Integumentary System Study Guide
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Last updated 12:54 AM on 1/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
What is the function of the skin?
* Maintains homeostasis by
* Regulating temperature
* Protecting underlying tissues
* Slowing water loss
* Housing sensory receptors
* Synthesizing certain chemicals
* Excreting wastes
* Regulating temperature
* Protecting underlying tissues
* Slowing water loss
* Housing sensory receptors
* Synthesizing certain chemicals
* Excreting wastes
2
New cards
What are the 2 layers of skin?
Epidermis & dermis
3
New cards
What is the subcutaneous layer?
A layer of adpiose tissue beneath the epidermis & dermis
4
New cards
What does the subcutaneous layer contain?
Made of fat, or **adipose** tissue
5
New cards
Nails consist of what type of cells?
Stratified squamous epithelial cells
6
New cards
What are the structures within the dermis?
* Made of **connective** tissues
* %%Papillary layer%%
* Dermal papillae
* Meissner’s corpuscle
* Capillary net
* Free-nerve endings
* Dermal ridges
* ^^Reticular layer^^
* Arrector pili muscle
* Hair follicle
* Sebaceous gland
* Pacinian corpuscle
* Sudoriferous gland
* %%Papillary layer%%
* Dermal papillae
* Meissner’s corpuscle
* Capillary net
* Free-nerve endings
* Dermal ridges
* ^^Reticular layer^^
* Arrector pili muscle
* Hair follicle
* Sebaceous gland
