AQA GCSE Physics - Electricity
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
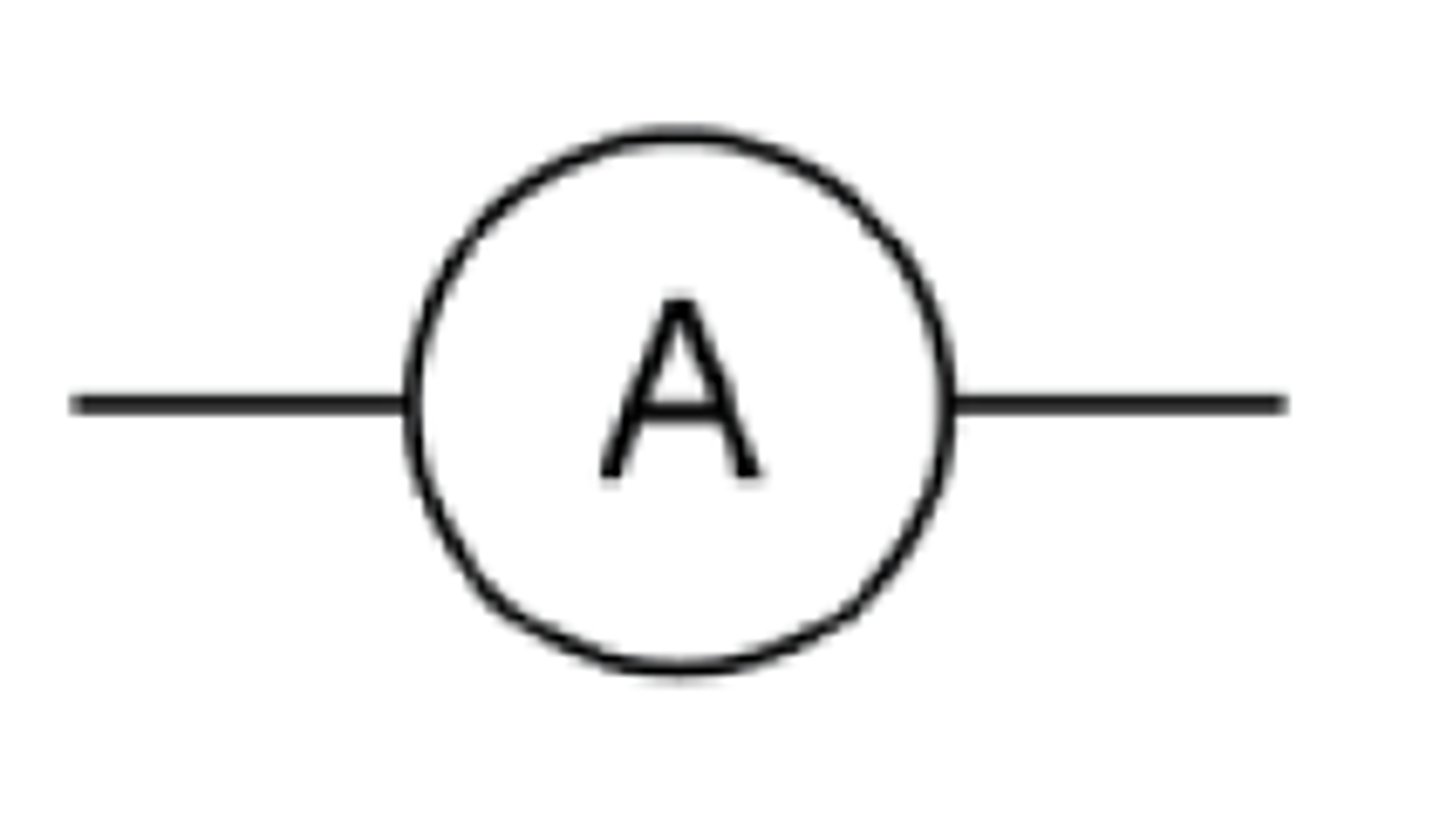
What is the circuit symbol for an ammeter?
What is the circuit symbol for a battery?
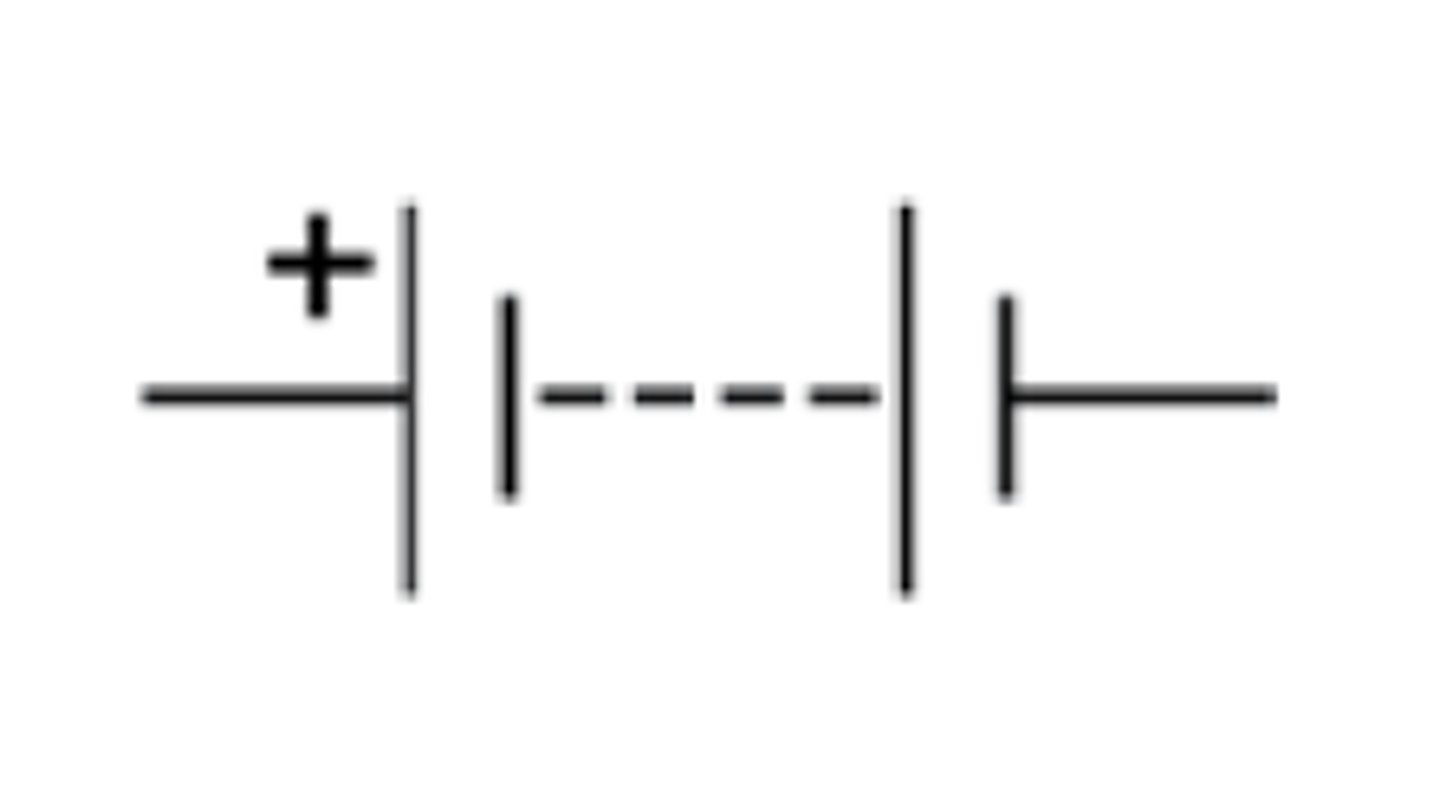
What is the circuit symbol for a cell?
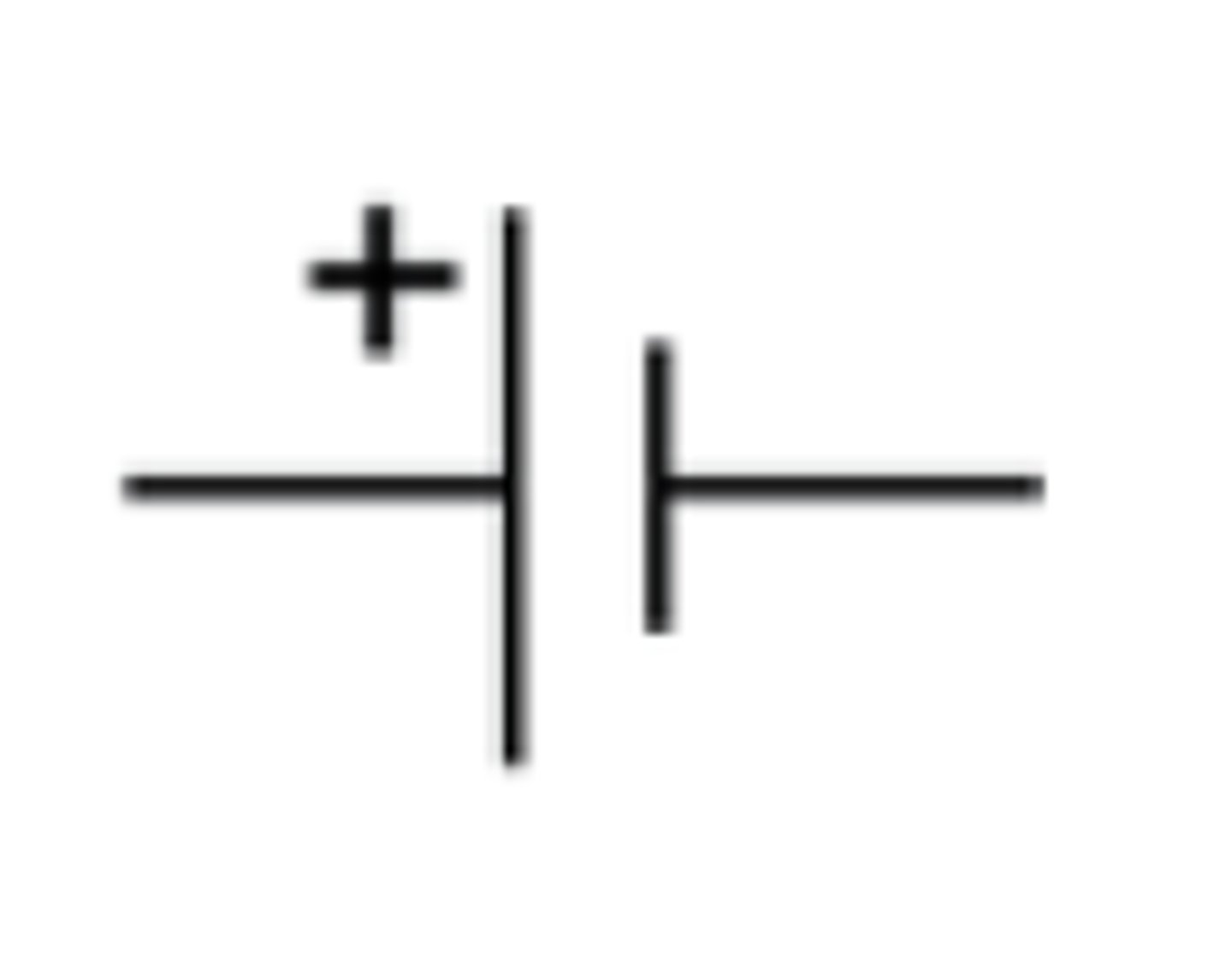
What is the circuit symbol for a diode?
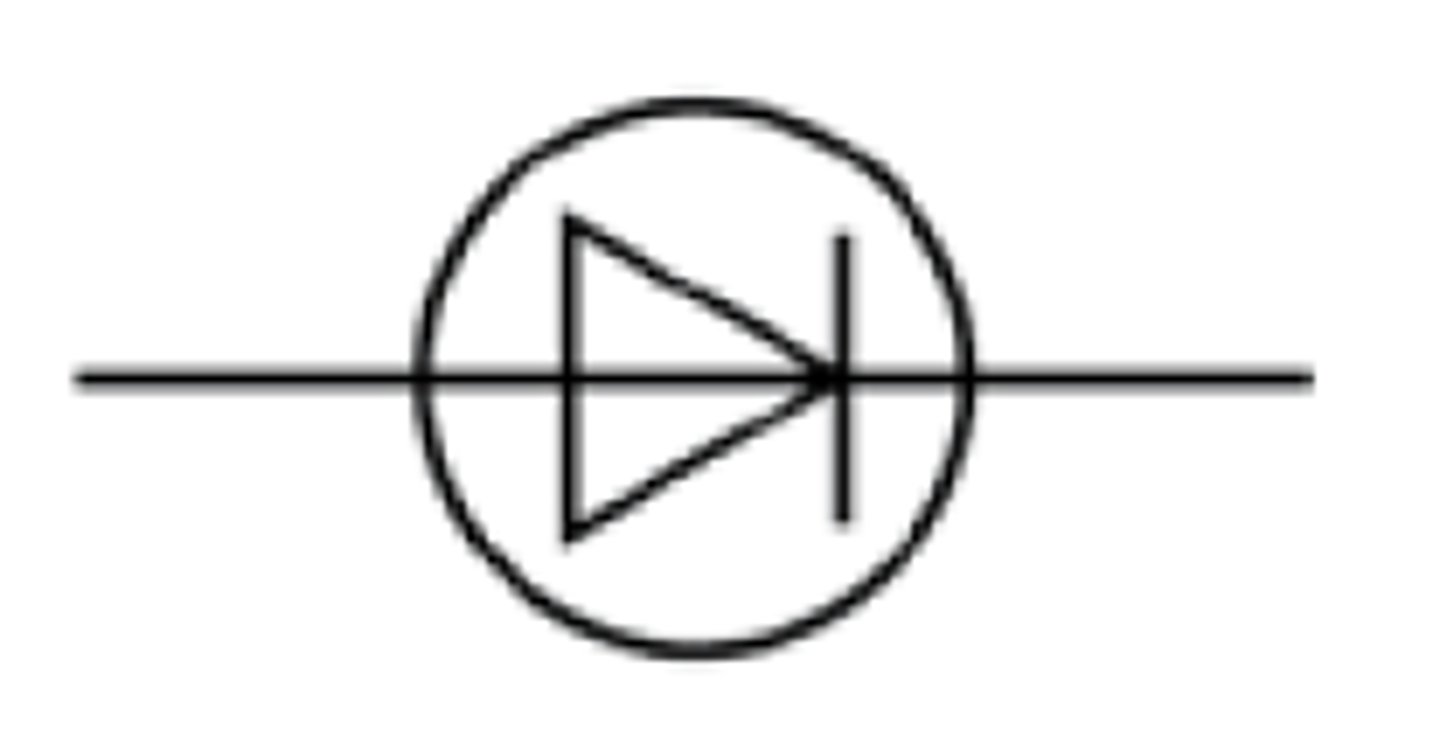
What is the circuit symbol for a fuse?
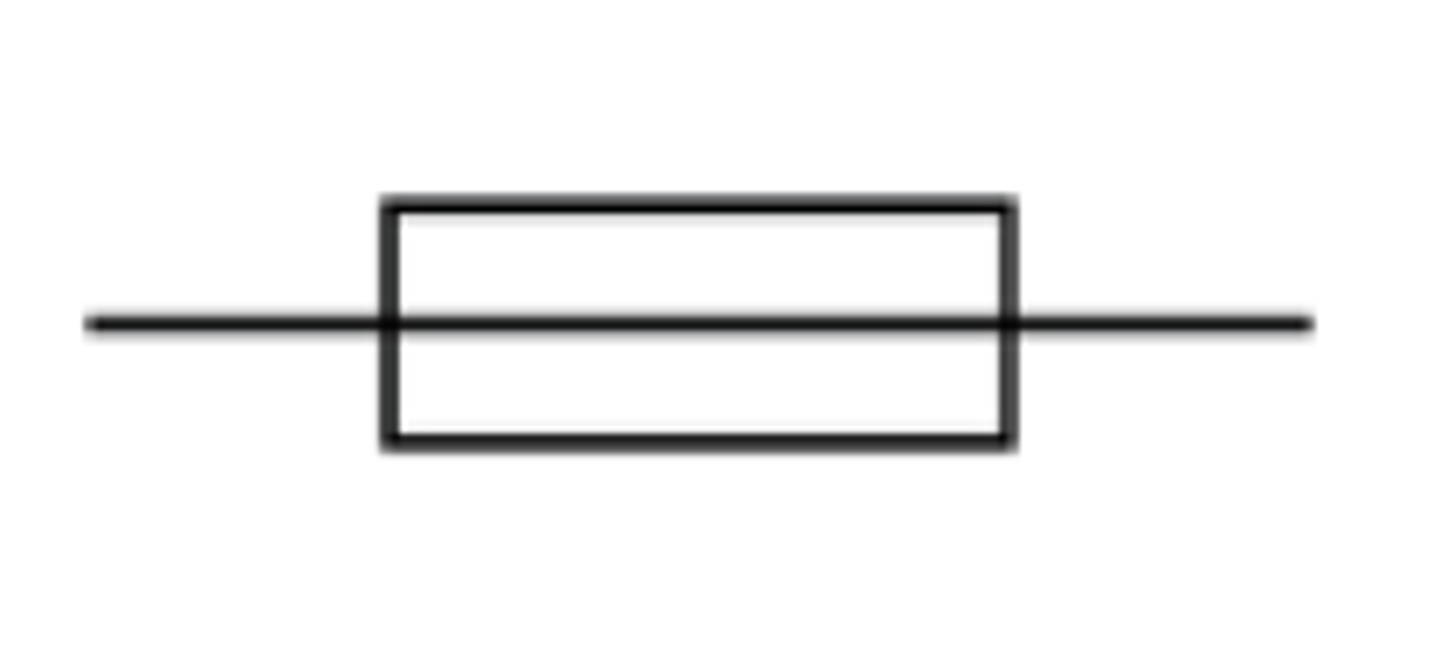
What is the circuit symbol for a lamp (bulb)?
