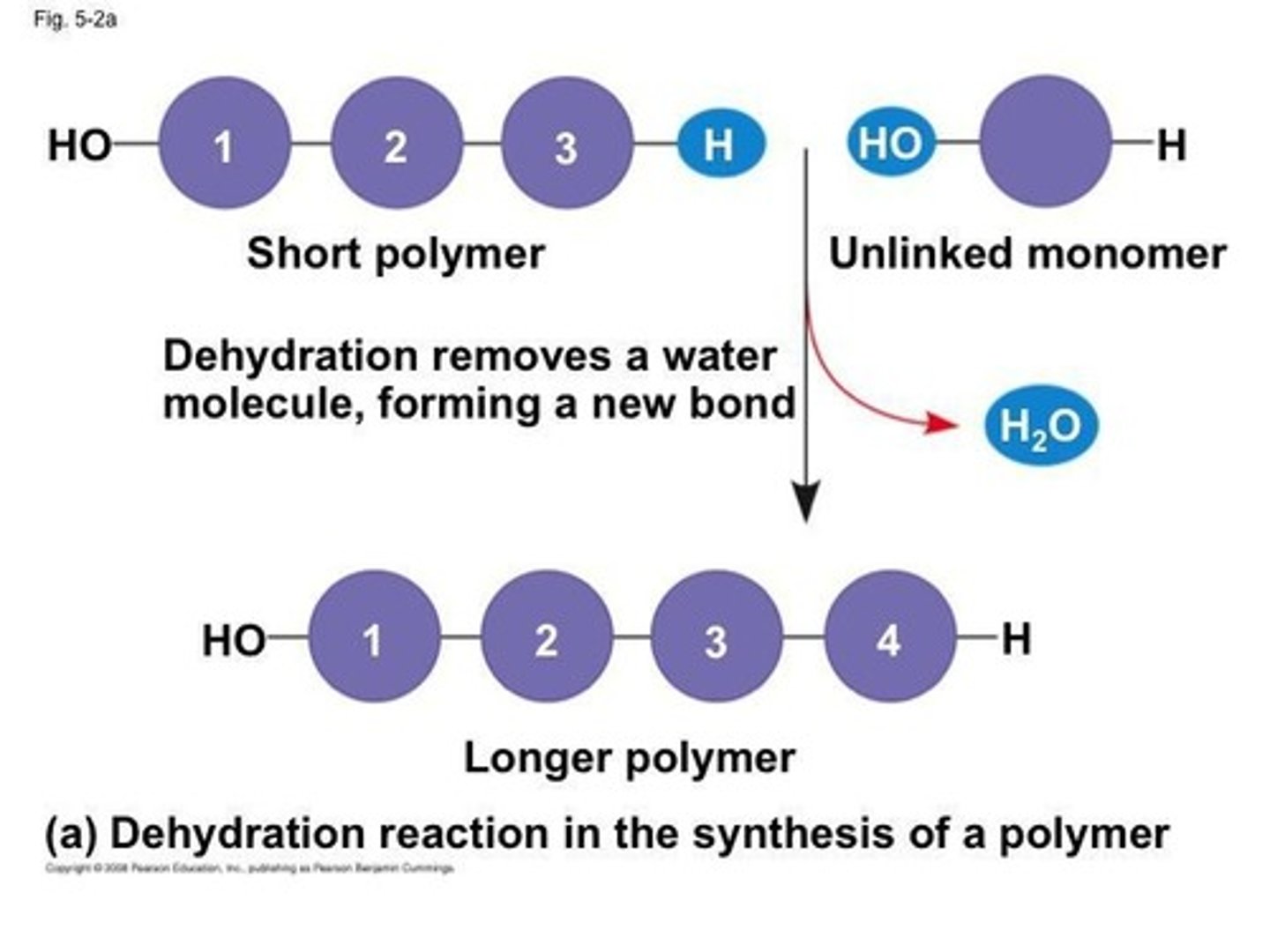
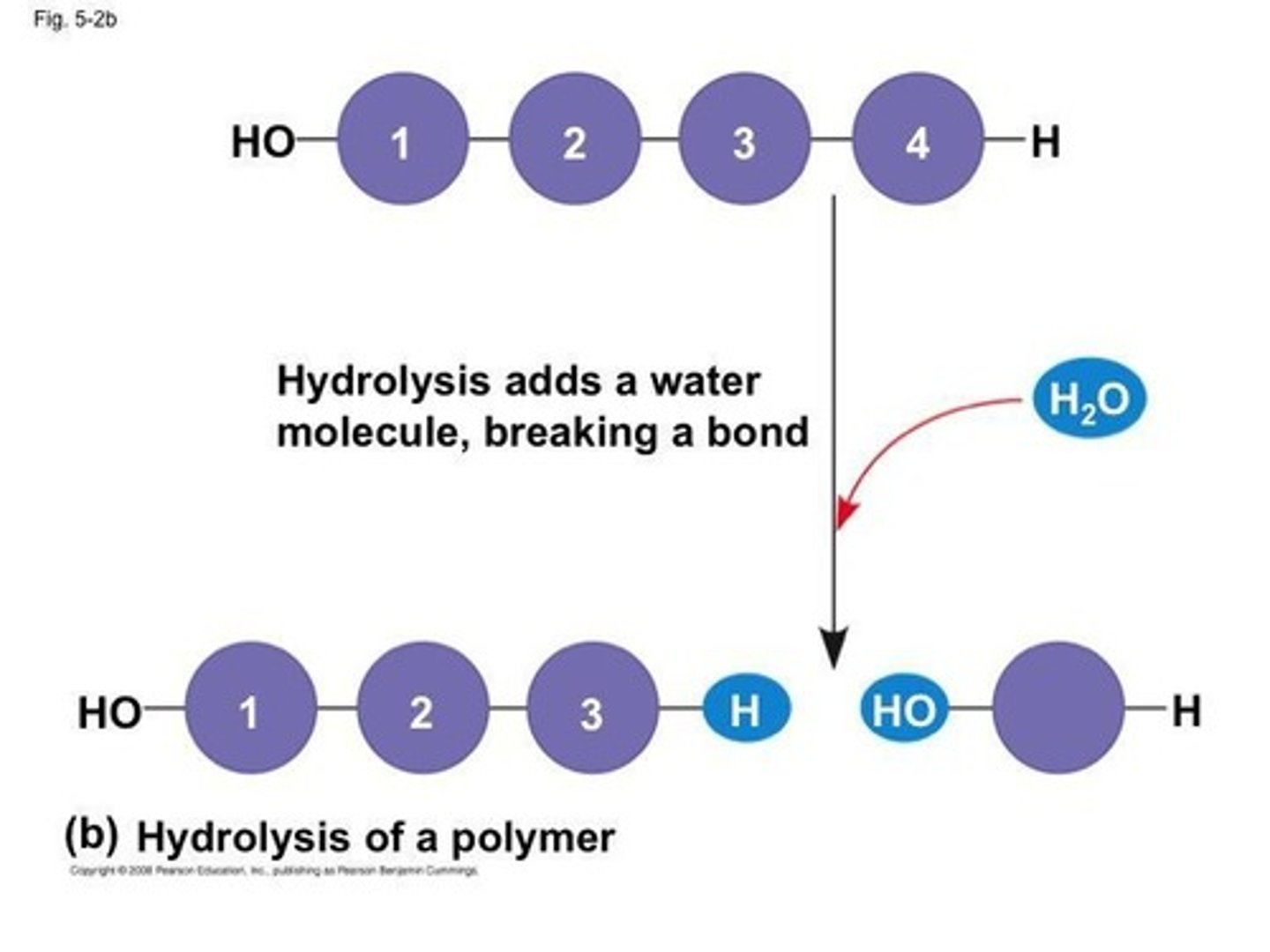
What is hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis is the addition of water to break bonds between monomers, resulting in smaller molecules.
What are hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons are molecules composed only of carbon and hydrogen.
