Case Studies of Human Disease Exam 2
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Innate Immunity
Quick & nonspecific immune respone (0-4 Hours)
Macrophage
Type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms, and stimulates the action of other immune system cells.
Dendritic Cells
Immune cell tat is found in tissues, such as the skin, boosts immune response by showing antigens on its surface to other immune cells.
Monocytes
Type of immune cell that is made in bone marrow and travels through the blood to tissues where it is needed, is then able to change into macrophage of dendritic cells.
Mast Cells
A type of white blood cell that is found in connective tissues all through the body, especially under the skin, near blood vessels and lymph vessels, in nerves, and in the lungs and intestines.
Neutrophils
A type of white blood cell (leukocytes) that act as your immune system's first line of defense. A subset of granulocytes that has a segmented nucleus.
Eosinophil
A type of white blood cell and a subset of granulocytes that is responsible for creating an inflammatory response. Focus on destroying invading germ cells.
Basophil
A type of white blood cell and a subset of granulocyte. Has enzymes which are released during allergic reactions and asthma.
Gamma-delta (γδ) T cells
a subset of T cells that promote the inflammatory responses of lymphoid and myeloid lineages, and are especially vital to the initial inflammatory and immune responses.
Natural Killer T Cell
type of T cell that also have certain features of natural killer (NK) cells. They can kill invading microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses, by releasing cytokines. They can also kill certain cells, such as cancer cells, either directly or by causing other immune cells to kill them.
Adaptive Immunity
Slow and specific immune response (4-14 days)
Humoral Immunity
Class of adaptive immunity. Production of antibodies and main defense against bacterial infection
Cell-mediated Immunity
Formation of lymphocytes that attack foreign material. The main defense against viruses, fungi, parasites, and some bacteria. Also rejects transplanted organs and eliminates abnormal cells that arise during cell division.
T-lymphocytes
Type of WBC that is diverse and an important group of lymphocytes that mature and undergo a positive and negative selection processes in the thymus. Can wipe out infected or cancerous cells and also maintain immunological memory and self-tolerance.
CD4+
help coordinate the immune response by stimulating other immune cells, such as macrophages, B lymphocytes (B cells), and CD8 T lymphocytes (CD8 cells), to fight infection. Helper T Cells
CD8+
Kill virus-infected cells and produce antiviral cytokines such as interferon-gamma. Have the primary job to kill toxic/target cells. Killer T Cells
B lymphocytes
Proliferate and mature into antibody-forming plasma cells
T lymphocytes
Proliferate to form a diverse population of cells that regulate the immune response and generate a cell-mediated immune reaction to eliminate antigen
Entry of Foreign Antigen Reaction
1) Recognition of foreign antigen
2) Proliferation of lymphocytes that are programmed to respond to the specific antigen form a large group of cells
3) Destruction of the foreign antigen occurs by the proliferated lymphocytes
MHC (Major Histocompatibility Proteins)
Present processed antigen to responding cells of the immune system and generates an immune response
MHC class I
Present on all nucleated cells
MHC class II
Only on B lymphocytes, macrophages, and related antigen-processing cells and some activated T-lymphocytes
Cytotoxic T Cells
Can respond only to antigens complexed with MHC class I proteins displayed on infected host cellsI
IgA
Mucus, Saliva, Tears, Colostrum. Tags pathogens for destruction
IgD
B-Cell receptor stimulates release of IgM
IgE
Binds to mast cells and Basophils. Allergy and antiparasitic activity
IgG (Most Common)
Binds to phagocytes. Main blood antibody for secondary responses. Crosses the Placenta
IgM
Primary first responder to new pathogen. B-cell receptor and immune system memory.
Hypersensitivity Type I
Allergy and Anaphylactic (immediate response). IgE antibodies fix to mast cells and basophils.
Anaphylaxis
Hypersensitivity reaction that may be life threatening. Severe generalized IgE-mediated reaction: Fall in blood pressure, sever respiratory distress
Antihistamine drugs
Often relieve many allergic symptoms.
Atopic person
Allergy-Prone individual
Allergen
Sensitizing antigen
Hypersensitivity Type II
Cytotoxic: Antibody combines with cell or tissue antigen, resulting in complement-mediated lysis of cells or other membrance damage. EX: Rh hemolytic disease, blood transfusion reactions.
Hypersensitivity Type III
Immune Complex: Ag-Ab immune complexes deposited in tissues activate complements; PMN attracted to site, causing tissue damage. EX: Rheumatoid Arthritis
Hypersensitivity Type IV
Delayed hypersensitivity or cell-mediated hypersensitivity: T lymphocytes are sensitized and activated on second contact with same antigen. Lymphokines induce inflammation and activate macrophages. EX: Tuberculosis, fungal and parasitic infections
Autoimmune disease
A patient forms antibodies against his or her own cells and tissues
Pathogenesis
Alteration of patient’s own antigens, causing them to become antigenic, provoking an immune reaction. EX: Systemic lupus erythematosus, Glomerulonephritis, Anemia, Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism
Neoplasia
Tumor Development
Benign
Slow growth rate, Expansion, Remains localized, Well-differentiated cells
Malignant
Rapid growth rate, Infiltration, Metastasis by bloodstream, poorly differentiated cells
Carcinoma
Involves epithelial tissue, most common form of cancer: 85% of all tumors.
Metastasis: Principally through lymph vessels.
Subtypes: Adenocarcinoma (internal organ) and Squamous cell carcinoma (skin)
Sarcoma
Arising from connective tissues, such as fat, bone, cartilage, and muscles.
