Chapter 1- Economics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
This means that there is never enough resources to satisfy all human wants
What is scarcity?
This is the study of trade-offs and choices that we make, given then fact of scarcity
What is economics?
This is what we give up when we choose one thing over another. could also be the value of the next best alternative
What is opportunity cost?
In a world of scarcity, it is impossible to
Meet all of society’s wants.
These are goods and services to which a consumer must pay to obtain; also called scarce goods, demand would be greater than supply if price was zero
What are economic goods?
These are goods and services that a consumer can obtain for free because they are abundant relative to the demand
What are free goods?
These are the inputs used in the production of goods and services to make a profit: land, economic capital, labor, and entrepreneurship, also called “factors of production.”
What are productive resources?
These is a factor of production, any natural resource, land, trees, plants, livestock, wind, sun, water, etc
What is land?
This is a factor of production, anything thats manufactured in order to be used in the production of goods and services.
What is economic capital?
This is a factor of production, any human service- physical or intellectual. Referred to as human capital
What is Labor?
This is a factor of production, the ability of someone (an entrepreneur) to recognize a profit opportunity, organize the other factors of production, and accept risk.
What is entrepreneurship?
You can choose to take public transportation or drive your car to get to school. If the fare for taking public transit increases while the cost of driving your car remains the same, this means that
Opportunity cost is what you give up when you choose one option over another. If the fare for public transit increases, taking the bus becomes more expensive, making driving relatively more attractive without changing its actual cost. Therefore, you're giving up less by choosing to drive instead of taking public transit.
So, the opportunity cost of driving decreases.
How do you find the full cost of something?
Direct (Out of pocket) Cost + Indirect (Opportunity) Cost
Smith’s theory of the division and specialization of labor implies that a worker skilled in engineering will
yield economic output that is sub-optimal if she were employed in something other than engineering-type functions
Explanation:
According to Adam Smith’s theory of the division and specialization of labor, individuals and workers are most productive when they specialize in tasks suited to their skills and expertise. If a skilled engineer is placed in a role unrelated to engineering, her potential productivity isn’t fully realized, leading to sub-optimal economic output — not necessarily negative, but less than what it could be if her talents were properly used.
