Supply, Demand, and Equilibrium
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Surplus
price is above the equilibrium price, meaning producers have excess goods (Qs > Qd)
Shortage
price is below the equilibrium price, meaning consumers want to buy more of a product than producers are currently producing

Equilibrium price
the price level where Qs = Qd

Double shift
simultaneous changes in demand and supply
Consumer surplus
the net gain to buyers, equal to the difference between the buyer's willingness to pay and the price
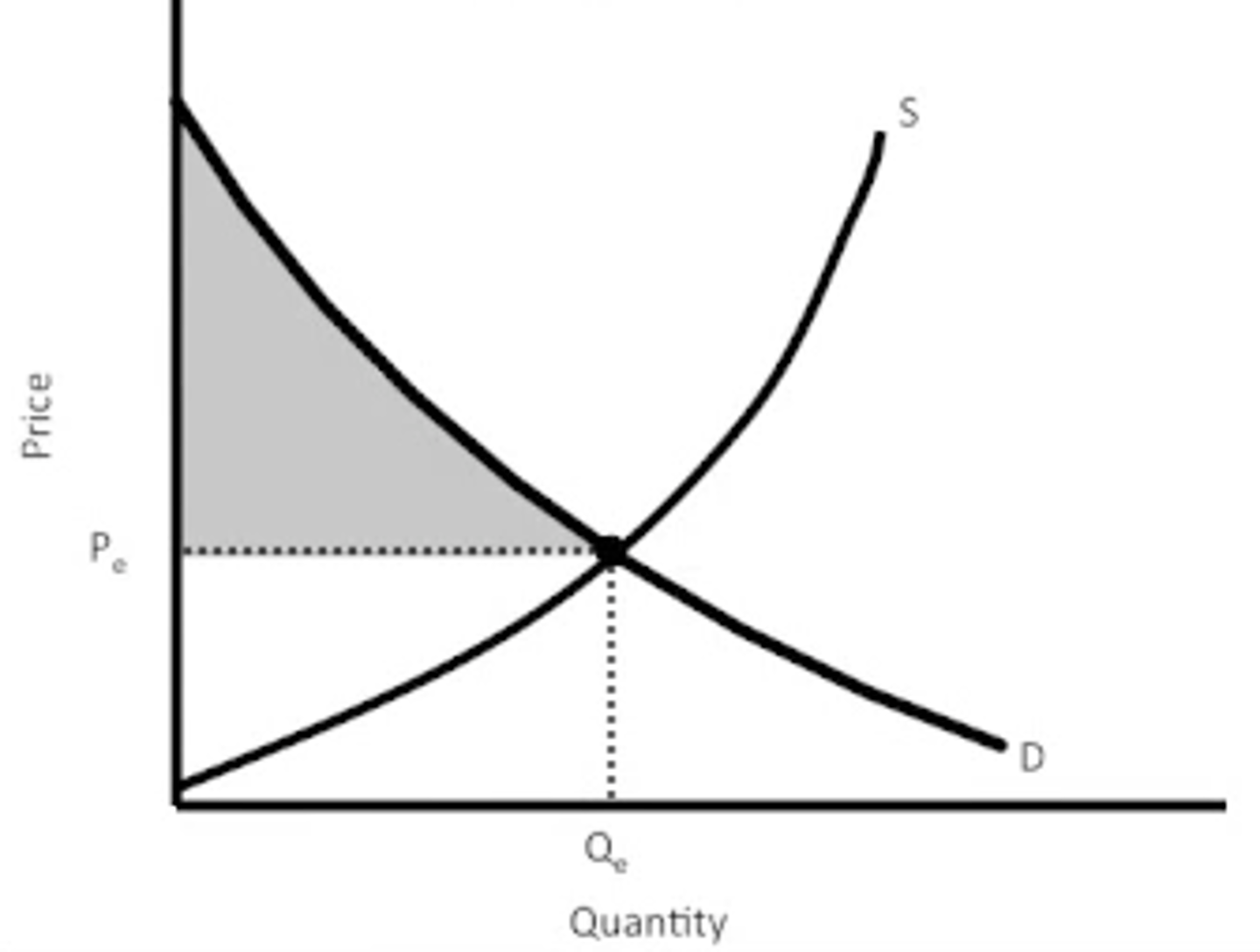
Producer surplus
the net gain to an individual from selling a good; it is the difference between the cost of producing the good and price received

Benefits of the Price System
1. Information
2. Incentive
3. Choice
4. Efficiency
5. Flexibility
information
pricing system conveys information to producers and consumers
Incentives
high prices encourage producers to produce, low prices encourage consumers to buy

