Biomedical Lab prelab Cards
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Absorbance
Absorbance. Units or Optical density,
Absorbance Units known as
AU or OD
Specfic gravity
dimensionless quantity
What Units to use for specfic gravity
Use density units density for calculations
Example of units to use
grams per centimeter cubed (g/cm3) or kilograms per meter cubed (kg/m3)
When is something unitless
ratio of quantities. all units cancel out
dont have true or expresssed units
where do derevied units come from
multiplying,dividing and powering base units
area unit
square meter (m²)
area units used in lab
m² and cm²
volume units
cubic meter (m³)
volume units used in lab
mL and L
speed/velocity units
meter per second (m/s)
speed/velocity units used in lab
m/s, moles/s, millimoles/s
amount of substance concentration unit
moles per cubic meter (mol/m³)
amount of substance concentration unit in lab
molarity (M), mM, nM
temp in unit
degree celicus (c degree sign)
temp in unit in lab
C and F
mass density unit
kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m³)
mass density unit in lab
g/mL
activity of enezyme in unitsAb
katal (one mole per sec)
activity of enezyme units used in lab
moles/time, mMoles/time
absorbance unit
-dont have true unit
other ways to say absorbance
absorance. units or optical density
absorbance abbervation
AU or OD or no units
specfic gravity
-dont have true unit
what does specfic gravity measure
dimensionless quantity
specfic gravity units used in lab
density units if ur dealing with density
OR
grams per centimeter cubed (g/cm³) or kilograms
per meter cubed (kg/m³)
molar concentrations
moles per unit volume
units used for molar concentrations
used units are moles per liter or mL, millimoles (mMoles) per liter or mL and nanomoles (nmoles) per micro liter (mL).
molarity (M)
moles of a substance present in 1000 mL (moles/L) of solution (total volume).
unit of concentration of a molecular species (molecule, ion,etc) in a liter of solution.
how molarity (M) expressed?
expressed in millimoles (mM)
what does solution volume include?
the volume of the solvent and the displacement volume of the solute.
Molarity formula
M = MOL/L = MOL/ 1000mL
What does 1 molar solution mean?
there is 1 mole of a solute in 1 liter of solution.
Normality (N)
equivalents of a substance present in 1 liter (1000 mL) of solution.
Mass in volume ratios
Mass of a dissolved ingredient per volume amount of mixtures containing that ingredient
mEq / per volume
mEq of an electrolyte or salt per unit of volume of solutions containing that electrolyte or salt
Molality (m)
moles (mol) of a solute/kg of a solvent containing that solute
(1 mol of solute per 1 kg of solvent is a 1 molal (1 m) solution)
Molarity (M)
mol of a solute/L of a solvent containing that solute
(1 mol of solute per 1 L of solution of that solute is a 1 molar (1 M) solution)
Normality (N)
1 Eq of solute per 1 L of solution of that solute is a 1 normal (1 N) solution.
normality formula
Molarity × largest valence ion of a compound)
what normality is?
Equivalents (Eq) of a solute/L of a solvent containing that solute
Parts per million (ppm)
Parts of a gas, liquid, or solid per 1 million part of another gas, liquid, or solid containing the first gas, liquid, or solid
% Volume in volume (% v/v)
mL of liquid per 100 mL of a solvent containing that liquid
% Weight in volume (% w/v)
g of a solute per 100 mL of a solvent containing that solute
% Weight in weight (% w/w)
g of a solute per 100 g of a mixture containing that solute
Ratio strength
1:R
|
1 in R
|
X:Y
X parts of one ingredient per Y parts of another ingredient in a mixture
R, X, and Y are whole numbers
ratio
express concentration as parts of the individual components or part of the components in the total mixture.
same units for numerator and denominator so they cancel out
what the unit part of weight
grams
what the unit part for milliliters
mL
molar ratio
ratio of the number of moles of one component in the reaction with the number of moles of another component in the reaction.
molar fraction
number of moles of a component as a fraction of the total number of moles.
