IGCSE Chemistry 0654 C1
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms

State the distinguishing properties of solids.
Fixed shape, fixed volume, cannot be compressed.

State the distinguishing properties of liquids.
No fixed shape, fixed volume, cannot be compressed.

State the distinguishing properties of gases.
No fixed shape, no fixed volume, can be compressed.
Describe the arrangement, separation, and motion of particles in a solid.
Closely packed, regular arrangement, vibrate in fixed positions.
Describe the arrangement, separation, and motion of particles in a liquid.
Closely packed, irregular arrangement, move around each other.
Describe the arrangement, separation, and motion of particles in a gas.
Far apart, random arrangement, move freely and quickly in all directions.
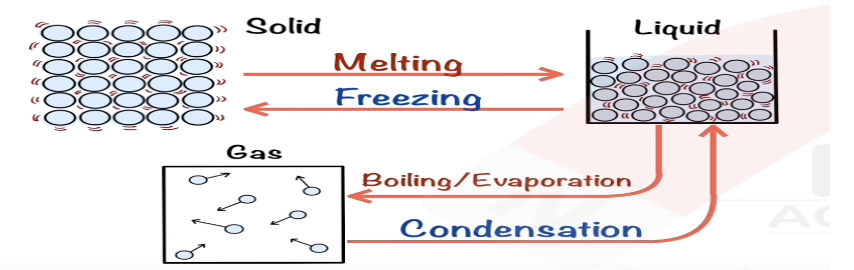
Describe melting in terms of kinetic particle theory.
Particles gain energy, bonds break, particles rearrange as a liquid.
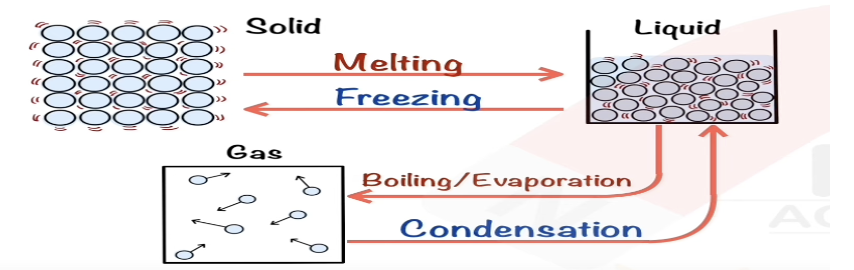
Describe boiling in terms of kinetic particle theory.
Particles gain more energy, bonds break, particles escape as gas.
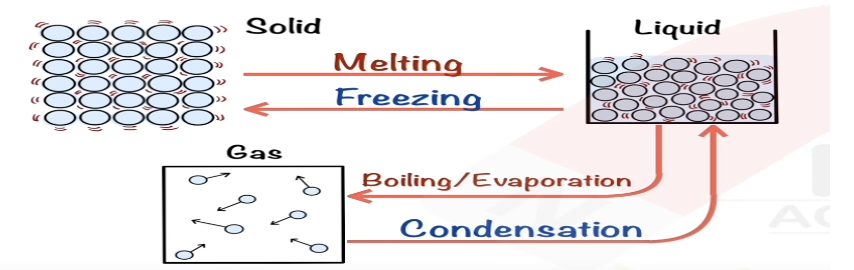
Describe evaporating in terms of kinetic particle theory.
Surface particles gain enough energy to escape as gas.
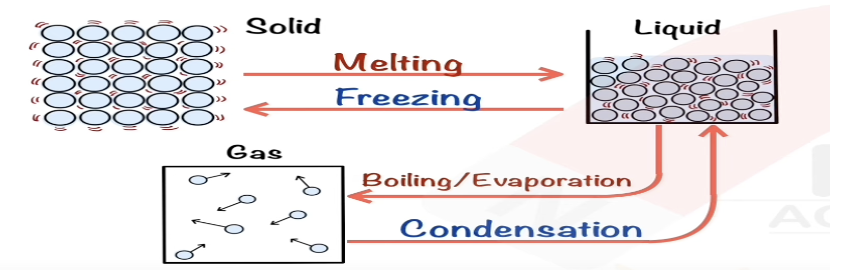
Describe freezing in terms of kinetic particle theory.
Particles lose energy, move closer, form bonds to become solid.
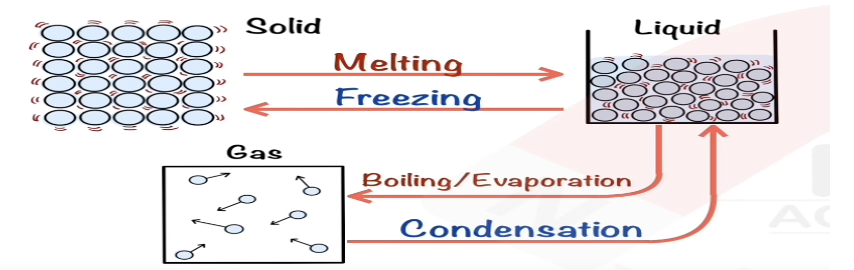
Describe condensing in terms of kinetic particle theory.
Particles lose energy, move closer, form bonds to become liquid.
Describe what happens when temperature increases at constant volume.
Particles move faster, hit walls more often, pressure increases.
Describe what happens when volume decreases at constant temperature.
Particles hit walls more often, pressure increases.
Explain what happens when a solid is heated below melting point.
Particles gain energy, vibrate more, move slightly apart, solid expands.
Explain what happens at the melting point.
Temperature is constant, bonds break, solid becomes liquid.
Explain what happens when a liquid is heated to boiling point.
Particles gain energy, move faster, take up more space, liquid expands.
Explain what happens at boiling point.
Temperature is constant, bonds break, particles become gas.
Explain what happens when a gas cools.
Particles lose energy, move slower, get closer, gas contracts.
Explain what happens during condensation.
Temperature is constant, particles form bonds, gas becomes liquid.
Explain what happens when a liquid cools.
Particles lose energy, move slower, come closer.
Explain what happens during freezing.
Temperature is constant, particles form bonds, liquid becomes solid.
Explain what happens when a solid cools.
Particles lose energy, move less, come closer.
Define diffusion.
Net movement of particles from high to low concentration.
Describe why diffusion does not occur in solids.
Particles only vibrate, cannot move freely.
Describe why diffusion occurs in liquids and gases.
Particles move and spread out by collisions.
Describe the effect of relative molecular mass on diffusion rate.
Greater mass = slower diffusion.
Explain why gases with lower molecular mass diffuse faster.
Lighter particles move faster.
Explain why gases with higher molecular mass diffuse slower.
Heavier particles move slower.
Explain why hot water evaporates more quickly than cold water.
Higher temperature gives particles more kinetic energy, so more escape as gas.
State two ways in which boiling differs from evaporation.
Boiling occurs throughout the liquid and only at boiling point; evaporation occurs at the surface at any temperature.
State three factors affecting the rate of evaporation.
Temperature, surface area, and air movement.
Explain how surface area affects rate of evaporation.
Larger surface area allows more particles to escape, increasing evaporation.
Explain how air movement affects evaporation.
Moving air removes water vapour, allowing more particles to escape.
Describe why evaporation causes cooling.
Faster particles escape, lowering average kinetic energy and temperatur