* Pacinian corpuscle
* Sudoriferous gland
7
New cards
%%Dermal papillae%%
Zippers together the dermis & epidermis
8
New cards
%%Meissner’s corpuscle%%
Sensory receptors that sense light touch
9
New cards
%%Capillary net%%
Delivers blood to & from the top of the dermis
10
New cards
%%Free-nerve endings%%
Sensory receptors that sense pain, heat, & cold
11
New cards
%%Dermal ridges%%
Large mound of dermal papillae in the hands & feet
12
New cards
^^Arrector pili muscle^^
Contracts to cause a hair to raise on end
13
New cards
^^Hair follicle^^
Where a hair grows from
14
New cards
^^Sebaceous gland^^
Oil glands
15
New cards
^^Pacinian corpuscle^^
Sensory receptors that sense heavy pressure
16
New cards
^^Sudoriferous gland^^
Sweat glands
17
New cards
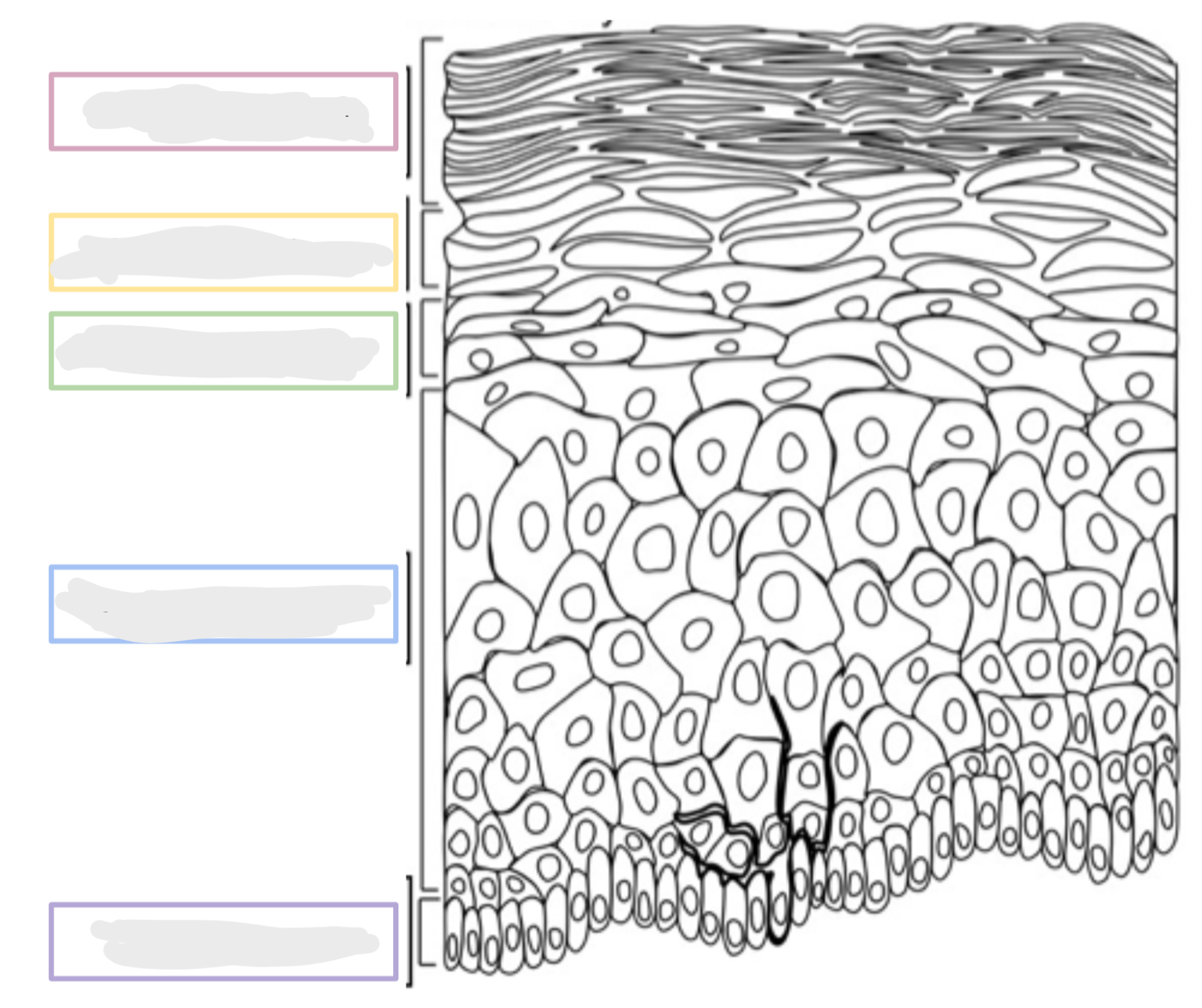
What are the layers of the epidermis?
* Stratum
* **C**orneum
* **L**ucidum
* **G**ranulosum
* **S**pinosum
* **B**asale
* **C**orneum
* **L**ucidum
* **G**ranulosum
* **S**pinosum
* **B**asale
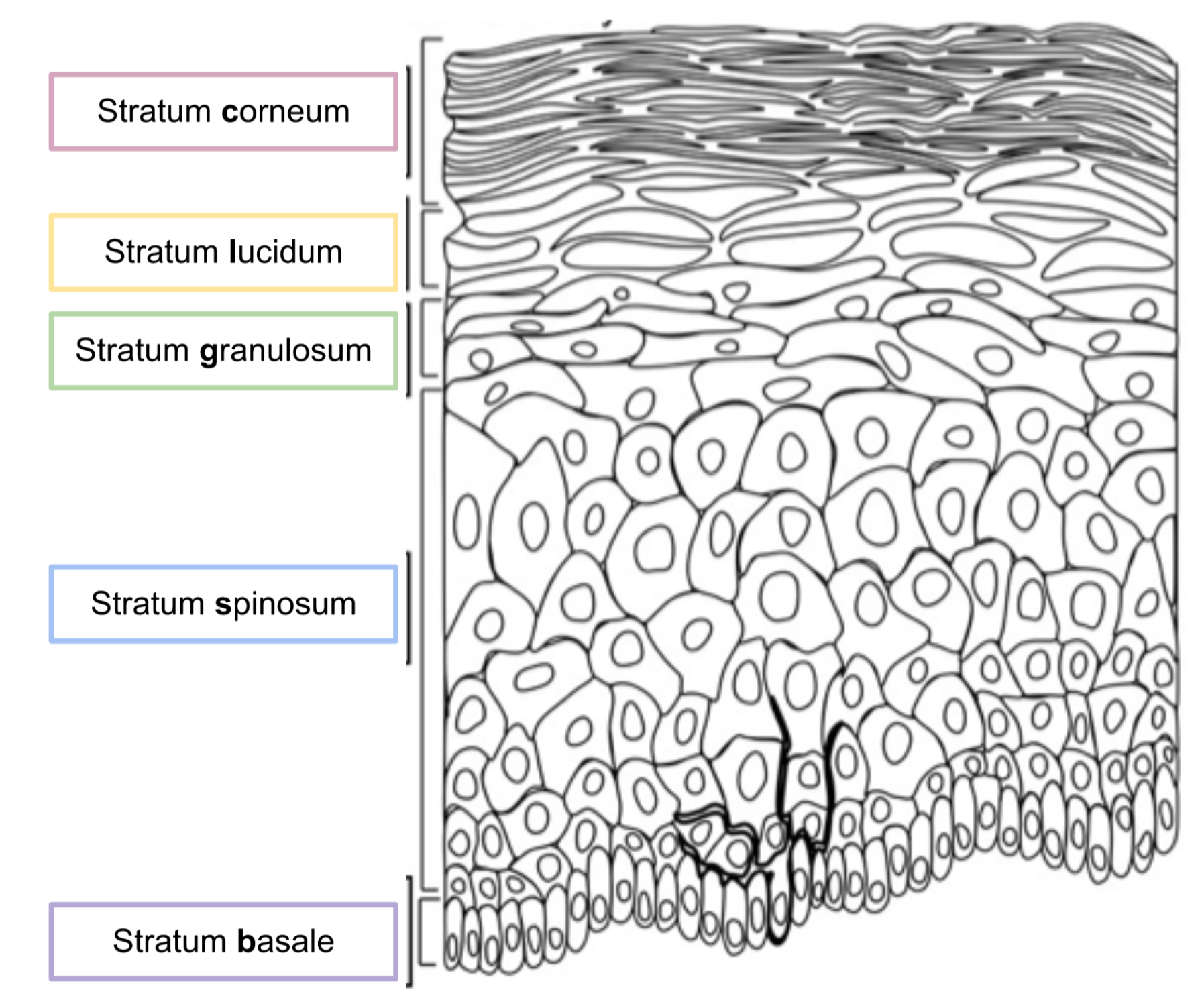
18
New cards
What are the characteristics of each layer of the epidermis?
* Made of **epithelial** tissues
* Stratum **c**orneum - most superficial layer; made of 20 to 30 layers of dead squamous cells; constantly shedding
* Stratum **l**ucidum - very thin; only found in thick skin; found in palms or soles; dead
* Stratum **g**ranulosum - living cells