Parts per million (ppm)
number of parts (g) per million parts of the total mixture.
units are mL for liquids or grams for solids.
what is Parts per million (ppm) used for?
generally used to express very low concentrations (e.g impurities such as metal ions).
concentration
express as the mass /units volume
percentage concentration
defined as the quantity of the substance in100 parts of the total quantity of the mixture
how can percentage be expressed?
expressed as % w/v, or % w/w or % v/v.
if density known?
% w/v can be converted to % w/w
solution
homogeneous liquid prepared by dissolving a solute(s) in a solvent(s)
Dissolution
the physical-chemical process where a solute (solid, liquid, or gas) disperses into a solvent to form a homogeneous mixture called a solution
aqueous solution
water is used as the solvent or co-solvents
nonaqueous solution
water immiscible organic solvents are used as solvent(s)
simple solutions
single solute in a solvent
way to remember: it’s single like u (me specfically me) :)
compound solution
more than one solute and /or more than one solvent
true solution
solute molecules completely dissolve in the solvent to give a clear, transparent homogeneous liquid
fact about true solution
cannot be separated via filtration and is able to transmit light.
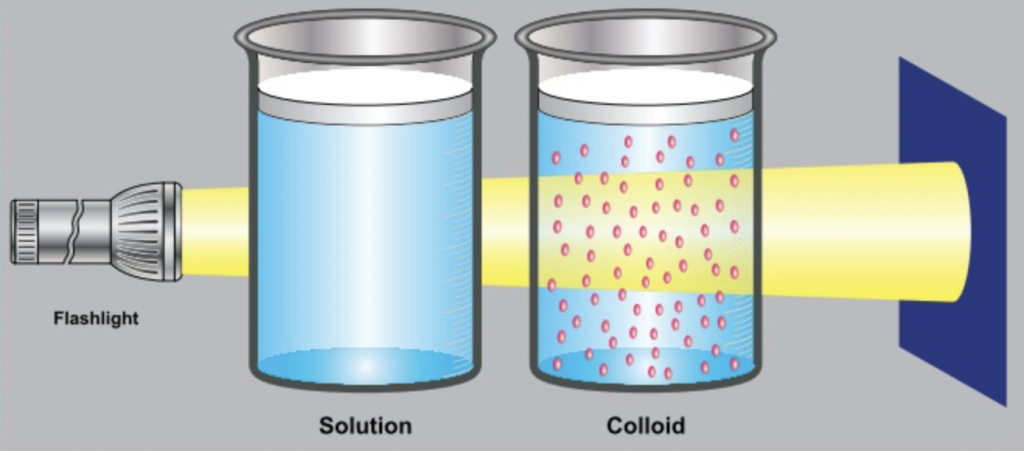
Colloidal solution
visibly clear, transparent homogeneous liquid.
colloidal solution reflects light (Tyndall effect)
Micellar solution
dispersion of micelles in a solvent (most usually water) using a surfactants
what does micellar solution form
clear or cloudy solution depending on the size of the micelles
saturated solution
contains maximum amount of solute in specified solvent volume and temperature
addition of more solute does not increase solubility
unsaturated solution
less than the saturation concentration
Addition of more solute will give clear homogeneous solution
supersaturated solution
Under certain conditions (pH), the equilibrium solubility exceeds saturation concentration
Unstable and easily precipitates or crystalizes
stock solution
concentrated solution which must be diluted before use
mix with water or another solvent to make it apporiate concentration
what is Stock solution
the orginal solution
has the higher concentration and needs to be diluted
what happens when diluted
concentration of the final solution is always lower than that of the stock (original) solution.
How dilution expressed?
Solute : Solvent
Dilution Factor
the factor by which the stock solution or an aliquot is diluted.
