optics 10l review
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
convex lenses
converge
f’ (secondary focus) is on the left side, principal f is on the right side
IN: parallel to pa OUT: through princiapl f
IN: through secondary f OUT: parallel to pa
IN and OUT through optical centre
concave lenses
diverge
principal f is on the left side, secondary is on right (where light seems to not focus)
IN: parallel to Pa, OUT: as if it had come through princiap f
IN: appears to pass through F’, OUT: parallel to PA
IN and OUT through optical centre.
sign convenctions if do, di, ho, hi, f, and m are postivite (lens)
do - always
di - real image, on the opposite side of the lens
ho - always
hi - upright
f - converging, convex
m - upright / virtual
if do di ho hi f m are negative (lens)
do - never
di - virtual (same side of lens)
ho - never
hi - inverted
f - divering, concave
m - inverted / real
where is the digital sensor in a camera on a ray diagram
between princiapl f and 2f, closer to 2f
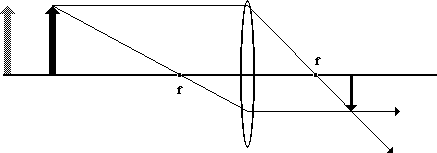
as the object moves closer to the lens, what happens to the height of the image? why? do cameras produce real or virtual images?
it will get bigger, so di gets smaller and the do gets better (inversely related)
produce real images bc because the light rays physically converge on the sensor or film to form the image.
This real image is inverted, but post-processing makes it appear upright for viewing.
The object distance gets smaller because the object is physically moving closer to the lens.
The image distance gets larger because the lens needs to move farther from the sensor to keep the image in focus.
Cameras have a fixed sensor position, so they adjust focus by moving the lens. When focusing on a nearby object, the lens is shifted farther from the sensor to ensure the light rays converge correctly on the sensor plane.
At the same time, the magnification increases, making the image larger on the sensor.
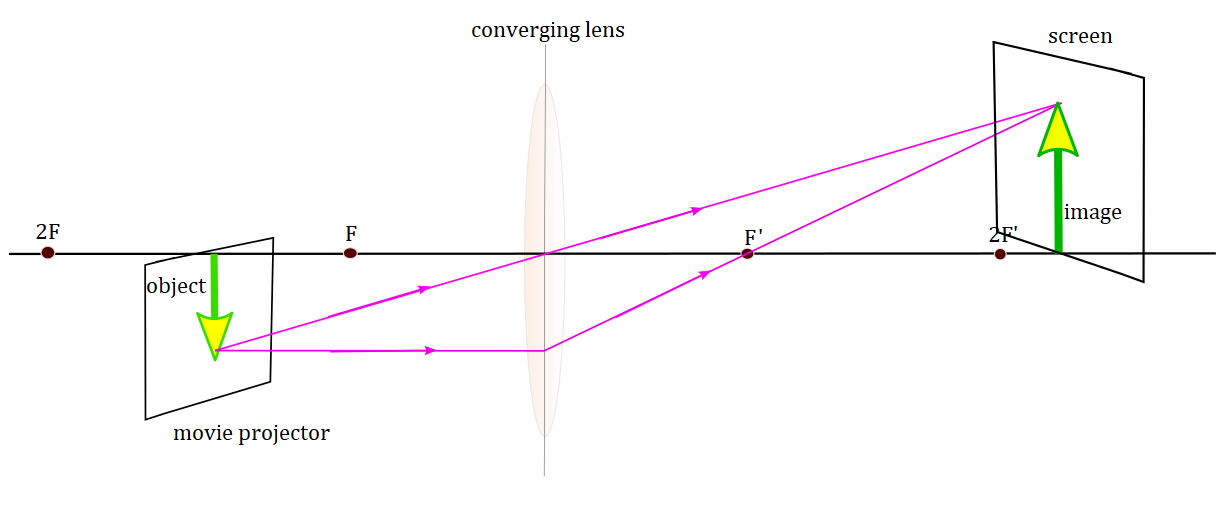
differences and similarties between cameras n projecters
sim - converging, real images that are inverted
differences - projecter is larger, inverted real image of a small object; the object (the film strip) lies between F ʹ and 2F ʹ, and the image is located beyond 2F.
