The Human Brain: Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cranial Nerves Description
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
The brain stem consists of how many primary regions
3
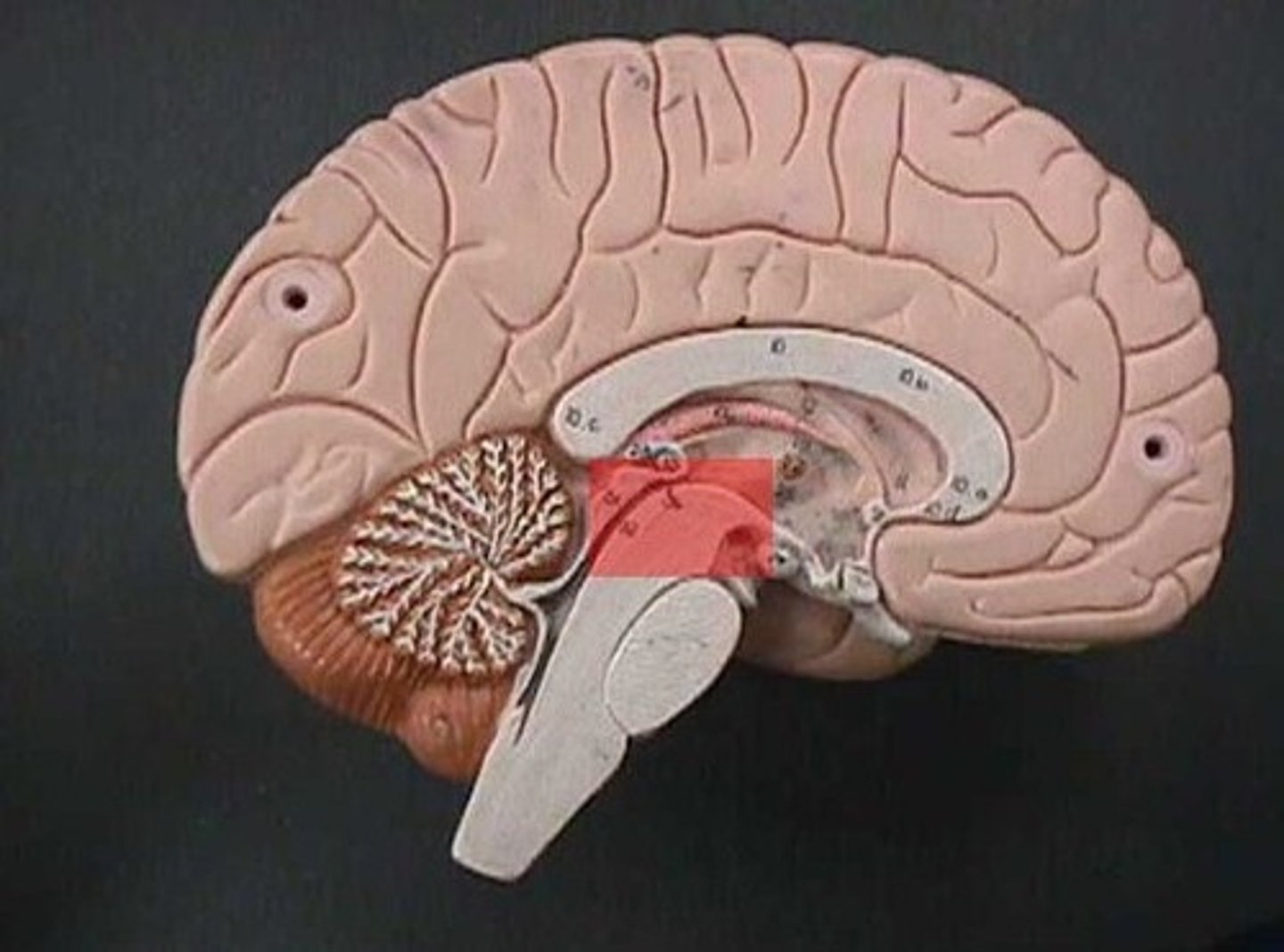
midbrain
pons
medulla oblongata
function of midbrain
involved in vision, hearing, motor control, and more.
function of pons
bridge. Contains tracts that connect the diencephalon and cerebrum to the cerebellum and medulla oblongata. Helps with breathing rhythm
medulla oblongata function