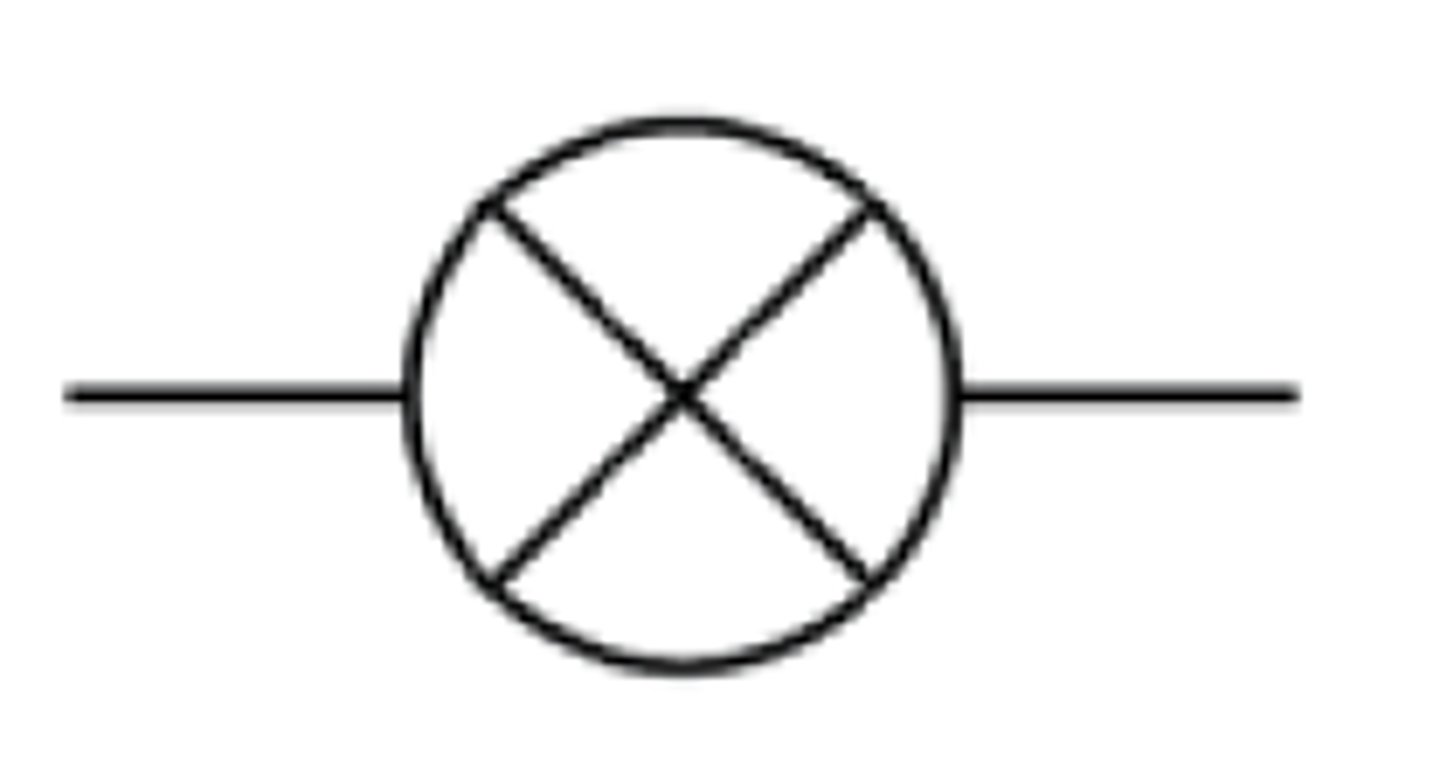
What is the circuit symbol for an LDR?
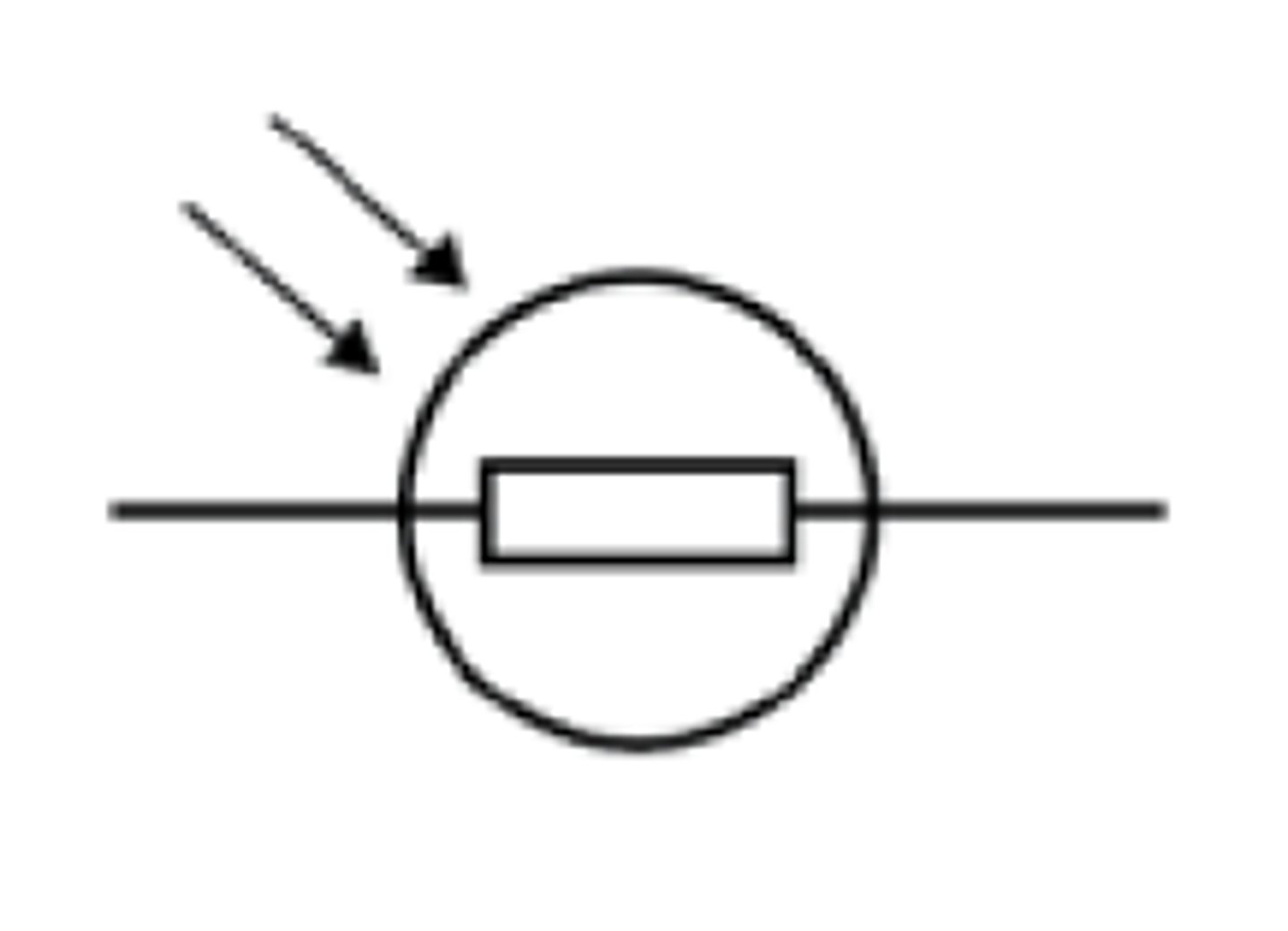
What does LDR stand for?
Light dependent resistor
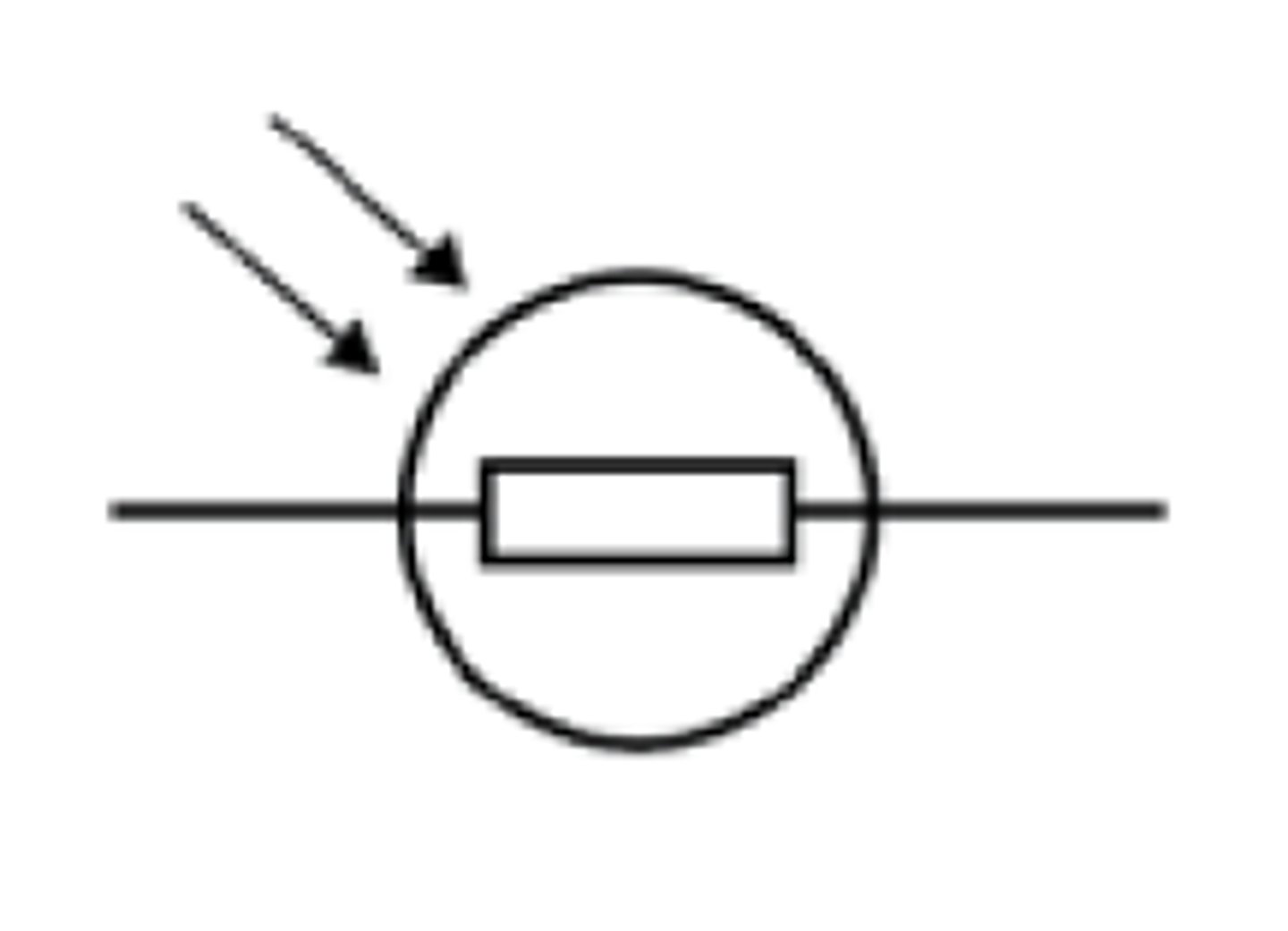
What is the circuit symbol for an LED?
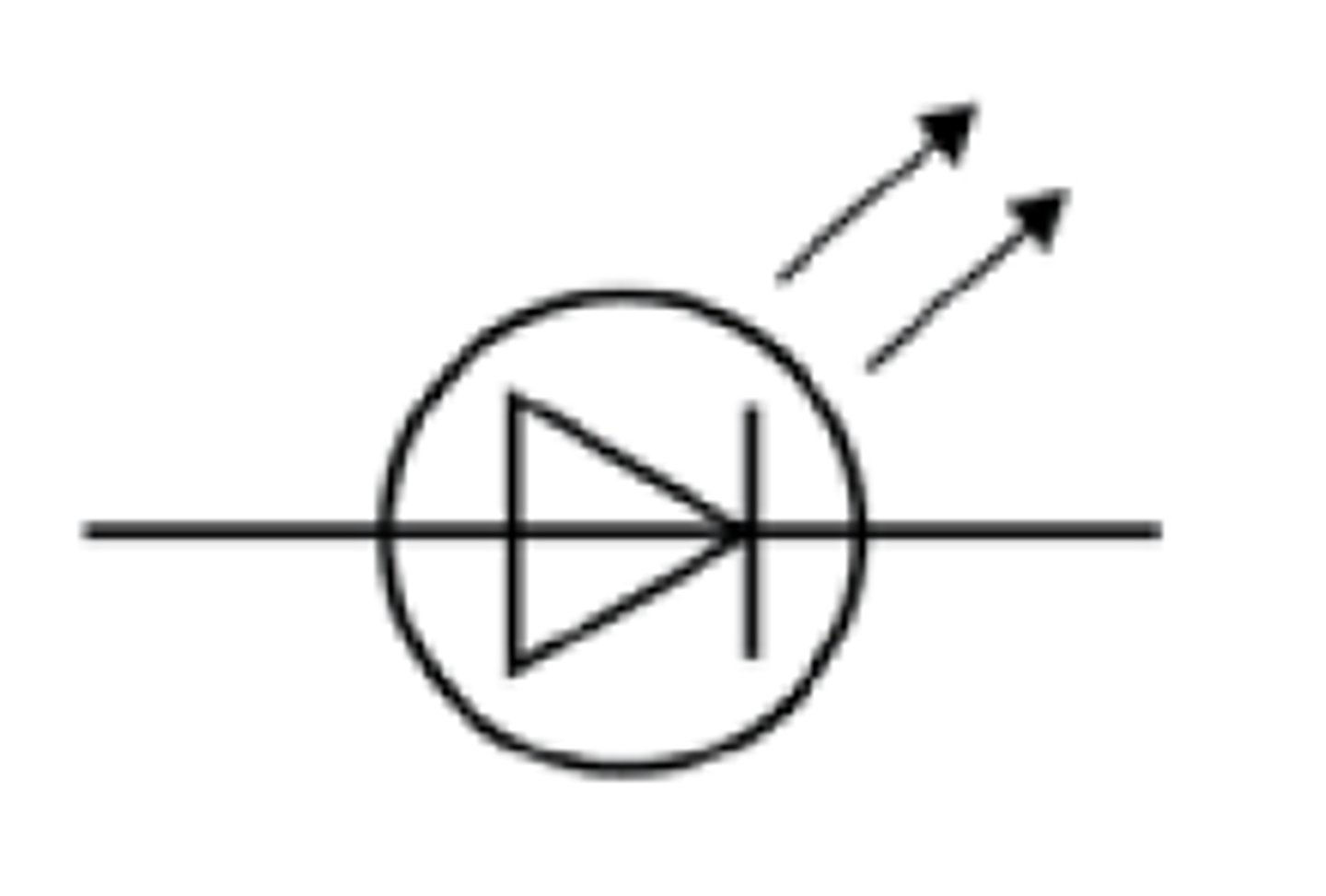
What is the circuit symbol for a resistor?
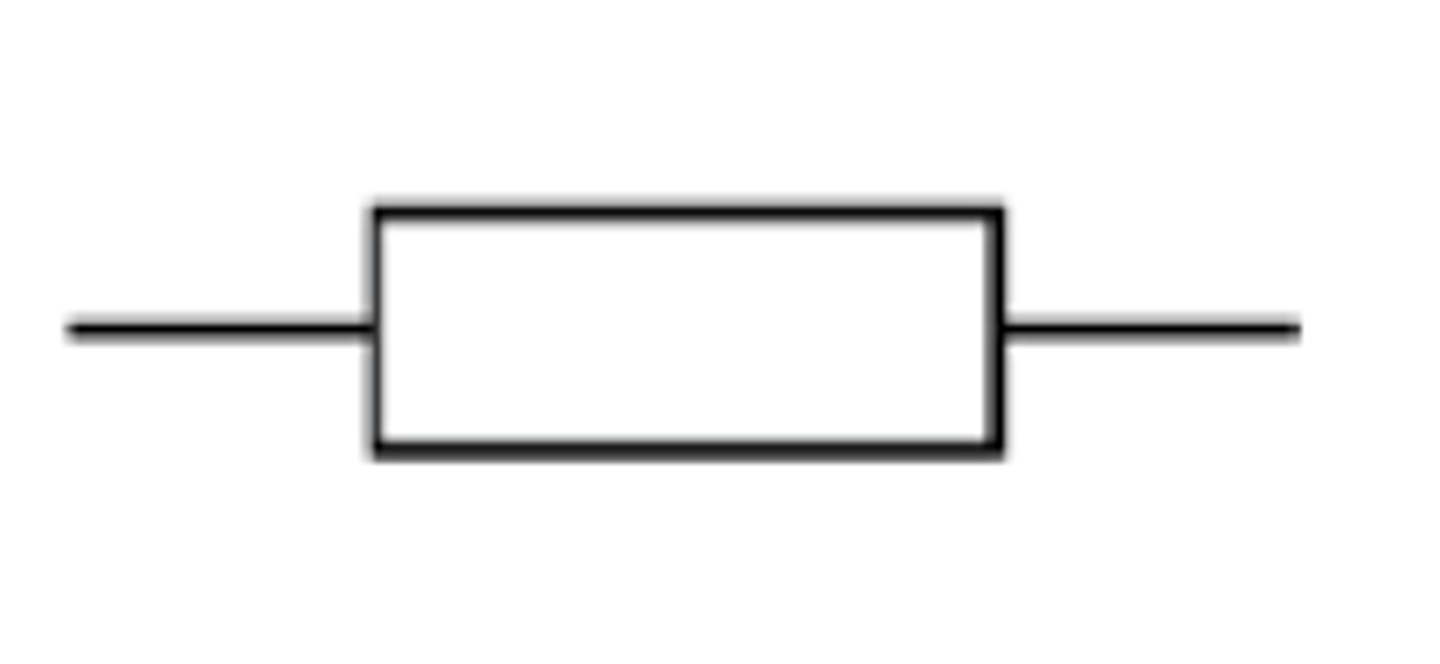
What is the circuit symbol for a closed switch?