camera - produce a smaller, inverted, real image of a large object; the object is beyond 2Fʹ (to focus properly), and the real image is located between F and 2F in the camera body
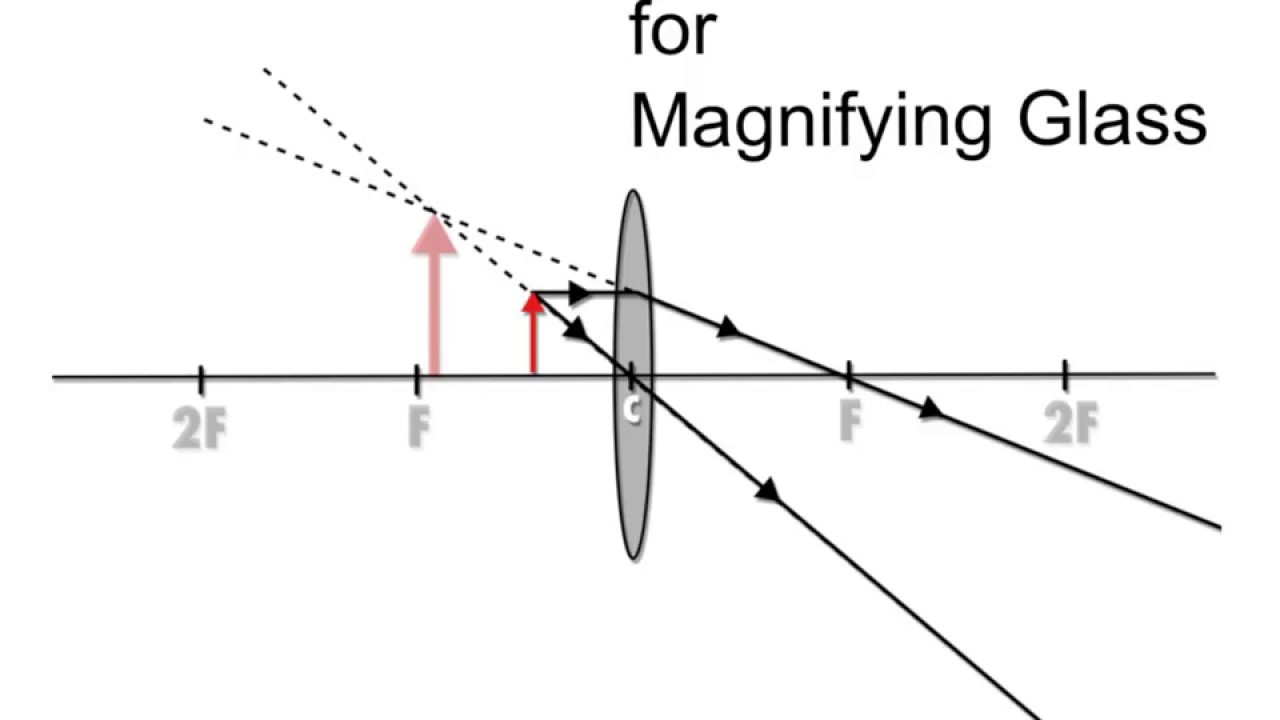
magnifying glass
A magnifying glass, or simple microscope, is a converging lens in
the object is located between the lens and Fʹ.
A larger, upright, virtual image is formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
similarites between a projecter and a magnifying glass and differences
sim - converging lens, produce a larger imagie
projecter -
the obkect (film strip) is between f’ and 2f’,
will produce an inverted real image
image will be produce beyond 2f and its inverted on the screen
magnifying glass -
object between lens and f’
will produce uprigt and virtual image on the same side as the object and
its upright when viewed through lens
for a camera to foucs on a second object further back, shoudld the lens move towards the object or backwards (further into the camera)
further into the camera
The lens needs to move backwards (closer to the sensor) to focus the image correctly.
