Lecture 4 BIOL 214
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Rise of atmospheric oxygen
O2 atmosphere: 2.5 BYA
O2 supports multicellularity
Compression fossils
Made by pressure on sediment
plants and simple organisms - bc don’t break
Cast and mold fossils
inmpression made by organism that has hard exoskeleton
nice imprint
Permineralized fossils
cell structure not destroyed
deposit of minerals within cells
petrified wood
Unaltered Remains
insects “amber”
burrows or feces of animals; trace fossils
Three factors effecting fossil accuracy
Geography: deposition areas [lowland/ marines likely b/c deposition]
Taxonomic bias: bones and shells are amenable to fossilization [some animals make better fossils]
Temporal bias: Earth’s crust recycled, so older rocks are rarer [things too old can’t be identified]
Best Record of Fossils
Vertebraes
Why have Origins of higher taxa not been documented
Organisms completely consumed
Sediemtns form only sporadically
Sediments must solidify into rocks
ROcks must be exposed/ accessible
Species
temporally distinct parts of single evolutionary lineage, different forms
diff forms called CHRONOSPECIES (change in lineage = anagenesis)
Cladogenesis
speciation - splitting of lineage
Pseudo extinction / taxonomic extinction
lineage changes so much that its original name disappears
contrasts with real extinction, in which a lineage fails to leave any descendants
Anagenesis
change so much now different species
chrono species for paleontologists
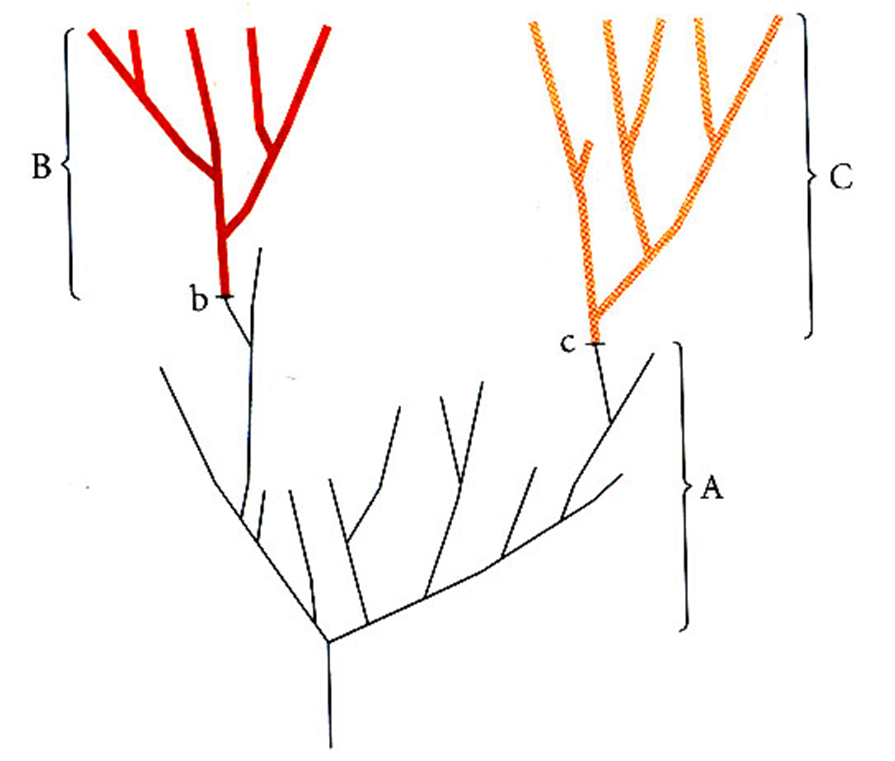
Identify chrono species and cladogenesis
A & B are different chrono species
A & C are different chrono species
B & C are different species from one another (cladogenesis)
Proterozoic Era Characteristics
2.5 BYA to 543 MYA
prokaryotes and eukaryotic algae
640 MYA
Oldest fossils of multicelled animals age
Trace Fossils
First evidence of animal life appeared less than 1 BYA
tracks, burrows, feces
Ediacaran Fauna
565-544 MYA
best known Precambrian animals
soft-bodied, lacking skeletons
crept or stood upon the sea floor
don’t fit modern phyla - sponges, jellyfish
radial MAYBE bilateral symmetry
Ediacaran Fossils
radial symmetry (sponges, jellyfish)
dickinsoniana
Paleozoic Era: Cambrian Period
541 - 485 MYA
“Cambrian explosion” started 530 MYA
almost all of modern phyla and skeletonized marine animals appear on record
explosion MAY have occurred 30 MYA or 5-10 MYA
BURGESS SHALE
Cambrian Fossils: Trilobites
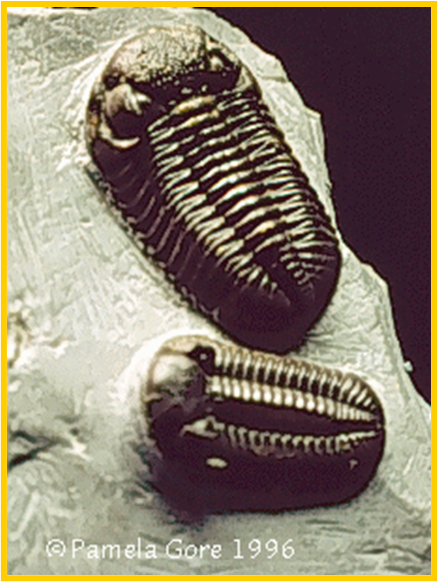

bilateral symmetry - more complex
appendages
segmentation
Crustacean
Cambrian: Arthropods and worms
Onychophoran

Chordates
First vertebrates (jawless)
What precipitated the Cambrian Explosion
diversification by increased O2 levels
Vacant ecological habitats —> diversification
Innovations related to multicellularity
NOT ENTIRELY SURE
The split occurred pre-Cambrian
primitive organisms (90% of Earth’s early history)
Diversification may have started…
Pre-Cambrian
Paleozoic Era: Ordovician (485-443 MYA)
Diversification with new classes
First land plants and jawed fish
ended with one of the largest mass extinctions
Early Devonian had…
The first terrestrial animals were arthropods
Oligotrophic
low nutrients in lake, low productivity, high oxygen levels
Late Devonian had…
The terrestrial vertebrates (tetrapod’s) had arisen
Devonian Period
Age of fish
massive emergence of aquatic species
Paleozoic: Carboniferous and Permian
widespread tropical swamp forests
gigantic dragonflies
reptiles
mammal-like reptiles
WORST extinction ever at the end of Permian
SLIDE 26 MUST KNOW
okay
Mesozoic Era
Triassic, then Jurassic, then Cretaceous
dinos, mammals and birds
mass extinction at the end
Eutherian mammals
mammals with placenta
humans
Cenozoic Era: Paleocene epoch (66-56 MYA)
mammalian radiation after extinction of dinosaurs
Pleistocene Epoch (1.8 MYA to 10k YA)
quaternary period
glaciations
Origin and extinction of large mammals
modern humans
Holocene Epoch (10k to NOW)
Current time
agriculture
domesticated animals
digital watches
MIGHT be the worst mass extinction BC OF CLIMATE CHANGE
Extinction Definition
failure of lineage to leave any descendants
Background Extinction
within any group, the chance of extinctions is constant, but the rate may vary
Is smaller range or larger range better for taxa
A larger range because it is less vulnerable to habitat
What has caused mass extinction
climate change MOST LIKELY
What caused KT Extinction
asteroid
impacted quartz —> lines on quartz
existence of iridium —> none on earth