wk2 - probability and parameter estimation
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
posterior probabilities
probability of the class after observing the data (evidence)
prior
probability of the class before observing the data (evidence)
likelihood
probability of observing a random data point given the class label (compatibility of the data with the given class)
evidence
probability of observing a (random) data point across all classes
Bayes Decision Rule
P(x|w1)P(w1) > P(x|w2)P(w2)
continuous random variable
a variable that cam take any value within a range (interval of real numbers)
- they are not countable
- they are measured not counted
what is the probability that a continuous random variable is equal to a specific value? P(X=x)
around 0, infinitely small
uniform distribution
every value within the range (a,b) is equally likely. therefore the probability density has a constant height of (1 / b-a)
total area under should equal 1
triangle distribution
the height of the triangle is chosen as (2 / b-a) with the total area being (base x height / 2)
univariate gaussian distribution
parameter μ controls location of the peak
parameter σ controls the width of the peak
defined for the range (-infinity < x < infinity)
also called the normal distribution
F(x) = P(X <= x)
cumulative distribution function
properties of the PDF
1. its values cannot be negative
p(x) >= 0 for all x
2. the area under the curve must equal to 1
bernoulli distribution
discrete probability distribution that models a random variable which takes only two possible outcomes (success / failure)
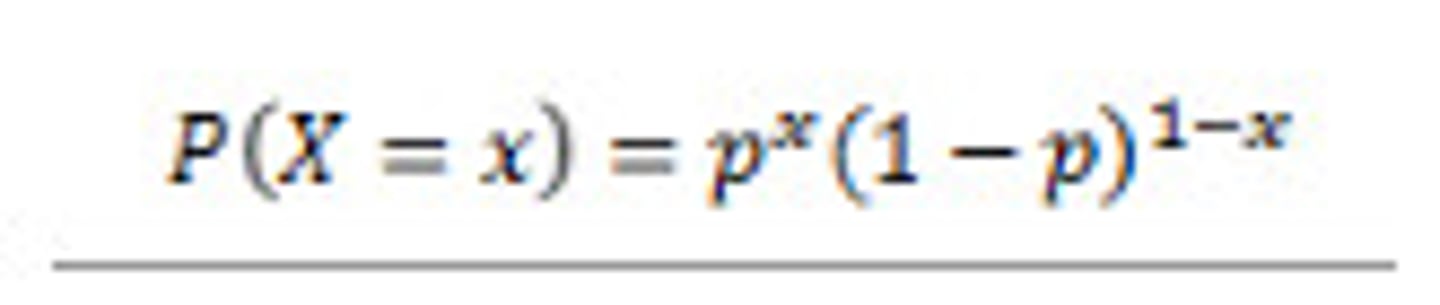
how are sample data stored in a matrix
each sample x is formulates as a N by L matrix, having N samples (rows) and L features (columns)
so each row is a sample, and how many columns is how many features it has
variance
this measures the spread of the data
to calculate this
you take away the mean from the sample, then square the result. do this for every one and then divide by how many you just did
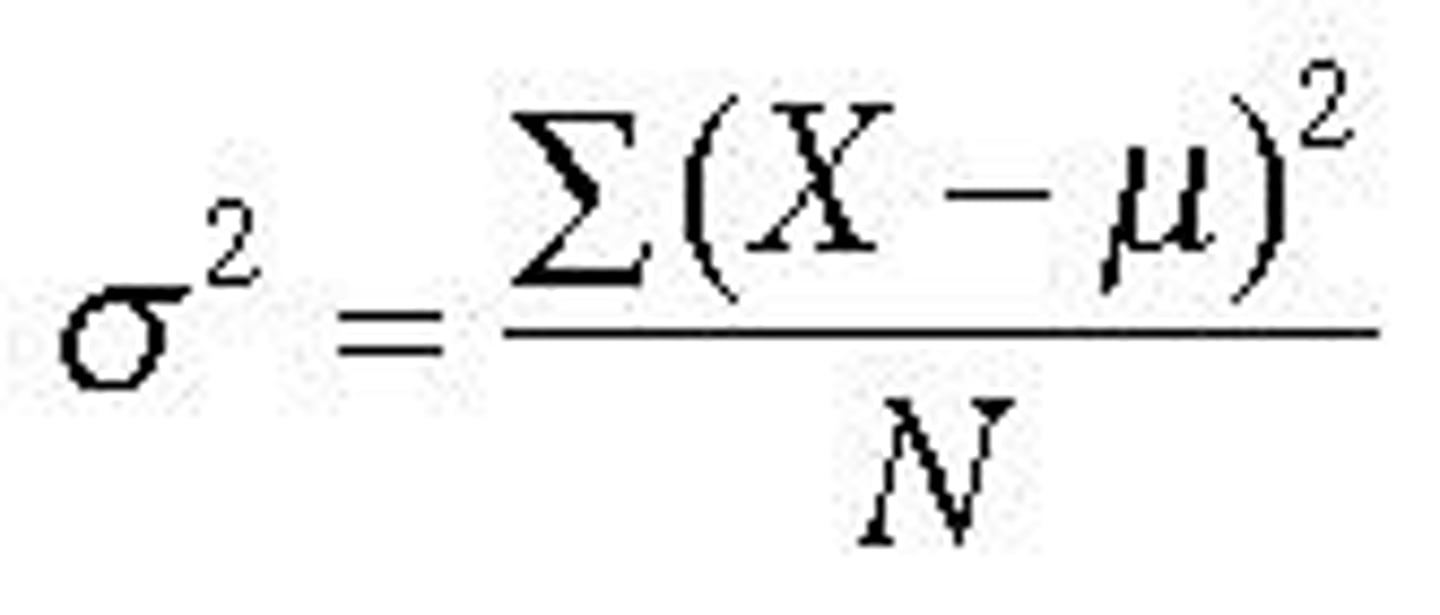