The image distance decreases as the object distance increases.
This adjustment ensures that the light rays from the object still converge properly on the camera sensor, maintaining a sharp image.
what type of images can cameras use to caputre images
most of the time, real images
old school will alwasy have real images
digutal sensors can make it upright
why can we only focus on 1 point in a camera
because the lens focuses light rays to converge at a single point on the sensor.
Light rays from other distances will not focus properly, causing those objects to appear blurry.
The depth of field allows for a small range of objects to appear somewhat in focus, but only one specific point can be sharply focused at a time.
The point of the lens is to focus light, so it can only focus on one object at a time
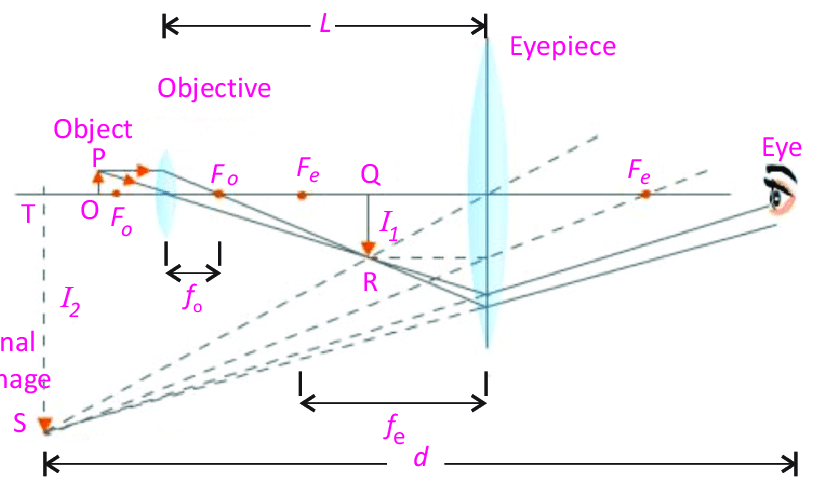
why would the objective lens and the eyepiece lens reversed in a compound microscope not work? why not?
bc it would prevent the microscope from forming a clear magnifed image, you need to create a real image first… the lens postion doesn’t matter tho.
the image formed would be out of focus or inverted,
and the lenses would not perform their intended roles properly in terms of magnification and image formation.
what type of image is produce by each len in a compound microscope? how do u calculate the magnication of an image using a cm?
objective lens is real
eyepiece lens is virtual
multiply the 2 M values
Why would the film strip in a movie projector never be located beyond 2F'?Where is the film strip actually located? Why?
If the film strip is beyond 2F’, the projected image will be too small and upside down.
The film strip is located between F′ and 2F′ to create a large, inverted image that can be projected clearly onto a screen.
why are projecters viewed upright
The projector lens creates a real, inverted image of the film. The film itself produces an upside-down image, and when the light passes through the lens, it also inverts it.
However, the screen acts like a mirror of sorts and reflects the image as it is projected onto it.
Since we are viewing the image from a distance (as viewers sitting in the theater), the inverted image on the screen appears upright to us.
refraction
the change of direction of light when it is entering in a new medium, the speed of light either slowing or speeding up depending on the density of the substance its travelling in
index of refraction
ratio of speed of light in a vacuum to speed of light to a medium
why doesn’t n go below 1?
bc it would imply that the speed of light is going faster than it is in a vacuum which is not possible due to enstian’s theory
c -
fastest light in a vacuum (light can travel)
v -
v and n
speed in a specific medium
v and n are proportional, if n increases, v descreased
apparent depth
Apparent depth refers to the depth at which an object appears to be when viewed from above the surface of a transparent medium (like water or glass).
This is due to the refraction of light as it passes from the water (or another medium) into the air, making the object appear closer to the surface than it actually is.
Explain why the index of refraction of a vacuum is n=1. Use the word “atoms”
and “Snell’s Law
In a vacuum, since n=1n=1, Snell’s Law implies that there is no refraction (or bending) of light as it enters or exits the vacuum from another medium.