Choice
the pricing system encourages many producers to enter the marketplace allowing choice among differing product
Efficiency
1. tells producers how to use resources - what has a high price (is needed) producers will produce more of that good
2. Price system allows consumers to choose how to best allocate their money to maximize their utility
Flexibility
market can respond to the supply and demand - changes in scarcity - of goods by raising or lowering the price
Ultimate Goal of a Firm
maximize profit
Revenue
the income firms make from normal business activities, usually the sale of goods and services to customers
Proft
total revenue - total cost
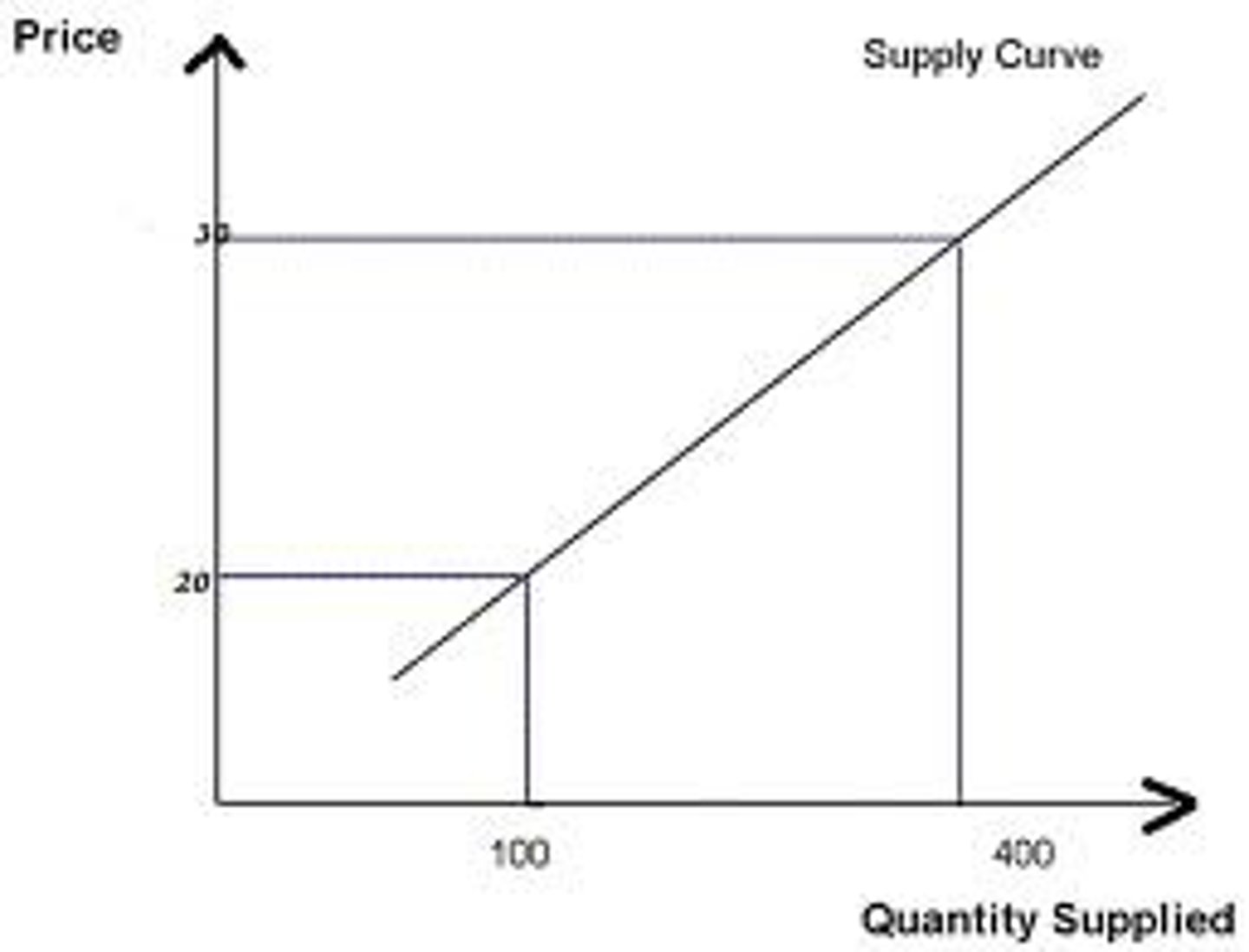
Supply
entire relationship between the price of a good and the quantity that producers are willing to sell
Quantity Supplied (Qs)
the amount of a good that will be supplied at a single, given price
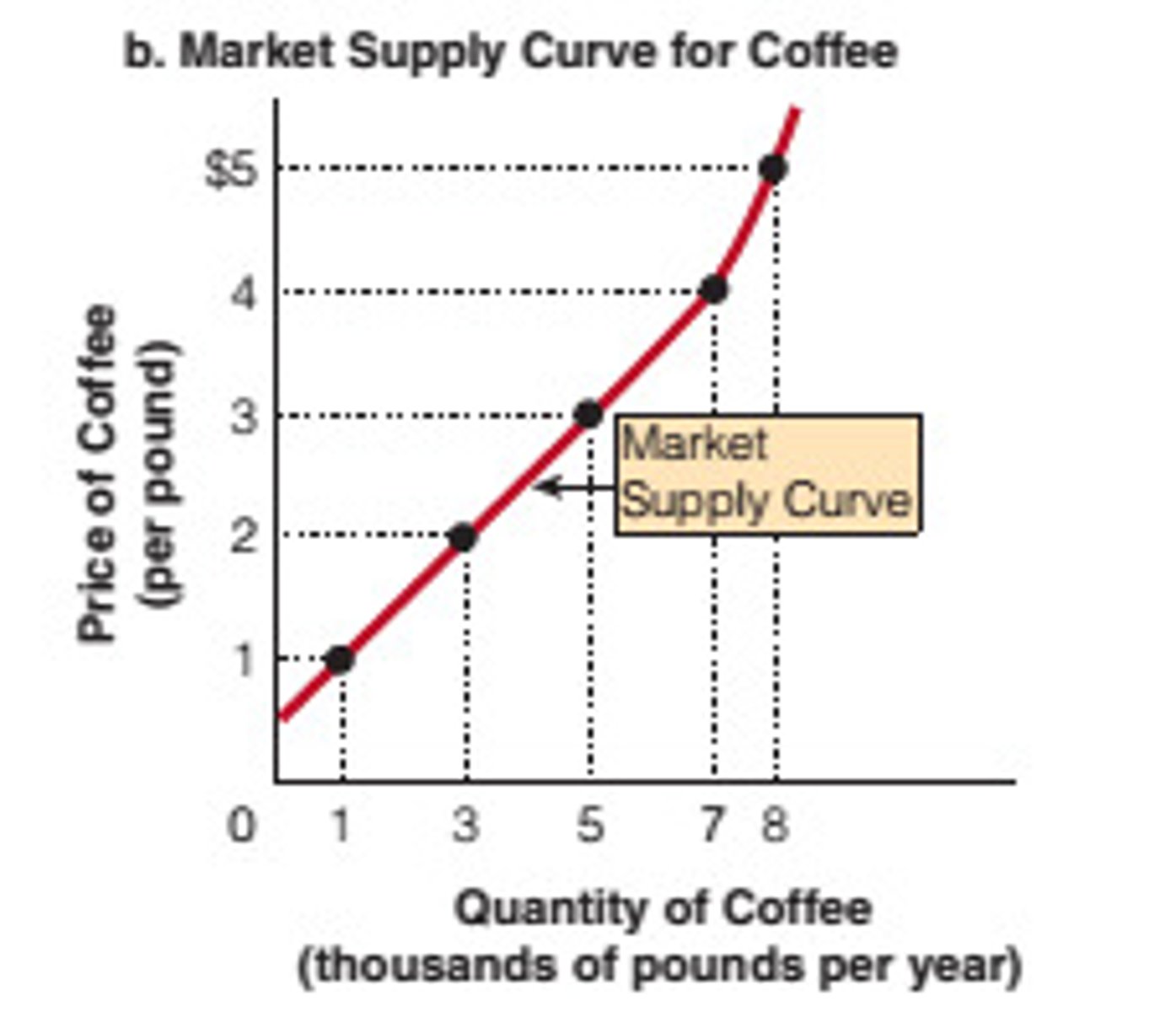
Law of Supply
as the price of a good or service increases, the Qs increases and vice versa
Endogenous variables
price and supply/demand (anything in the graph)
Exogenous Variables
outside the graph (influencers, income changes, etc.)
Shifters of supply
1. Price of an input resource changes
2. Price of substitute in production
3. Price of complement in production
4. Technological change
5. Number of producers/competitiveness of market
6. Expectations about price
Input resource price change
1. An input resource is a resource used in production of a good (land, labor, capital)
2. If the cost of an input increases, the total cost increases and decreases profit, so firms produce less product (shift left) and vice versa