Contains motor tracts ventrally and sensory tracts dorsally. involved in heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, vomiting, sneezing, and more.
Cerebral aqueduct
function of cerebral aqueduct
passwayway through the midbrain that allows CSF flow inferiorly from the third ventricle to fourth ventricle
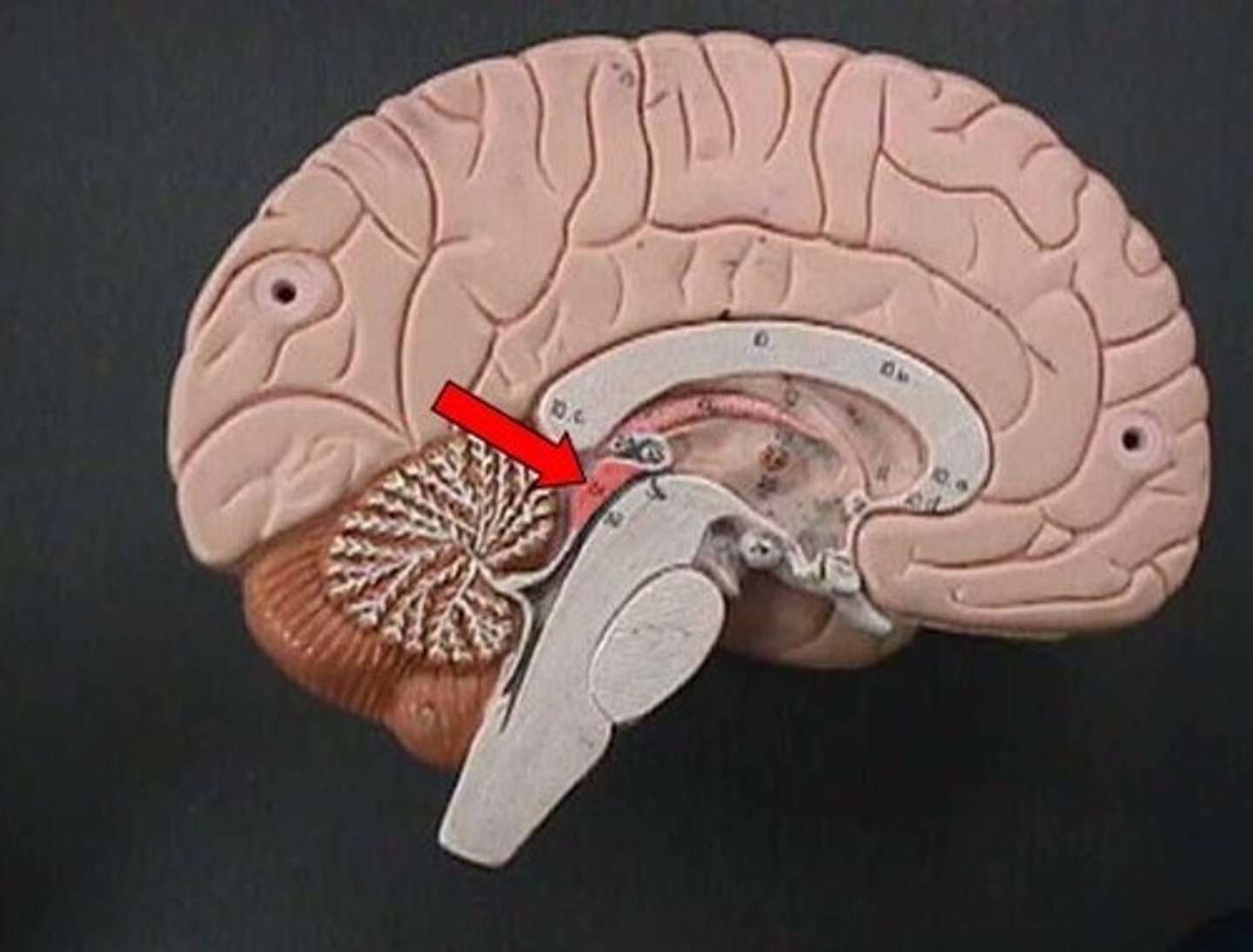
tectum
tectum function
involved in auditory and visual reflexes
the 4 bulging structures that project posteriorly from the tectum are the
corpora quadrigemina
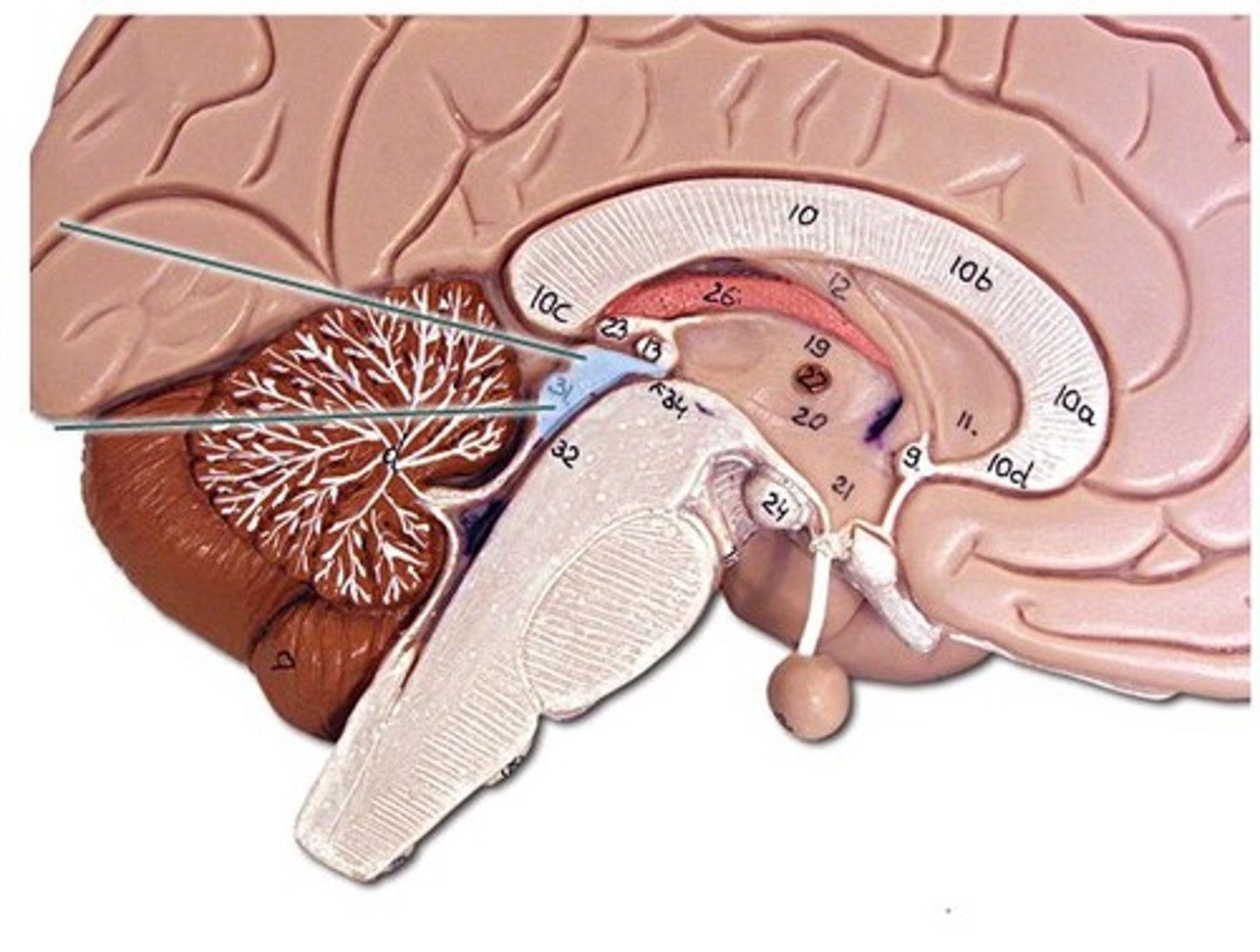
corpora quadrigemina
2 superior components of the corpora quadrigemina are called the