An economy is composed entirely of two equally sized farms A and B producing both eggs and milk. Farm A is better at producing eggs than Farm B which is better at producing milk. Then in order to maximize output, Farm A should
Abandon the production of milk to fully specialize in the production of eggs and then trade with Farm B for milk
This is the way in which the work required to produce a good/service is divided into tasks performed by different workers
What is the division of labor?
This is when the average cost of producing each individual unit declines as total output increases
What is economies of scale?
This is when workers or firms focus on a particular task for which they are well suited within the overall production process
What is specialization?
Why does the division of labor increase production?
It increases production efficiency by allowing workers to focus on specific tasks, leading to greater expertise, faster work, and lower costs.
What are the goals of macroeconomics?
Growth in the standard of living, low unemployment, and low inflation
Government expenditures on public schools is classified as ________ policy.
fiscal
These are economic policies that involve government spending and taxes. Think of government revenue and taxes
What are fiscal policies?
This is the branch of economics that focuses on broad issues such as growth, unemployment, inflation, and trade balance
What is macroeconomics?
This is the branch of economics that focuses on actions of particular agents within the economy, like households, workers, and businesses
What is microeconomics?
These are policies that involve altering the level of interest rates, the availability of credit in the economy, and the extent of borrowing
What are monetary policies?
How is price represented on a graph?
What is the y-axis?
How is quantity represented on a graph?
What is the x-axis?
How do you find the x-intercept?
This is when y=0
How do you find the y-intercept?
This is when x=0
Formula for slope
Rise/ Run: Change in vertical axis/ Change in horizontal axis
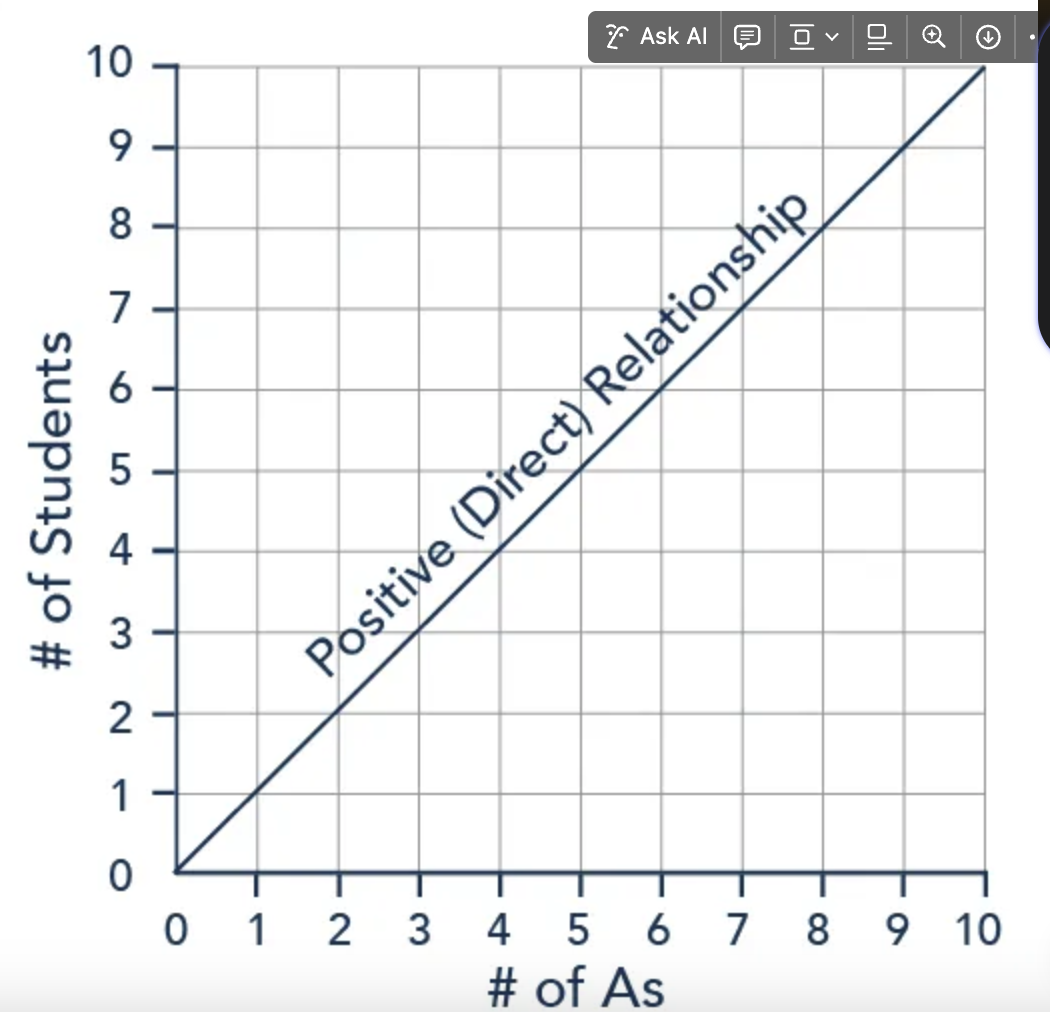
This means that two variables are positively related; when x increases, so does y, and when x decreases, y also decreases
In economics, price and quantity supply have a positive relations, firms will supply more when price is higher
What is a positive slope?
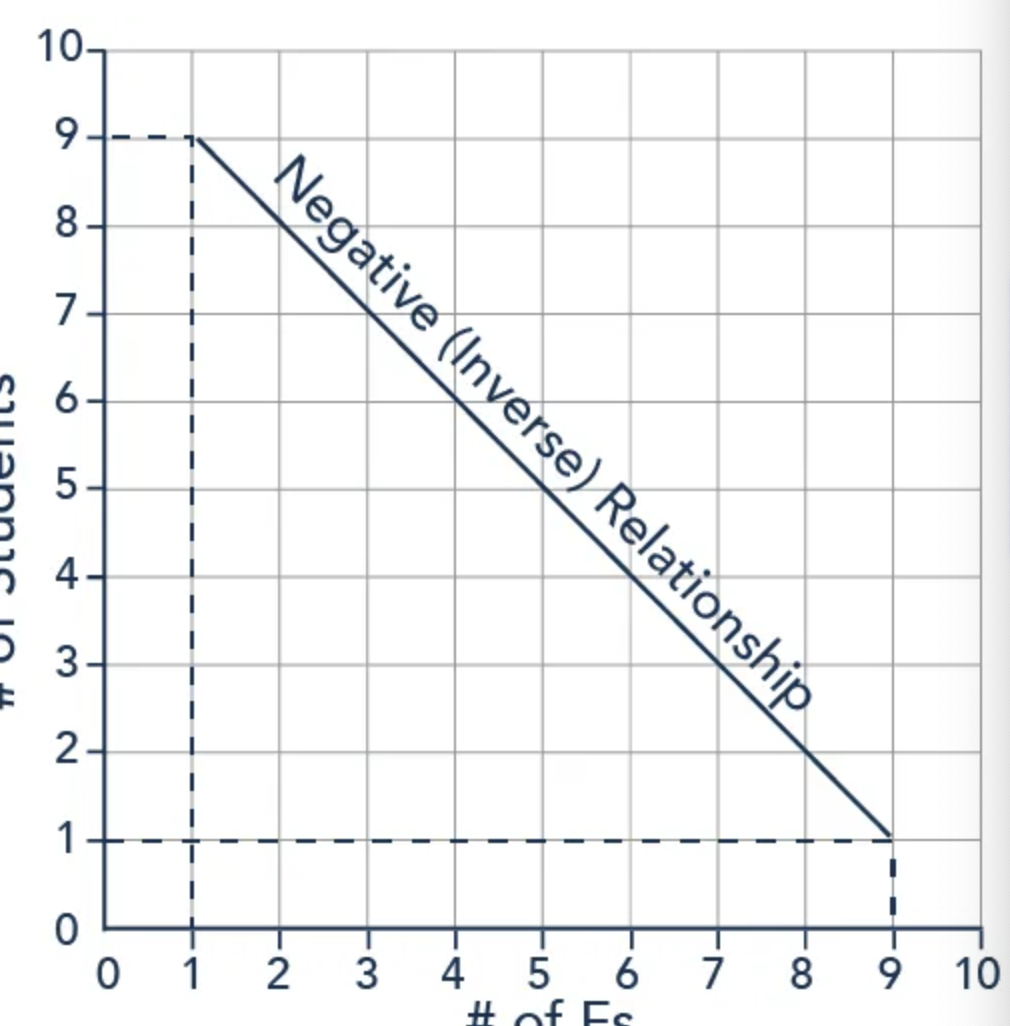
This is when two variables are negatively related; when x increases, y decreases. When x decreases, y increases
In economics, price and quantity have this relationship: consumers will purchase less when the price is higher.
What is a negative slope?
This means that y is constant no matter the value of x, the line is flat
What is a slope of zero?