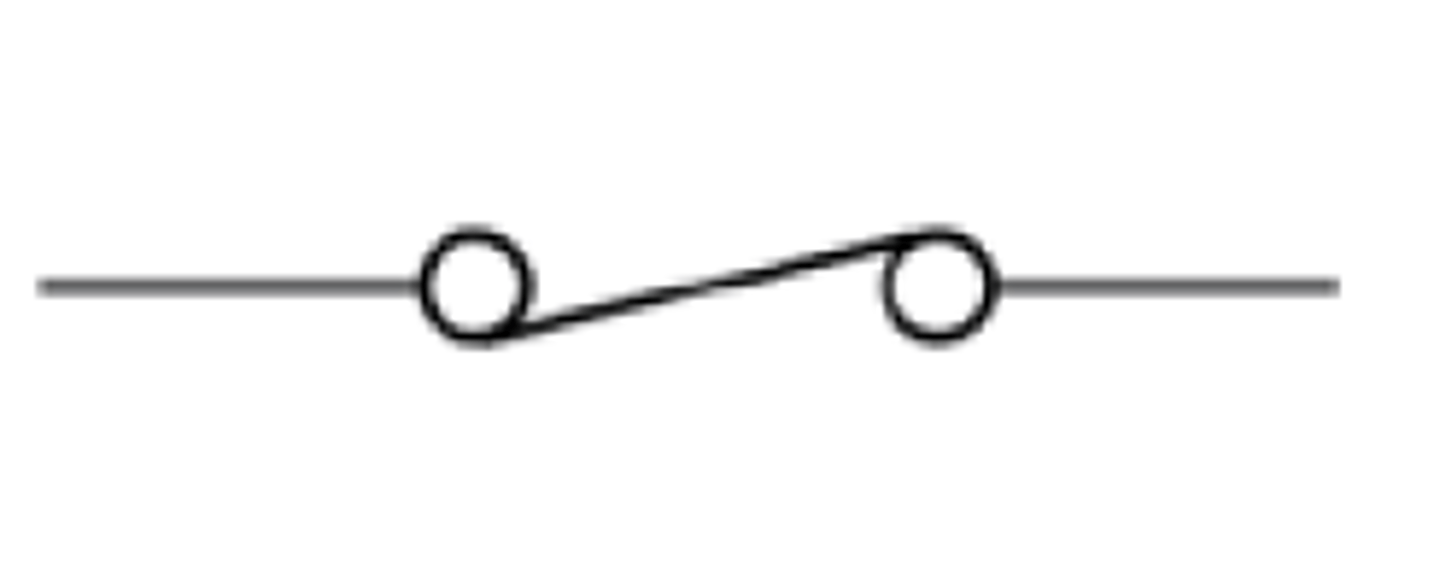
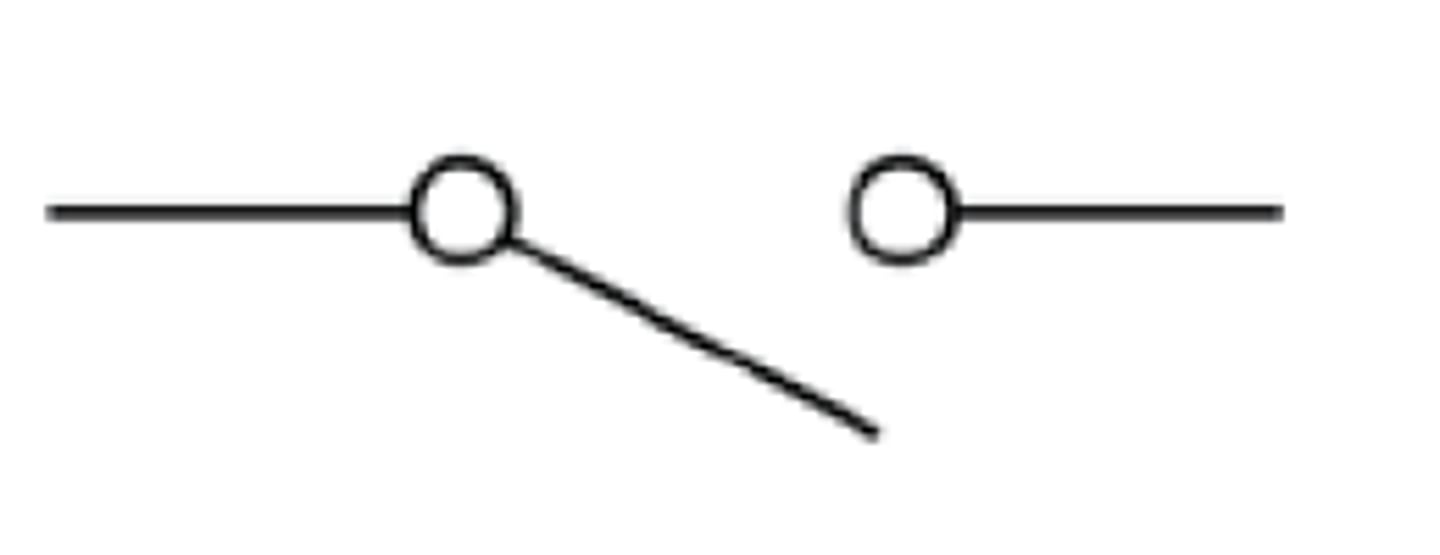
What is the circuit symbol for an open switch?
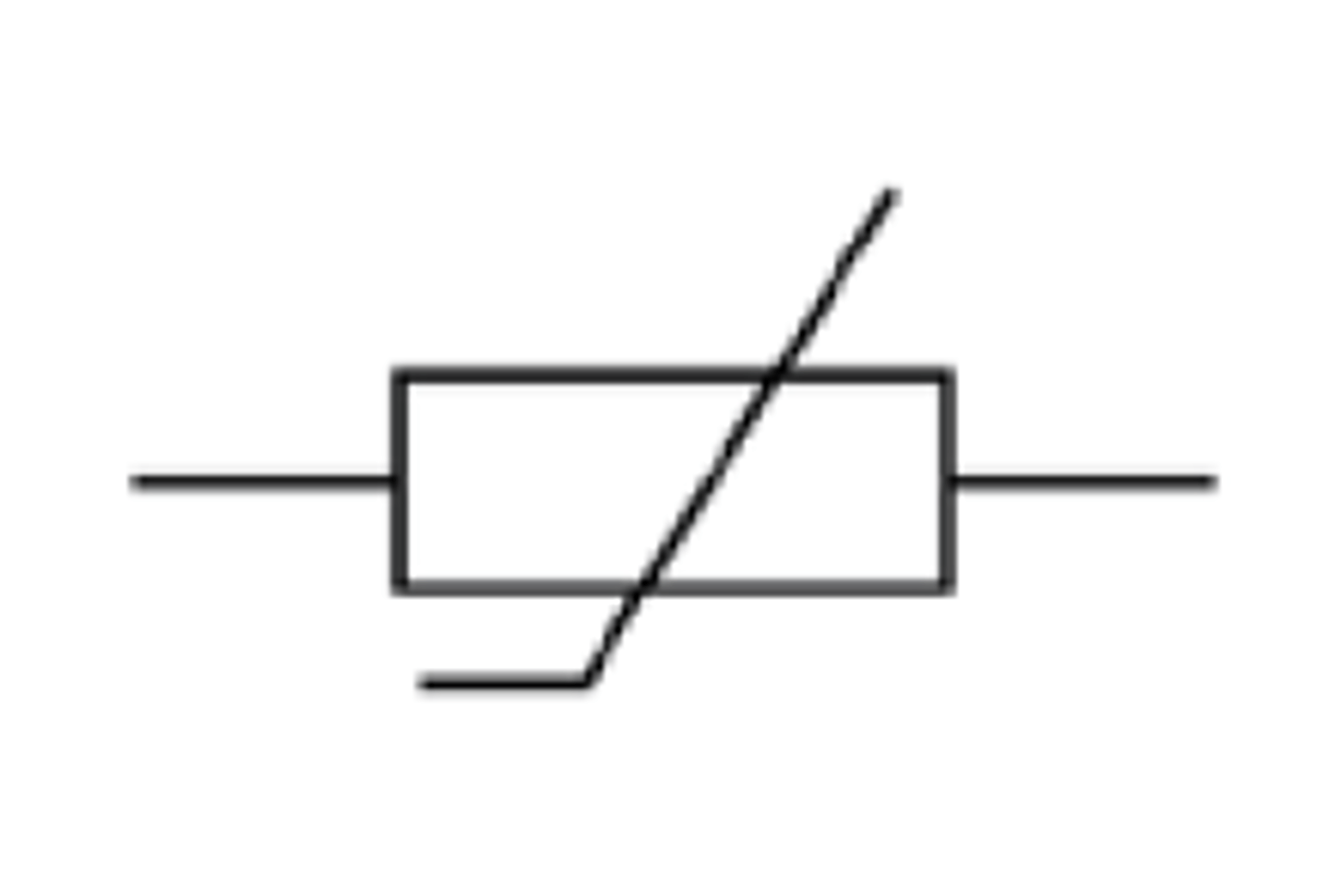
What is the circuit symbol for a thermistor?
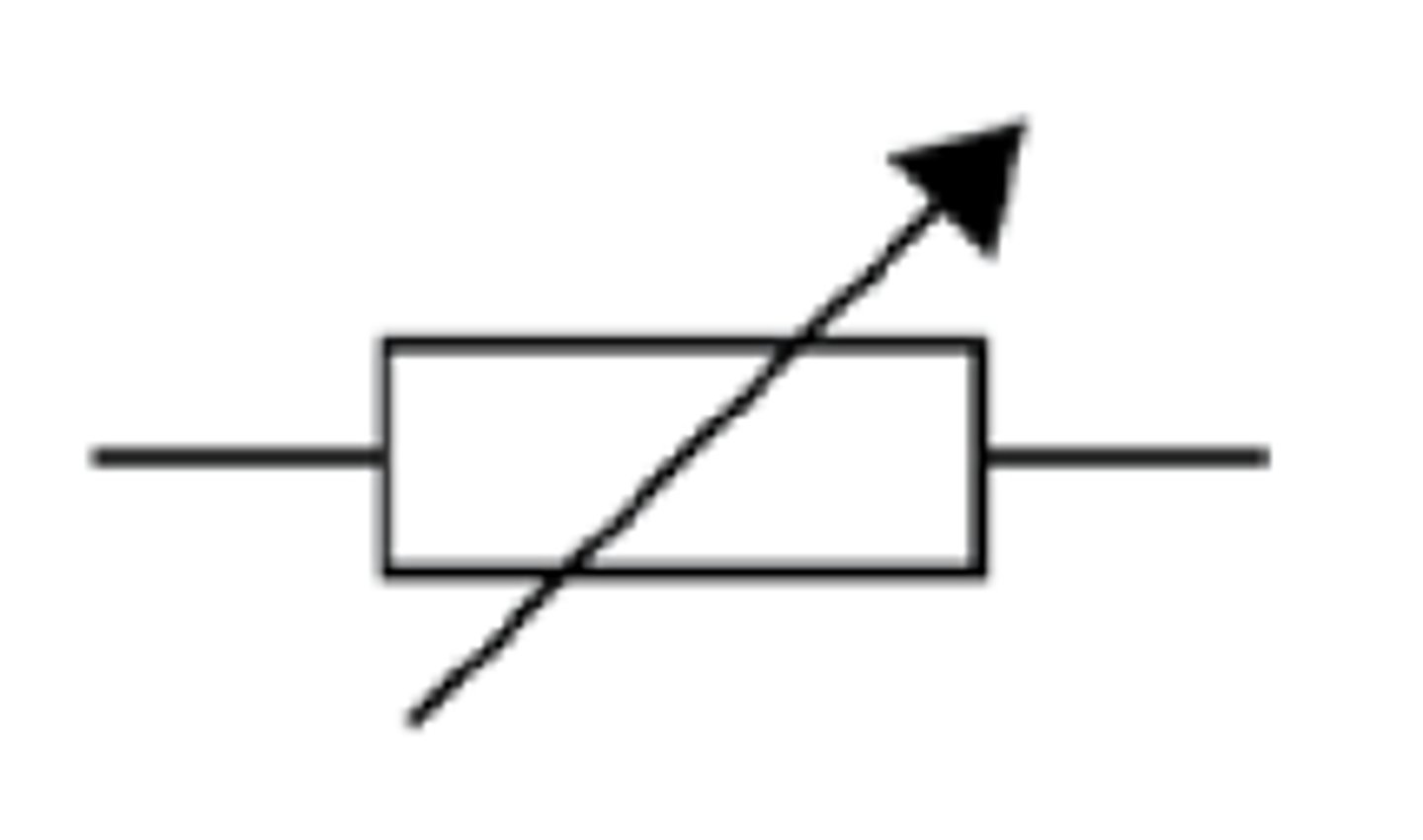
What is the circuit symbol for a variable resistor?
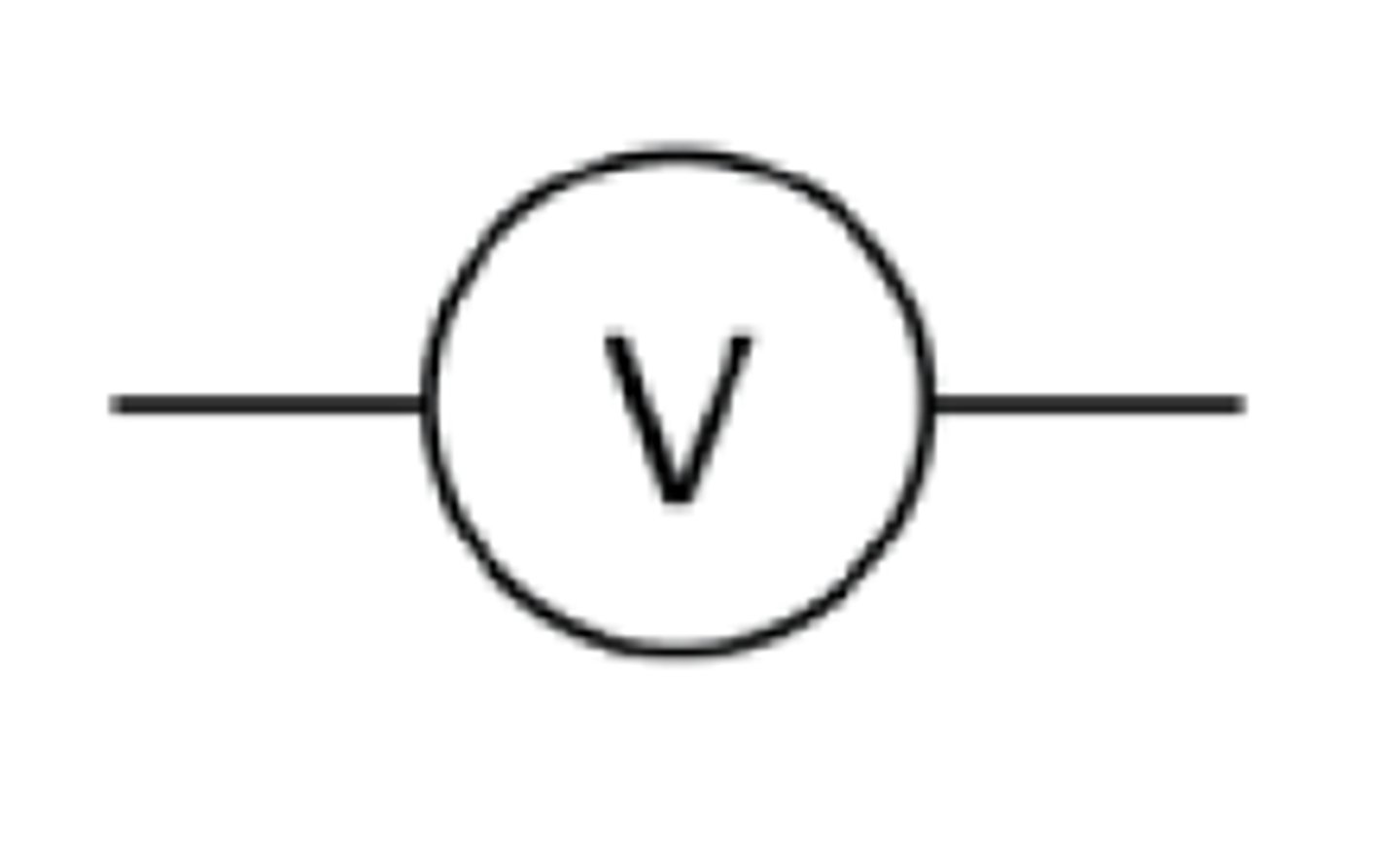
What is the circuit symbol for a voltmeter?
For electrical charge to flow through a closed circuit the circuit must include a source of _________ __________
Potential Difference
Electric current is a flow of electrical ______
Charge
The size of an electric _______ is the rate of flow of electrical charge
current
What is the equation for charge?