superior colliculi
superior colliculi function
visual reflexes including the coordination of the eye and head movement
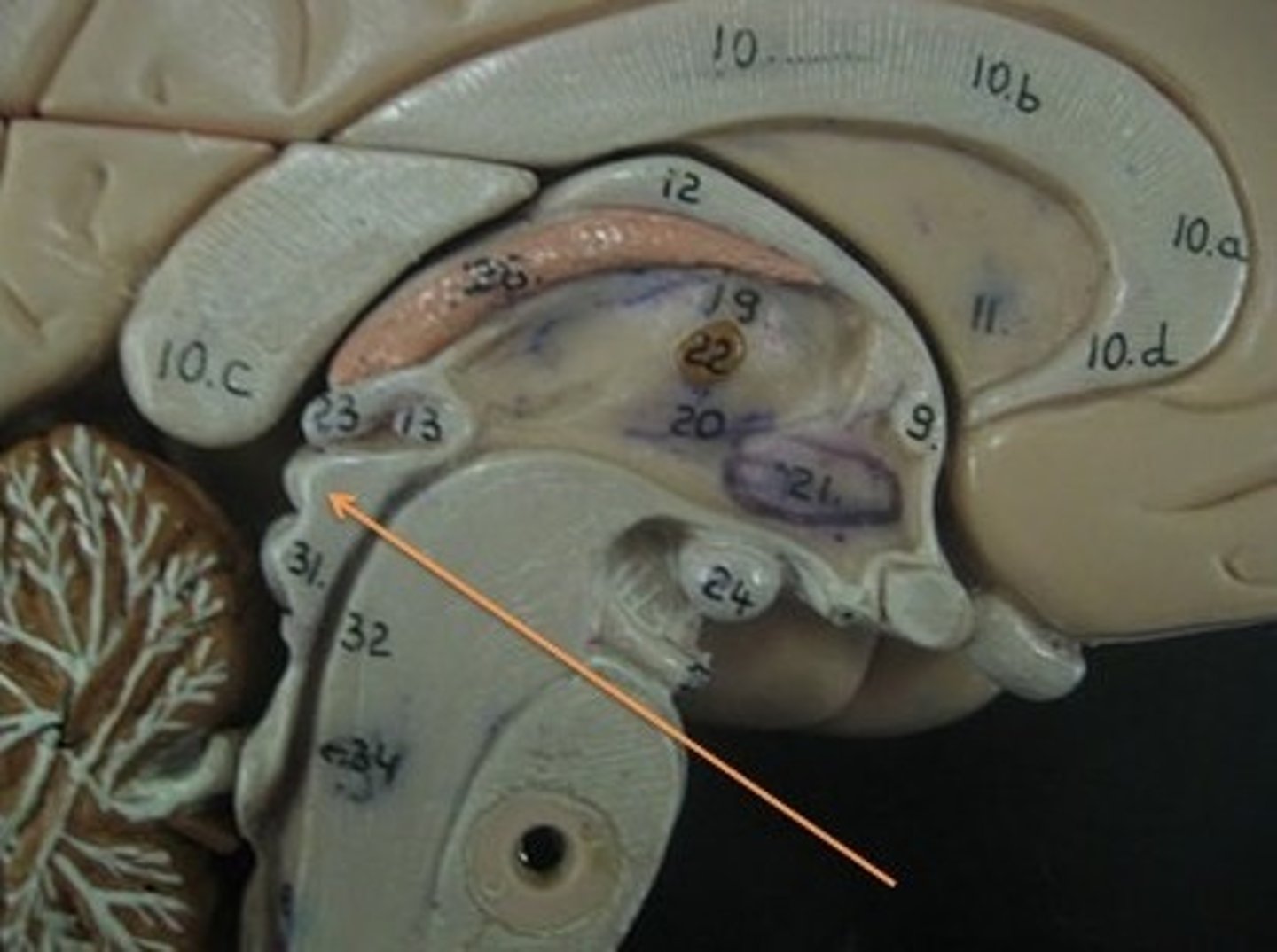
superior colliculi
The two inferior components of the corpora quadrigemina are called
inferior colliculi
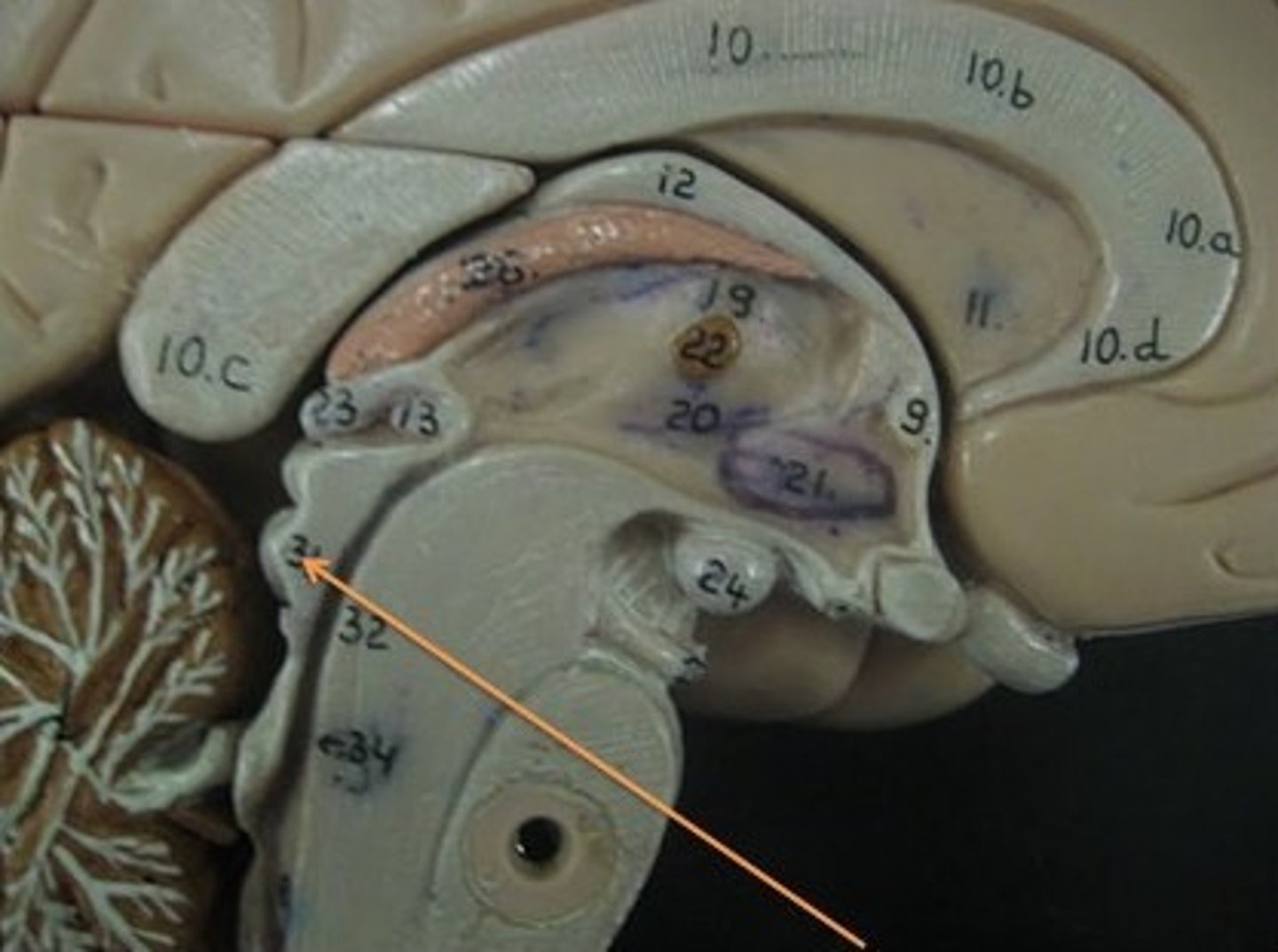
inferior colliculi
inferior colliculi function
auditory reflexes such as the startle reflex
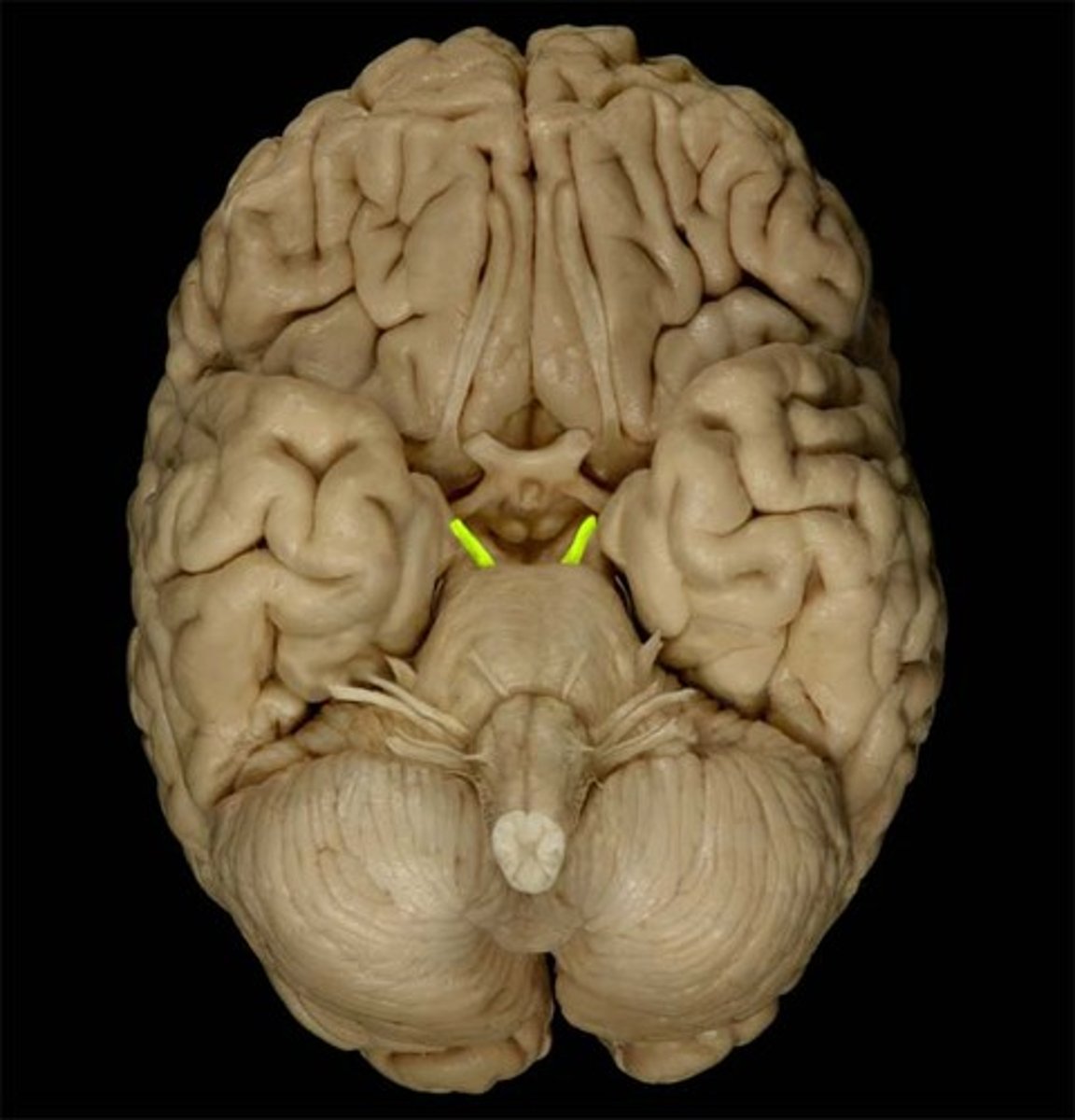
oculomotor nerves
what is cranial nerve III
oculomotor cranial nerve
function of oculomotor nerve