Less common but spreads more rapidly, Little differentiation, lacks form (anaplasia),
Metastasis: Bloodstream
Leukemia
Neoplasm of blood cells, usually does not form solid tumors
Proliferates diffusely within bone marrow, overgrows and crowds out normal blood forming cells.
Neoplastic cells (blasts) spill over into the bloodstream, and large numner of abnormal cells circulate in the peripheral blood.
Lymphoma
Malignant tumor of lymph node
Melanoma
Malignant skin tumor; melanocytes
Blastoma
Pediatric malignant solid tumor (retionoblastoma - eye / nephroblastoma - kidney)
Adenoma
A term often used to refer to a benign tumor derived from epithelial tissue
Neoplasms
Derive from a single stem cell. An abnormal mass of tissue that forms when cells grow and divide more than they should or do not die when they should.
Cancer (Progression)
Usually the result of multiple genetic insults such as activation of oncogenes or loss of function of one or more tumor suppressor genes
Tumors
Derive blood supply from tissues they invade
Malignant tumors frequently induce new blood vessels to proliferate in adjacent normal tissues to supply the demands of the growing tissue
The malignant tumor may outgrow its blood supply causing necrosis in areas with the poorest blood supply
Metastasis
Tumor spreads from site of origin to sites near and far within the body
Via Blood Vessels (Hematogenous)
Via Lymphatic Vessels (Lymphatic)
Travel Patterns of Spread
Colon → Liver
Breast → Axillary lymph nodes
Lung → Brain
Kidney, Prostate → Bone
Pancreas → Liver
Testicle → Retroperitoneum
Melanoma → Lymph nodes, etc.
Apoptosis
Programed cell death if a cell sustains a significant degree of DNA damage
Ph1 Chromosome
Best known chromosomal abnormality
Reciprocal translocation of ends of chromosomes 9 and 22
Oncogene on translocated piece of chromosome 9 exhibits increased activity
Oncogene
Abnormally functioning gene that stimulates cell growth excessively, leading to unrestricted cell proliferation.
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Function by preventing DNA replication and completion of mitosis
Normally suppress cell proliferation
Exist in pairs at corresponding gene loci on homologous chromosomes
EX: p53: “guardian of the genome”, Rb: function identified in childhood cancer, retinoblastoma, APC: controls cell-cell adhesion, NF1: association with tumors of the nervous system
Mutation
Any change in the normal arrangement of DNA nucleotides on the DNA chain
Early Warning Signs of Tumors
Unintentional Weight Loss
Bleeding tendency
Persistent cough
Change in bowel and bladder habits
Postmenopausal bleeding
Palpable lump
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
Cancer secreted substance, concentration related to size of tumor and its possible spread
Alpha fetoprotein
Normally produced by fetal tissues in the placenta but not adult cells; elevated in primary carcinoma of the liver
Human chorionic gonadotropin
Normally produced by the placenta; elevated in testicular carcinoma
Prostate specific antigen (PSA)
Normally produced by prostate epithelial cells, may be elevated in prostate cancer
Cancer Antigen 19-9
Elevation in pancreatic cancer
Cancer Antigen CA-153
Elevation in ovarian cancer
Tumor Treatments
Surgery
Radiotherapy
Hormones
Anticancer drugs
Adjuvant chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Eliminates cells that divide frequently usually found in: Mouth, skin, hair, bone marrow, digestive tract, kidneys, bladder
Pathology
Study of disease
Autopsies - Indications of Death
Homicide
Suicide
Accidental
Natural
Unknown
Historical Roots of Autopsies
Vesalius - Founder of Modern Human Anatomy
Morgagni - First to propose sign and symptoms were due to findings during autopsies
Virchow - Virchow technique (removal and dissection of organs one by one)
Fluorescein
Fluid used for the identification of blood at crime scene by making blood glow fluorescent
Rigor Mortis
Stiffening or contraction of muscles
Loss of oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production
Begins throughout body at same time
Begins 2 hours after death, maximum at 12+hours, remains for 12 hours, resolves over the next 12 hours (12-12-12 rule)
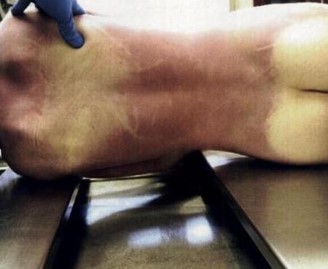
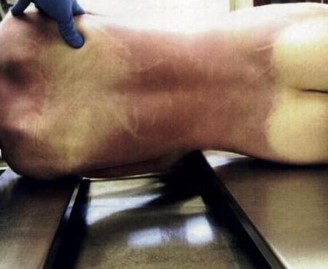
Livor Mortis
Dark “bruise-like” discoloration due to blood settling into dependent parts of the body
Can help determine TOD and can indicate whether a body was moved
A corpse facing upwards will have lividity on back; one laying on left side will have lividity along left side of body
Algor Mortis
Body temperature
Temperature equilibrates between body and surrounding enviornment
Formula: Hrs since death = (98.6 - corpse core temp) / 1.5
Putrefaction
Generalized decay, decomposition
Bloating
Marbling
Insect infestation
Feeding by animals/birds
General Internal Exam
1) Y-Shaped Incision
2) Chest plate removed (Stryker Saw)
3) Organs removed, weighed, examined
4) Calvarium removed, brain removed & weighed
5) Toxicology samples taken
Body Fluids Sampled for Toxicologic Analysis
Bile, Urine, Vitreous Humor (eye fluids best preserved), Blood, Stomach Contents
Serous
Clear, pale yellow
Serosanguinous
Yellow-red with blood
Sanguinous
Bloody
Purulent
Pus containing (exudate)
Pulmonary Embolus
Thromboembolism travels from deep veins of extremities (legs most commonly)