
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Crystal
solid material with a definite repeating pattern, occurring in a specific order
Mineral
a naturally occurring, inorganic, crystalline solid with a narrowly defined chemical composition and characteristic physical properties
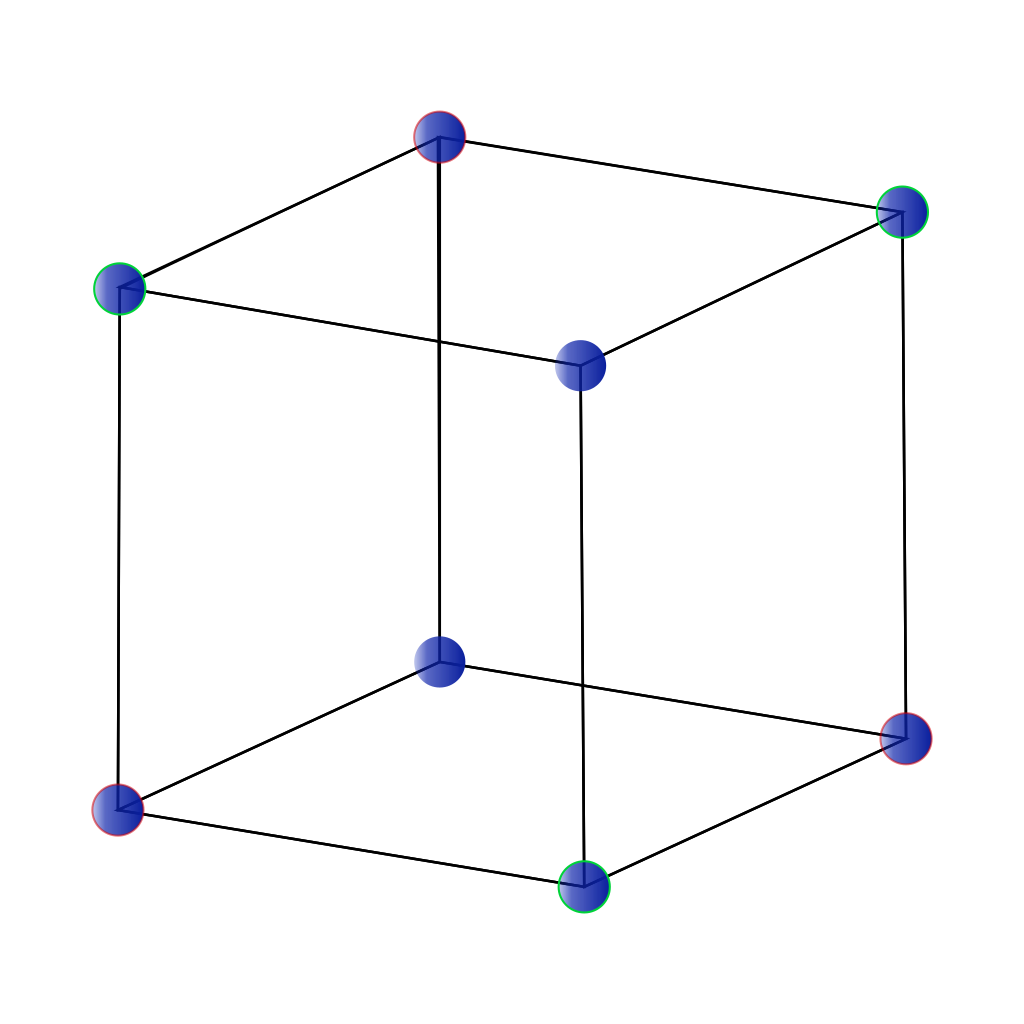
Cubic Crystal
Tetragonal Crystal
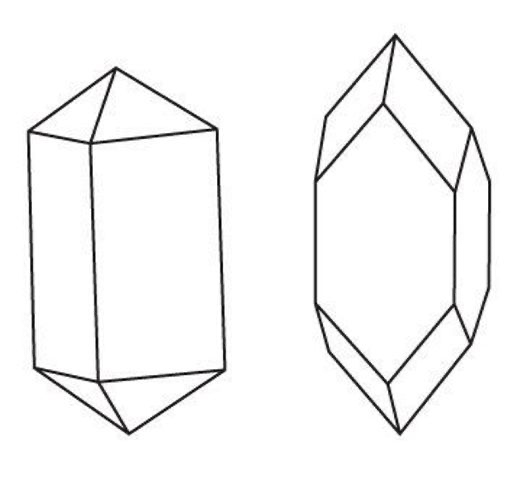
Triclinic Crystal
house-shaped crystal
Monoclinic Crystal
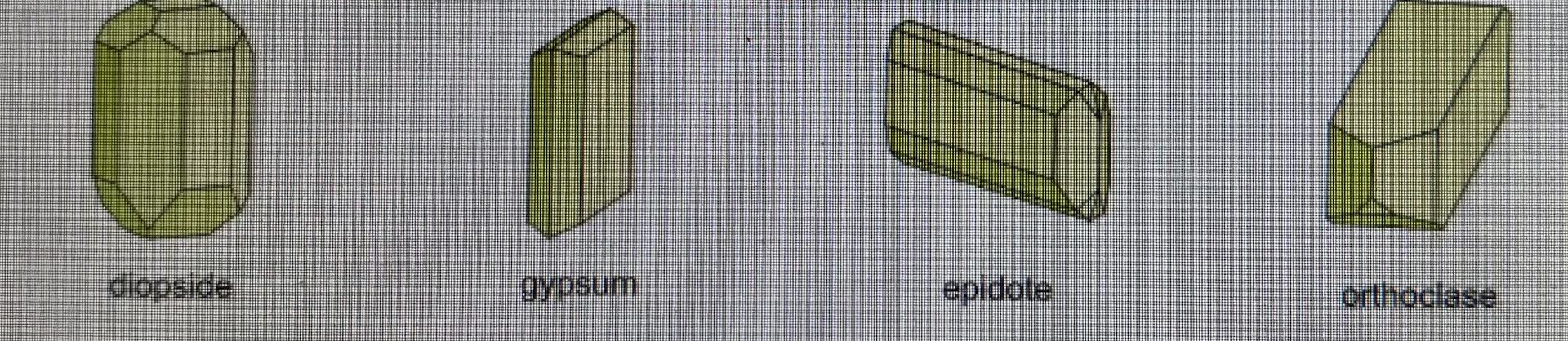
hexagonal crystal
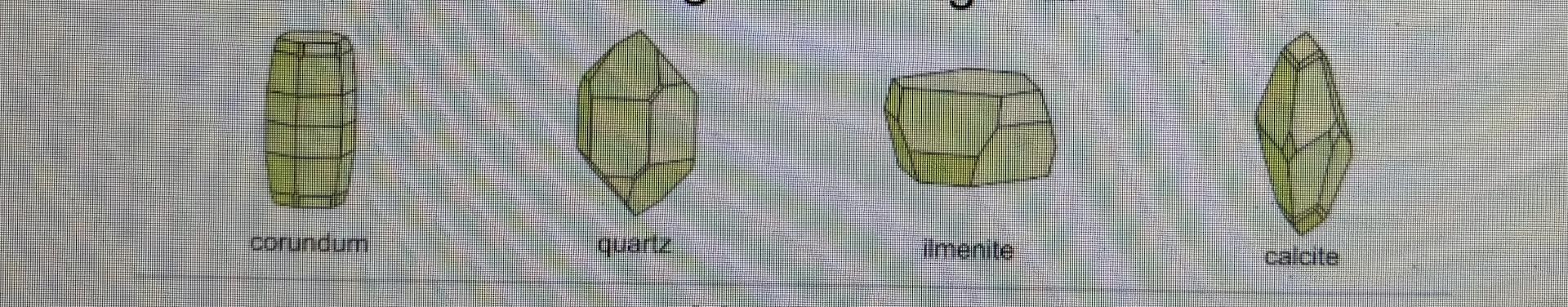
Orthorhombic crystal
Color
Physical property — color of the mineral
Streak
Physical property — color of a fine powder from the mineral
Hardness
Physical property — how resistant the mineral is to scratching
Luster
Physical Property — How light reflects from the mineral surface
Cleavage
Physical Property — breaking of the mineral along lines of crystallographic weakness; may be zero or multiple directions
Fracture
Physical Property — How the mineral breaks, not due to crystal structure; conchoidal is common
Specific Gravity / Density
Physical Property — a measure of the mass of mineral per unit volume (space it takes up)
Crystal Form
Physical Property — the ideal shape of the mineral from the arrangement of atoms in the crystal lattice structure
Crystal Habit
Physical Property — A distinctive shape from growth of the mineral
Magnetism
Physical Property — Being Magnetic
Acid Reaction
Physical Property — When dilute hydrochloric acid is placed on a mineral containing carbonate, a reaction occurs where CO2 is produced
Taste
Physical Property — halite is salty, sylvite is bitter, clay minerals stick to your tongue
Odor
Physical Property — What the mineral smells like
Feel