responsible for controlling a variety of muscles involved in eye movements as well as dilation and constriction of the pupil
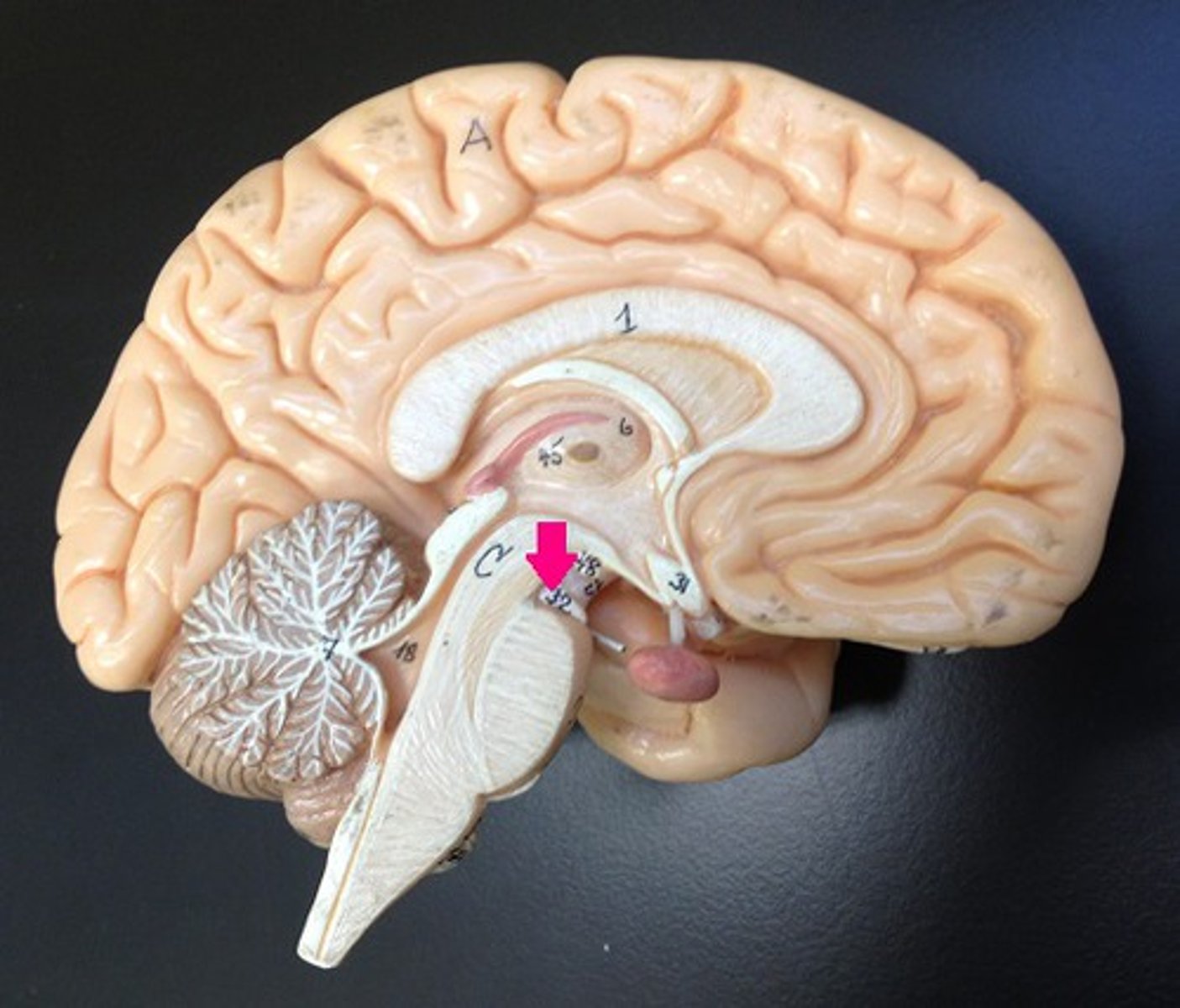
oculomotor nerve
pineal gland
pineal gland function
produces melatonin, a hormone involved in sleep cycles.
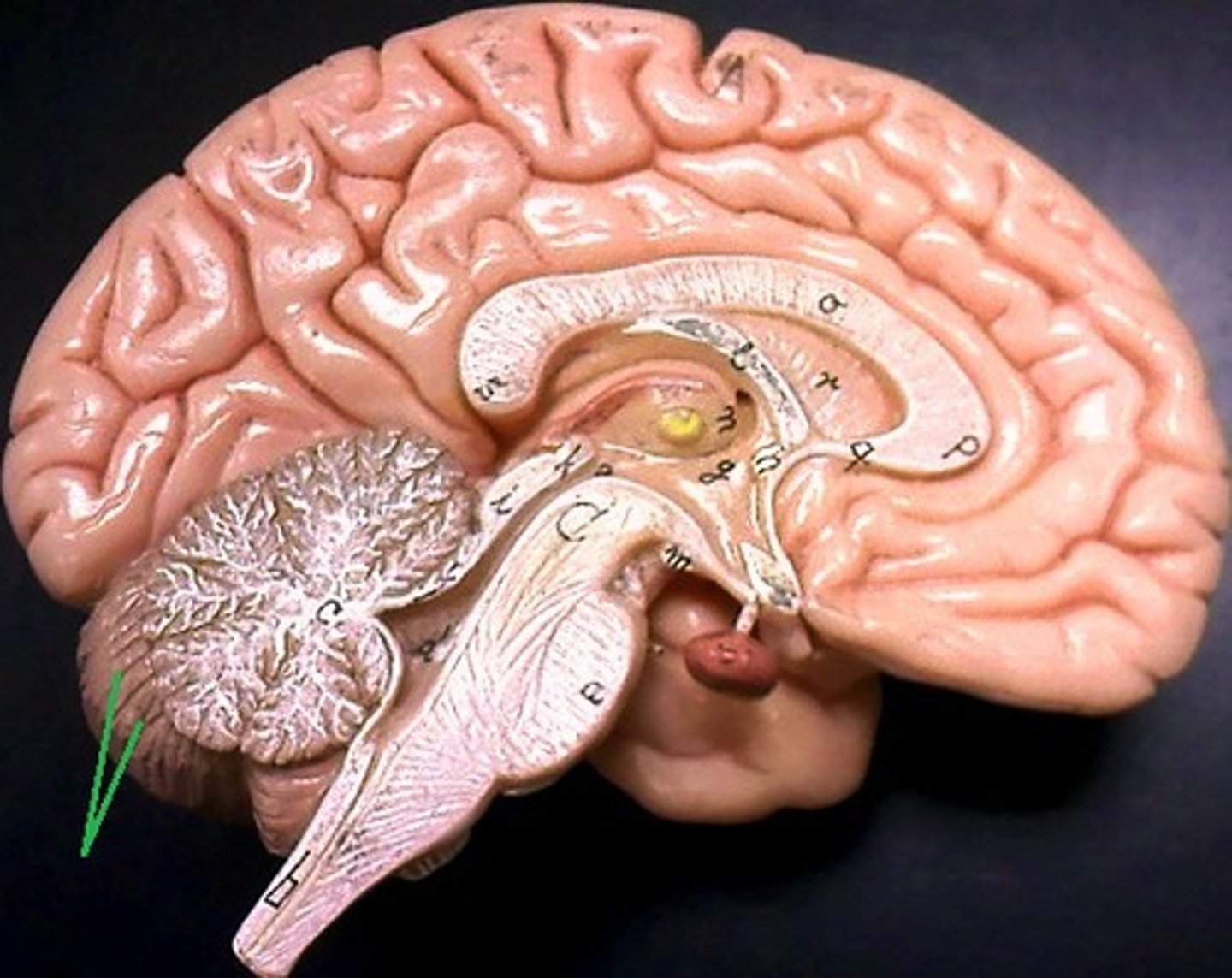
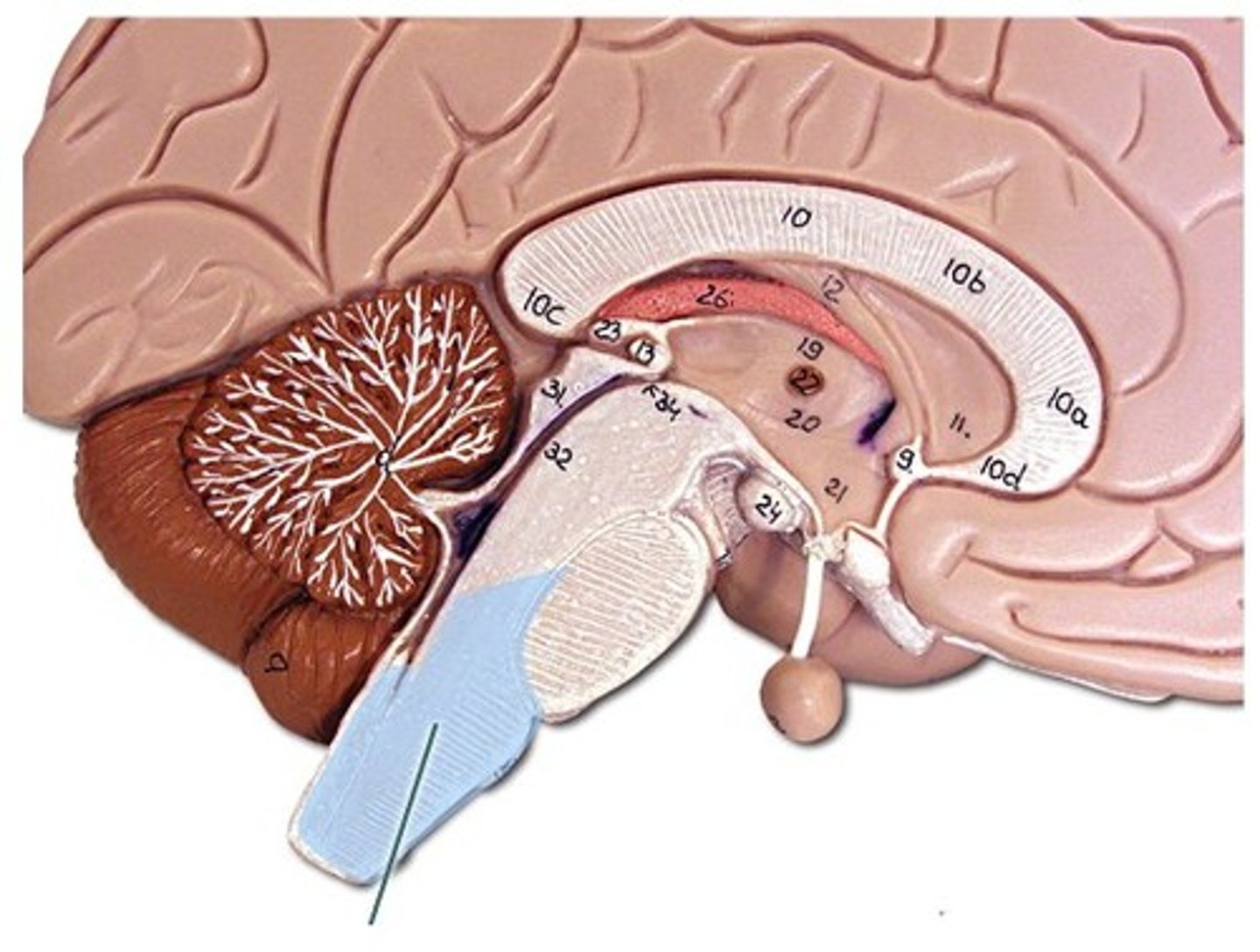
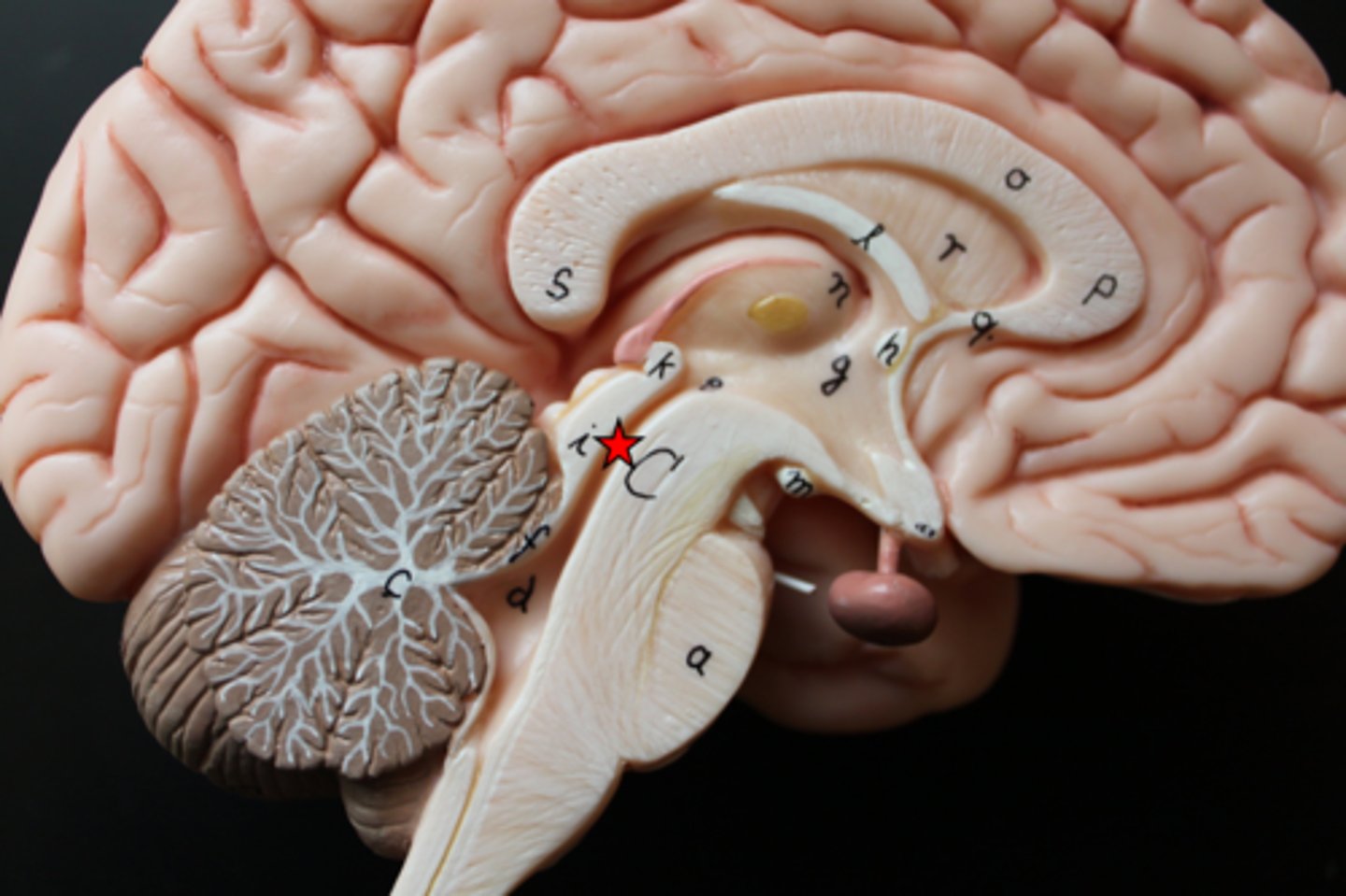
folia
small folds in the cerebellum are
folia
the white matter of the cerebellum is collectively referred to as the
arbor vitae
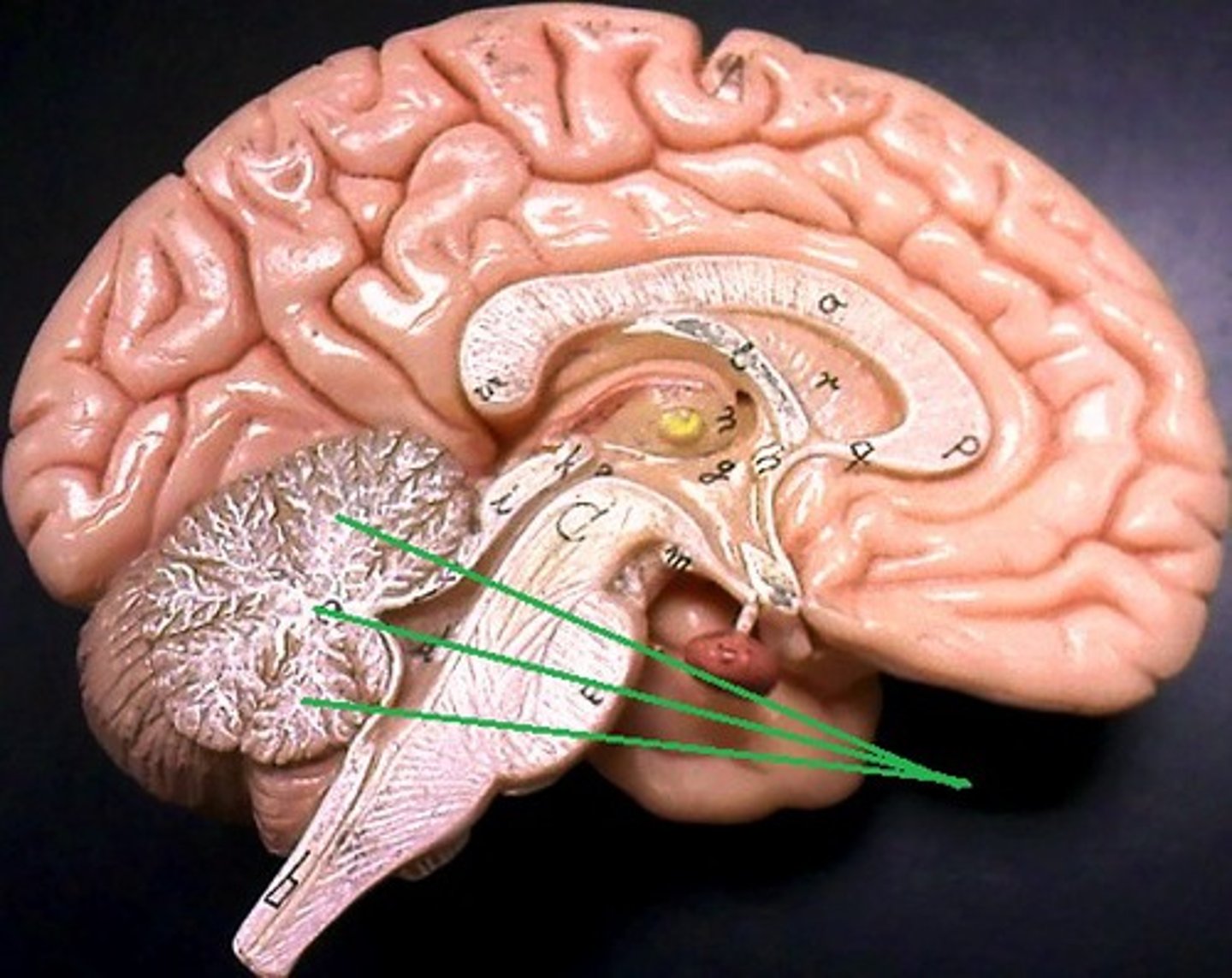
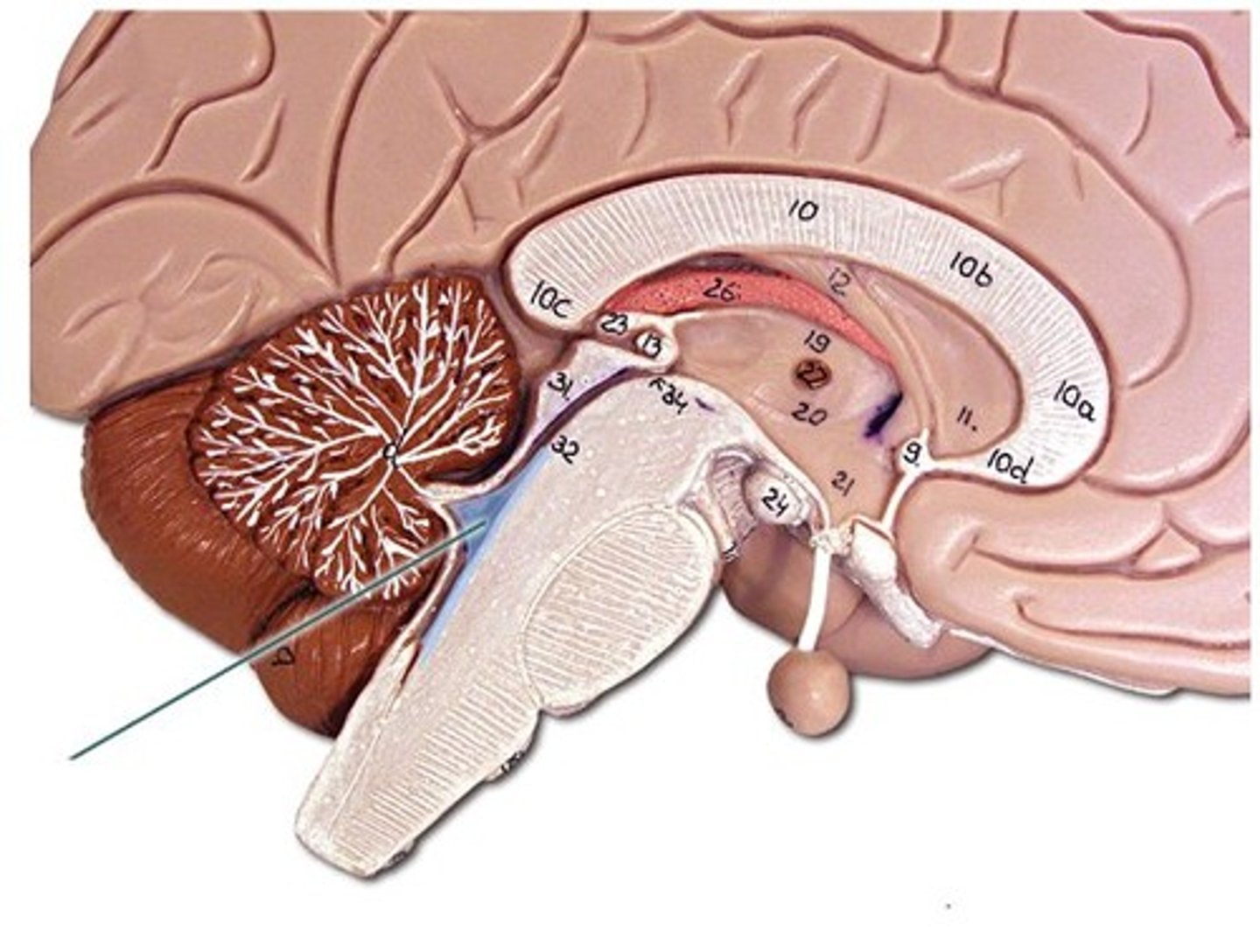