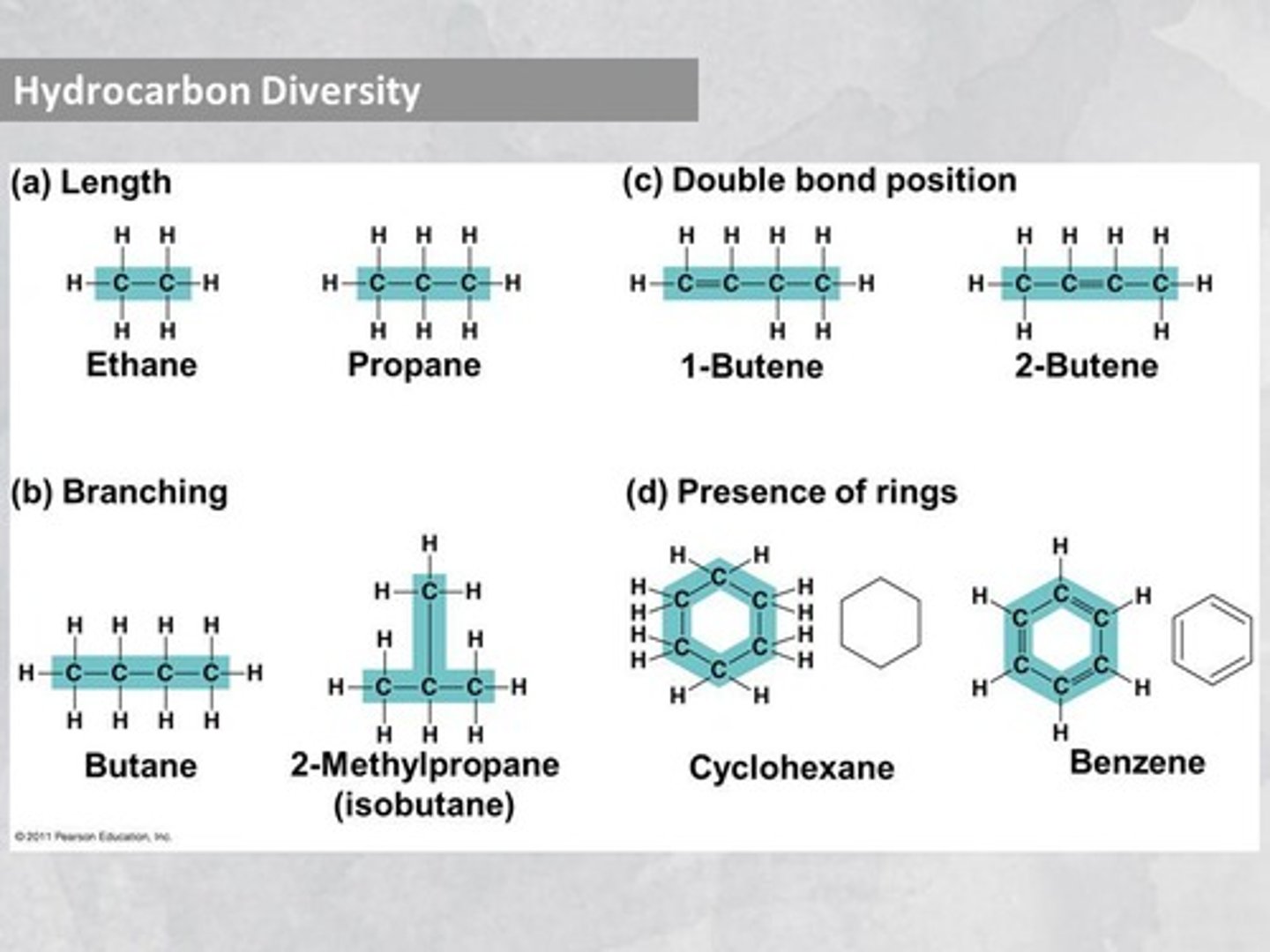
What is a carbon skeleton?
The carbon skeleton is the framework of carbon atoms in an organic molecule to which functional groups attach.
What are functional groups?
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that determine the chemical properties of those molecules.
What are the monomers and polymers of nucleic acids?
Monomer: Nucleotide; Polymer: Polynucleotide.
What are the monomers and polymers of proteins?
Monomer: Amino Acids; Polymer: Polypeptide.
What are the monomers and polymers of carbohydrates?
Monomer: Monosaccharide; Polymer: Polysaccharide.
