bi303 phenotypic plasticity
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
phenotypic plasticity
genetically encoded flexibility
ability of a single genotype to produce multiple phenotypes irt environmental conditions
powered by regulatory genes that ‘switch on’ structural genes
acclimation - individual shift in range of physiological tolerance - REVERSIBLE
developmental response - change in environment influences individual development - NOT REVERSIBLE
reaction norm
set of one genotype’s possible phenotypes
example - alaska vs michigan swallowtail caterpillars
AK - always cold, less change, loses plasticity. less steep rxn norm
MI - more temp variation, more change, keeps plasticity. steeper rxn norm
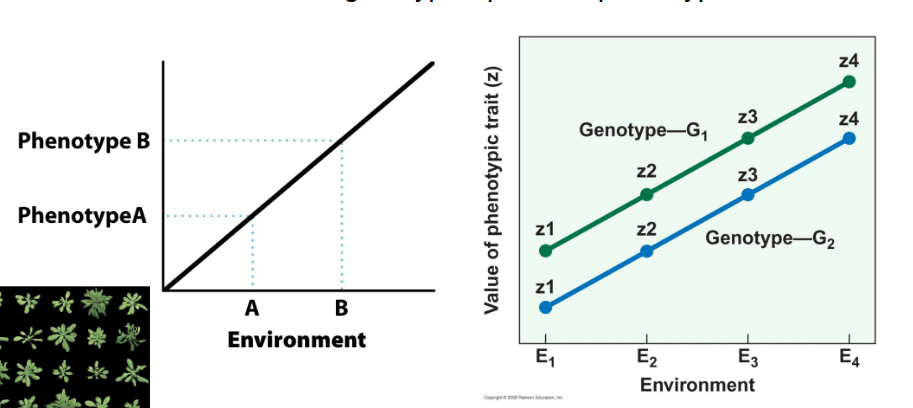
reaction norm framework
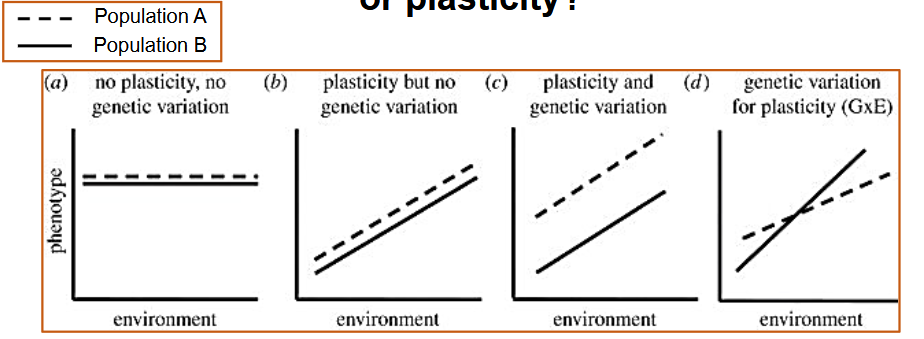
genetic variation vs plasticity
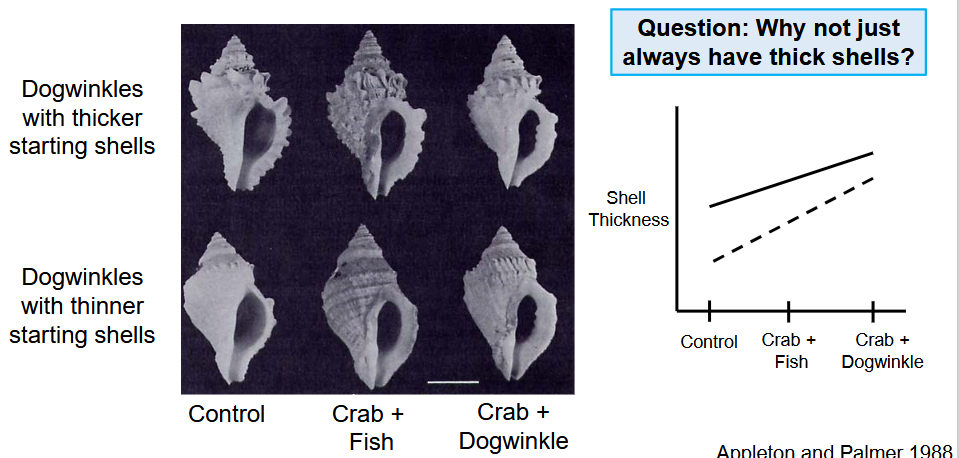
dogwinkle snail case study
control, crab eating fish, crab eating snail
control - normal shell
crab eating fish - thicker shell
crab eating snail - thickest shell
responds in shell thickness. yes, visible plasticity/response to environment
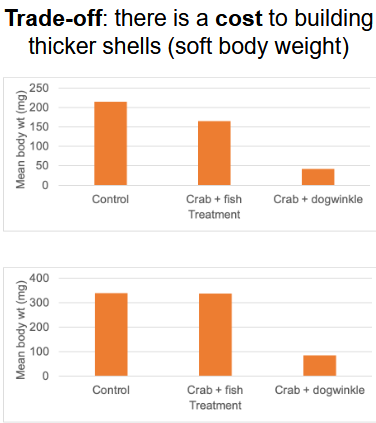
case study - why not always have thick shells?
ENERGY WASTE - the more energy given to grow shell, the lesser the body weight