Price of a substitute in production
1. Substitutes are two or more goods that can be produced using the same factors of production
2. If the price of a substitute in production decreases, then the supply of the original good will increase (shift right) and vice versa

Price of a complement in production
1. Complements are two or more goods that are jointly produced using a given resource
2. If the price of a complement in production increases, the supply of the other good will increase (shift right) and vice versa

Technological Change
1. Products that make producers more efficient
2. New technology will increases profit over time because it would make a firm more efficient and lower its cost (shifts right)

Number of Producers (Competiveness of Market)
If more producers enter the marketplace, the supply of a good will increase/shift right and vice versa

Producer expectations about price
If producers expect the price of a product to rise in the future, they will hold back their inventory (shift left) to sell at a high price in the future and vice versa

Subsidies
direct payments to encourage the production of a certain good or service

Taxation
1. a mandatory payment to the government to fund services
2. an increase in a tax on producers will decrease supply (shift left) and vice versa
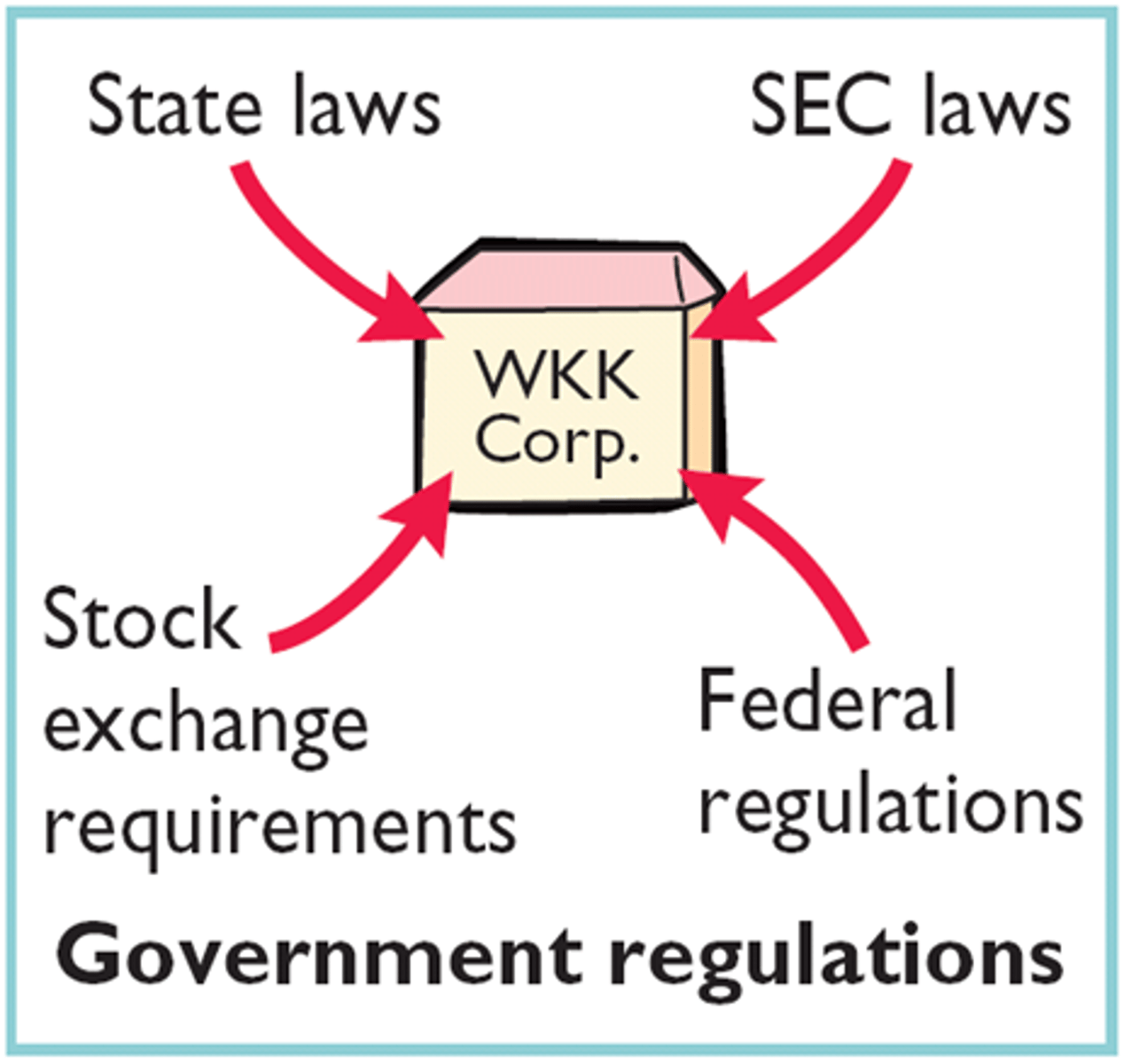
Government regulations
1. laws that control the way businesses can operate
2. Increase in government regulations = decrease in supply and vice versa
