Soils and Engineering
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
The two systems of soil classification
Pedological Classification - Soil Weathering, texture, chemistry, profile thickness, etc
Engineering Classification - Soil texture, degree of plasticity (Atterberg Limits)
Overview of Mechanics
As water content increases, the shear strength decreases
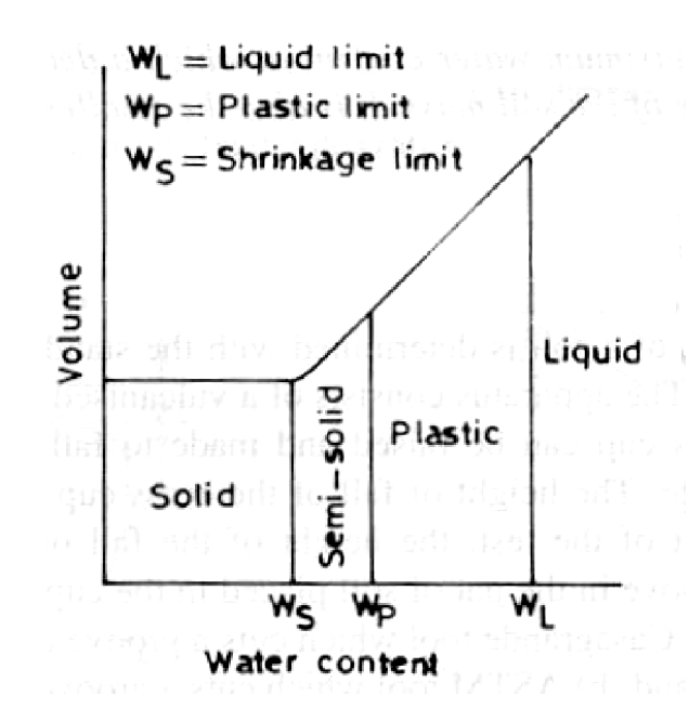
Plastic Limit
Water content at which the soil is a plastic
less water content than liquid limit
wide range of shear strengths at plastic limit
defined as the moisture content % at which the soil begins to crumble when rolled into 1/8 diameter threads.
Liquid limit
soil is practically a liquid
shows minimal shear strength
defined as the moisture content required to close a distance of 0.5 inch along the bottom of a groove after 25 blows of the liquid limit device
Plasticity index (PI)
difference between liquid limit and plastic limit
important measure of plastic behavior
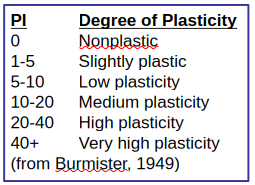
PI vs Degree of plasticity
Unified system - classification scheme - symbol v soil type and index property

Unified system procedure
Determine the percent passing through the #200 sieve (boundary between sand and silt/clay)
if less than 50% passes, then it is a coarse grained soil (gravel and sand)
if greater than 50% passes, then it is a fine grained soil (silt and clay)
Father of soil mechanics
Carl Terzaghi
Voids lead to
lead to settling when pore space within the soil mass decreases under heavy loads - structural cracks or complete failure
objective of soil compaction
decrease void space and increase density - improves strength and volume stability