Physical Property — How the mineral feels (soapy, greasy, rough)
Facets
How a crystal WANTS to break
Crystal Lattice
a definite, repeating pattern in crystals
Felsic
silicate minerals, magma, and rocks which are enriched in the lighter elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium
Mafic
igneous rock or magma that is relatively high in magnesium and iron content
Igneous/Magmatic Rocks
Rocks formed from crystalized/solidified magma (molten rock)
Sedimentary Rocks
rocks formed from bits and pieces of sediment
Metamorphic Rocks
rocks produced from other rocks, generally beneath earth’s surface, by heat, pressure, and chemically active fluids
Silicates
Minerals that have Oxygen and Silicon, most common on earth
Siliciclastic sedimentary rocks
cemented quartz grains with varying grain size.
Chemical sedimentary rocks
formed by (bio)chemical precipitation carbonates, evaporites, iron-rich, phosphates.
Biochemical sedimentary rocks
formed from organic processes
Volcanic Sedimentary rocks
sedimentary rock UNDER igneous rocks
Non-foliated Metamorphic rocks
rocks that have no layers
Foliated metamorphic rocks
planar arrangement of layers within a metamorphic rock
Fossil
any preserved remains, impressions, or traces of a living organism from the geological past
Fossilization
when after death, the organism’s tissues are replaced by minerals
Trace fossilization
disturbed sediments preserved through diagenesis
Permineralization
Permeate the pore space and crystallize. Occur in porous tissue such as bone and wood.
Recrystallization
involves a change in crystal structure, NOT chemical
Replacement
substitution of original skeletal material
Carbonization
the organism is preserved as a residual, thin film of carbon
Molds/casts
the organism leaves an imprint in the sediment