Elasticity of Supply
sensitivity of Qs to a change in price
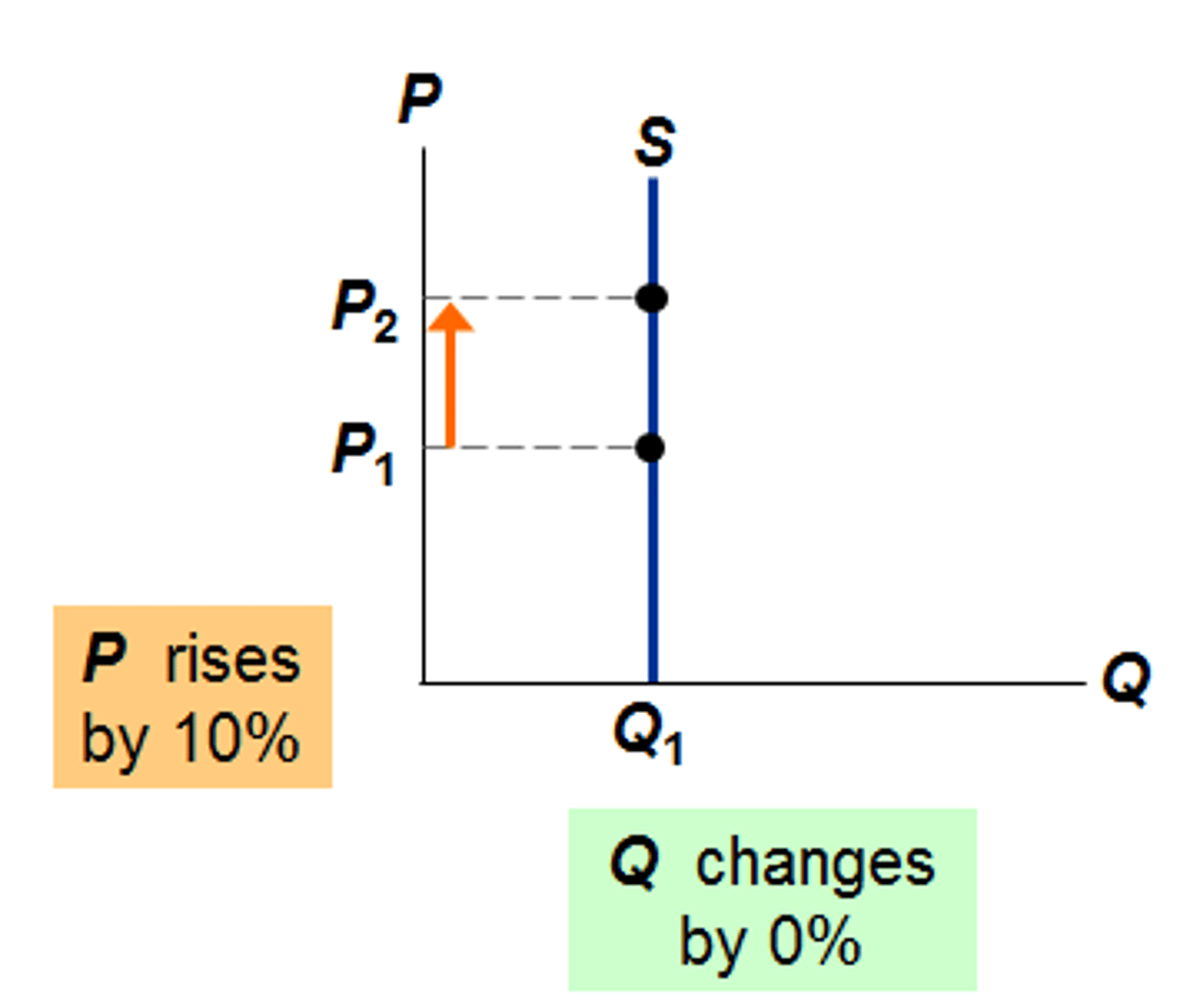
Inelastic supply
exists when Qs is insensitive to a change in the price level (expensive, scarce resources, lengthy production time)
Elastic supply
exists when Qs is very sensitive to changes in the price level (inexpensive, easy & quick to produce, accessible resources)
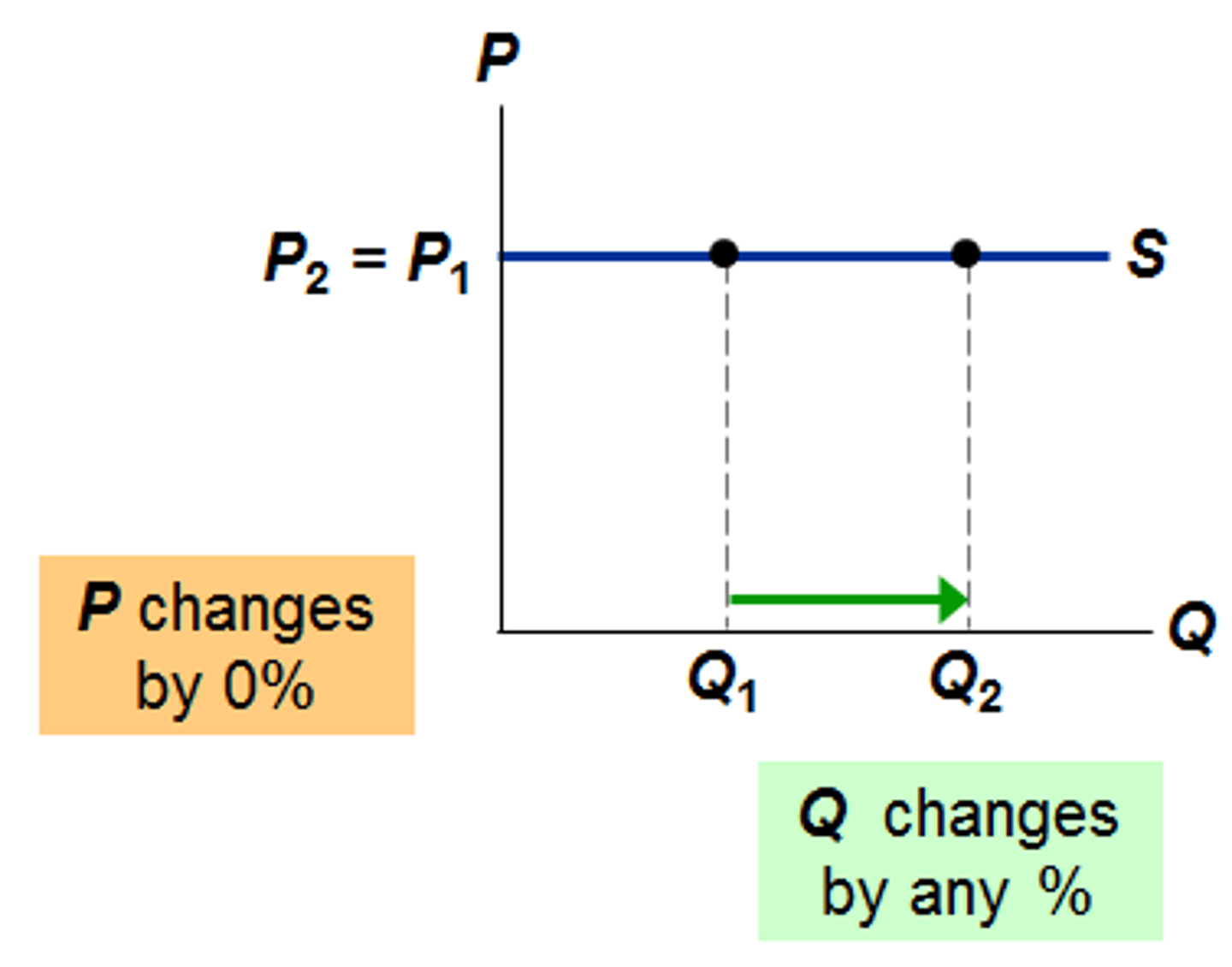
Demand
shows how much of a good or service consumers will be willing and able to buy at various prices
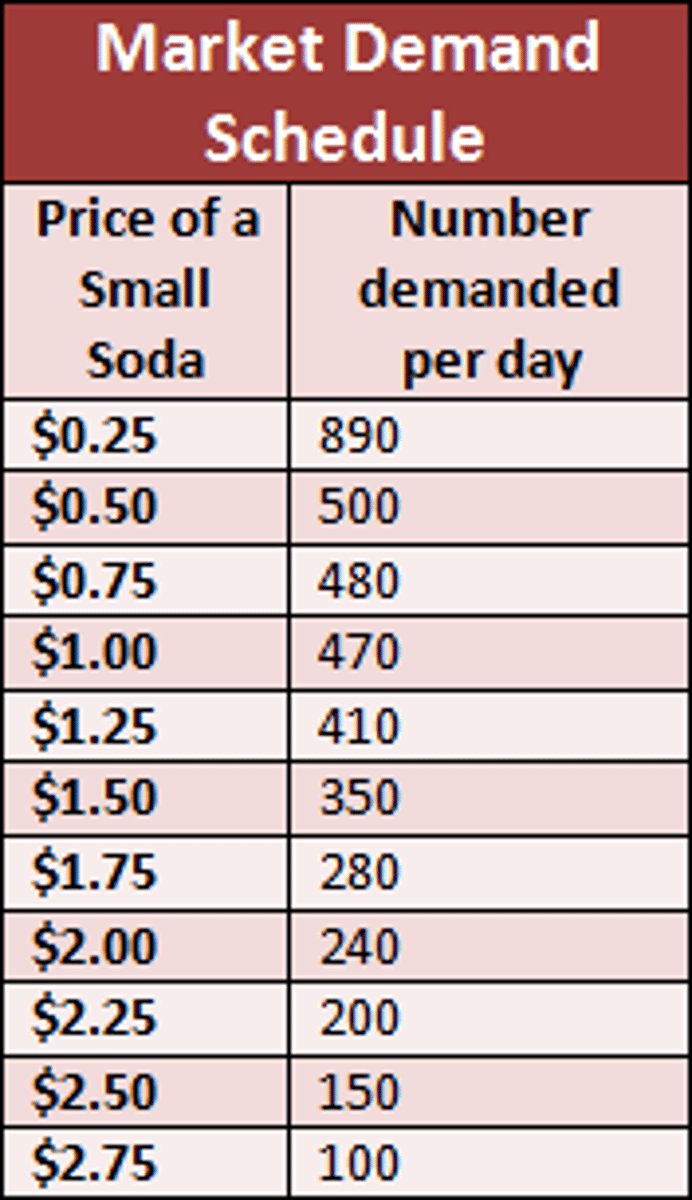
Quantity Demanded (Qd)
shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy at a specific price
Individual Demand Curve
illustrates the relationship between Qd and price (P) for an individual consumer