current x time
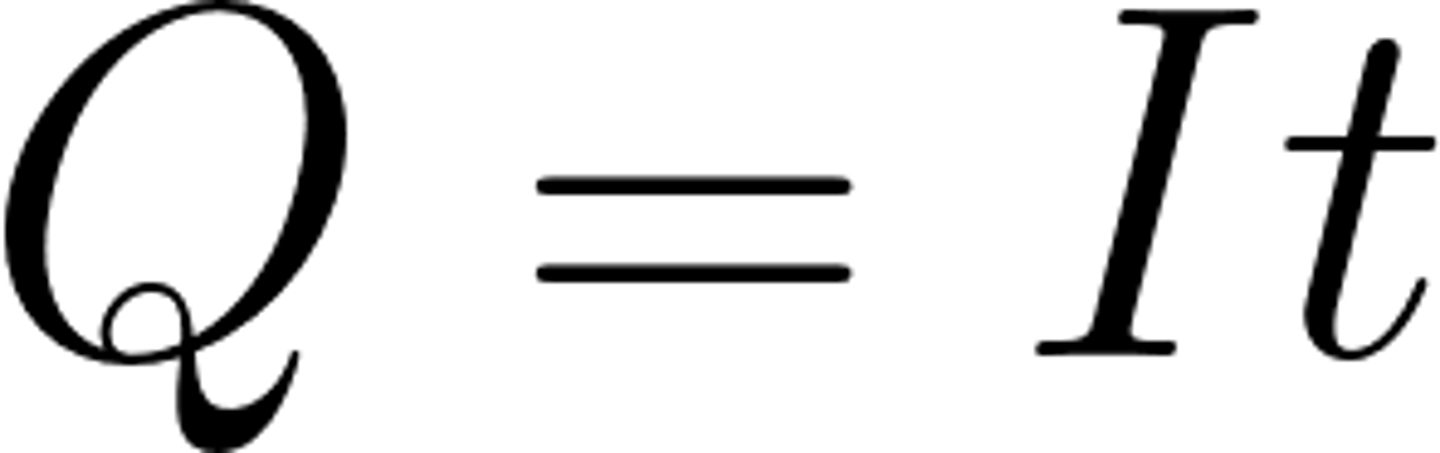
Unit of charge flow, Q
coulombs, C
Unit of current, I
amps, A
Unit of time, t
s
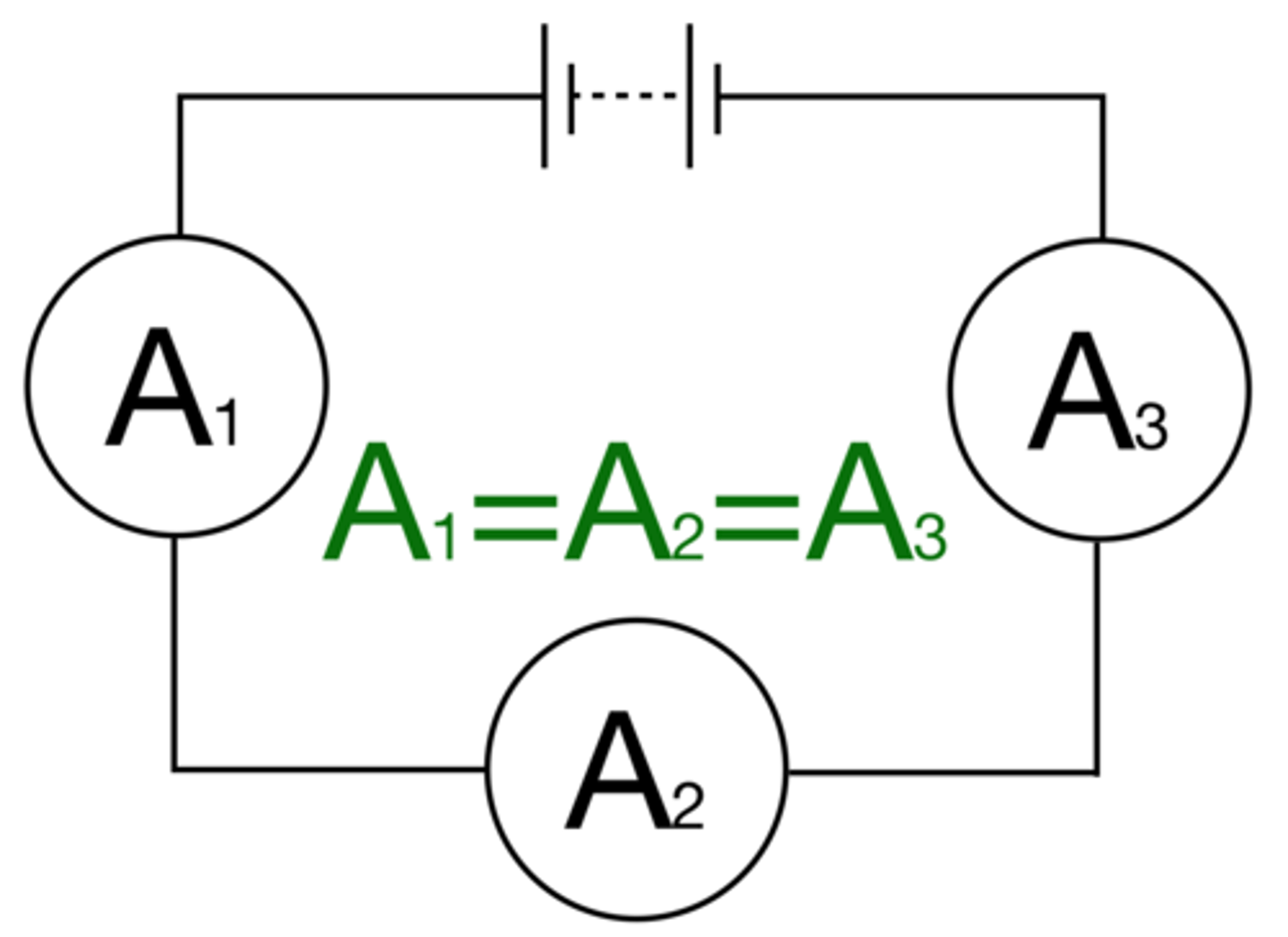
Current has the same value at any point in a ______ circuit
series
The current (I) through a component depends on both the __________ of the component and the potential difference (V) across the component
Resistance (R)
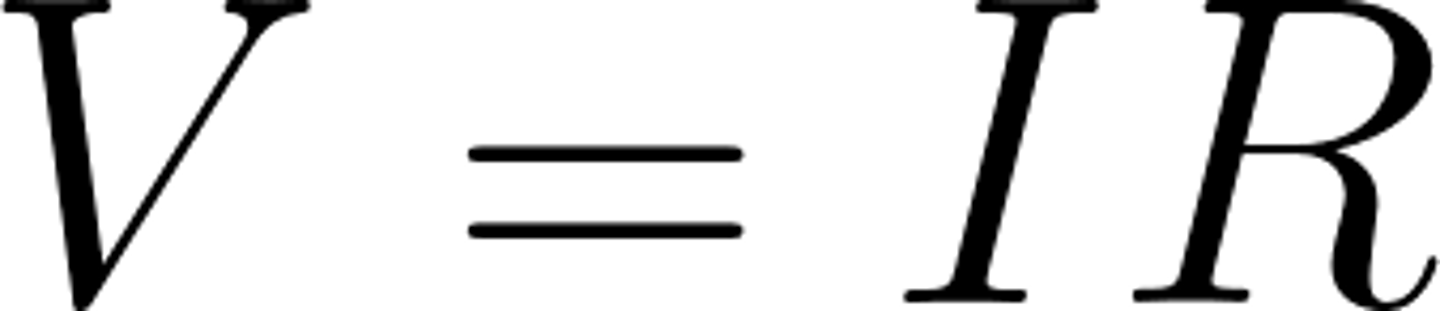
For a given potential difference (voltage), the greater the resistance of the component the smaller the _______
current
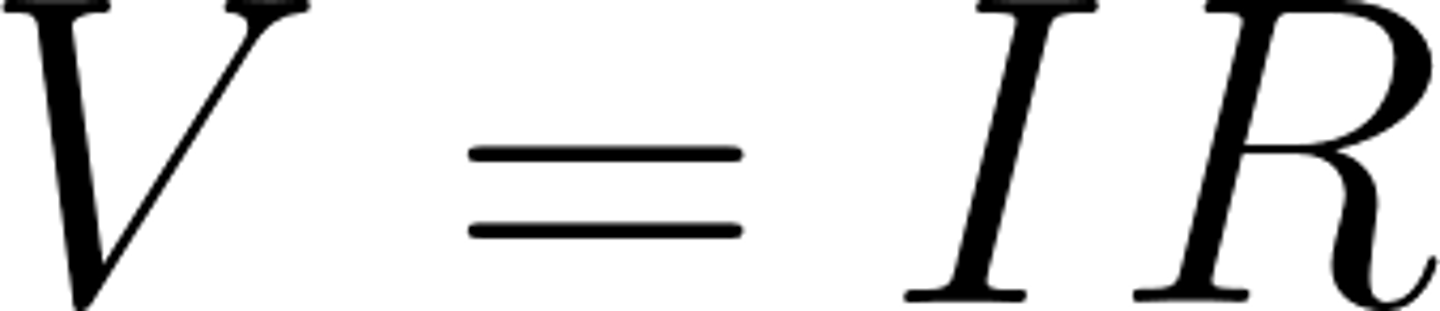
What is the equation for potential difference?
potential difference = current x resistance
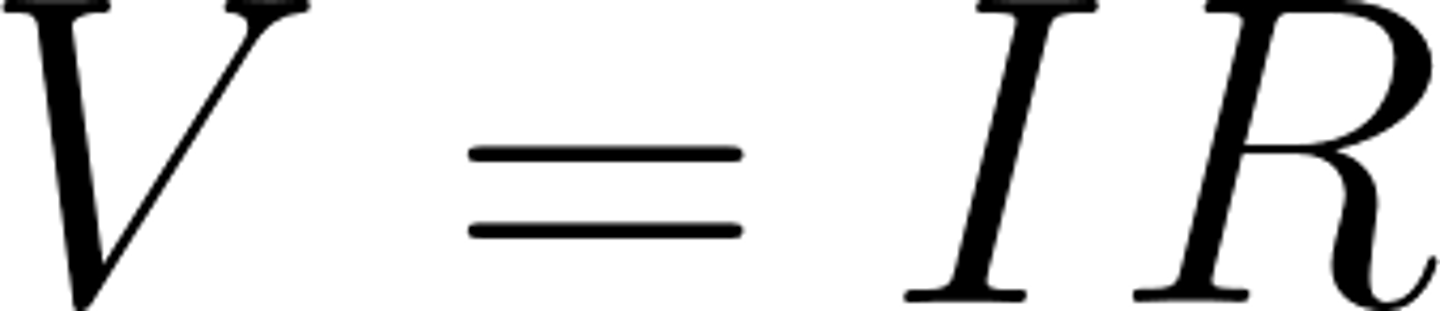
Unit of potential difference, V
volts, V
Unit of resistance, R
ohms, Ω
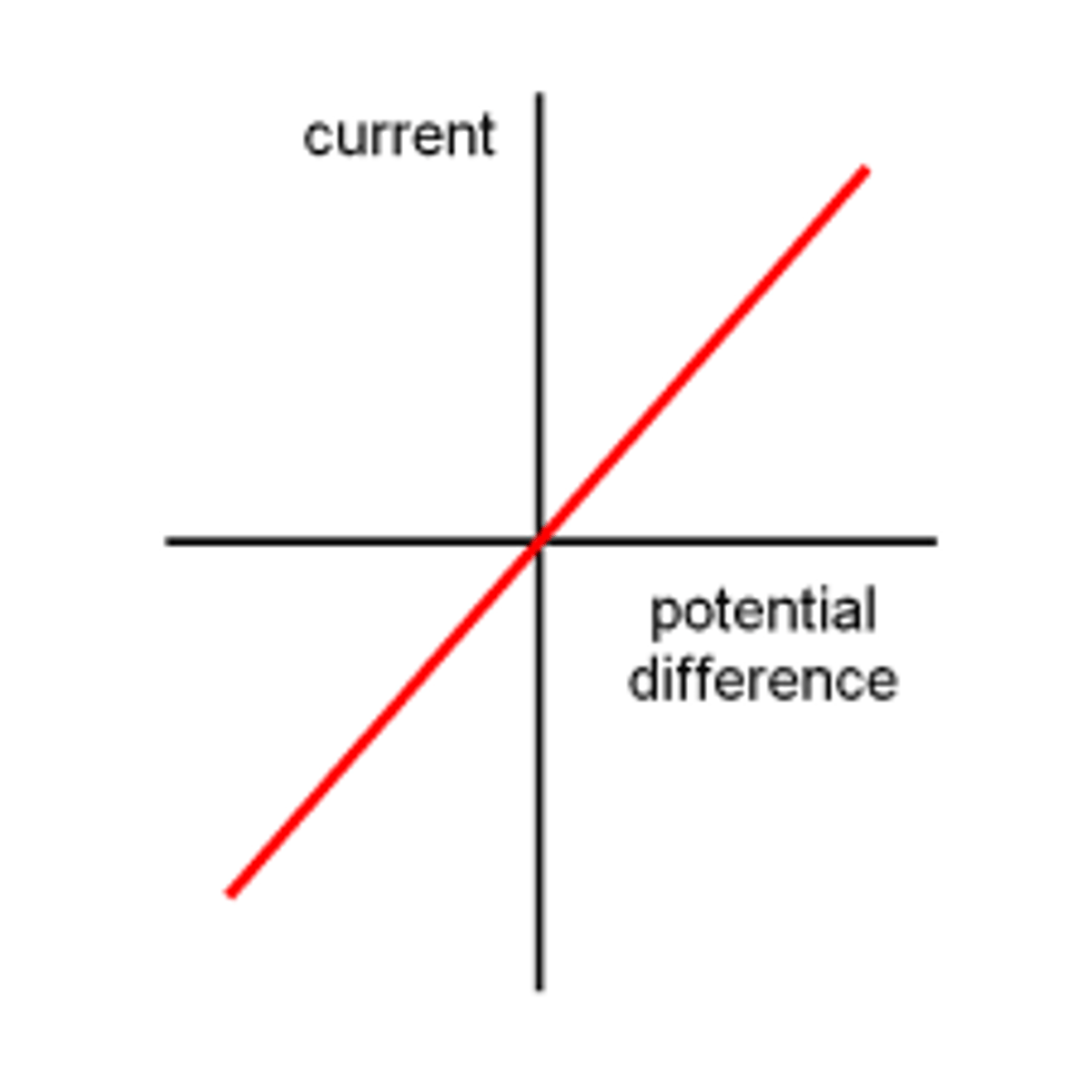
The current through an ohmic conductor (at constant temperature) is ________ ____________ to the potential difference across the resistor.
directly proportional
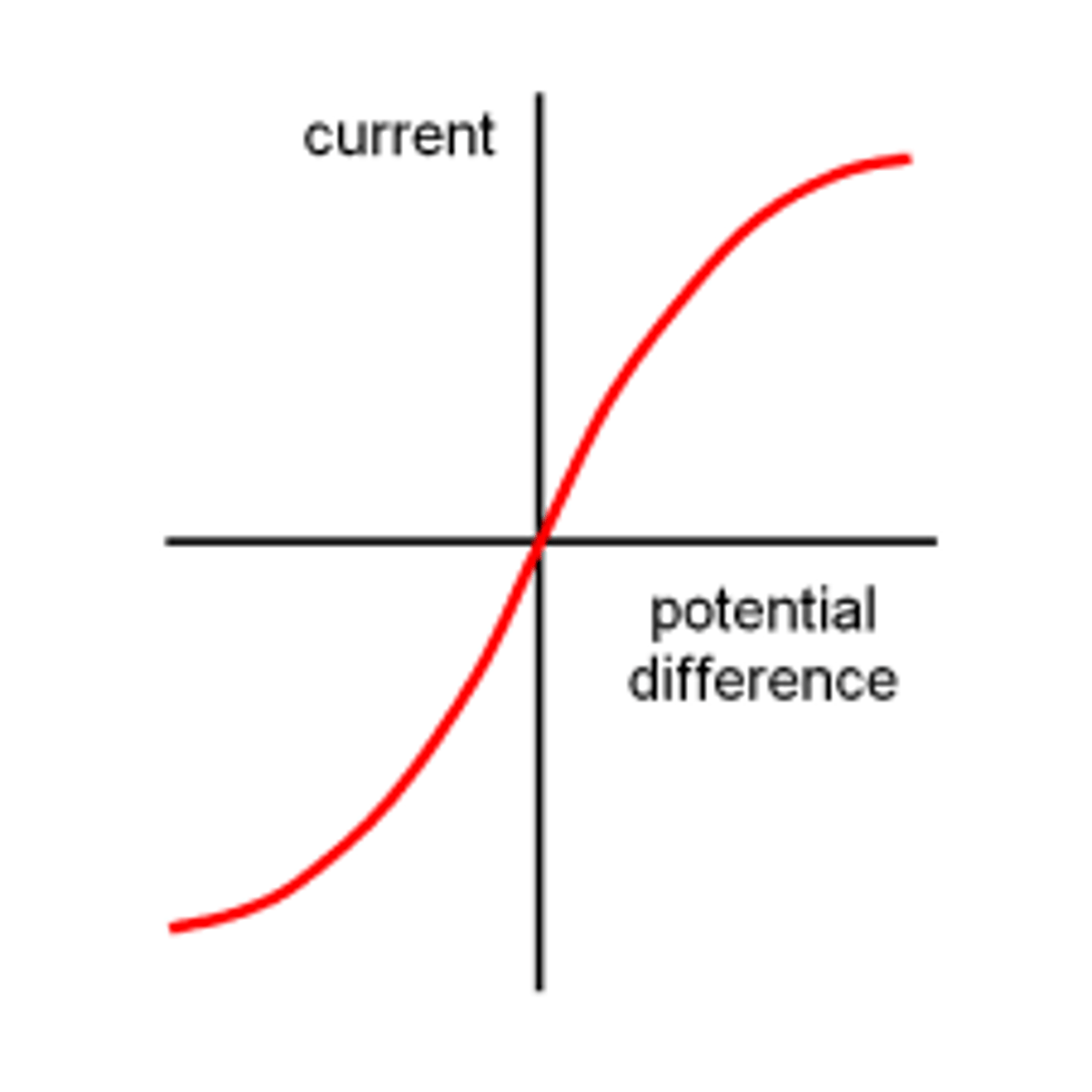
