W4L8: Nucleophilic addition reactions: the basics
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Aldehydes and ketones
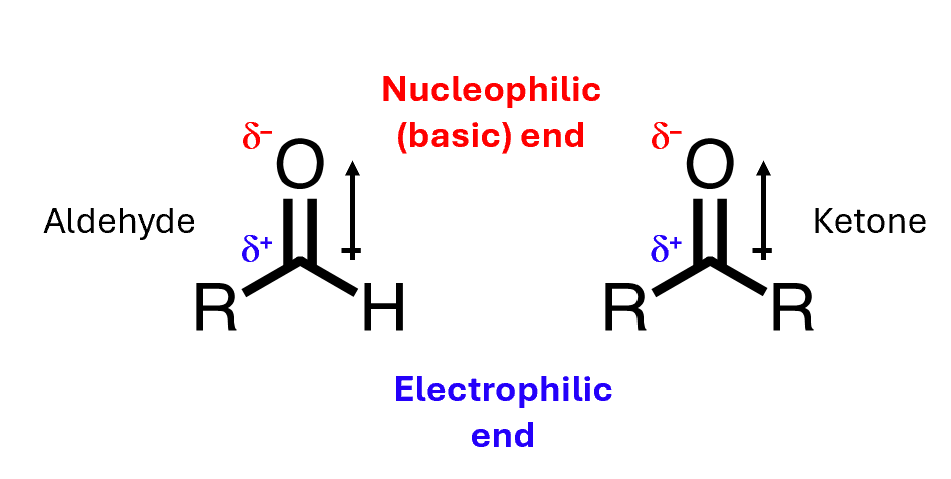
Aldehydes and ketones contain a highly polar C=O bond
Oxygen is very electronegative, and it draws electron density towards itself, giving a partial positive charge down on the carbon and a partial negative charge up on the oxygen.
That means that carbonyls can act as nucleophiles or as electrophiles.
The oxygen end, being negative, is nucleophilic, and therefore also basic
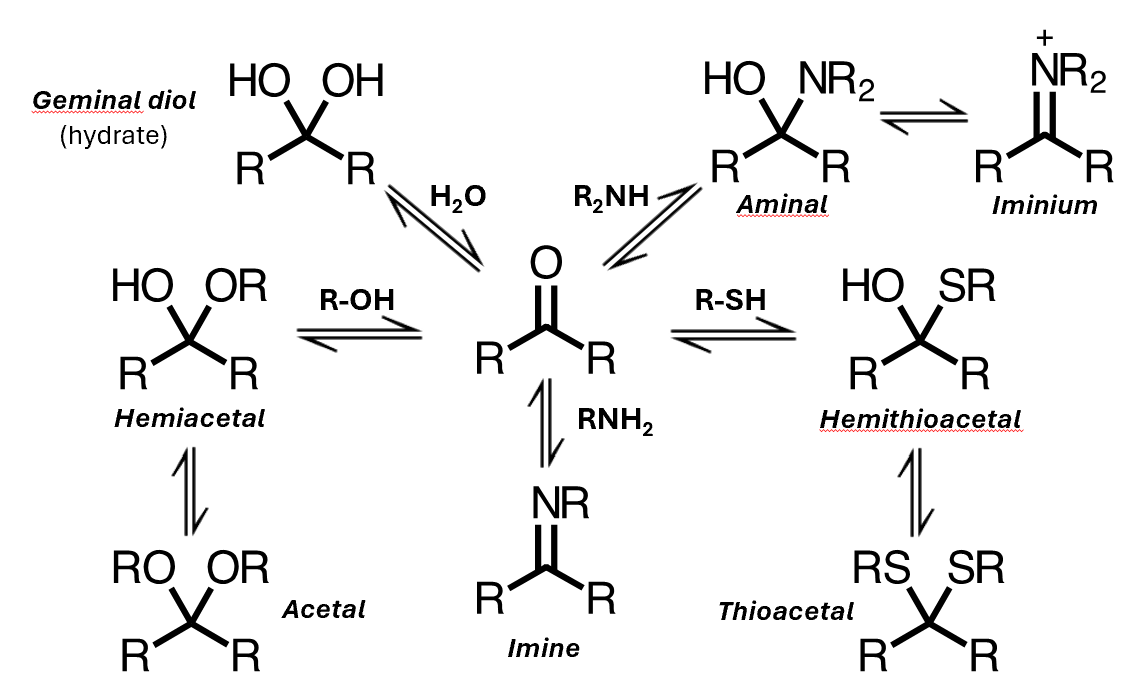
Nucleophilic addition to carbonyls