arbor vitae
why is the arbor vitae called that
early anatomists thought it resembled a coniferous tree of the same name.
the cavity between the cerebellum and the brain stem is
the fourth ventricle
fourth ventricle
function of fourth ventricle
receives CSF from the 3rd ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct and allows it to move into the central canal of the spinal cord and into the subarachnoid space.
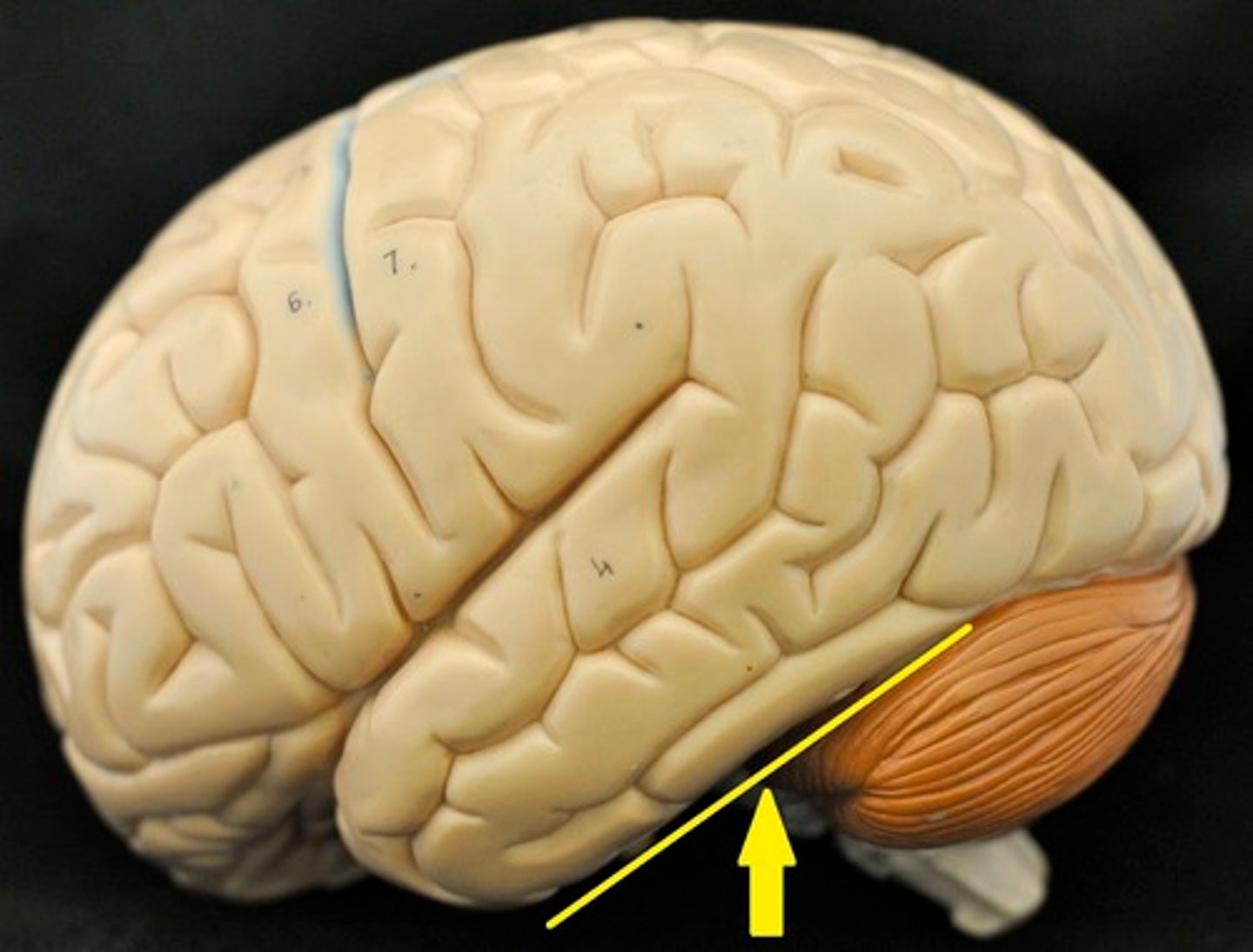
transverse fissure
function of transverse fissure
separates the cerebellum and the occipital lobe of the cerebrum.