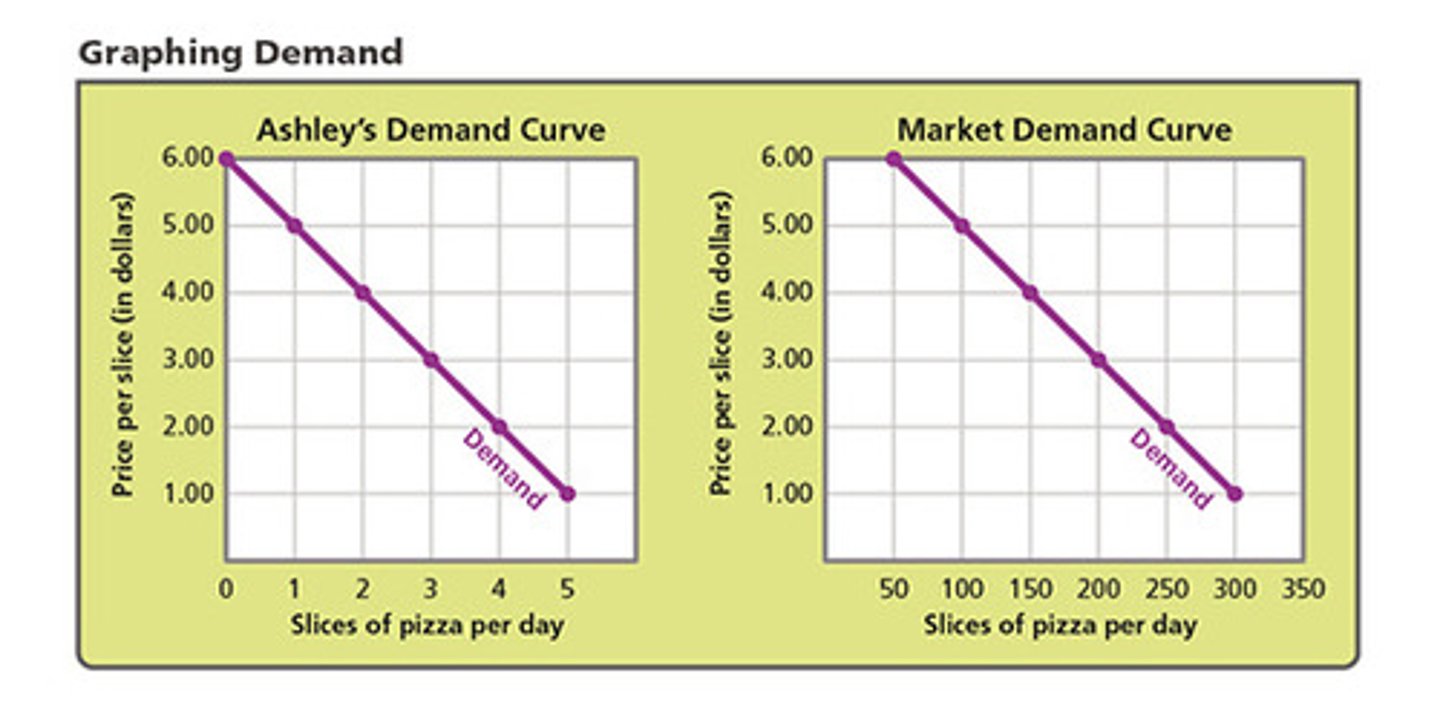
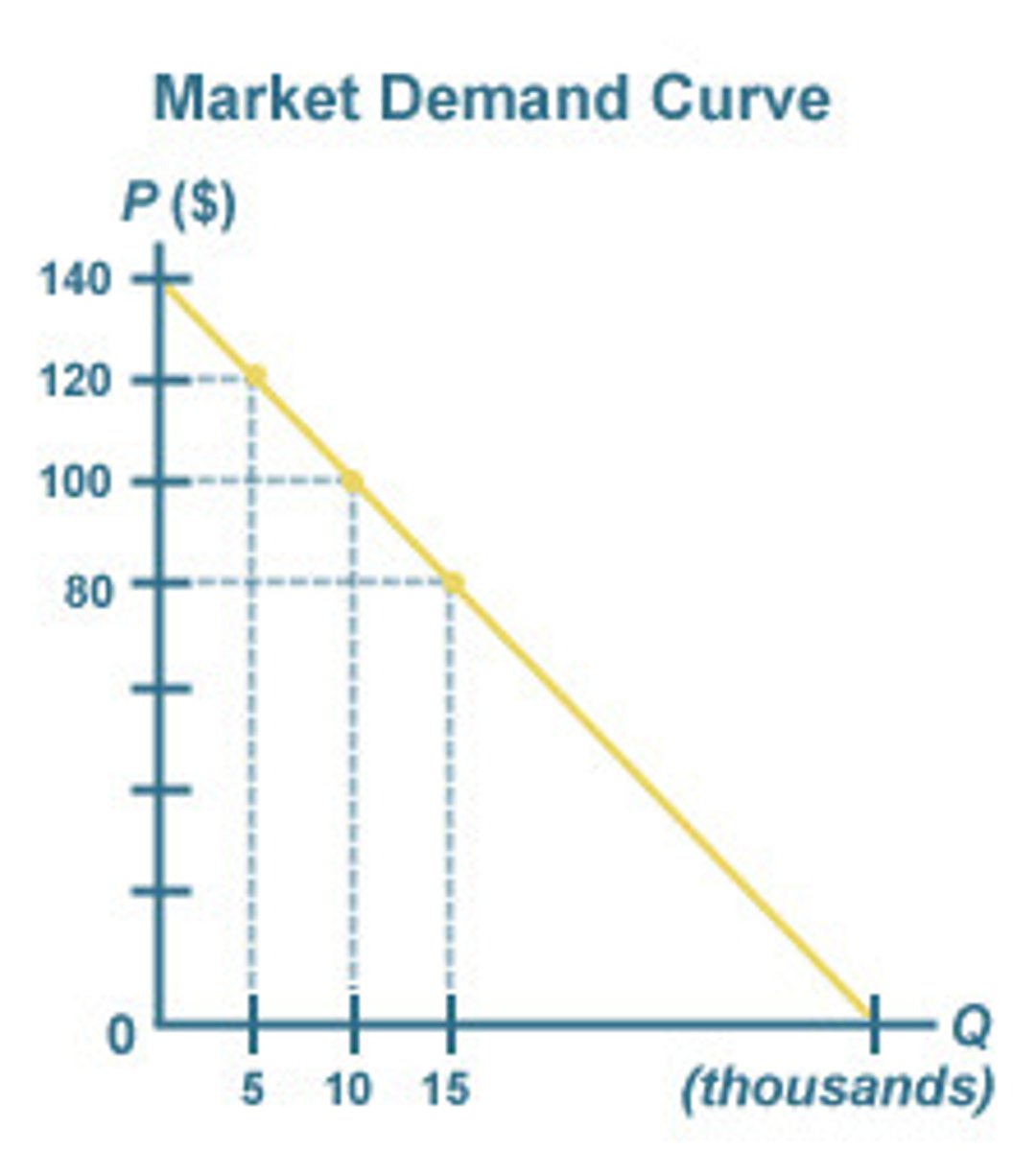
Market Demand Curve
illustrates the relationship between Qd and P for an entire market of consumers; sum of all individual demand curves
Law of demand
a higher price for a good or service, other things equal, leads people to demand a smaller quantity of that good or service and vice versa
Movement along the curve equals
a change in Qd or Qs that results in a change of price
Shifters of demand (TRIBE)
1. Taste and preferences
2. Related goods
3. Income
4. Buyers - number of consumers
5. Expectations of consumers
Tastes and preferences
if consumers start to prefer a product, demand will increase (shift right) and vice versa