Solute: Solution
concentration factor
initial volume divided by the final solution volume.
solute
solid liquid or gas used to form solution with solvent
solvent
the liquid
what does solublity depend on?
depend on ablity of solute to interact and form bonds with solvent
requirement for solute
sufficent energy to overcome intermolecular forces that keep solvent molecules together
solvation
dissolving
solute molecules can diffuse independently through the solution
saturated
maximum solublity
intrsnic solubilty
max amount of solute to dissolve in specfic volume of solvent (saturationn at specfic temp and pressure)
unsaturated
concentration LESS than intersnic solublity concentration
What happens with insoluble compounds?
unable to assoicate with solvent and form bonds with its molecules (remains immiscble or undissolved in solvent)
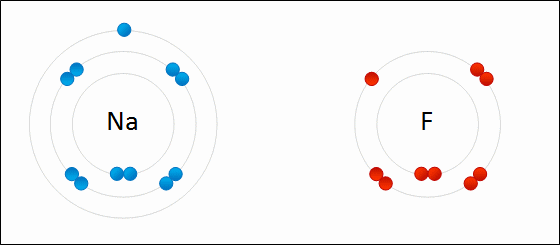
Ionic Bonds
metal atom loses electrons to nonmetal
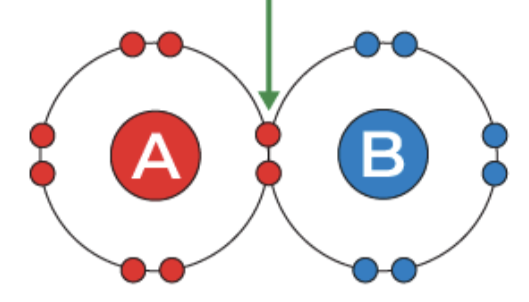
covalent bond
two nonmetals share electrons
Hydrogen bond
Hydron attracts F,O,N
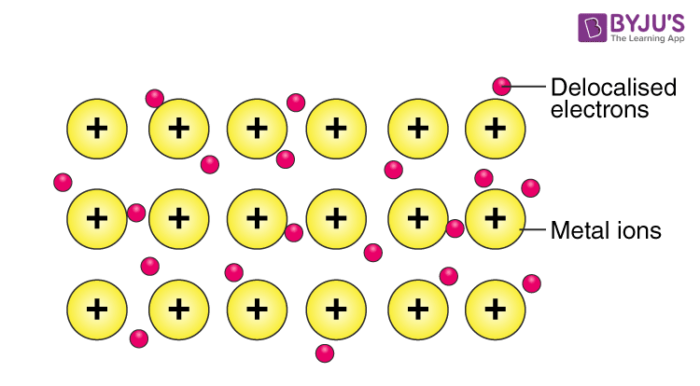
Metallic Bonds
postive metals ions attract conducting electrons
what is mass
measure of the amount of matter in a substance
what is weight
meausre the force of gravity acting on an object
relationship between mass and weight
they are proportional
why is mass and weight proportional
gravitational force on earth is a constant
units
metric units in life sciences is grams (g)
Smaller units used are milligrams (mg), micrograms (the werid looking m g) and nanograms (ng),
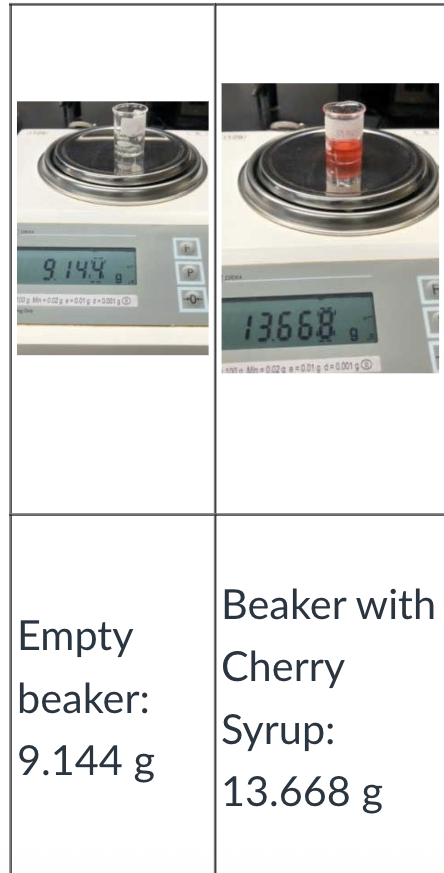
Calculate the weight of the syrup
Beaker WITH SYRUP - Beaker WITHOUT
13.668g - 9.144g
Answer: 4.524g
units
used to provide information about measured entity or result of a calculation