* Stratum **s**pinosum - living cells
* Stratum **b**asale - living cells; mitotic; deepest layer; pushing the more superficial layers up & causing them to shed off
* Stratum **c**orneum - most superficial layer; made of 20 to 30 layers of dead squamous cells; constantly shedding
* Stratum **l**ucidum - very thin; only found in thick skin; found in palms or soles; dead
* Stratum **g**ranulosum - living cells
* Stratum **s**pinosum - living cells
* Stratum **b**asale - living cells; mitotic; deepest layer; pushing the more superficial layers up & causing them to shed off
19
New cards
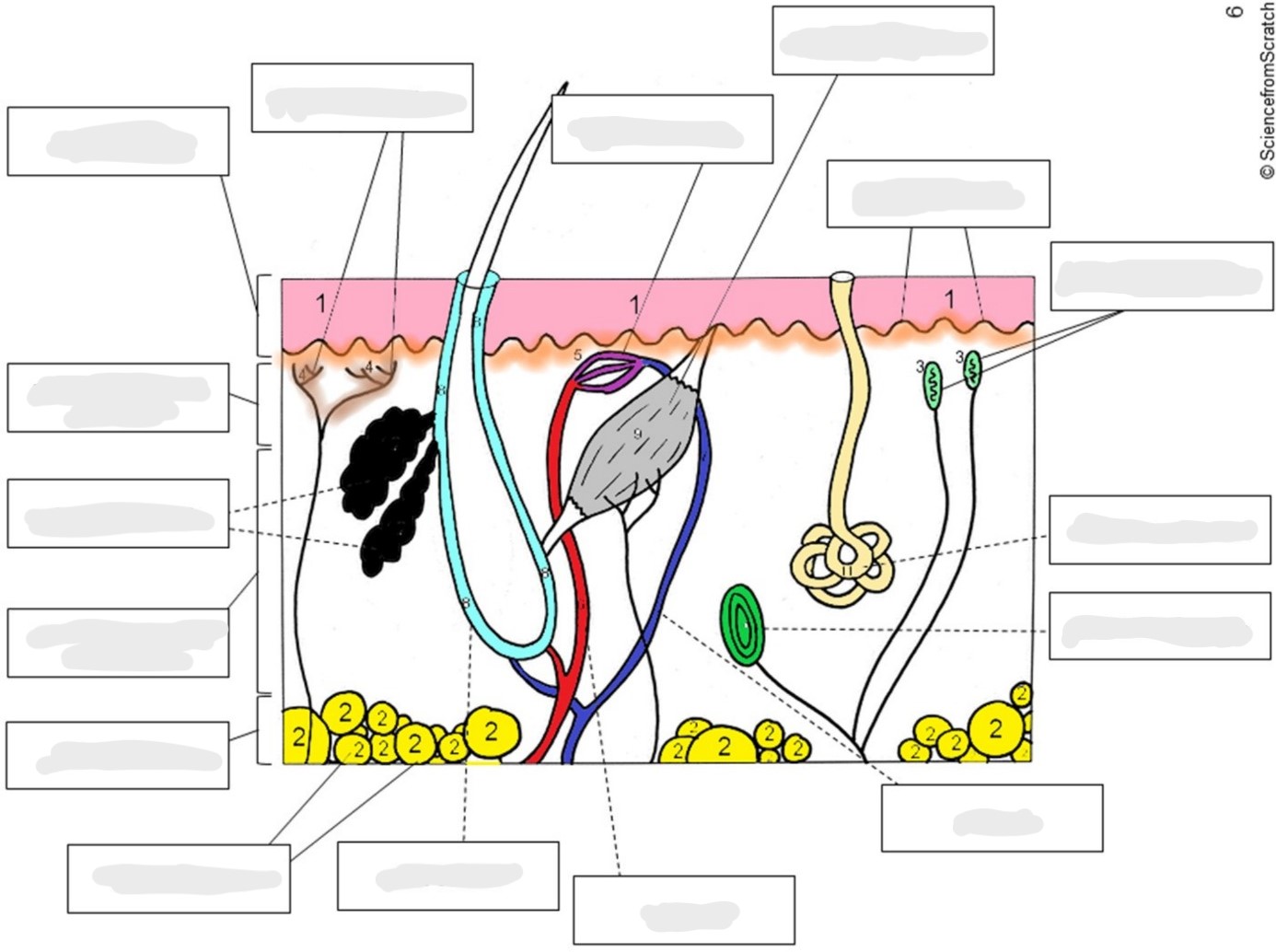
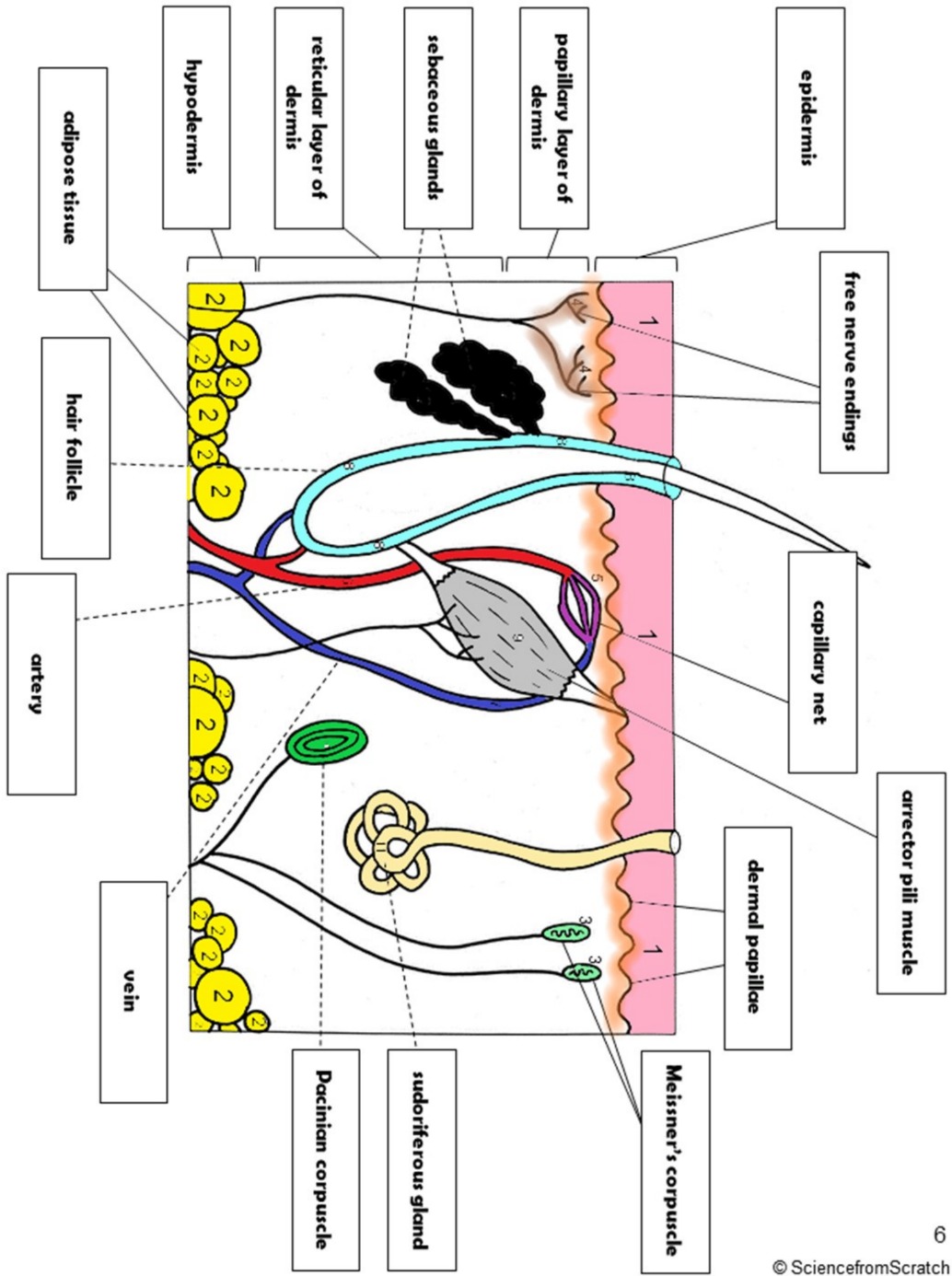
Where are all of these structures located?