Price of related goods - substitutes
The rise in the price of one good leads to an increase in the demand for the other good and vice versa
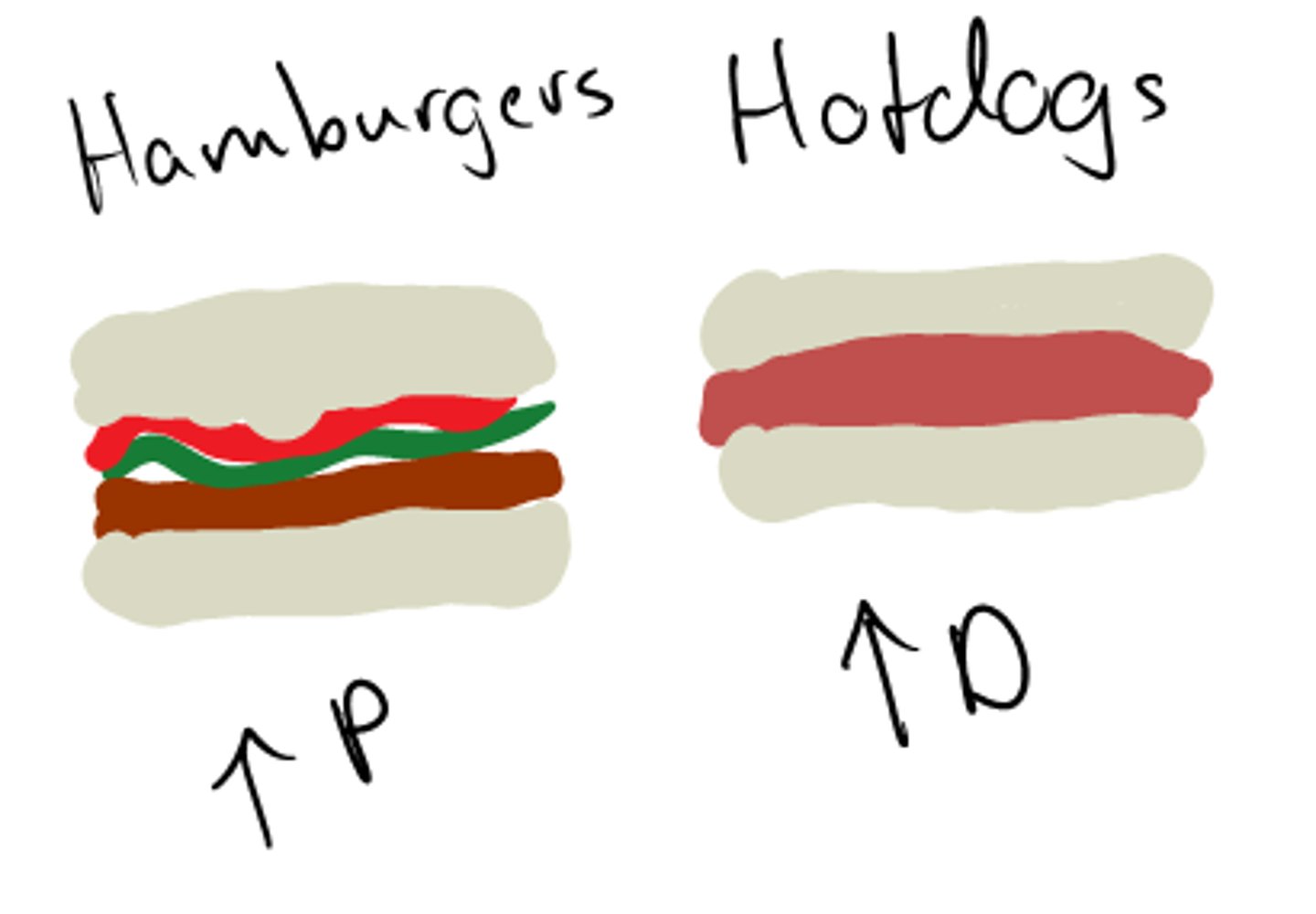
Price of related goods - complements
a rise in the price of good leads to a decrease in demand for the other good and vice versa