The resistance of components such as lamps, diodes, thermistors and LDRs is not constant; it changes with the _______ through the component
current
The resistance of a filament lamp increases as the ___________ of the filament increases
temperature
The current through a diode flows in ___ _________ only
one direction
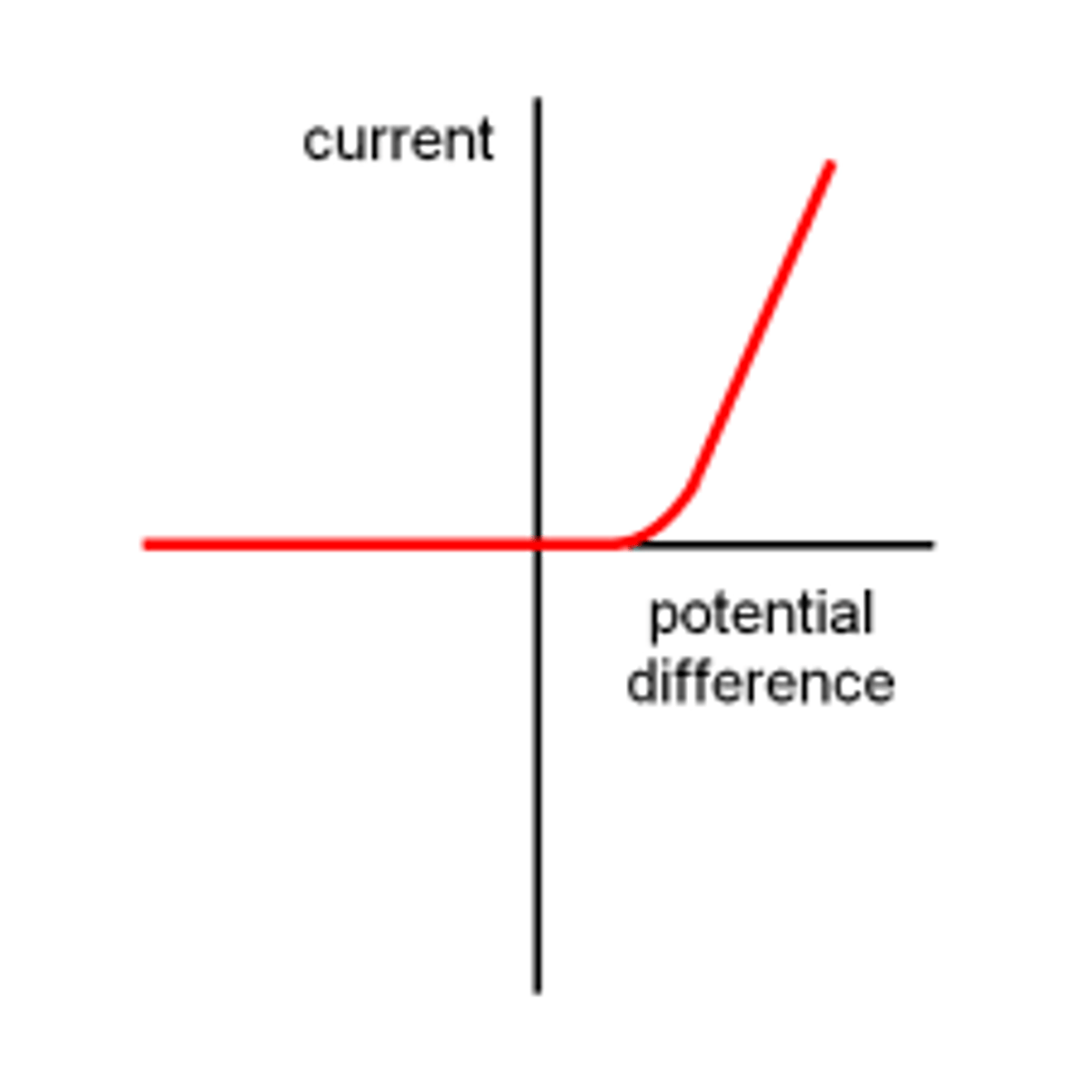
The _____ has a very high resistance in the reverse direction
diode
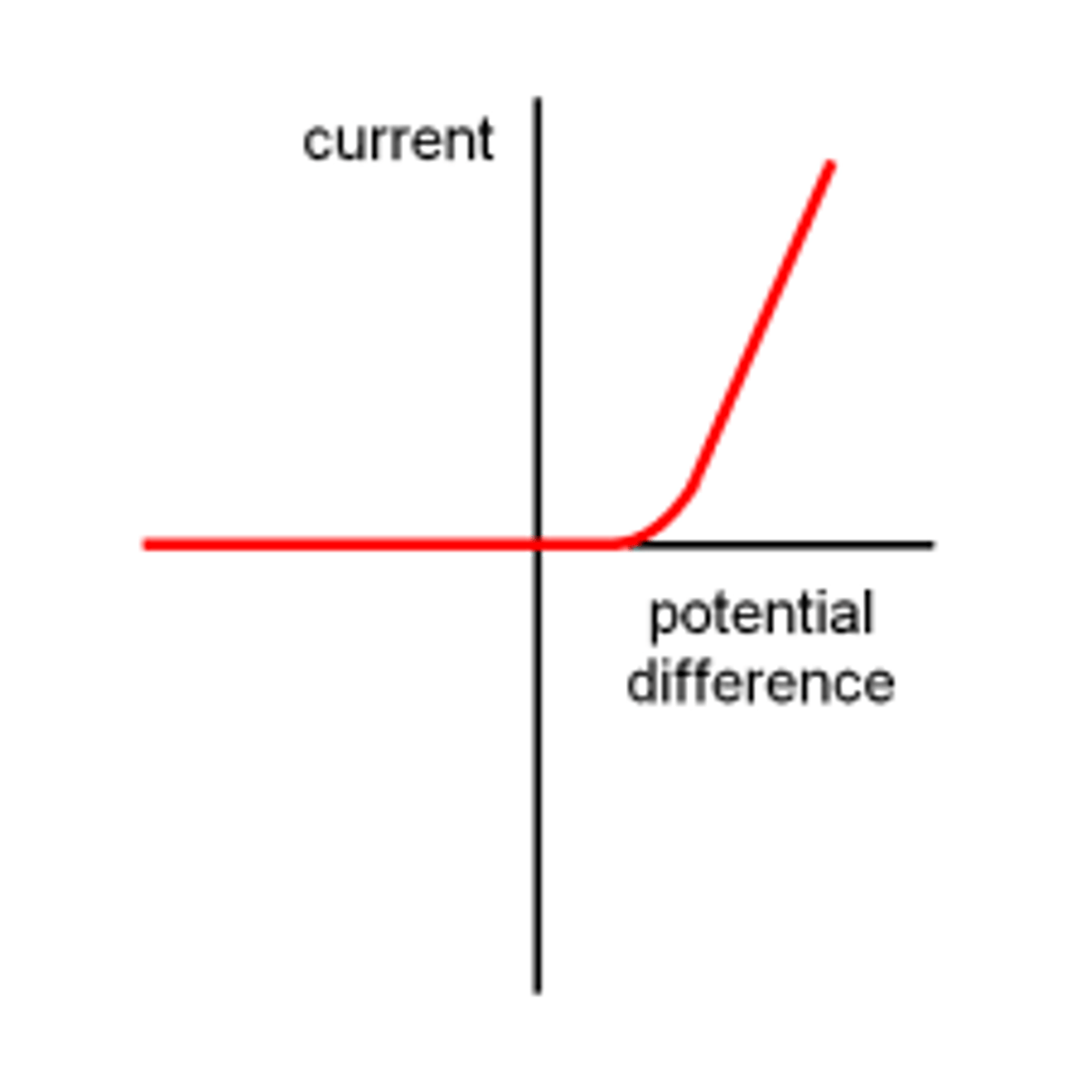
The resistance of a __________ decreases as the temperature increases
thermistor
The resistance of an LDR decreases as _____ _________ increases
light intensity
An ___ can be used to switch lights on when it gets dark
LDR
A __________ can be used to switch heaters on when it gets cold
thermistor
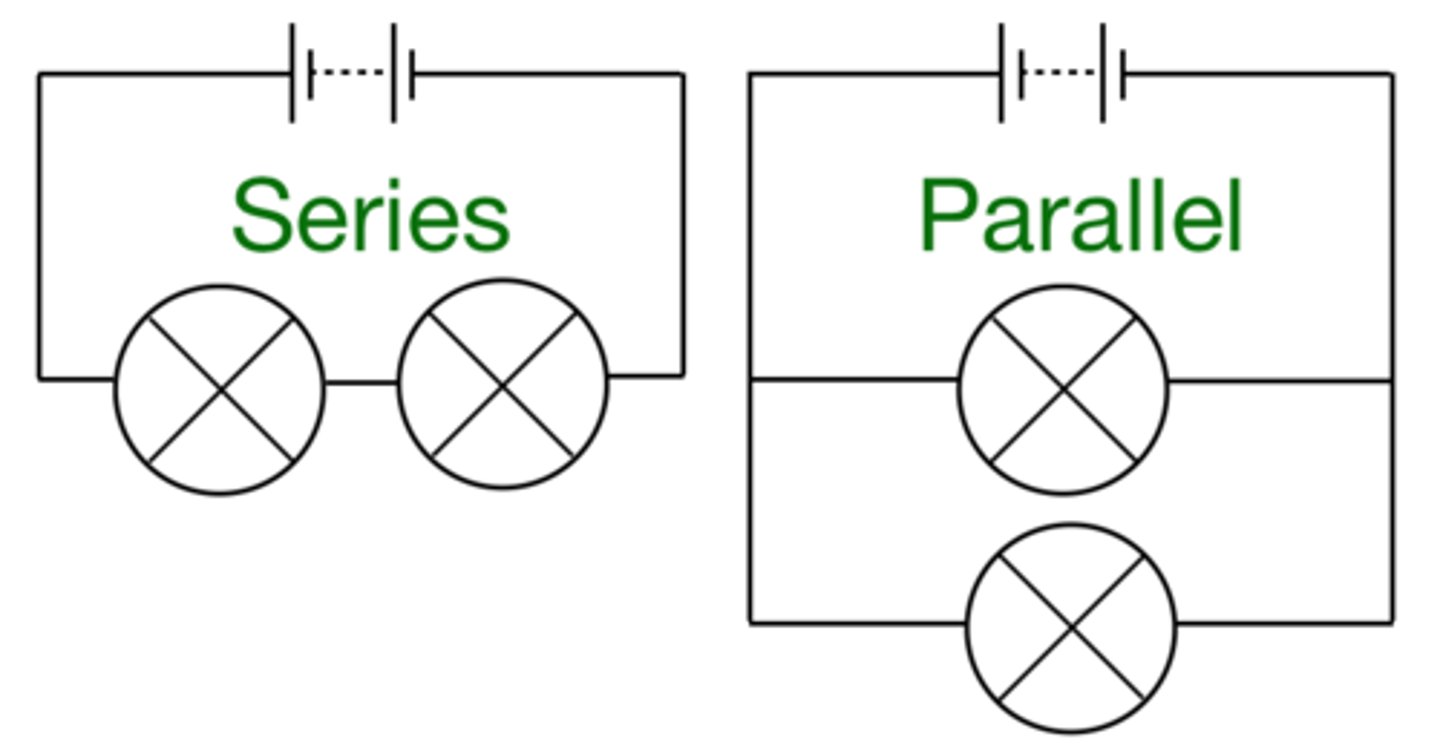
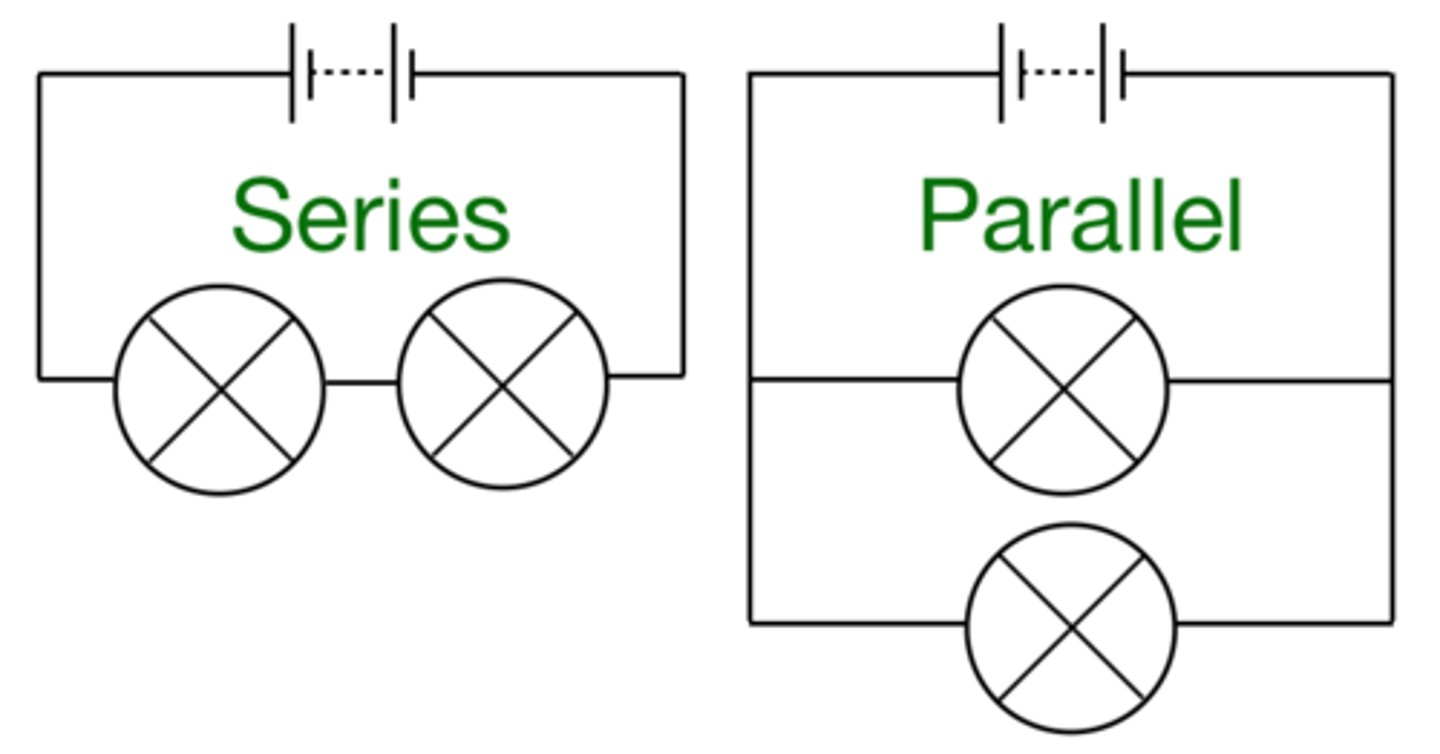
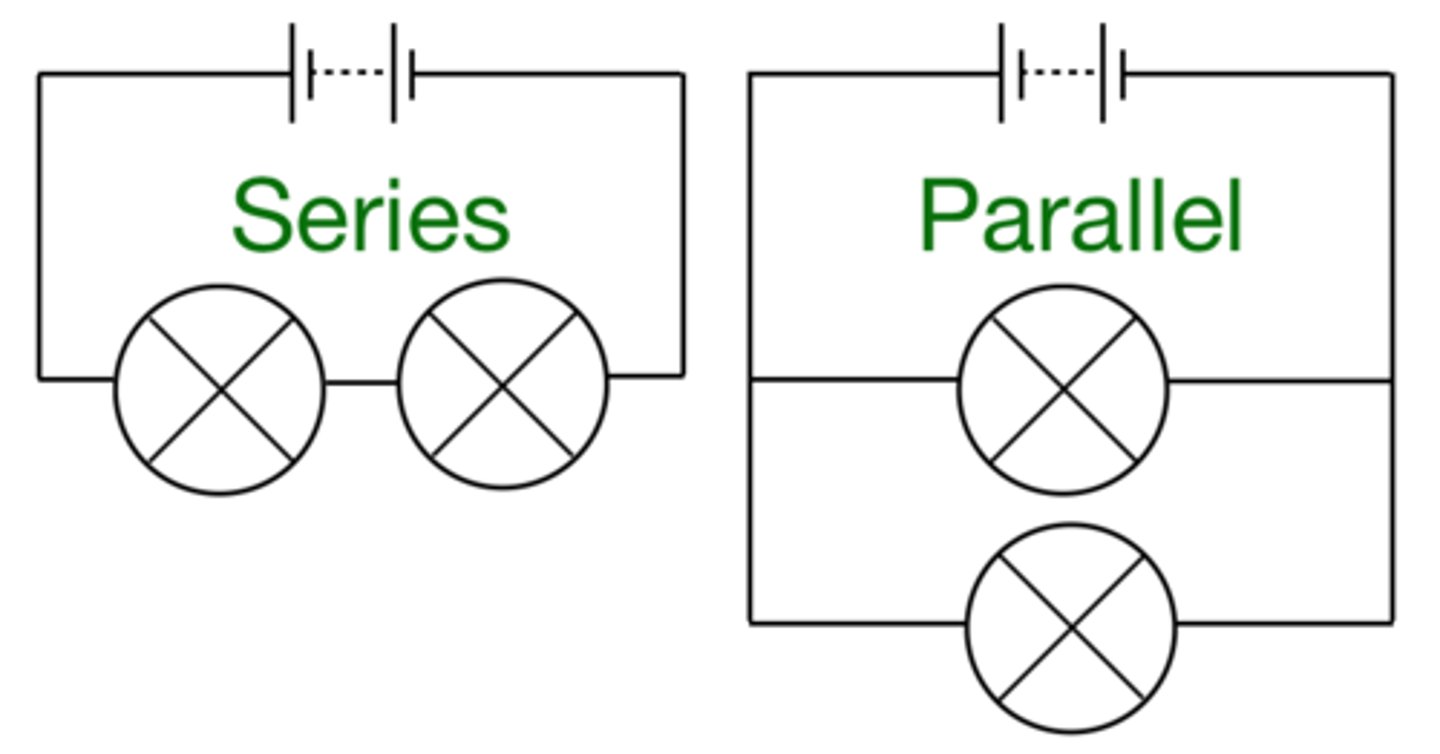
There are two ways of joining electrical components, in series and in ________
parallel
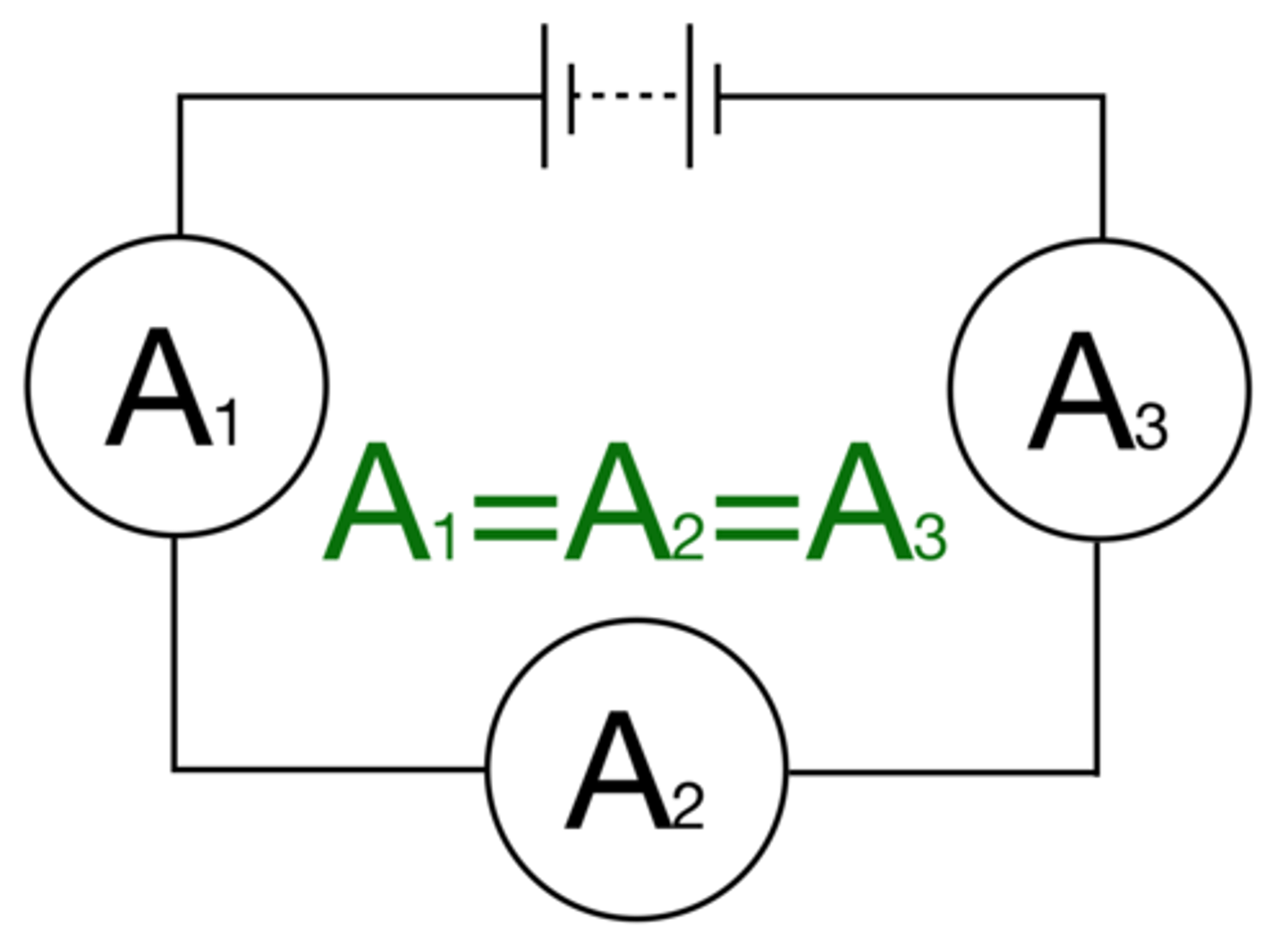
For components connected in series there is the same _______ through each component
current