Index fossil
allow geologists to correlate sedimentary strata from different locations
Importance of the Ediacaran Biota
represents the earliest known assemblage of complex multicellular organisms
Cyanobacteria
caused the Great Oxidation
Trilobites
filter-feeders
Sponges
Single-organism
Cnidaria
Major reef-builders
Ostracods
easily fossilized
Brachiopods
peaked in the Paleozoic
Bryozoan
often resemble coral
Crinoids (Echinodermata)
sessile filter-feeders
Conodonts
lived for around 300 million years
Graptolites
colonial filter feeders
Cephalopods (Orthoceras)
long, straight shell
(Gastropods and Bivalves)
appeared in Ordovician
Armored Fish
appeared in Devonian
Shark
appeared in early Jurassic
Precambrian era
Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic
Paleozoic era
Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, Permian
Mesozoic era
Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
Unconformity
a break in time in an otherwise continuous rock record
silicate structure
4 oxygen atoms surrounding a silica atom
Nesosilicates
simplest silicates; single tetrahedrons like the picture above; ex. Olivine, garnet, zircon.
Sorosilicates
two tetrahedrons joined at a single corner (each tetrahedron sharing 1 oxygen); ex. Epidote and allanite.
Cyclosilicates
tetrahedrons sharing 2 oxygen corners each, forming rings; ex. Beryl and tourmaline.
Inosilicates
double/interlocking “chained” lines of tetrahedrons; ex. Pyroxene and amphibole.
Phyllosilicates
continuous sheets of tetrahedrons, each sharing all three corners; ex. Kaolinite, talc, muscovite, and biotite.
Tectosilicates
three-dimensional interlocking of tetrahedrons, where all 4 points are sharing oxygens with other tetrahedrons; ex. Quartz and orthoclase.