Comparison of Dispute Resolution Methods & POJ: KK9
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
the third party (is there a third party?, role of third party, is the decision binding?)
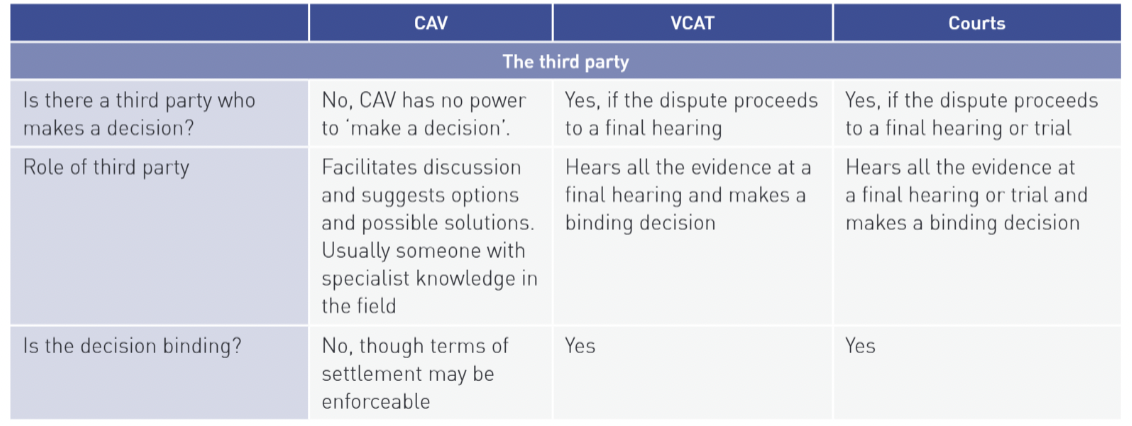
processes and procedures
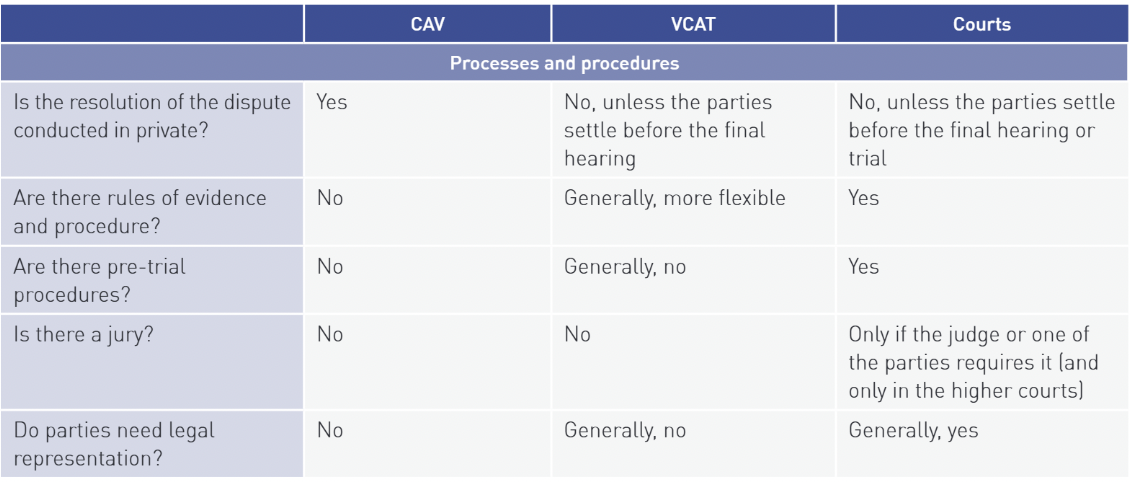
types of civil disputes
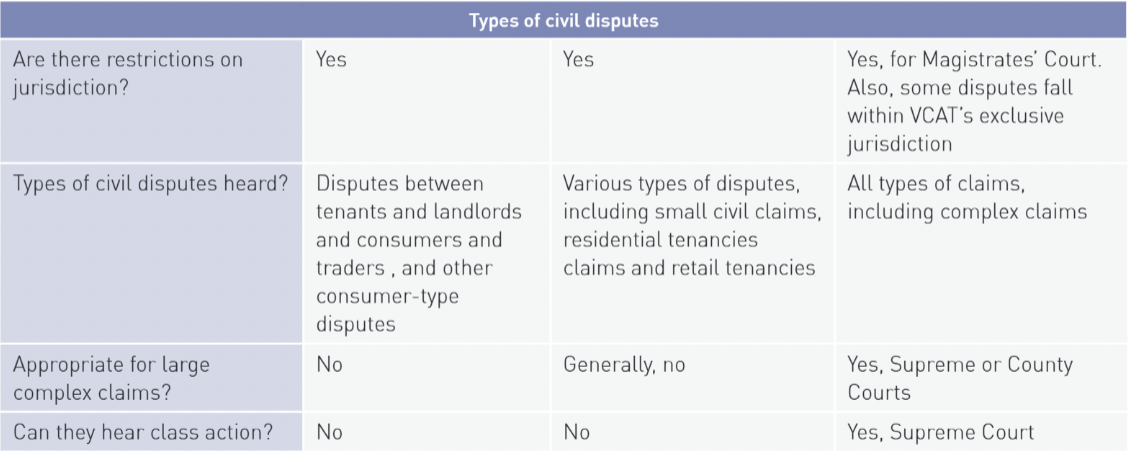
dispute resolution methods
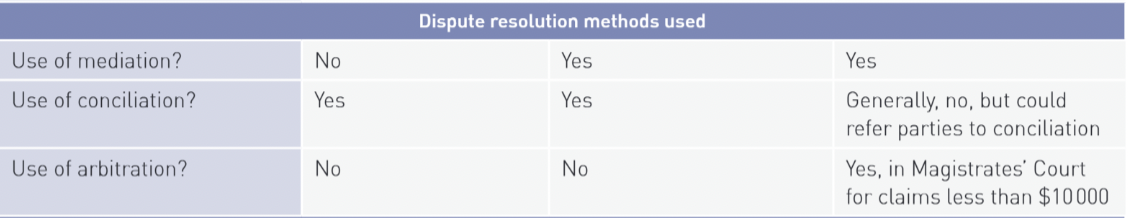
hierarchy and appeals

fairness
disputes are resolved by those with expertise - therefore outcomes are just
vcat members are independent and unbiased leading to a fair outcome
cav ensure procedural fairness by allowing both sides the opportunity to present their claim
each list at vcat has a specialised jurisdiction, meaning triburnal personnelle gain expertise in resolving disputes in that area of law, leading to fair outcomes
informal atmosphere at vcat ensures people can present their case how they wish to
at cav parties come to a mutually agreed to resolution themselves that will benefit them both
equality
achieves
VCAT prohibits the use of legal representation in some lists, ensuring one party will not have advantage over another
flexibility in vcat’s hearing process ensures equaliy for self-represented party as vcat member can ensure that they an equal opportunity to understand the processes, and present their case
not achieve
not all consumer complaints fall under the jurisdiction of CAV
similar civil disputes could be handled differently through different bodies
access
achieve
vcat generally less expensive than courts
cav’s conciliation service is free
vcat generally offers a speedy resolution of disputes
vcat conducts hearings in various locations across victoria - as well as online or by phone
cav’s conciliation process can be conducted over the phone
not achieve
Legal representation is becoming more common in VCAT, increasing costs
VCAT has an increasing caseload, increasing delays in some lists
cav and vcat both have limited jurisdictions
cav does not accept many claims, and conciliation service is limited