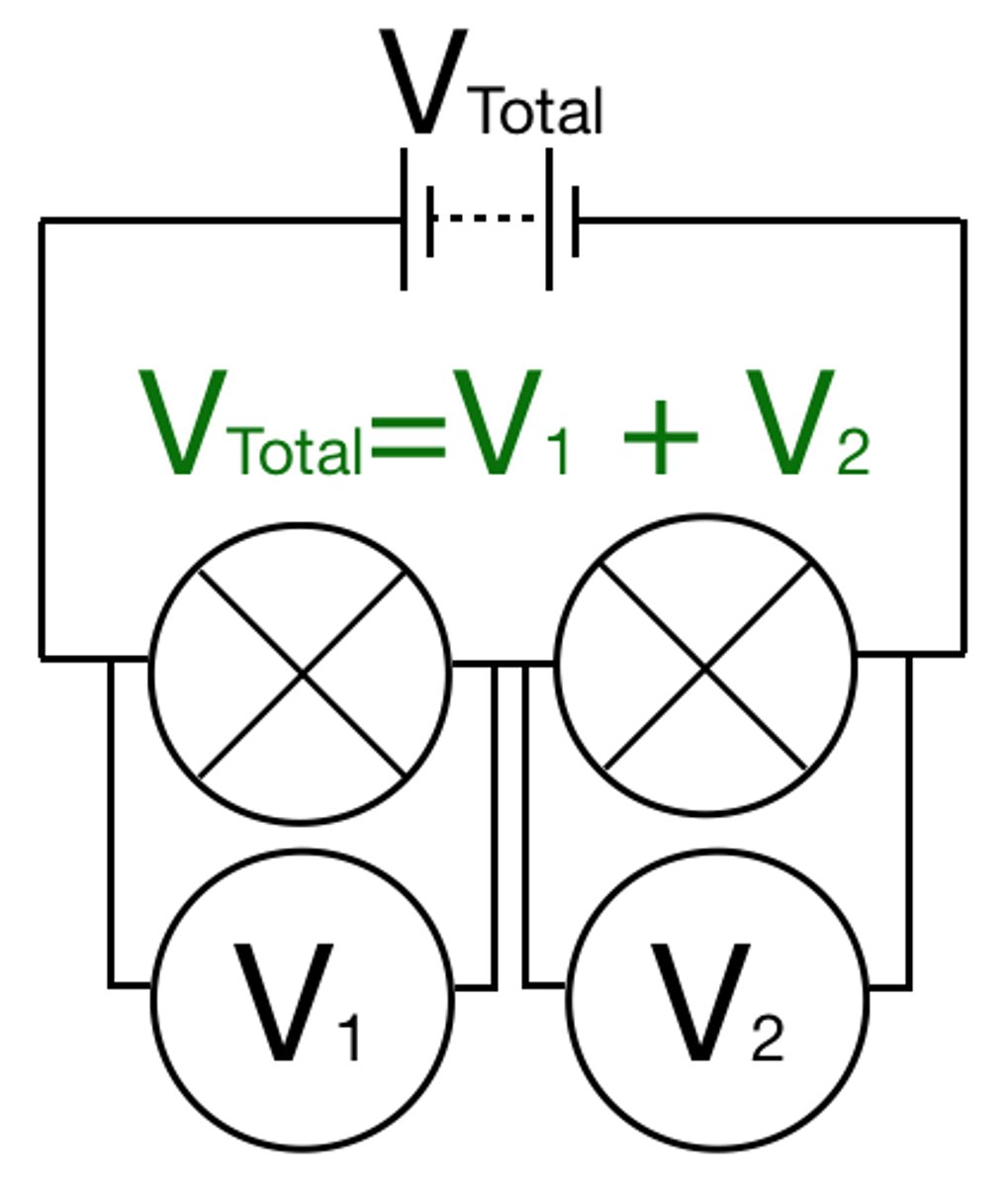
For components connected in series the total potential difference of the power supply is ______ between the components
shared
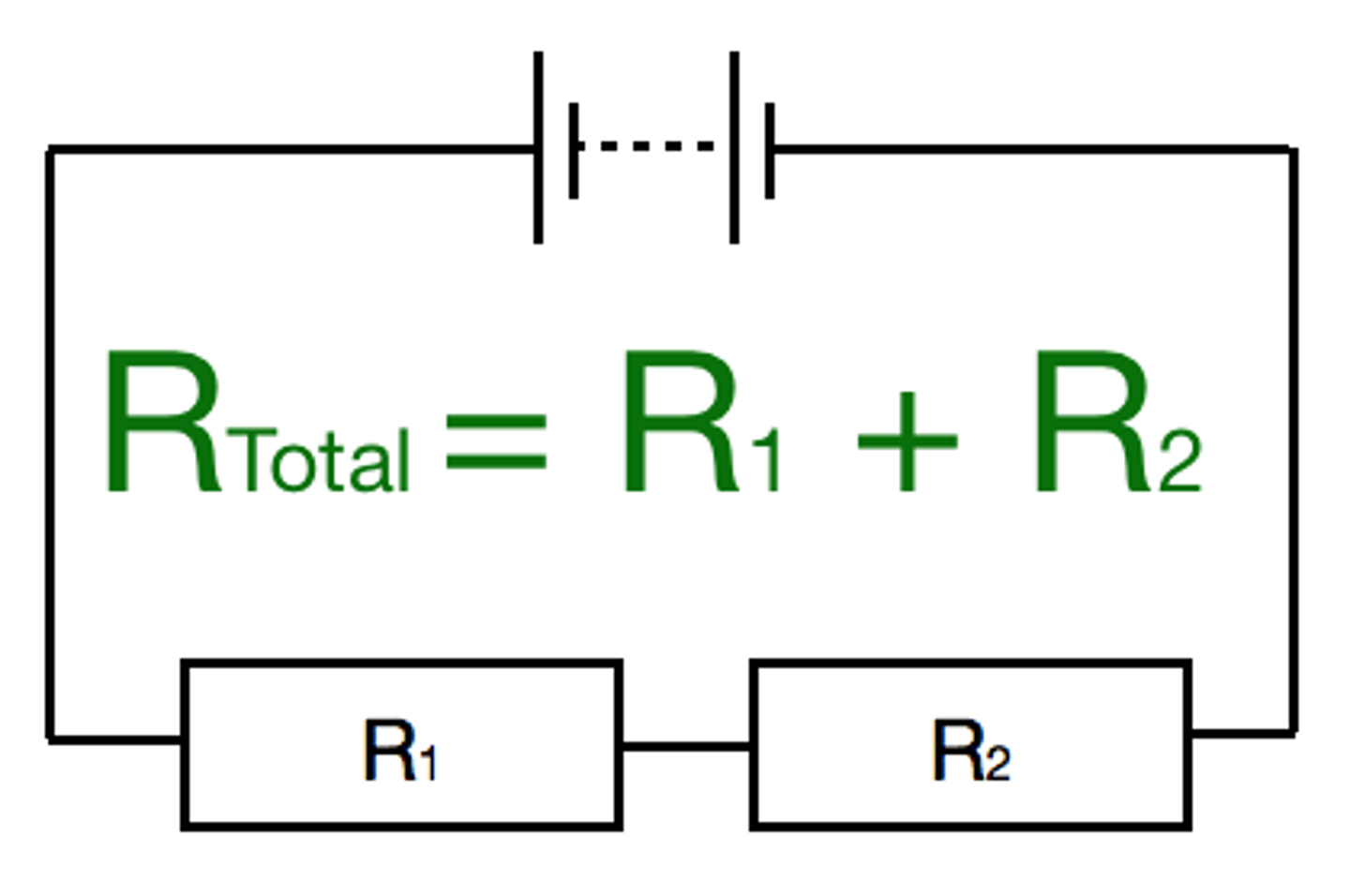
For components connected in series the total __________ of two or more components is the sum of the __________ of each component
resistance
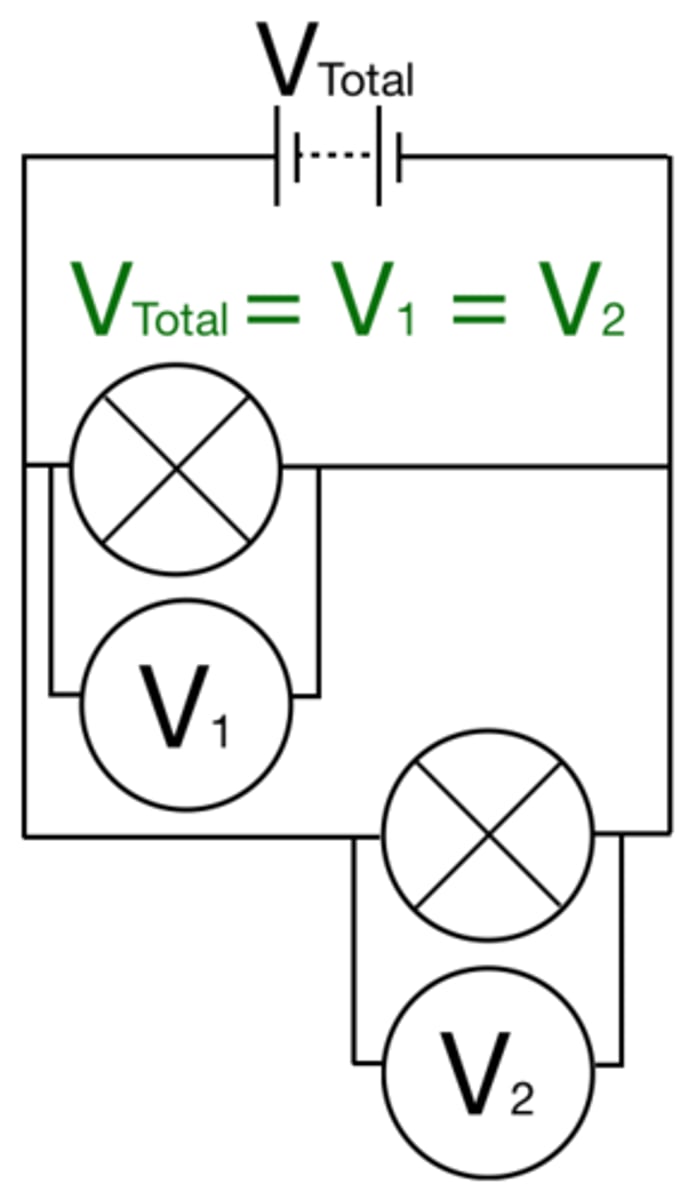
For components connected in parallel the potential difference across each component is...
the same
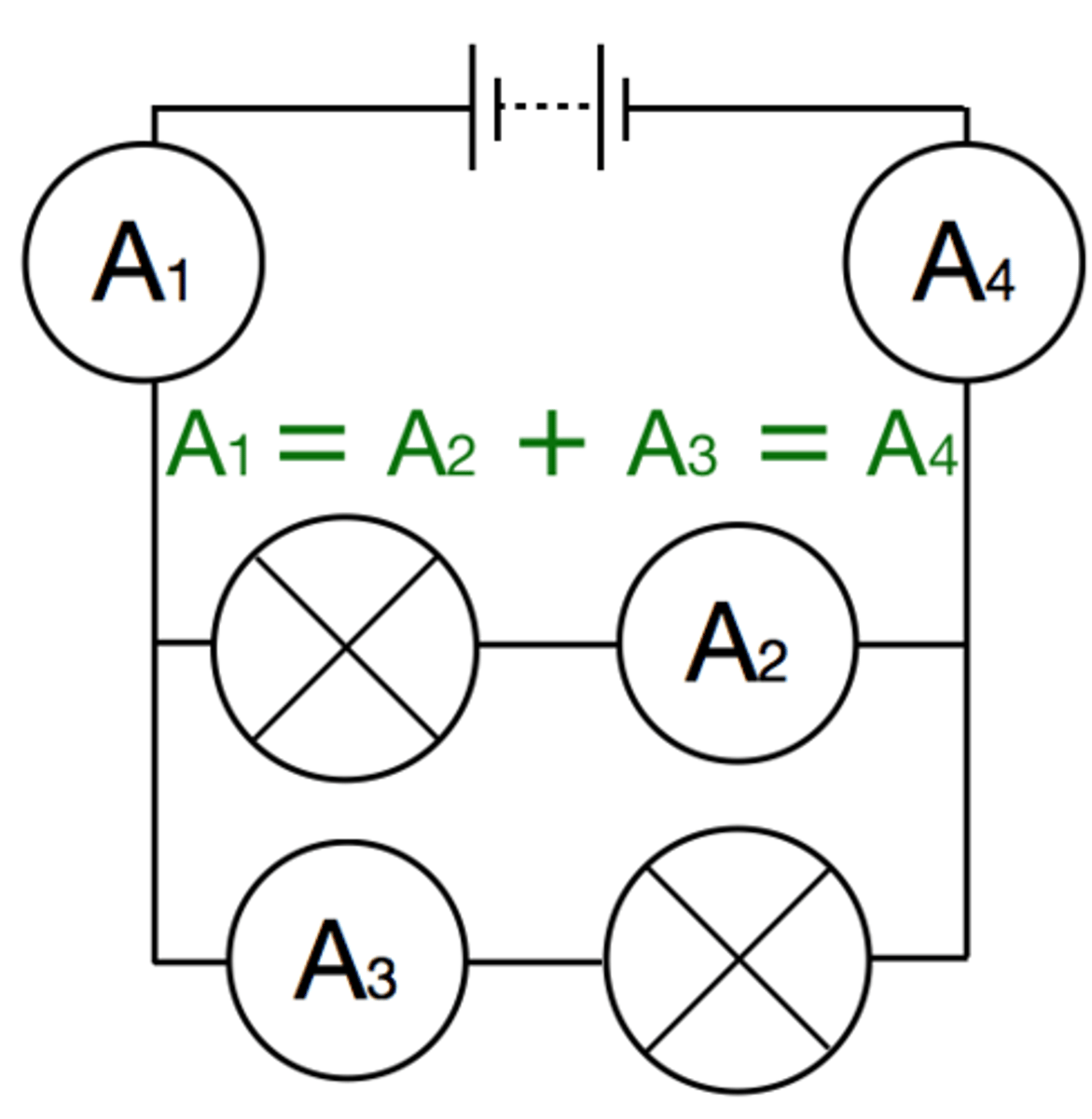
For components connected in parallel the total _______ through the whole circuit is the sum of the _______ through the separate branches
current
For components connected in parallel the total resistance of two or more resistors is ____ ____ the resistance of the smallest individual resistor
less than
Mains electricity uses __________ ______
alternating current
In a series circuit, components are connected in...
one loop
The alternating current used in UK mains electricity has a frequency of ____
50Hz
In a parallel circuit, components are connected in...