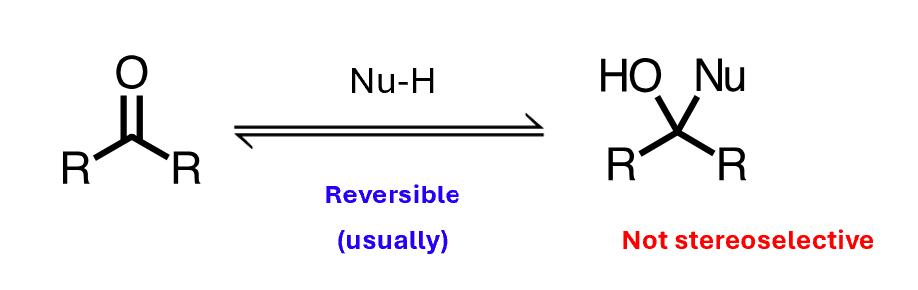
Nucleophiles can add to aldehydes and ketones
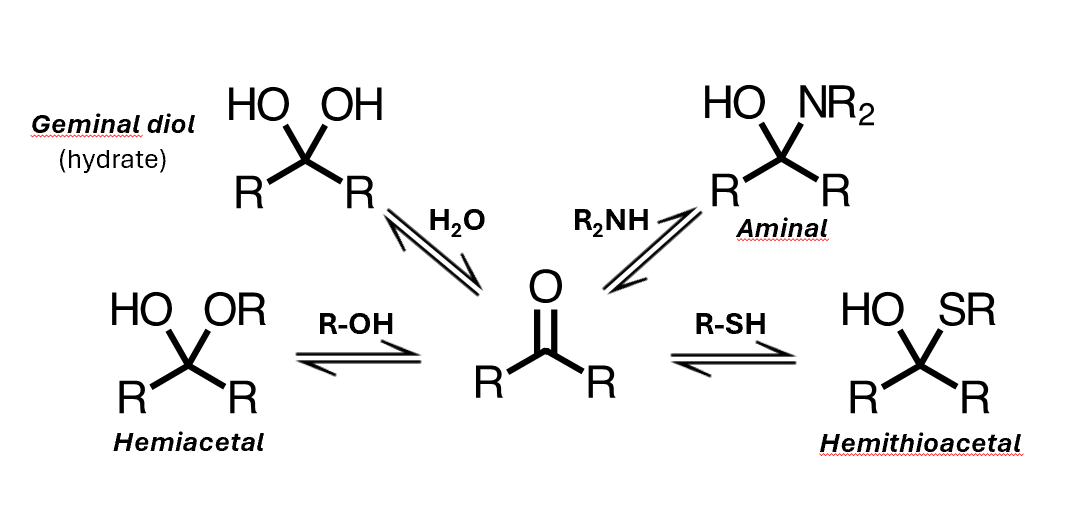
Neutral nucleophiles
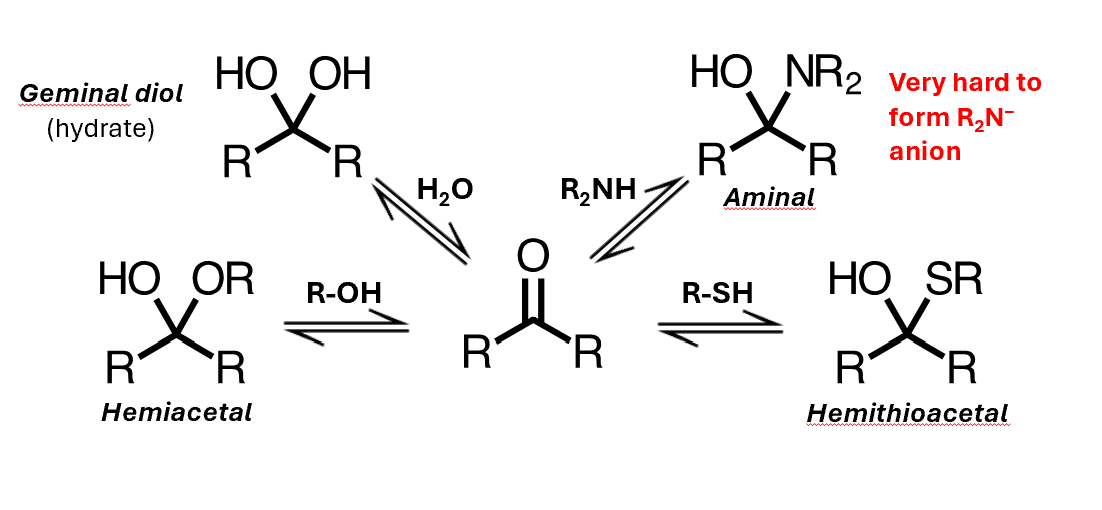
You can get addition of water, to form a geminal diol, or you can get addition of an alcohol to give a hemiacetal, where you have an alkoxy group instead of this hydroxyl
A hemiacetal is not just an alcohol plus an ether – its reactivity is different to either of those species
Addition of a thiol gives the analogous hemithioacetal, and addition of an amine gives an aminal
Added the nucleophilic atom to the carbon, and added a proton to the oxygen.