* Epidermis
* Free-nerve endings
* Capillary net
* Arrector pili muscle
* Dermal papillae
* Meissner’s corpuscles
* Sudoriferous gland
* Pacinian corpuscle
* Vein
* Artery
* Hair follicle
* Adipose tissue
* Hypodermis
* Reticular layer of the dermis
* Sebaceous glands
* Papillary layer of the dermis
* Epidermis
* Free-nerve endings
* Capillary net
* Arrector pili muscle
* Dermal papillae
* Meissner’s corpuscles
* Sudoriferous gland
* Pacinian corpuscle
* Vein
* Artery
* Hair follicle
* Adipose tissue
* Hypodermis
* Reticular layer of the dermis
* Sebaceous glands
* Papillary layer of the dermis
* Epidermis
* Free-nerve endings
* Capillary net
* Arrector pili muscle
* Dermal papillae
* Meissner’s corpuscles
* Sudoriferous gland
* Pacinian corpuscle
* Vein
* Artery
* Hair follicle
* Adipose tissue
* Hypodermis
* Reticular layer of the dermis
* Sebaceous glands
* Papillary layer of the dermis
* Free-nerve endings
* Capillary net
* Arrector pili muscle
* Dermal papillae
* Meissner’s corpuscles
* Sudoriferous gland
* Pacinian corpuscle
* Vein
* Artery
* Hair follicle
* Adipose tissue
* Hypodermis
* Reticular layer of the dermis
* Sebaceous glands
* Papillary layer of the dermis
20
New cards
What does the body do to regulate temperature?
* In response to increased body temperature, the skin can cool the body down by sweating or dilating blood vessels located in the dermis. The dilated vessels allow heat to be released & make you turn red when warm.
* In response to lowered body temperature, the blood vessels constrict, preventing heat loss. Tiny muscles in the dermis can also pull hair upright in an attempt to trap heat near the skin surface, causing goosebumps. Free-nerve endings can activate muscles to shiver, generating heat.
* In response to lowered body temperature, the blood vessels constrict, preventing heat loss. Tiny muscles in the dermis can also pull hair upright in an attempt to trap heat near the skin surface, causing goosebumps. Free-nerve endings can activate muscles to shiver, generating heat.
21
New cards
What happens when there is inflammation of the skin?
* Blood vessels dilate & become more permeable, causing tissues to become red & swollen.
* Superficial cuts are filled in by reproducing epithelial cells.
* Deeper cuts are closed off by clots, covered by scabs, & eventually filled in by fibroblasts, making connective tissue. Blood vessels extend into the area, injured tissues are replaced, & the scab falls off.
* Large wounds leave scars, & healing may be accompanied by the formation of granulations.
* Superficial cuts are filled in by reproducing epithelial cells.
* Deeper cuts are closed off by clots, covered by scabs, & eventually filled in by fibroblasts, making connective tissue. Blood vessels extend into the area, injured tissues are replaced, & the scab falls off.
* Large wounds leave scars, & healing may be accompanied by the formation of granulations.
22
New cards
Be able to **describe** the degrees of burns.
* 1st degree burns can usually be treated at home with cool water & aloe. The epidermis is the only level affected, & the wound is considered superficial. The skin becomes pink but doesn’t blister or scar, & no underlying tissues are damaged.
* In 2nd degree burns, both the dermis & the epidermis are damaged. Skin will appear swollen, red, & shiny, or wet. Blisters will usually form on a 2nd degree burn.
* 3rd degree burns affect every layer of the skin, often completely destroying the epidermis & dermis. Often, these burns don’t hurt because the underlying nerve tissue has been destroyed as well. Skin will appear white, charred, & leathery.
* In 2nd degree burns, both the dermis & the epidermis are damaged. Skin will appear swollen, red, & shiny, or wet. Blisters will usually form on a 2nd degree burn.
* 3rd degree burns affect every layer of the skin, often completely destroying the epidermis & dermis. Often, these burns don’t hurt because the underlying nerve tissue has been destroyed as well. Skin will appear white, charred, & leathery.