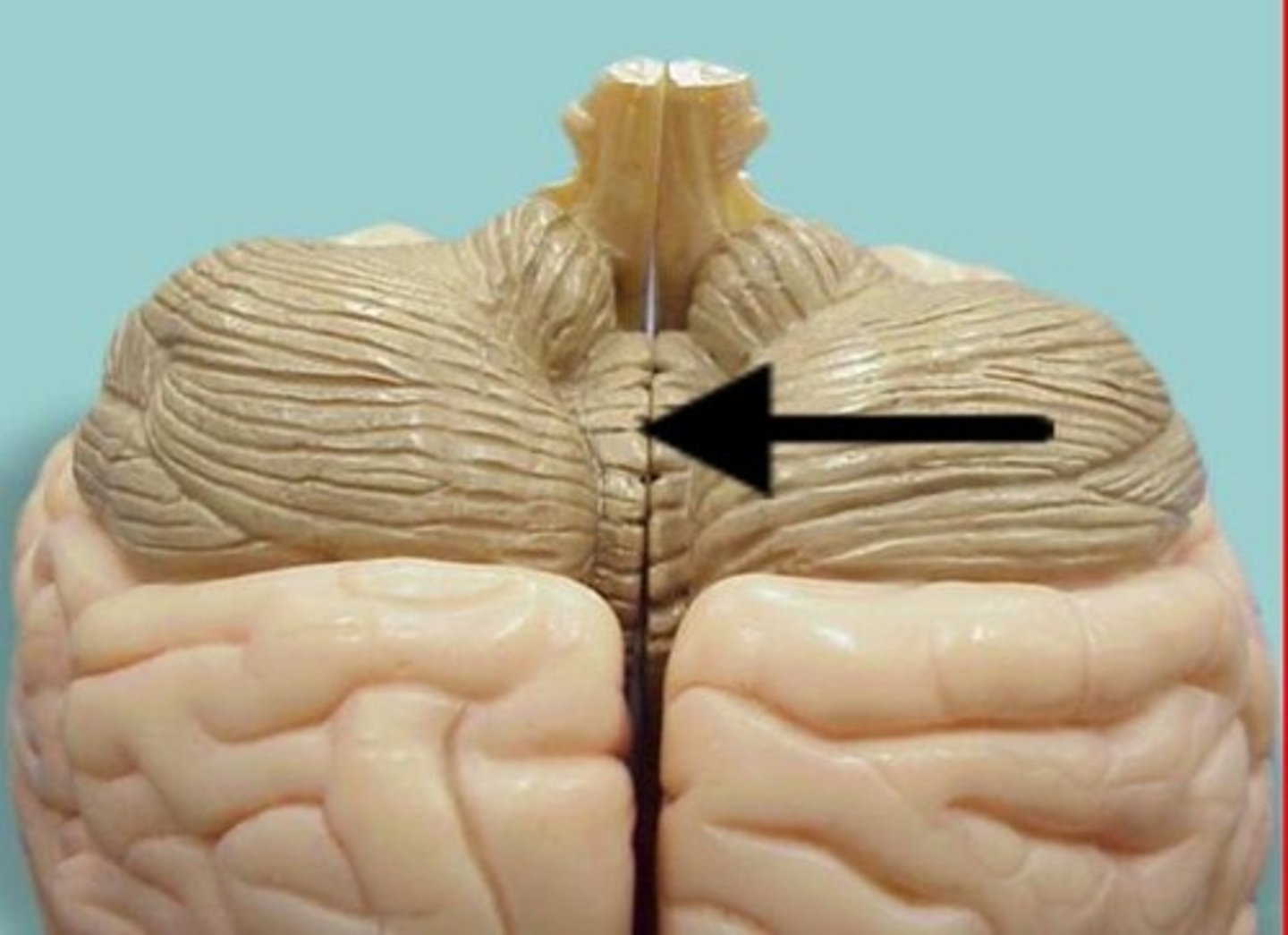
vermis
Write the cranial nerves that correspond with this saying
Oh
Oh
Oh
To
Taste
And
F
Very
Good
V
After
Head
Olfactory
Optic
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Abducens
Facial
Vestibulocochlear
Glossopharyngeal
Vagus Nerve
Accessory
Hypoglossal
what type of nerve is cranial nerve I
sensory
what is cranial nerve I
olfactory
What is cranial nerve II
optic
What is cranial nerve IV
Trochlear
what type of nerve is cranial nerve II
sensory
What type of nerve is cranial nerve III
motor
what type of nerve is cranial nerve IV
motor
What type of nerve is cranial nerve V
Both
what is cranial nerve V
trigeminal
what is cranial nerve VI
abducens
what type of nerve is cranial nerve VI
motor
what is cranial nerve VII
Facial
what type of nerve is cranial nerve VII
both
what is cranial nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear
what type of nerve is cranial nerve VIII
sensory
what is cranial nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal
what type of nerve is cranial nerve IX
both
what is cranial nerve X
vagus nerve
what type of nerve is cranial nerve X
both
what is cranial nerve XI
accessory
what type of nerve is cranial nerve XI
motor
what is cranial nerve XII
hypoglossal nerve
what type of nerve is cranial nerve XII
motor
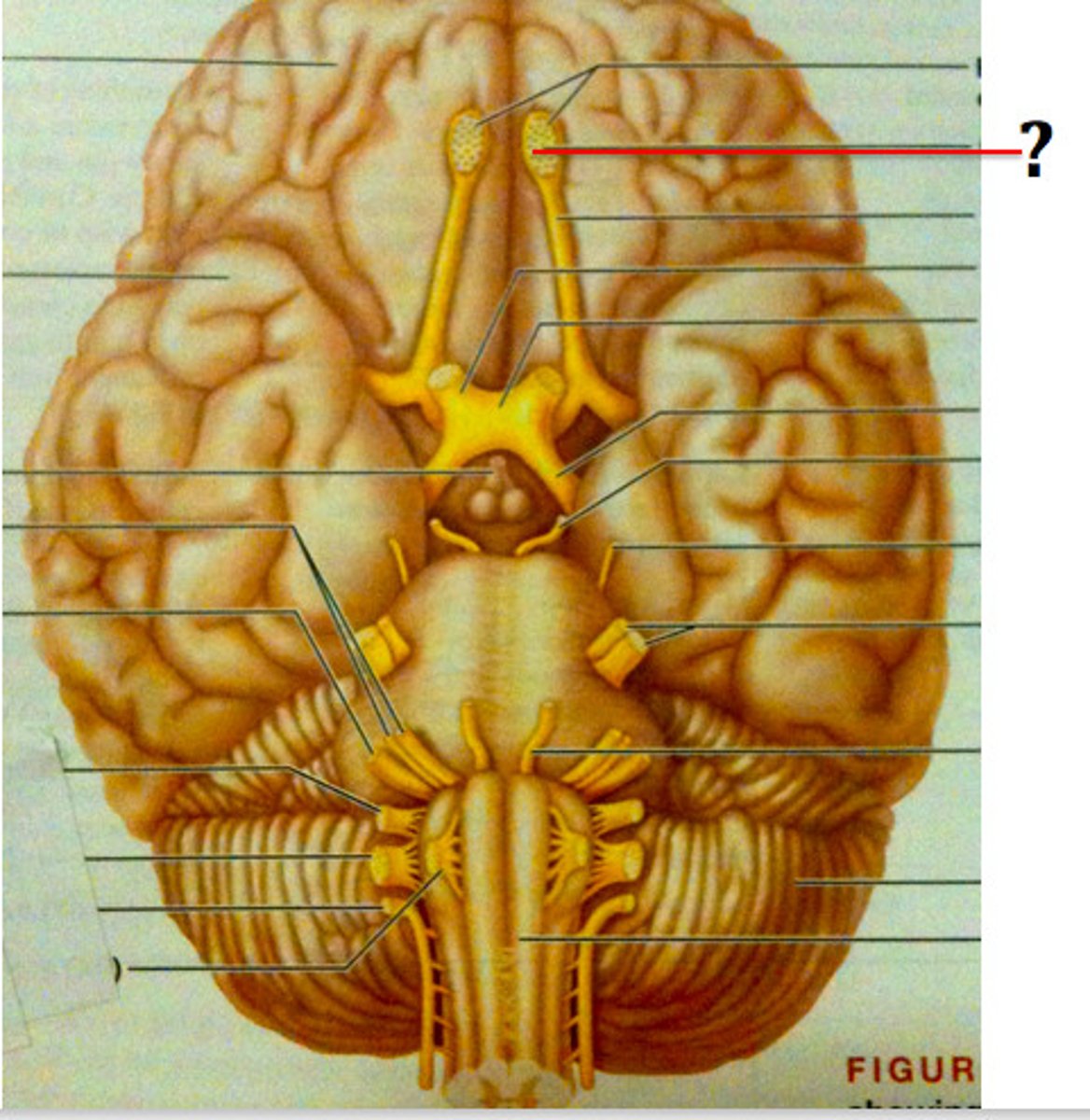
