Seed Plant Final Vocab
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
cultivation
behaviors involved in managing plant resources (clearing, burning, plowing, selective breeding, planting, and harvesting)
domestication
type of evolution in which selection occurs under human influence
artificial selection
an evolutionary process in which humans consciously select for or against particular features
genetic engineering
modify the genes to enhance the capabilities of the organism beyond what is normal
transgene
an artificial, manipulated gene, that incorporate all appropriate elements critical for gene expression, derived from a different species
CRISPR
a technology to selectively modify the DNA/ edit the genes of living organisms
transient expression
the production of a recombinant protein over a short period (1–14 days) following DNA transfer (temporary expression of genes)
molecular farming
the production of pharmaceutically important and commercially valuable proteins in plants (instead of food, feed, or fiber)
medicinal products
substances or combination of substances that is intended to treat, prevent or diagnose a disease
secondary metabolites
substances manufactured by plants that make them competitive in their own environment
major developmental hormones
Six main types: Auxins, abscisic acid (ABA), cytokinins, ethylene, gibberellin (GA), and brassinosteroids (BR)
defensive hormones
regulate plant defence to pathogens →salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) (sometimes ethylene and ABA)
polar transport
directional cell-to-cell transport of functional molecules, enables plants to sense and respond to developmental and environmental signals
PIN proteins
drive directional auxin flow through their polar localization within the cell
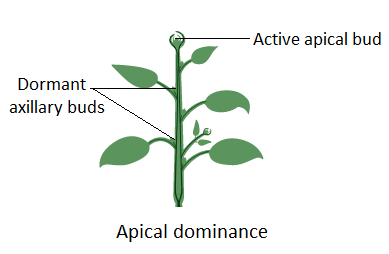
apical dominance
central stem of the plant is dominant over (i.e., grows more strongly than) other side stems
conjugation
the transfer of DNA in a site- and strand-specific manner from a donor to a recipient cell (typically in bacteria)
biosynthesis
the process by which living things use chemical reactions to create products useful for cellular metabolism
the final products are macromolecules
catabolism
the set of metabolic processes that break down large/ complex molecules
senescence
the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics (like aging)
triple response
an adaptation that enables seedlings to overcome obstacles, such as debris, and successfully emerge into the light during germination
expansins
small extracellular proteins that promote turgor-driven extension of plant cell walls
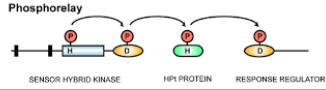
phosphorelay
aids phosphoryl group transfer to initiate a change in cell state or activity
auxin
involved in cell elongation
can change the pH of the wall, allowing the wall to expand
has a nucleus receptor
directly alters cell physiology
can release repression
involved in leaf abscission (fall off in fall)
cytokinin
involved in cell division
natural & synthetic types
in RAM →lateral bud stimulated apical dominance, stimulates leaf expansion, delays leaf senescence, enhances stomatal opening (in some species)
has a plasma membrane receptor
involved in a signaling cascade, phosphorelay to release repression
ethylene
gaseous hormone
promotes fruit ripening
homeostasis is controlled by biosynthesis → triple response: reduced elongation, hypocotyl swelling, apical hook exaggeration
involved in leaf abscission (fall off in fall)
has an ER receptor
involved in a signaling cascade
can release repression
abscisic acid (ABA)
synthesized in chloroplasts (plastids) of leaves
water regulating
inhibits shoot growth and effect of gibberellins (GA)
can be inactivated through oxidation & conjugation
water stress promotes signaling
releases into cytoplasm when needed
plasma membrane and cytosolic receptors
directly impacts transcription factors
release of repression (if snRK2 pathway is present)
direct physiological impact → tugor pressure and ion channels
calcium & nitric oxide signaling cascades
Gibberellins (GA)
promotes germination
induces maleness in dioecious flowers
induces fruit development w/out seeds
biosynthesis occurs in specific tissue
excess GA stimulates GA-inactivating enzymes
directly impacts expansin enzymes -. stimulates cell elongation
nucleus receptor
release repression
Brassinsteroids (BA)
steroid hormone, specifically paracrine
promote shoot growth (along w/ auxin)
differentiation of vascular development
transportation isn’t a big deal
excess BR stimulates BR-inactivating enzymes
conjugation allows for some reversible storage
Low BR → BIN2 is active (p)
High BR → BSU1 and BSK5 are active(p) (BIN is removed and transcription is activated)
plasma membrane receptor
phosphorelay
release repression
tropism
the movement of plants or their parts in a particular direction in response to an external stimulus
phototropism
the growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus
phototropin
the blue light receptor for phototropism
an indicator of “good” light
gravitropism
the growth of the plant in a specific direction in response to gravity
positive gravitropism ex.→ roots
negative gravitropism ex.→ stems
starch-statoliths
specialized starch-containing plastids (amyloplasts), found in the root cap
sense gravity
hydrotropism
the growth of plant structures towards (+) or away (-) from moisture
thigmotropism
the growth of a plant in response to movement or touch
thigmomorphogenesis
the response by plants to touch, to alter their growth patterns
circadian rhythm
a natural cycle of behavior and physical changes which repeats daily
is regulated
anticipates daily occurences
cryptochrome
a photoreceptor that is sensitive to blue light and regulates the circadian rhythm
phytochrome
a class of photoreceptor proteins that respond to red light and far-red light
control many aspects of plant development (like germination)
photoperiodism
the physiological reaction of organisms to the length of light or a dark period (can be daily or seasonal)
etiolation
the process in which plants grow long, pale and unhealthy due to lack of light
dormancy
the state of a plant when growth, development, and physical activity are temporarily stopped
nastic movements
non-directional responses to stimuli that occur rapidly (ex. sensitive mimosa plant)
thigmonastic movement
non-directional response to touch (a type of nastic movement)
pulvini solar tracking
the orientation of a plant towards the sun and following it throughout the day
done by pulvini, a joint-like structure which can cause movement of plant organs via changes in turgor
heliotropism
the directional growth of a plant in response to sunlight