more than one loop
The potential difference of UK mains electricity is about ___ Volts
230
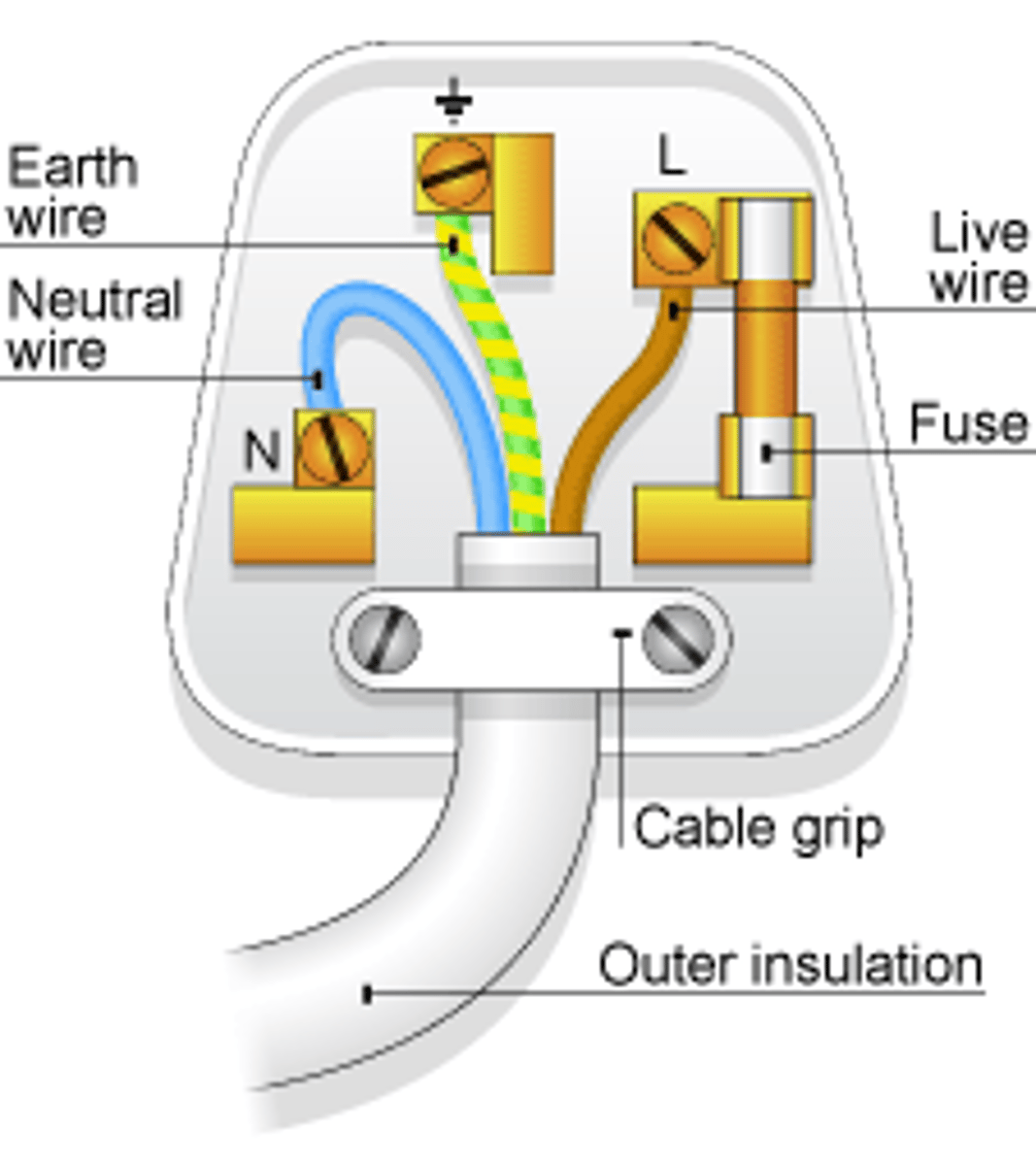
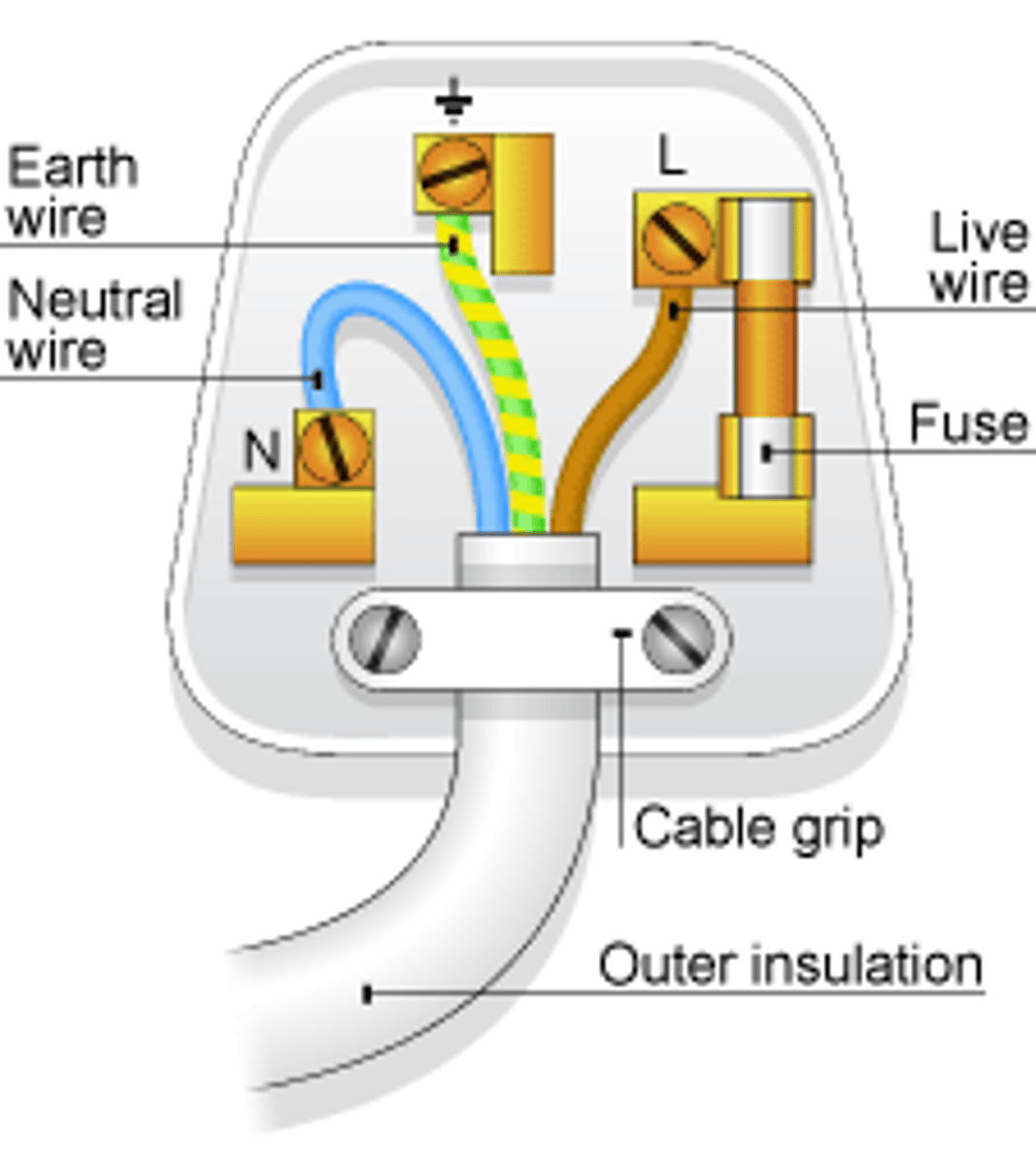
Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains using _____-____ _____
three-core cable
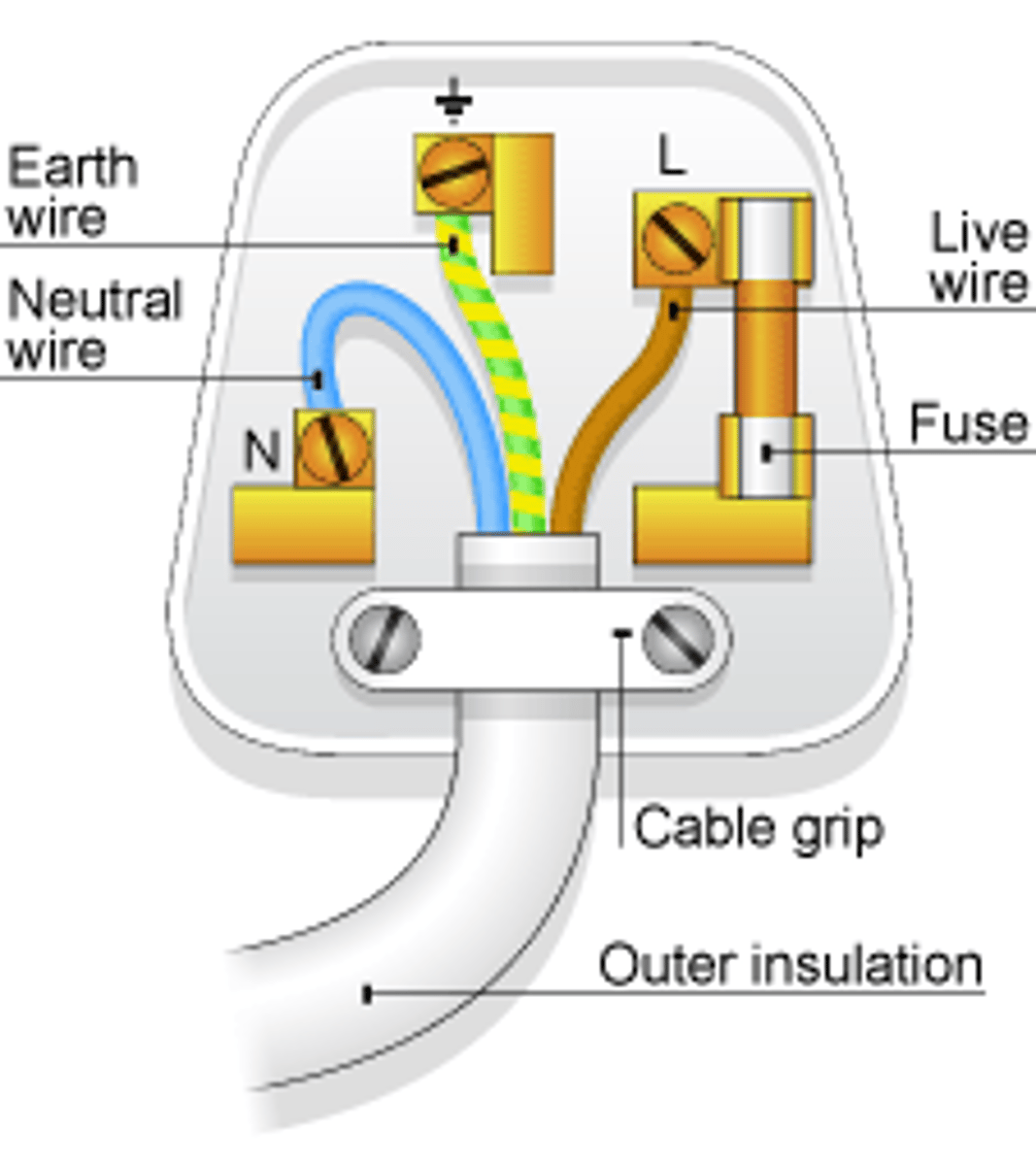
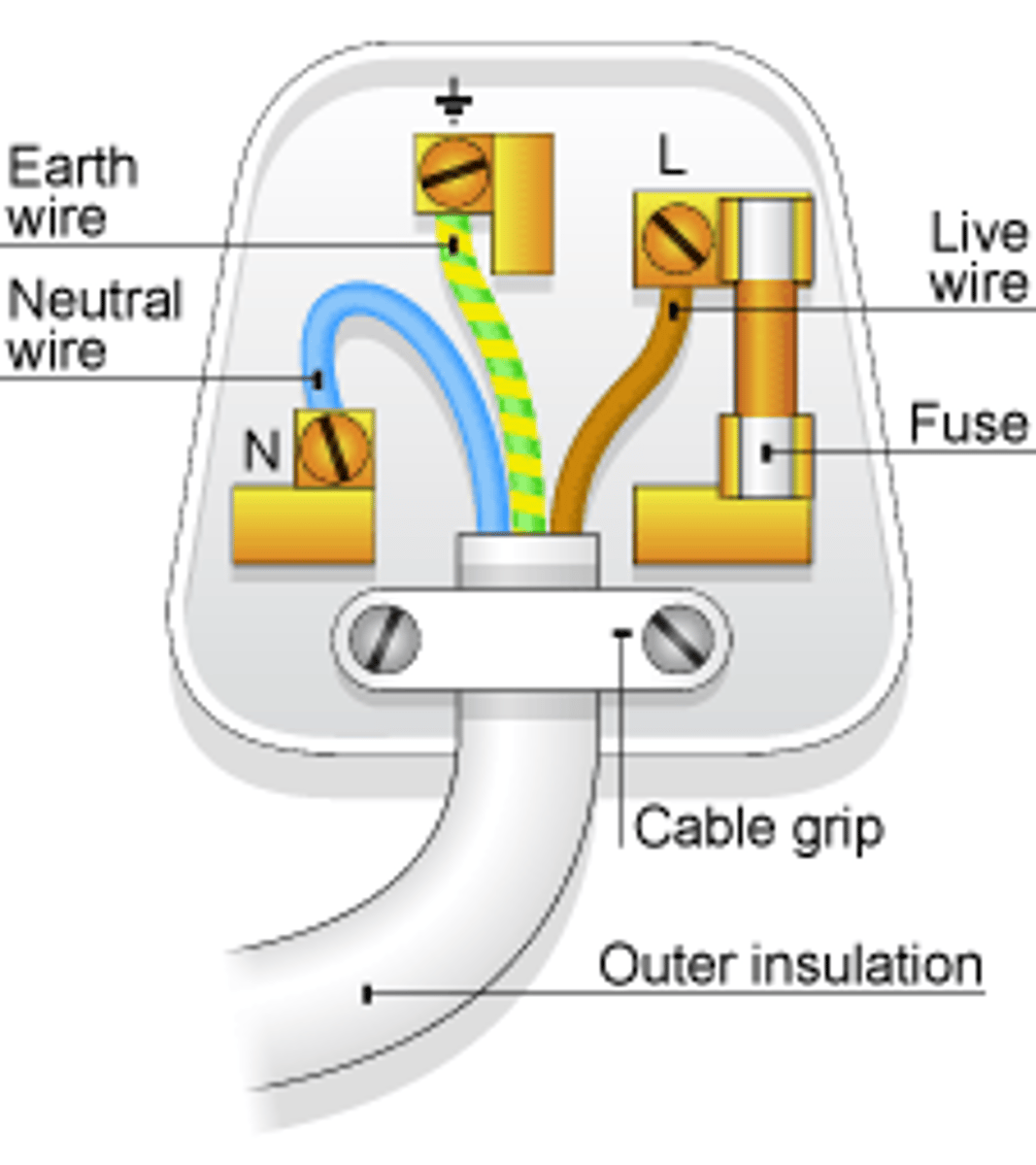
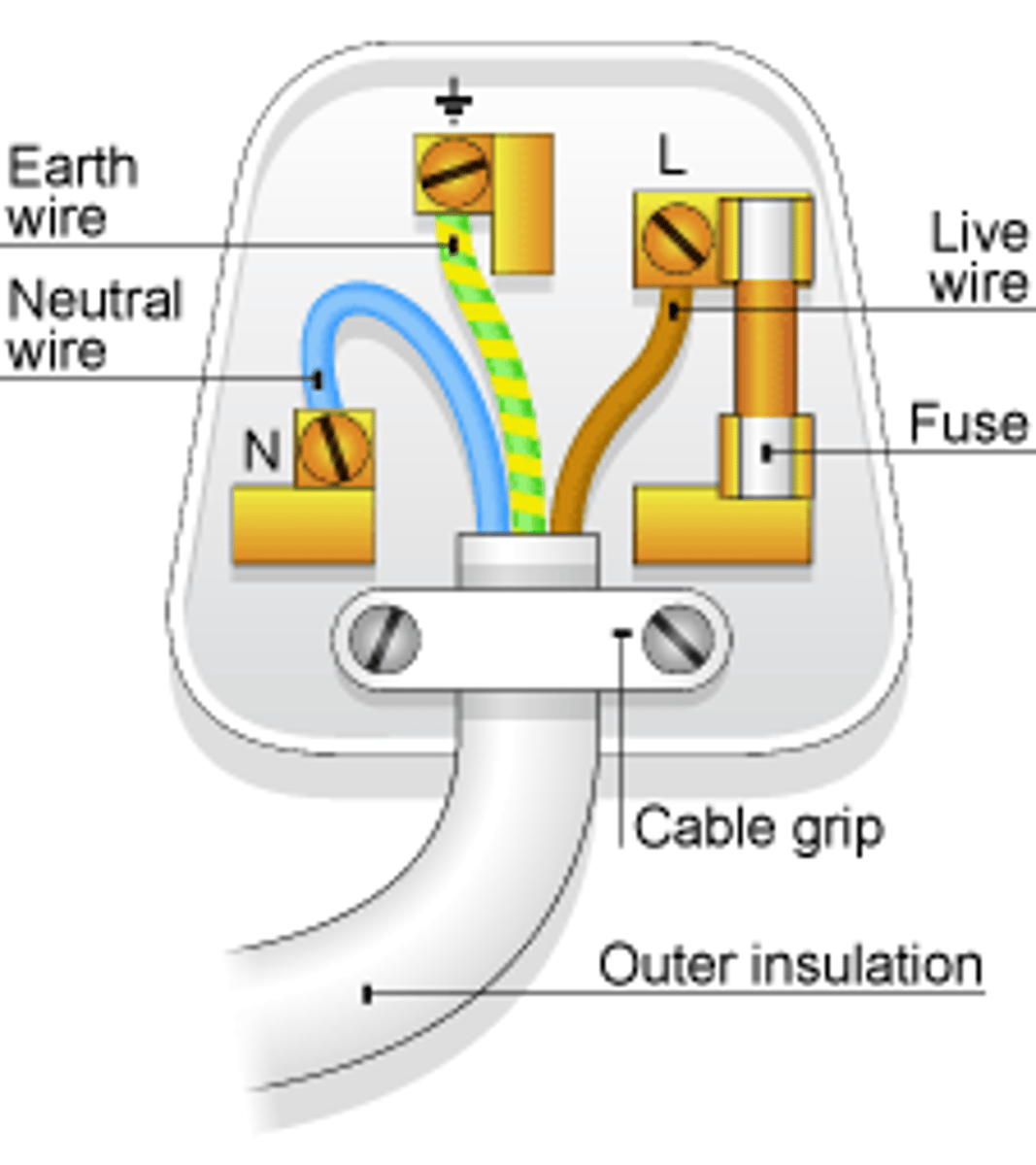
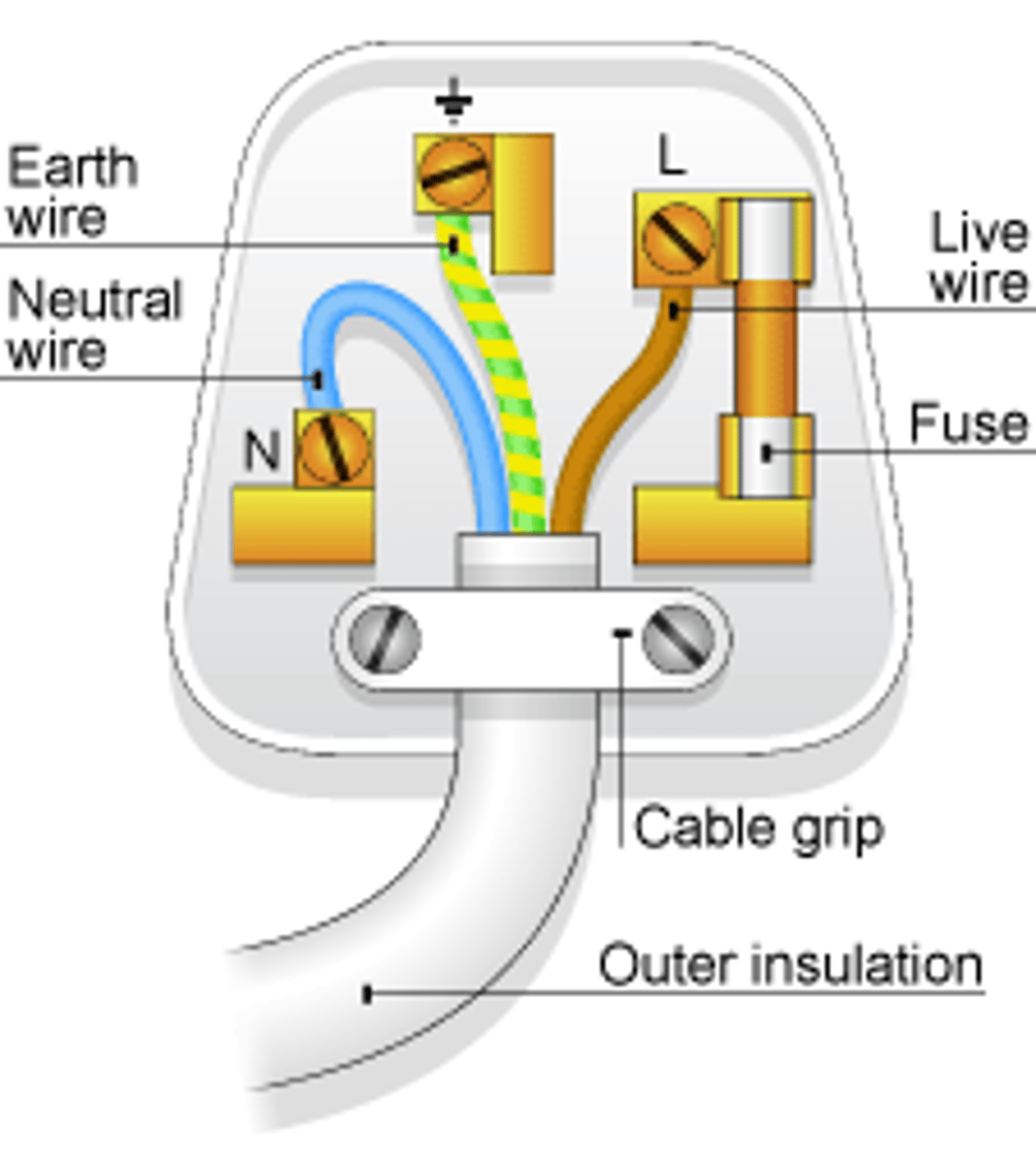
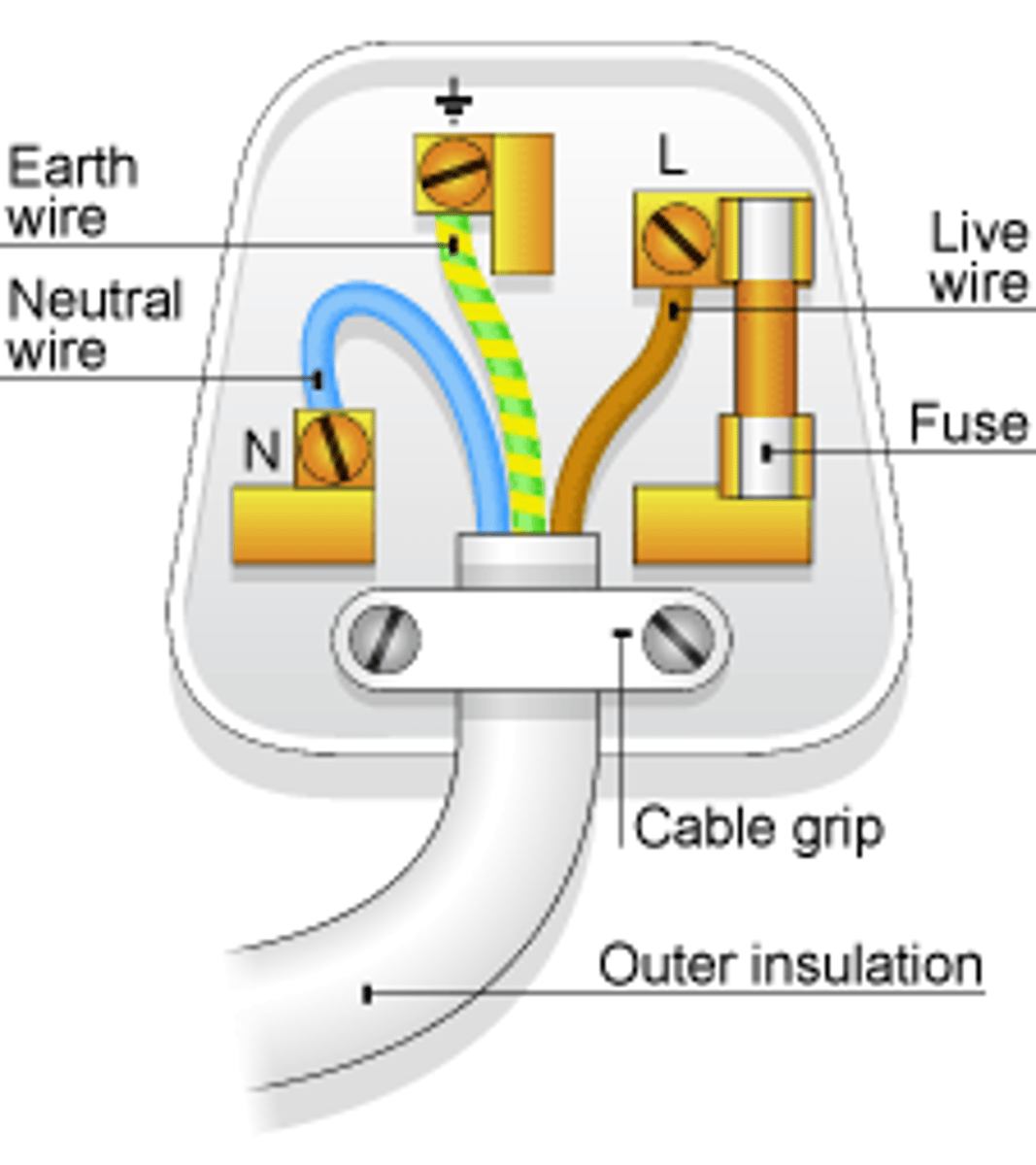
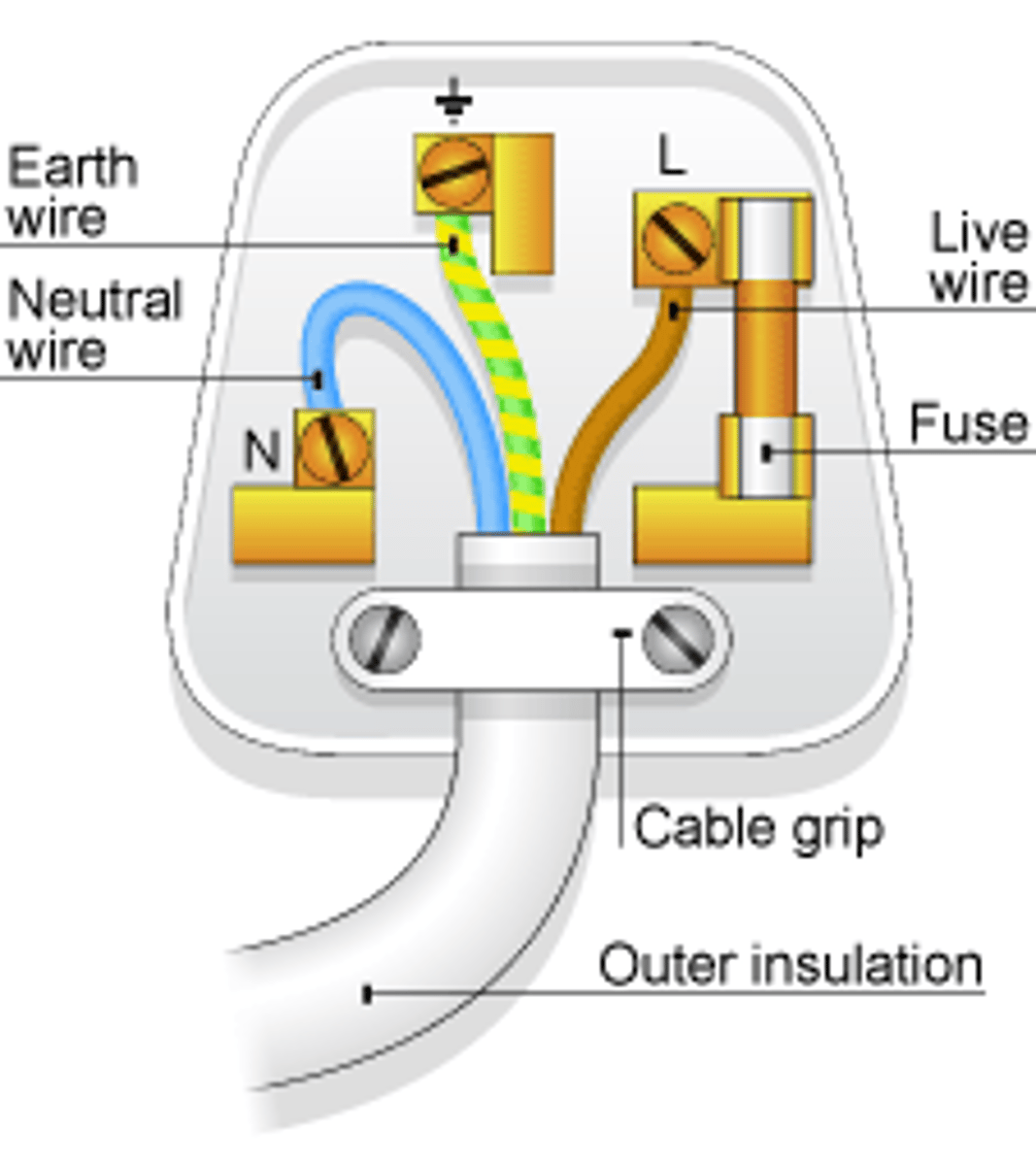
The _____ wire carries the alternating potential difference from the supply
live
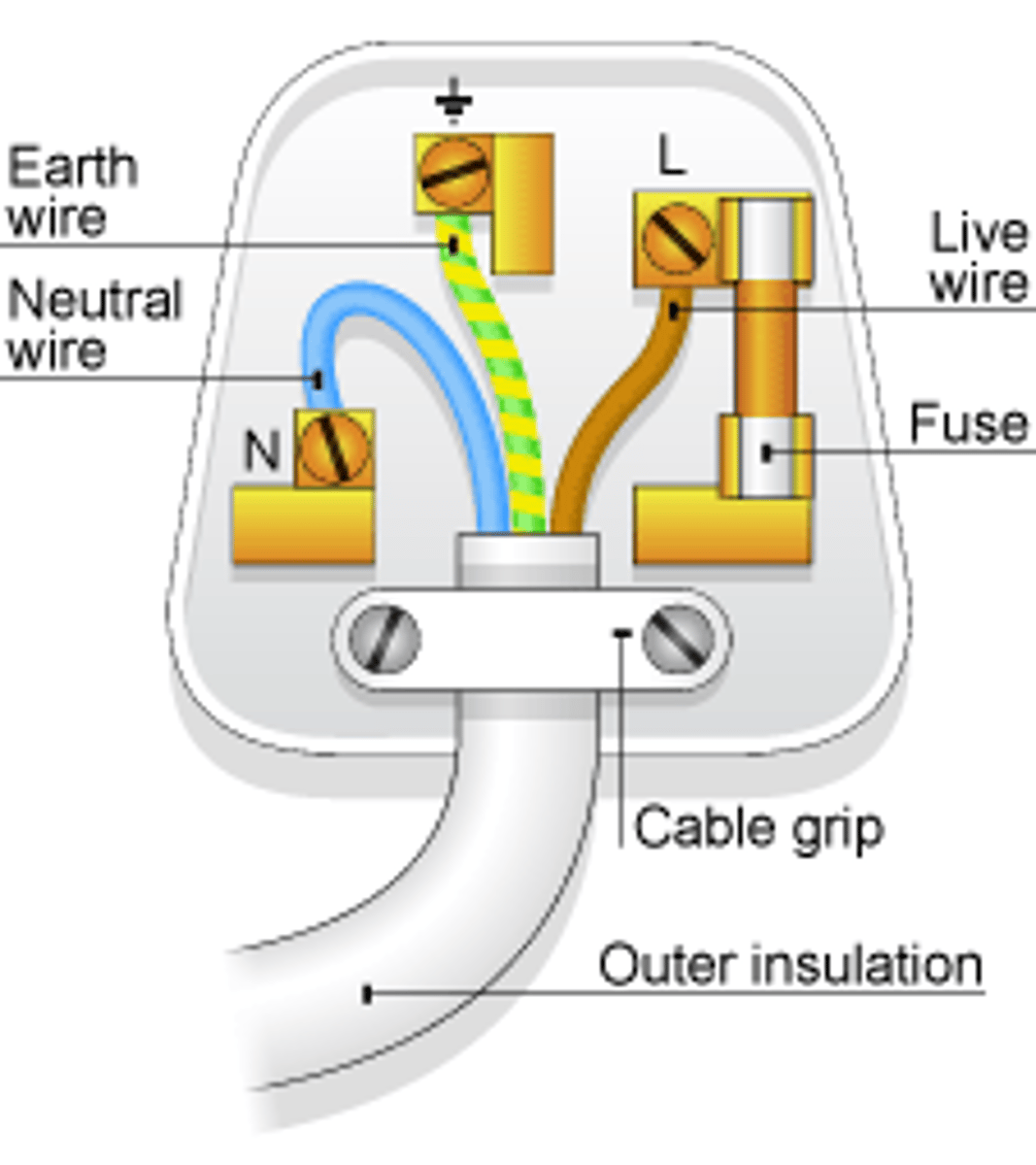
The ______ wire completes the circuit
neutral
Direct potential difference induces current to...
flow in one direction