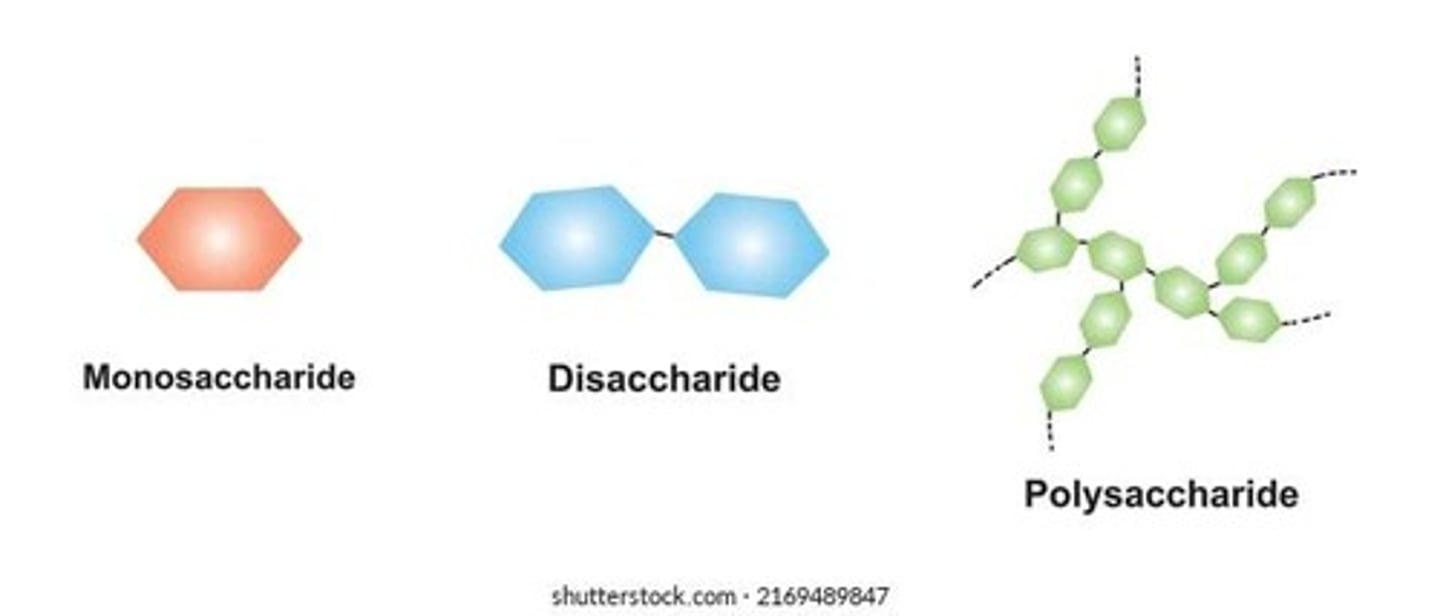
What is the difference between simple sugars and complex carbohydrates?
Simple sugars include monosaccharides and disaccharides, while complex carbohydrates are polysaccharides.
What is the role of polysaccharides in energy storage?
Polysaccharides like starch and glycogen serve as energy reserves in organisms.
What is the structural role of cellulose?
Cellulose provides structural support in plant cell walls.
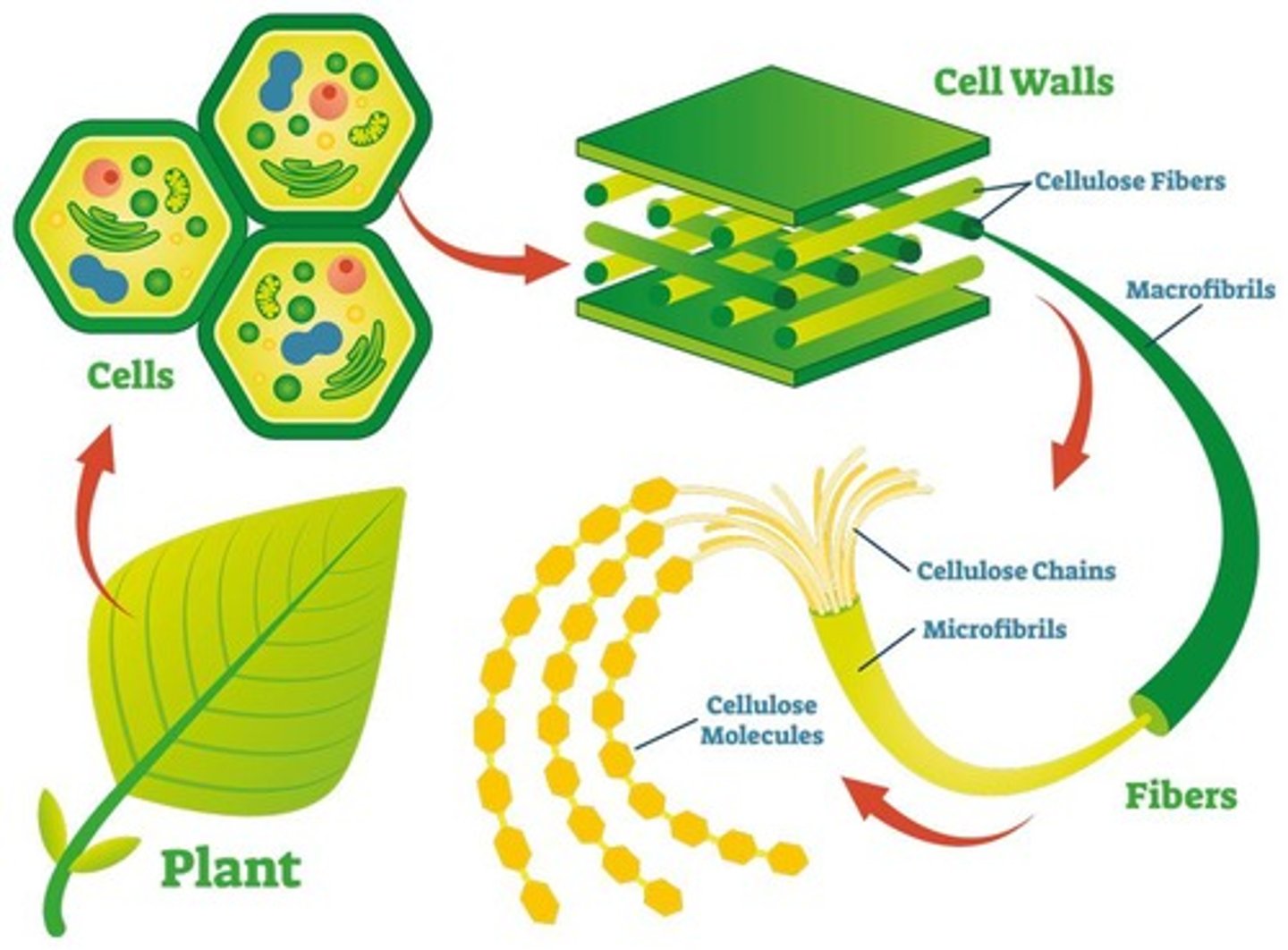
What is chitin and where is it found?
Chitin is a structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of arthropods and the cell walls of fungi.
What is the common ending for many carbohydrates?
Many carbohydrates end with the suffix -ose.
What is the importance of aqueous chemistry in biology?
Biological reactions occur in aqueous solutions, affecting the behavior of ionic compounds and molecules.
What is the molecular formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
What type of sugar is glucose classified as?
A hexose
What is the primary function of glucose in cellular respiration?
To create ATP energy for the cell
What are the building blocks that glucose can form?
Polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose
What distinguishes alpha glucose from beta glucose?
In alpha glucose, the hydroxyl group (-OH) on the 1' carbon is below the ring; in beta glucose, it is above the ring.
What is a disaccharide?
A molecule created when two monosaccharides join together during a condensation reaction.
What are examples of disaccharides?
Sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), maltose (glucose + glucose)
What are the two major functions of polysaccharides?
Energy storage (starch and glycogen) and structural material (cellulose and chitin).
What is starch and where is it found?