This is because there are no atoms in a vacuum to alter the speed or direction of light.
why does n have no units
Because c and v are both speeds and can be expressed in the same units of m/s, the units in the equation divide out, so n has no units.
why does a spoon look discombobulated
Light coming from the part of the spoon below the water’s surface must travel through the water into air.
The speed of light increases as light goes from water into air so, if it hits the water–air boundary at an angle, light will bend away from the normal.
The human brain perceives light to travel in a straight line, so it will project
these light rays backwards to a virtual light
source behind the real spoon
This is similar to how the brain projects
light rays to form a virtual image in a
plane mirror.
why does tir have light bending away from the normal
light needs to bend away from the normal in order for light to reflect back on itself,
because at higher angles of incidence, the light can no longer refract into the less dense medium. Instead, it reflects back into the denser medium, where the angle of incidence and reflection are the same.
why are diamonds so sparkly?
due to the cut of the diamond faces, and the high index of refraction for diamond; results in the total internal reflection of light
Diamonds have a high refractive index, → . This causes a small critical angle of 24.4°, so when light hits the diamond at a steep angle, it reflects. Once light is inside the diamond, it bounces around within the diamond because of its high refractive index and the way it has been cut. Here’s where TIR comes in:
When light tries to exit the diamond (moving from denser diamond to less dense air):
If the angle of incidence inside the diamond is greater than the critical angle (~24.4° for diamond-air), total internal reflection occurs.
The light reflects back inside the diamond instead of escaping.
fibre optics are used for
Fibre optics uses light to send information through a glass cable.
To keep the light from escaping, the cable needs a small critical angle.
This ensures that the light stays inside the cable by reflecting off the walls.
Materials like high-purity glass and certain plastics, like Lucite, have a small critical angle and are used for this purpose.
fibre optics use and endoscopes
Fibre optics is used in:
(phones, computers, TVs)
(for lighting the instrument panel in cars)
(for viewing inside the body)
Endoscope: A fibre-optic device used by doctors to check the health of internal organs.
It has two fibre-optic bundles:
One sends light into the body.
The other carries the reflected light back.
Colonoscopy: A common procedure for people over 50, where an endoscope is used to check for growths in the colon that could lead to cancer.
triangular prism
A triangular prism also causes total internal reflection.
The critical angle for glass is about 41.1°. If the angle of incidence is greater than 41.1°, light will reflect completely inside the prism.
Prisms are more effective than mirrors for reflecting light because they reflect almost 100% of the light, while mirrors lose some light through absorption and wear over time.
Optical devices like cameras and binoculars use prisms instead of mirrors.
The light leaving the prism can be 90° or 180° from the incoming light, depending on how the prism is positioned.
properties of light
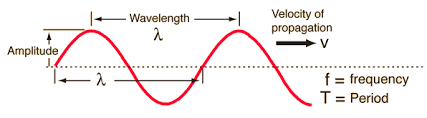
light energy travels very fast (c = 3.0 × 10^8 m/s)
light travels in a straight line but also as waves (electromagnetic waves)
radiates (no medium needed)
transferred throguh radiation
electromagnetic spectrum
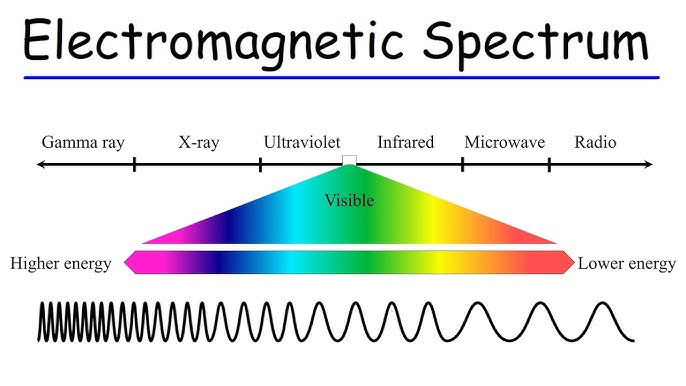
red has long waves but low energy
violet has high waves and high energy
radiation
form of electromagnetic energy ex. sunshine, x rays, radiant heating systems
light energy
form of electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength
photons - tiny packets of energy produced from the movement of atoms
incandescence (heat)
production of light as a result of high temp.