Normal good
a good that consumers demand more of when their incomes increase and vice versa

Inferior good
1. a good that is less desirable than expensive alternatives
2. a good that consumers demand less of when their income increases and vice versa

Changes in expectation
if consumers expect the price of a good to fall, they will decrease demand now and buy at a lower price in the future and vice versa
Number of buyers
if the number of consumers increases, demand increases and vice versa
Elasticity of demand
how sensitive Qd is to change in the price of a product
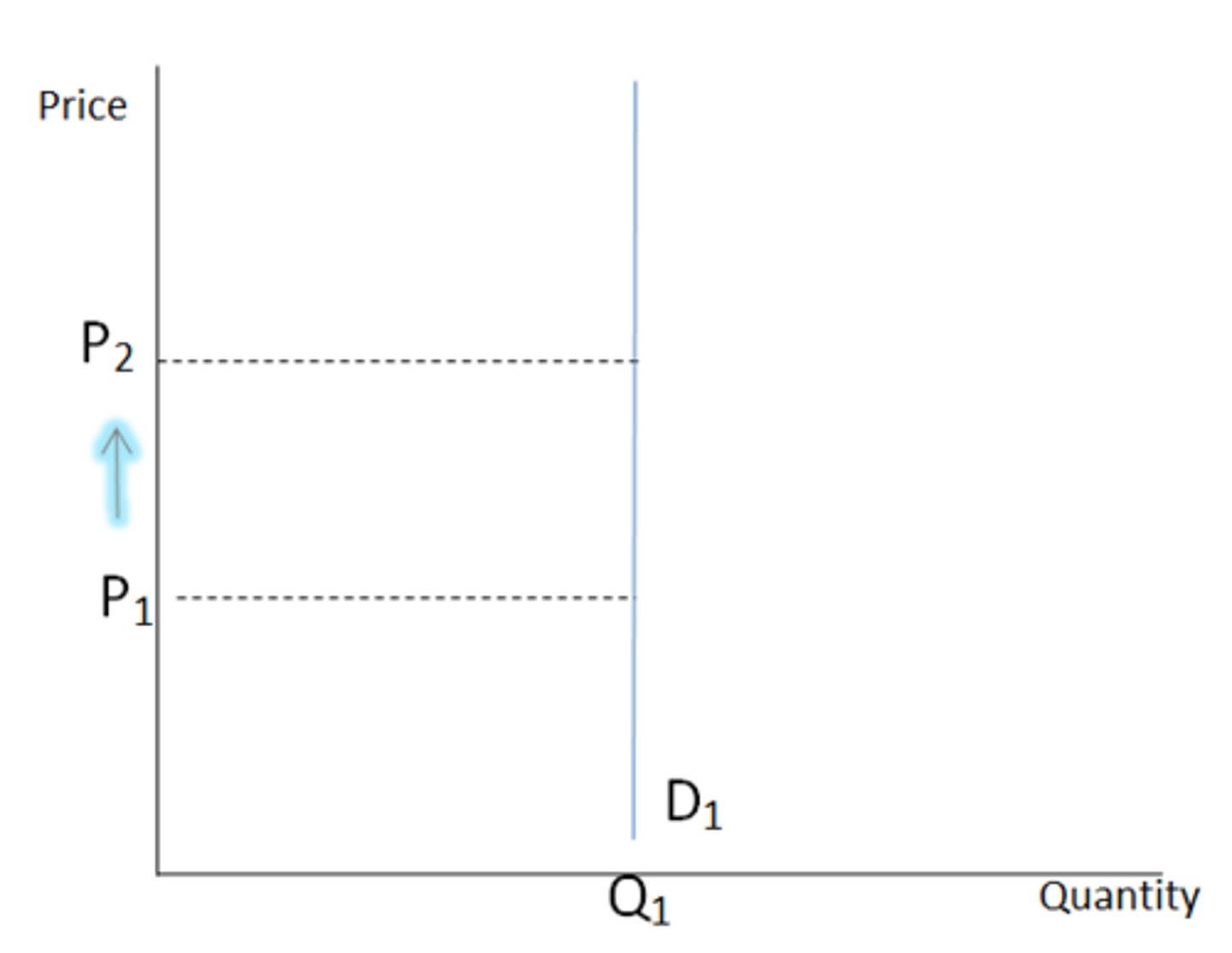
Inelastic demand
Qd is not sensitive to a change in the price level of a product (ex. necessities, few to no substitutes available, small portion of consumer's income)
Elastic demand
Qd is very sensitive to a change in the price of a product (ex. large portion of consumer's income, many substitutes, not a necessity)