Neutral nucleophiles: mechanism
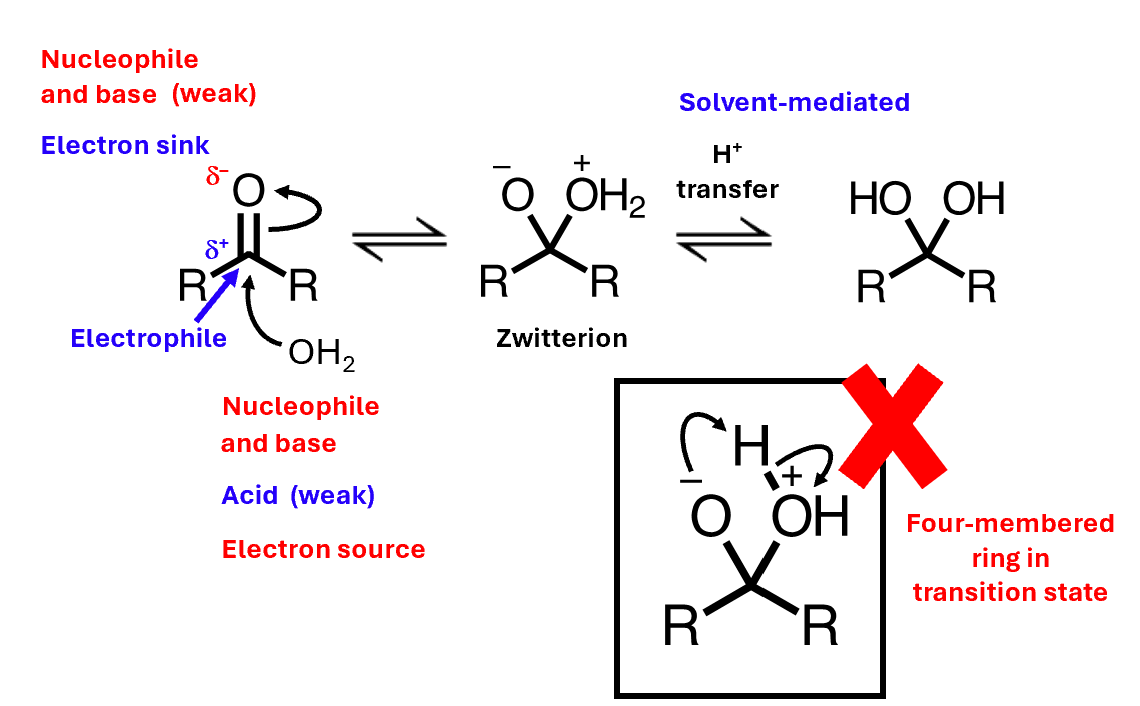
Base catalysis: mechanism
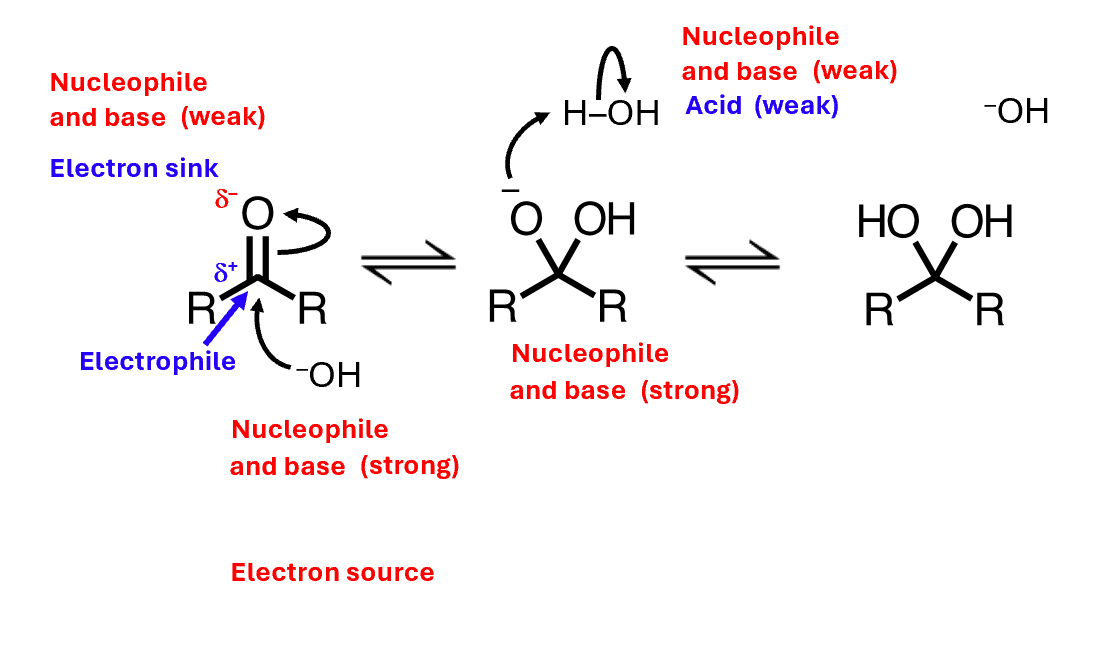
Base catalysis
Base catalysis allows us to reach equilibrium much faster than we would in the neutral reaction, and it works for all the species you met previously except the aminal