electric discharge (electrons changing orbits)
process of producing light by passing an electric current through a gas
ex. lightning, neon lights
fluorescence (phosphors — hg → UV → phosphors) immediate
immediate emission of visible light, a result of the absorption of UV light
ex. clothes that glow in black light
phosphorescence (slow release)
producing light by absorption of UV light, resulting in the emission of visible light over an extended period of time
ex. glow in the dark stickers
chemi and bioluminscence (chemical reaction)
direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction w little or no heat produced
chemi - ex. ) glow sticks
triboluminscennce (friction)
production of light from friction, result of scratching crushing or rubbing certain crystals
ex.) rubbing quartz crystals , biting lifesaver in dark
led (semiconductors one direction)
light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in semiconductors
ex.) Christmas lights
laser
has one continuous straight line, same wavelength so same colour
normal
perpendicular line to a mirror surface, 90 degrees to a mirror
laws of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Oi and Or and normal lies in the same place
SALT
size - large small same
attitude - upright or inverted
location - object / image
type - virtual or real
virtual - light doesn’t meet and doesn’t interept usually the same orientation as an object can’t be projected, divergent
real - light converges and meets at a point
pros and cons of incandescent light
very bright, cheap, easy to make
cons - waste energy by producing more energy to heat, becomes hot, inefficient, unsafe
why use a coil of a wire in a incandenset bulb rather than a straight wire
allows electrons to resist and is compact in the bulb (a straight wire would need to be long to have the same reisitance as a coil)
not enough resistance the light doesn’t emit, too much and the light will overheat and break
how is biolumiencese used in medicine
idtinfy tumors and rapid growing cells
freq. of microwave
speed of light
2450MHz
freq. x wavelength = speed of light
294 million m/s
electromagnetic wave spectrum order highest to lowest
increase in photon energy, decrease in wavelengths
gamma → x rays → ultraviolet → visible light → infrared radiation → microwaves → radio waves
applications for electromagnetic types of light
gamma - used in cancer radiation treatment
x rays - used to see through the body
ultraviolet - gel manicures
visible light - sunlight, any light we can see
infrared radiation - remote controls, fibre optic cables
microwaves - microwaves, wi-fi routers, bluetooth
radio waves - am and fm radio broadcasting, tv broadcasting, gps
why is Rudolph’s nose red n not blue?
Red light scatters less in fog and snow compared to blue light, which is why red is used for stop signs and tail lights.
meaning a blue glow would be harder to see in fog or snowy conditions.
what is ‘scattering’
light waves interact with small particles; causing the light to spread out in different directions.
The # of scattering depends on the wavelength of the light.
Shorter wavelengths (like blue or violet light) scatter more because they are closer in size to the particles causing the scattering.
Longer wavelengths (like red light) scatter less because they are much larger than the particles and pass through more directly.
y is the sky blue.. why r sunsets red
sunlight passes through the atmosphere. The blue wavelengths of sunlight scatter in all directions, making the sky appear blue.
At sunrise or sunset, the sun is lower in the sky, so light travels through more atmosphere. The blue light scatters out, leaving the longer red and orange wavelengths, which is why sunsets are red.
he sky doesn't appear violet because:
The sun emits less violet light compared to blue.
Our eyes are more sensitive to blue light than violet light.
electro magnetic spectrum in order of colours
ROYGBIV
Red light - longest wavelength, less scattered, used for low-light conditions or to penetrate through fog and mist like stop signs
organe - we use red for ultmiate emergencies, but the things that we still need to see like warning signs
yellow - most visible colour in daylight so we can see school buses
green -It’s a color that signals go or approval, and it contrasts well with red and yellow.
blue -Blue is calming, yet it stands out in dark environments and is associated with authority for police