An energy storage polysaccharide found in plants, made of α-glucose.
What are the two types of starch?
Amylose (linear, coiled structure) and amylopectin (highly branched).
What is glycogen and its primary function?
An energy storage polysaccharide found in animals, primarily in the liver and muscles.
What is cellulose and its role in plants?
A structural polysaccharide found in plant cell walls, made of β-glucose.
Why can't humans digest cellulose?
Humans cannot break the β-glucose linkages in cellulose.
What are glycoproteins?
Sugar-protein molecules that serve various functions including cell recognition and communication.
How do glycoproteins relate to the ABO blood typing system?
Different blood types have different glycoproteins (antigens) on their surface.
What is the significance of the phrase 'like dissolves like' in relation to glucose?
Glucose is polar and dissolves easily in water, which is also polar.
What happens to glucose during oxidation?
It loses electrons and can be broken down to release energy for ATP production.
What are the other common hexoses besides glucose?
Galactose (found in dairy) and fructose (found in fruits).
What is the role of glycosidic linkages in carbohydrates?
They connect monosaccharides together to form disaccharides and polysaccharides.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
Polar covalent bonds involve unequal sharing of electrons, while nonpolar bonds involve equal sharing.
What is the electronegativity of oxygen?
3.44
What type of bond is formed between carbon and hydrogen?
A nonpolar covalent bond.
What is the significance of hydrogen bonds in relation to polar covalent bonds?
Polar covalent bonds allow for the formation of hydrogen bonds, which are crucial for many biological processes.
What is the primary structural component of plant cell walls?
Cellulose