That's because the other reactants are relatively easy to deprotonate under base catalysis, but amines are not - their anions are too unstable
Acid catalysis: mechanism
faster
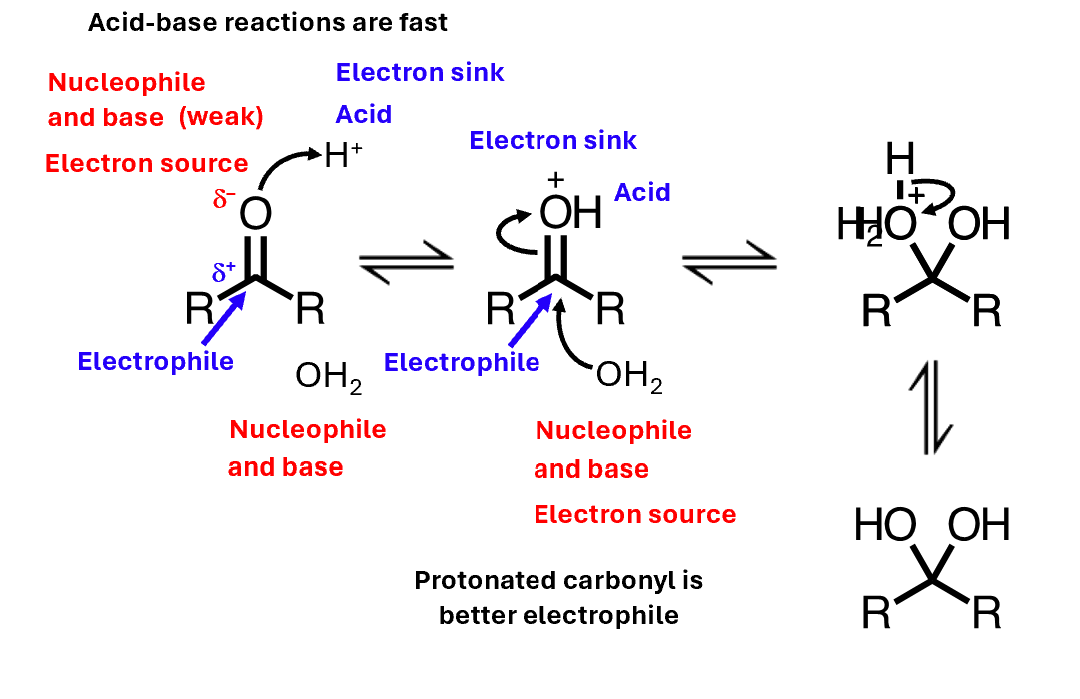
Acid catalysis: further reaction