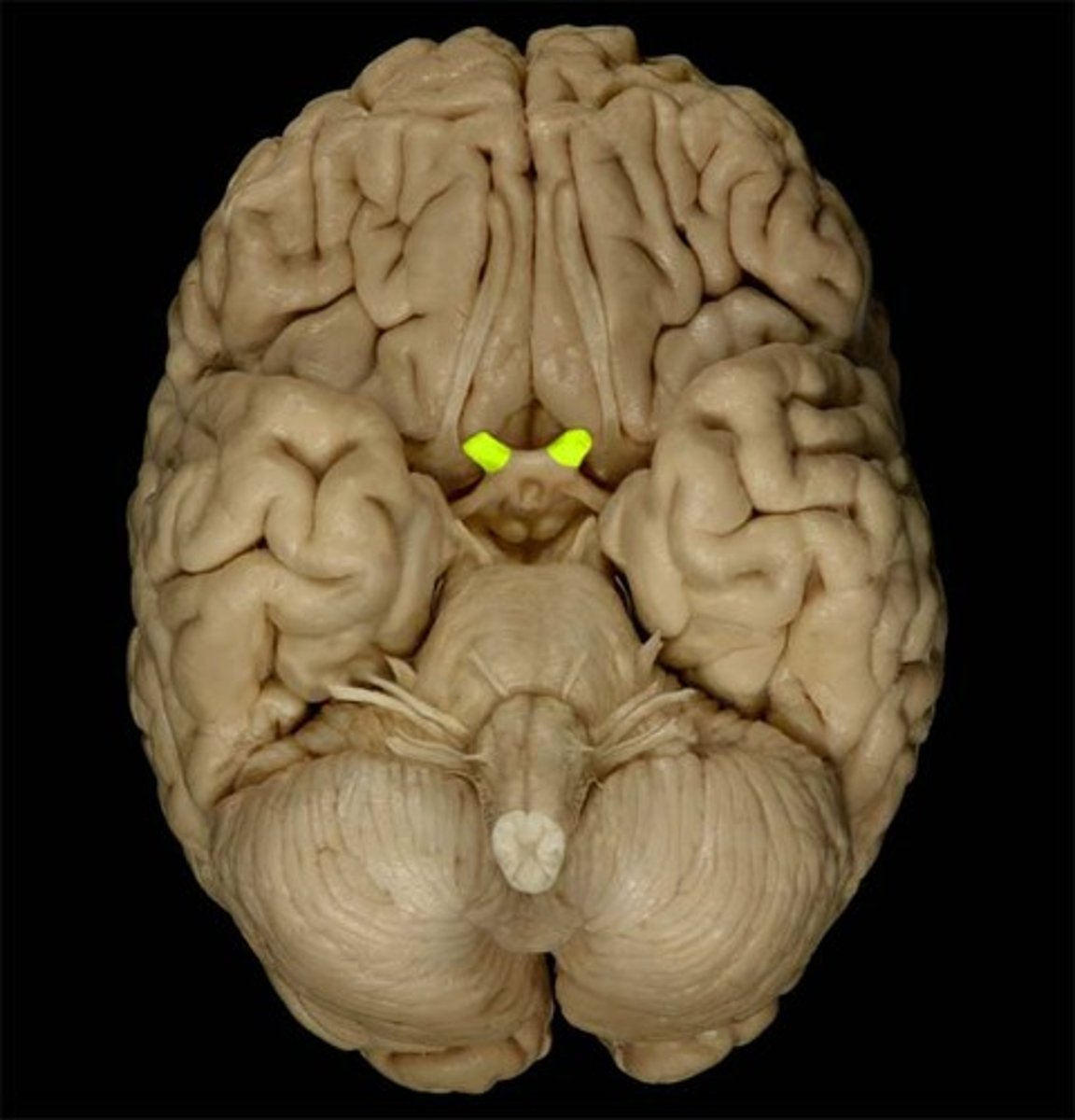
olfactory bulb
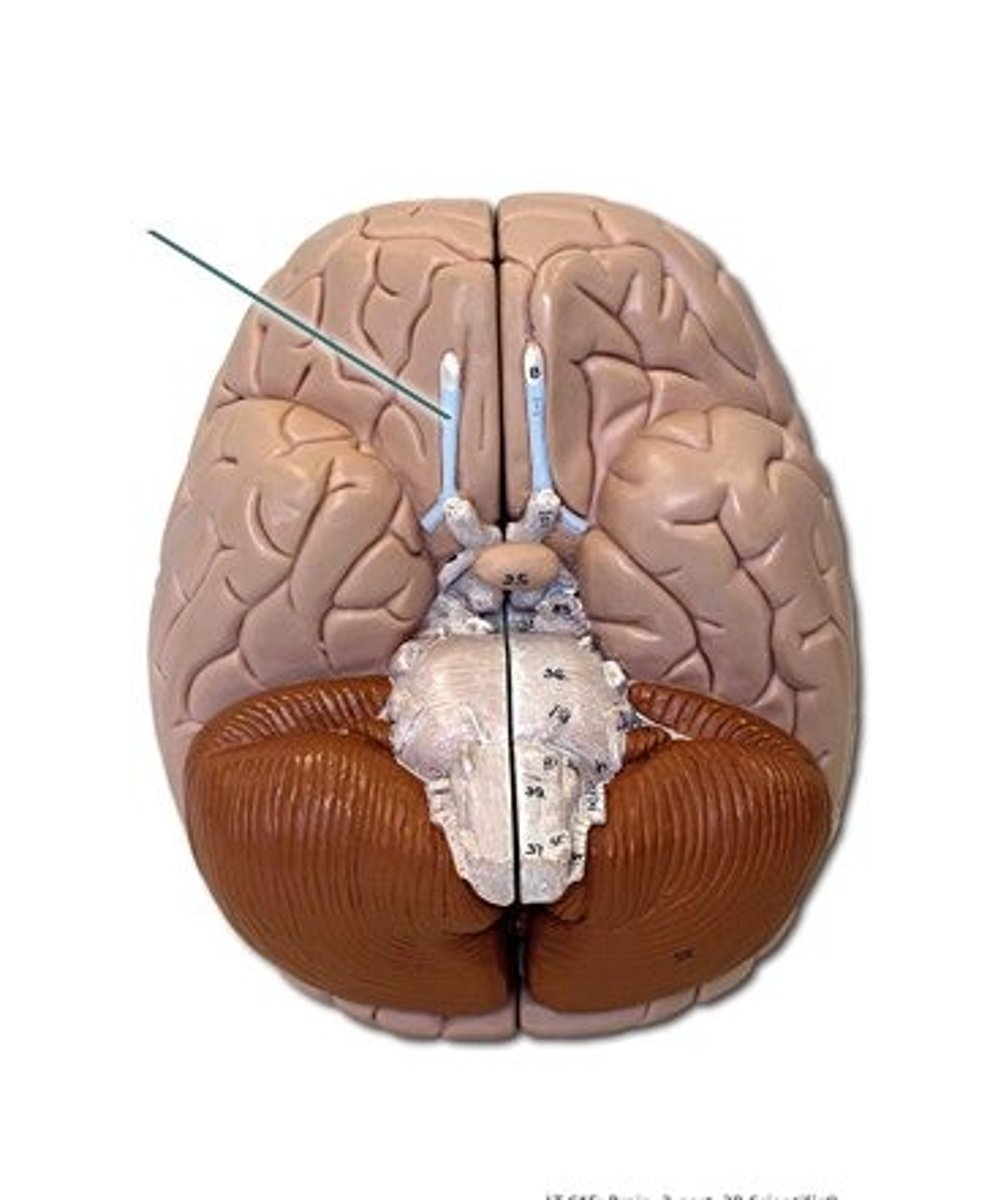
olfactory tract
optic nerve
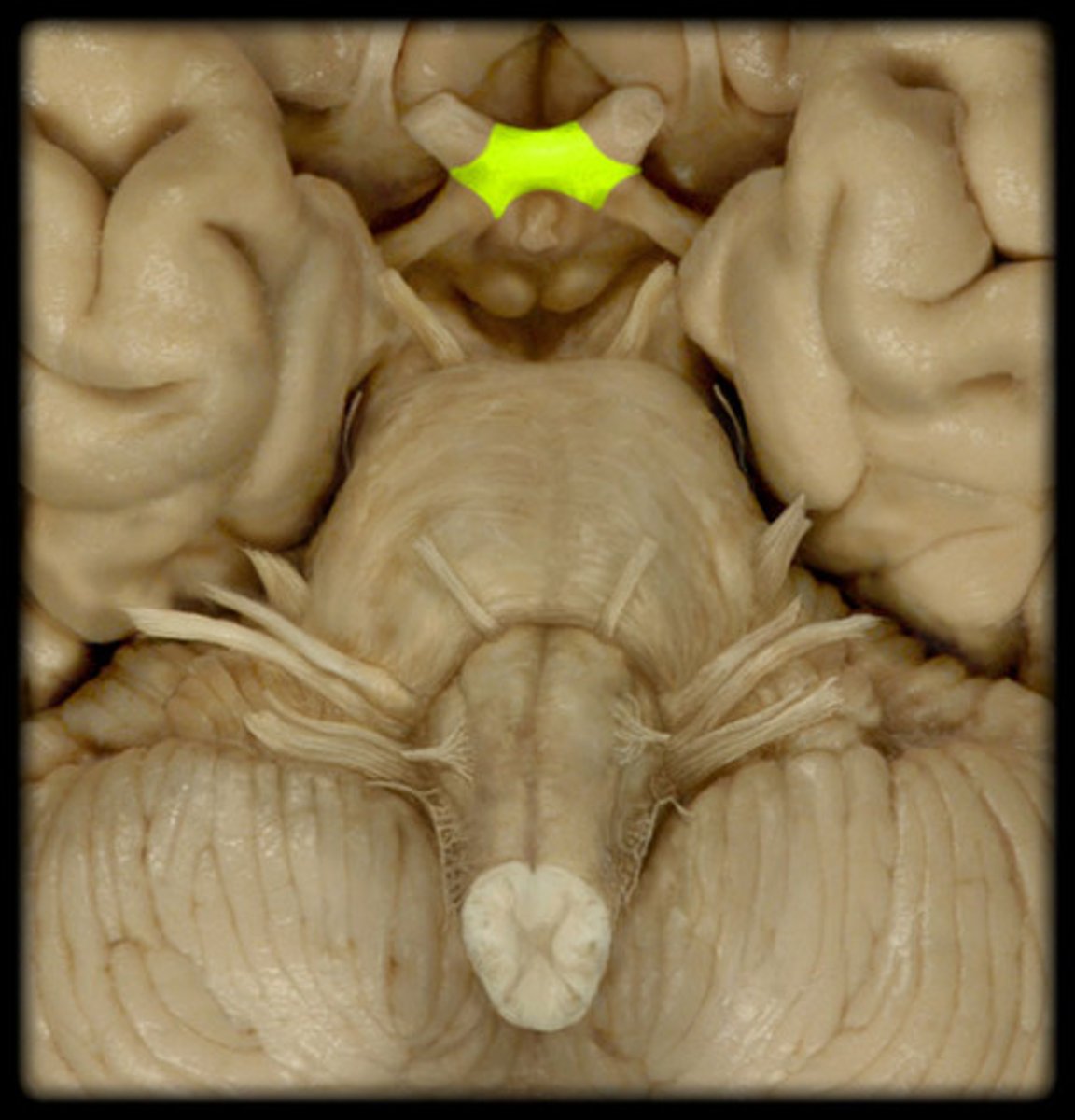
optic chiasm
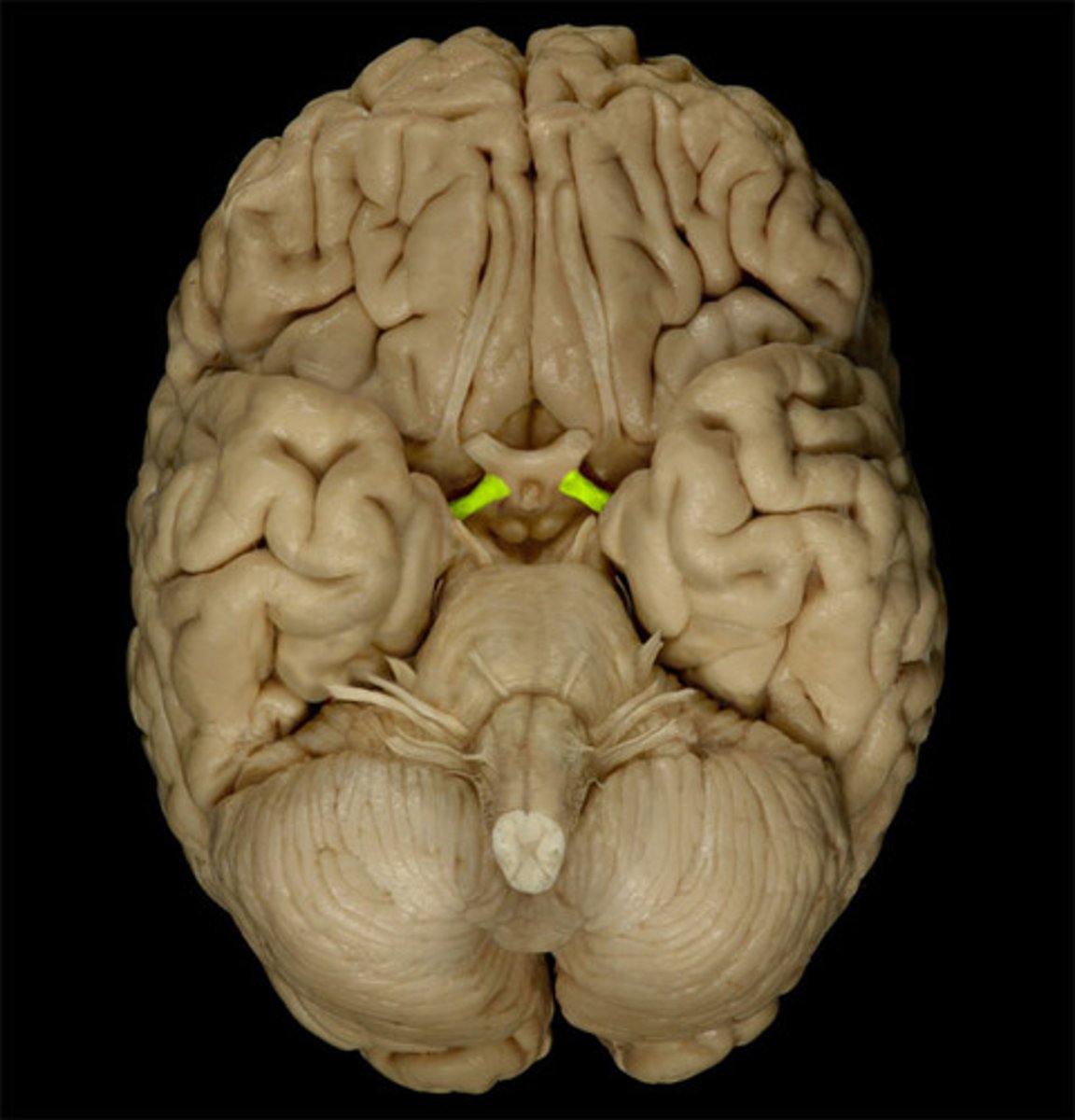
optic tract
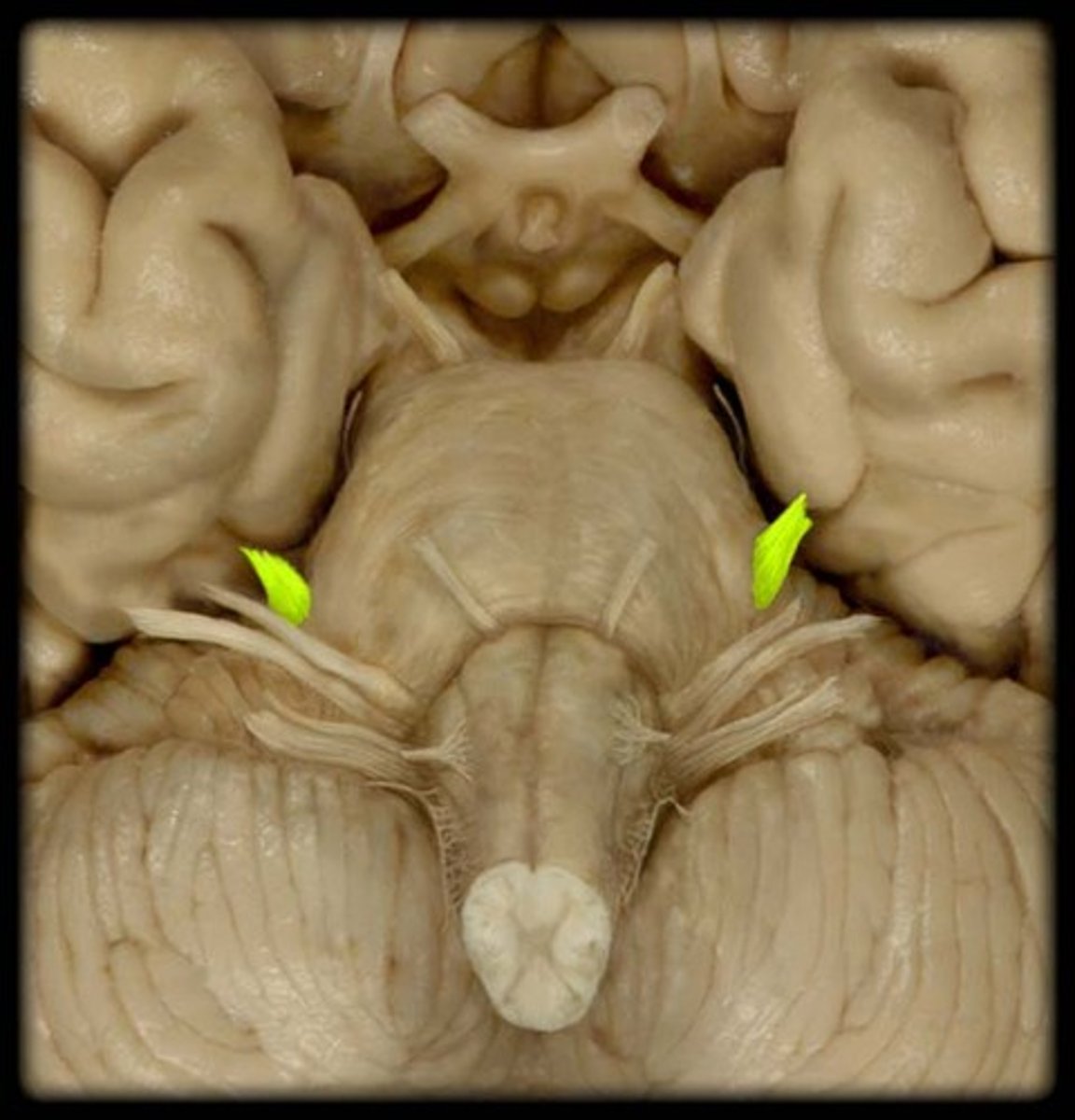
trigeminal nerve
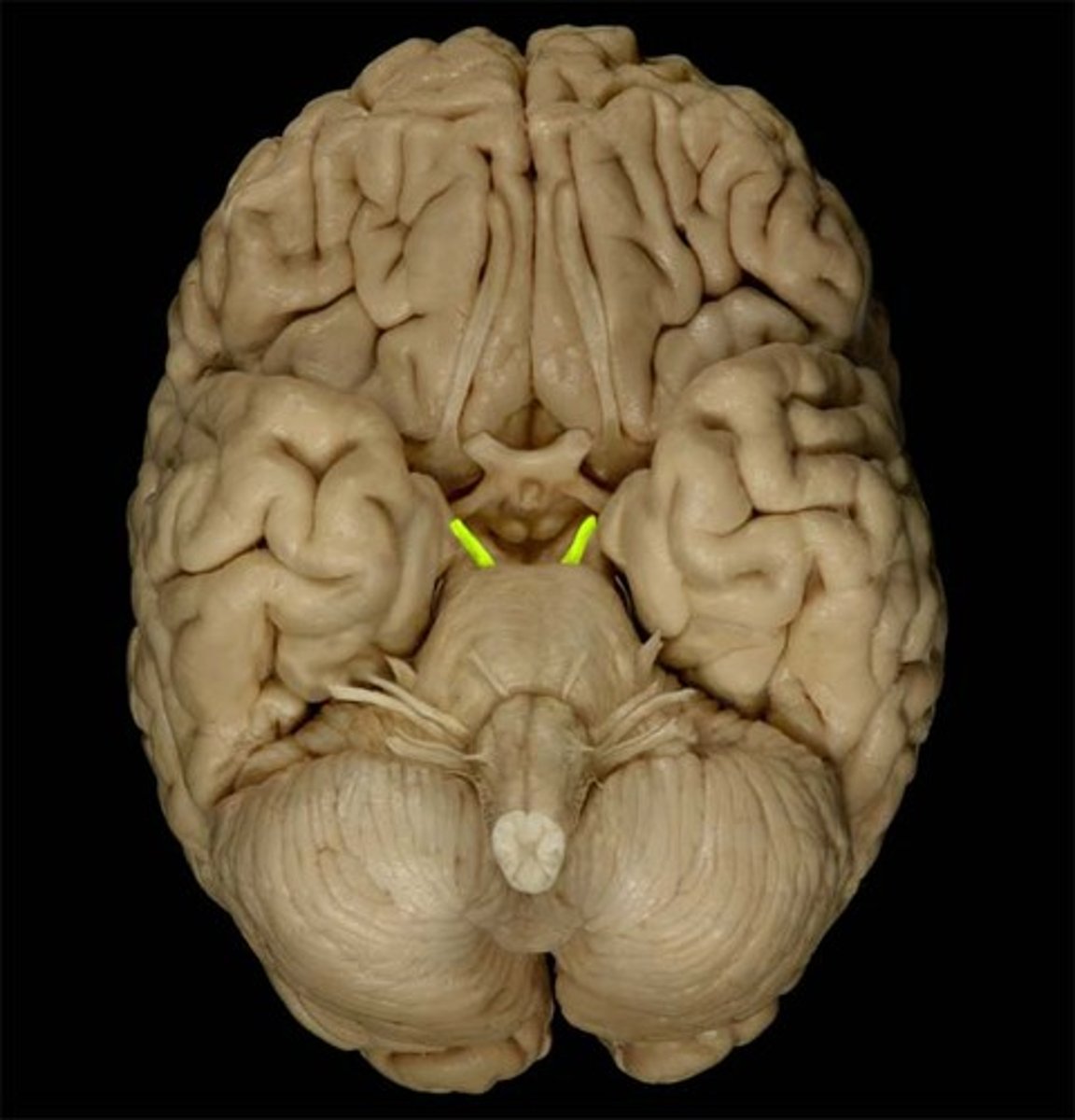
oculomotor nerve inferior view
function of olfactory bulb
receives input from olfactory neurons coming from the nasal cavity
function of olfactory tract
carries olfactory information to the cerebrum, where it can be sorted, processed, and interpreted
function of optic nerve
vision and carries axons from the retina of the eye.
function of optic chiasm
the site at which some axons in each optic nerve carry over to the other side
function of optic tract
carry axons from both optic nerves onward to the thalamus
function of trigeminal nerve
carries sensory information from the fact and motor commands to chewing muscles
An Aqueduct is a man made structure built to carry water over long distances. What flows through the cerebral aqueduct
cerebral spinal fluid
A blow to the back of the head that damages your medulla oblongata may be fatal. Why?
It can affect your head, regulate breathing patterns, and rhythmic motions. This can result in a person's unexpected death
What problems would a person have if his oculomotor nerves were damaged
have trouble moving eyes as 4/6 eye muscles are there
what if the optic nerves are damaged
vision would be damaged or loss
Both tracts and nerves primarily consist primarily of axons. What is the difference between a tract and nerve
Tracts are in the CNS and nerves are in PNS
How does the structure of the olfactory nerves differ from other cranial nerves
multiple olfactory nerves attaches each sides of the brain but other cranial nerves are only in paried
The cranial nerve generally innervate structures of the head and neck. Which pair of cranial nerves also innervates various structures in ventral body cavity.
vagus nerves carries info to and from organs in ventral body cavity
to what parts of the body does the vagus nerve connect to the brain
head, neck, thorax, abdomen
structures involved in transmitting and processing the sense of vision
optic nerve
optic chiasm
optic tract
thralamas
occipital lobe
structures involved in sense of smell
olfactory nerve
olfactory bulb
olfactory tract
hypothalamus
temporal lobe
Function of trochlear nerves
eye movement
function of abducens
eye movement
function of facial
facial recognition
function of vestibulacholar
balance
function of glossopharyngeal
sense of taste
vagus nerve function
controls digestion, heart rate and other vital functions. Ventral body functions
accessory nerve function
sensations
hypoglossal function
tongue motion