covariance
measure of association / correlation between two variables. it describes how the two variables relate or change together
times together the difference between sample and mean for two different variables for every one in the sample and divide by however many.
if both tend to increase or decrease togetherm then the covariance is positive
if one increases while the other decreasesm the covariance is negative
if they are independent, the covariance is closer to zero.
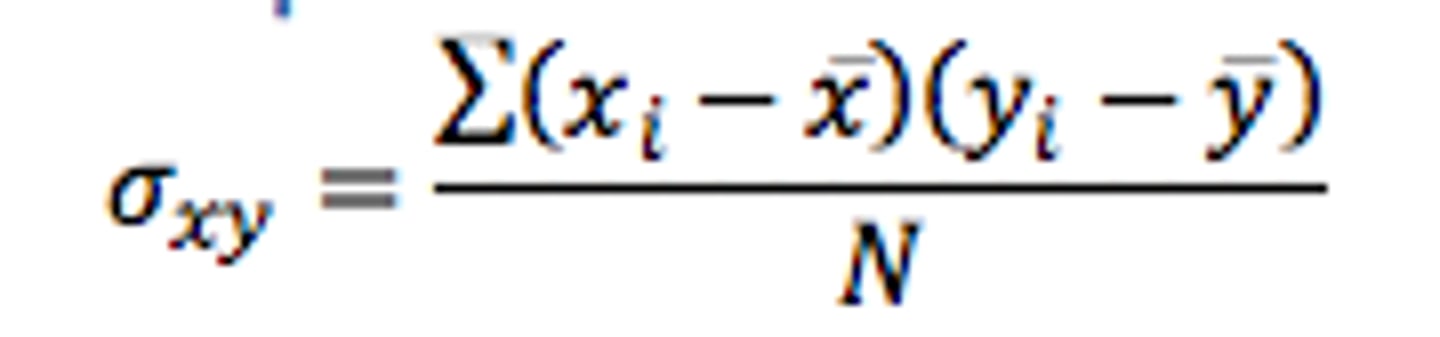
covariance matrix
the diagonal elements are the variances
the off-diagonals are the covariances
population statistics
refers to the entire group of data points that we are interested in studying. e.g. all adults in the UK.
population parameters are the true but usually unknown values that describe the population
sample statistic
a subset of the population selected for analysis
used to estimate population parameters
sample mean
unbiased estimate of the population mean
sample covariance
biased estimate of the population covariance
unbiased estimate of the population covariance
( N / (N-1) ) S
parameter likelihood function
it expresses the probability of observing the given data (random samples) as a function of the parameters θ
think of it as the probability that all the datapoints came from the distribution with parameters θ
maximum likelihood estimate (MLE)
estimates the parameters θ that best maximise the likelihood based on the data
why do the maximum likelihood estimate?
this function is to estimate the parameters θ that make the observed data most probable. by maximising the likelihood function p(X;θ), we find the parameter values that best explain the observed data.
what does sample independence mean for the likelihood function
we can factorise the probabilities.
product operator
used to represent a product of the sequence (just times everything together)
how to find the MLE
we need to find the values of θ where
∂p(X; θ) / ∂θ = 0
the gradient of the likelihood is zero when θ = MLE
log likelihood
this is easier
L(θ) = ln p(X; θ)