23
New cards
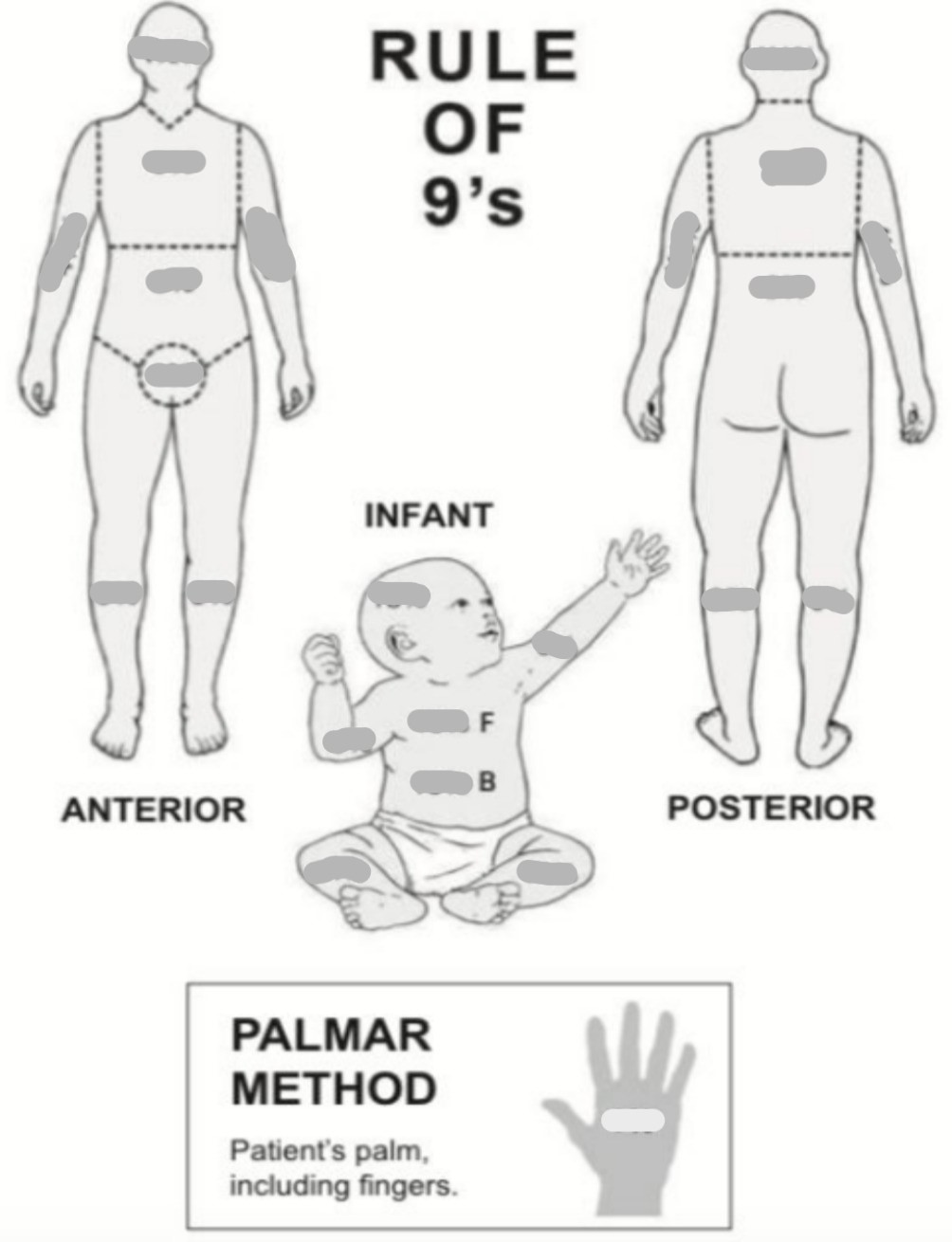
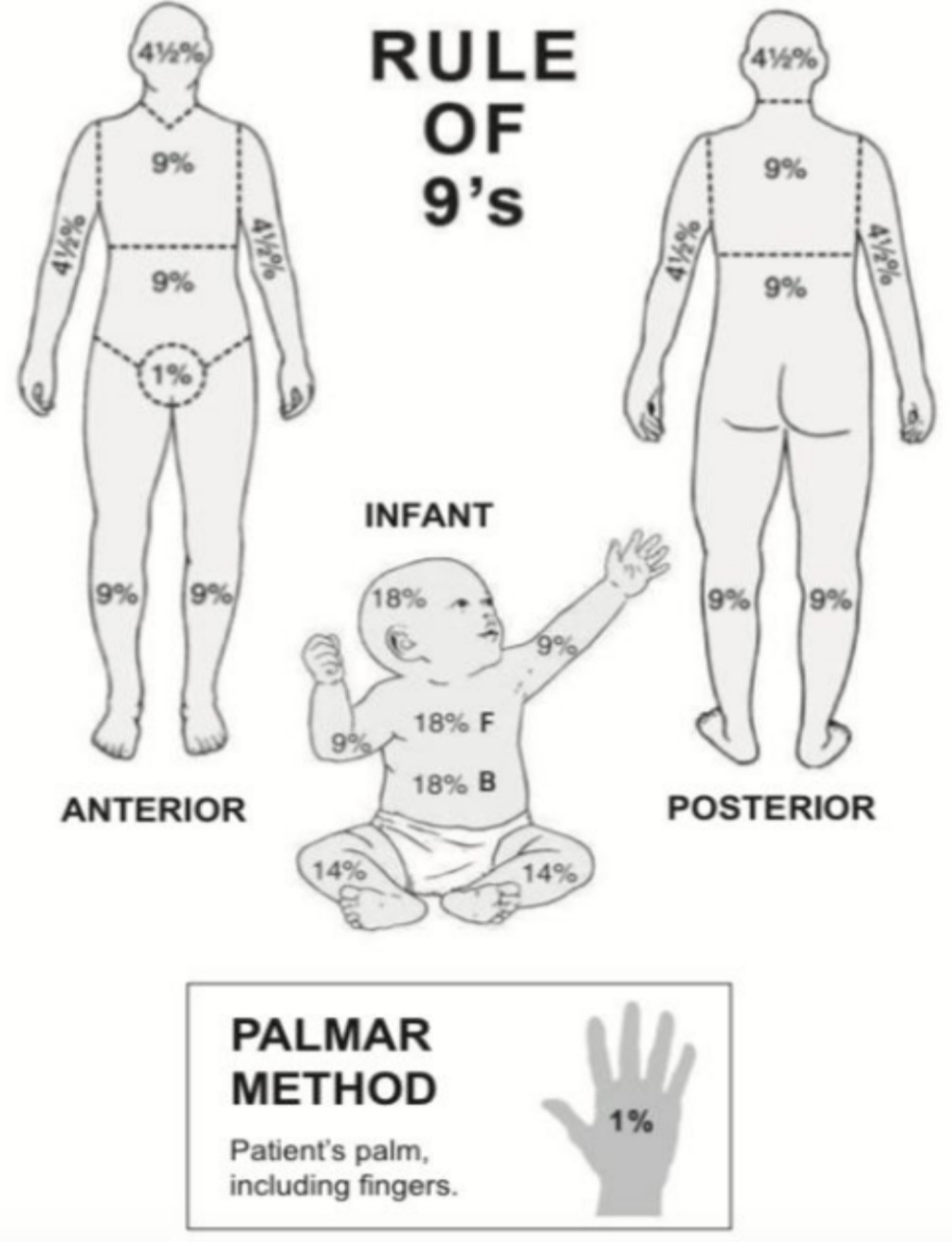
What is used to assess burn patients?
The Rule of 9’s
24
New cards
What are the long-term effects of burn victims?
* Contracture
* Inability to sweat
* Dry or even cracked skin
* Discoloration
* Sensation changes
* Inability to sweat
* Dry or even cracked skin
* Discoloration
* Sensation changes