The ______ wire is a safety wire to stop the appliance becoming live
earth
Alternating potential difference induces current to...
alternate the direction of flow
The potential difference between the live wire and earth is about ___ Volts
230
The potential difference across the neutral wire is at, or close to ___ Volts
0
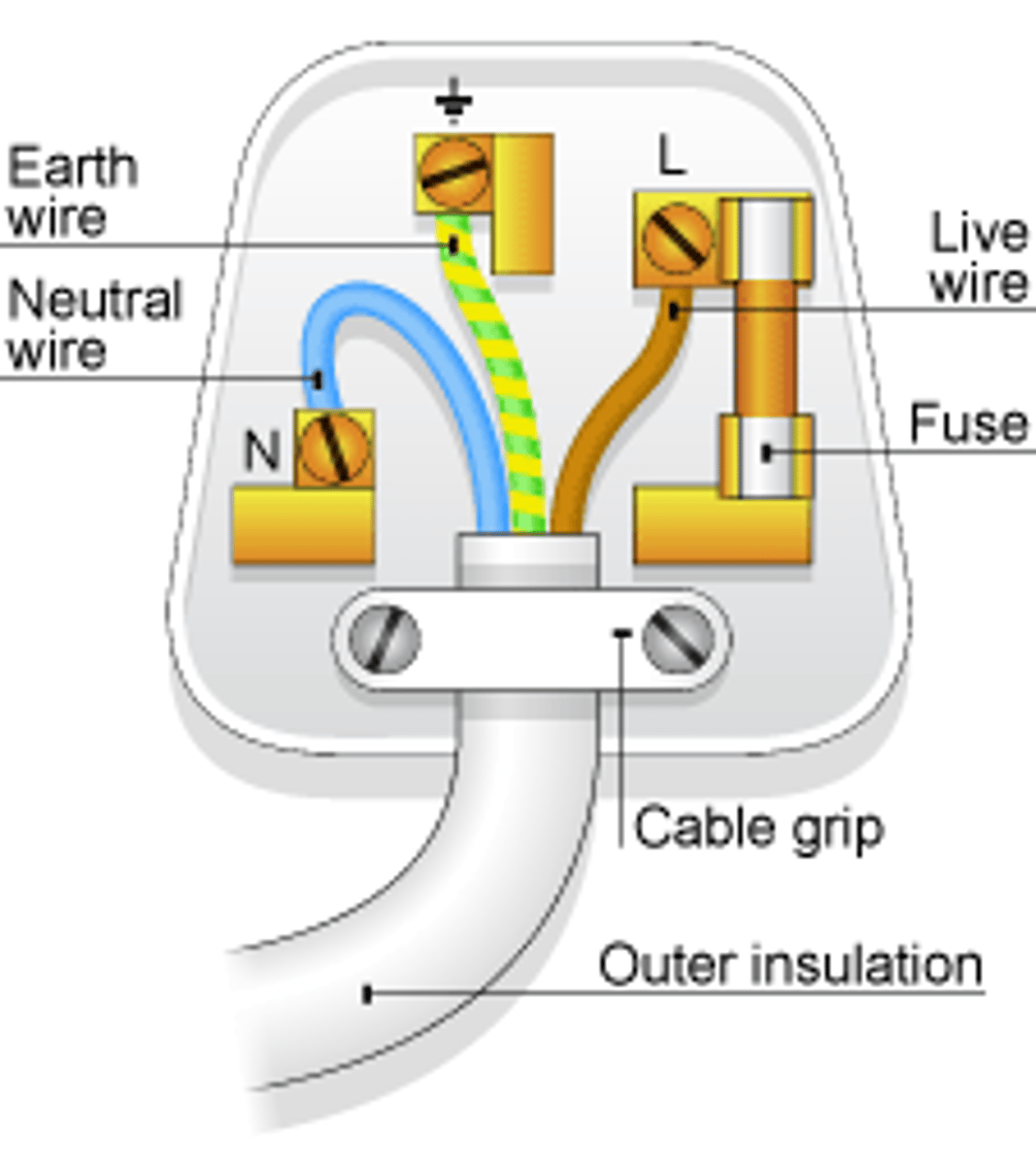
The colour of the insulation covering the LIVE wire is...
brown
For a given resistance, as the potential difference across a device increases, the _______ through a device will also increase
current
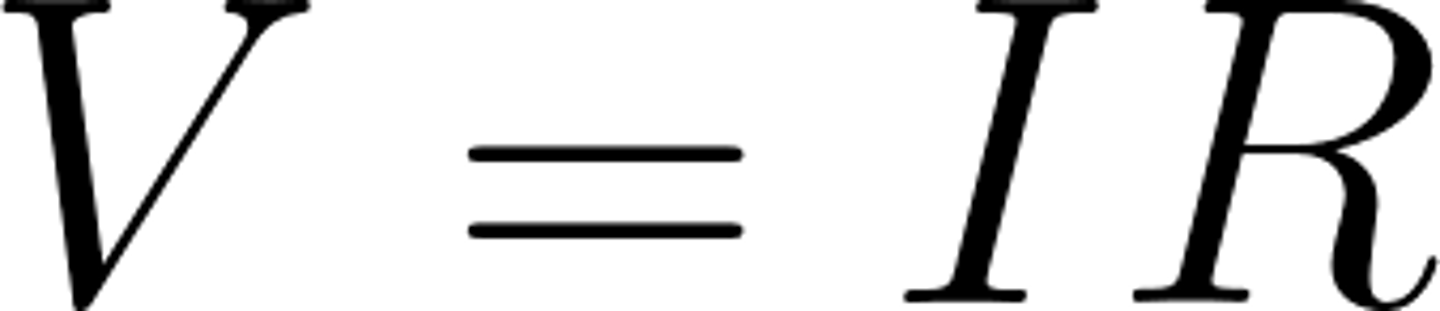
The colour of the insulation covering the NEUTRAL wire is...
blue
If the current through a device increases, the amount of ______ transferred per second (power) will also increase
energy
The colour of the insulation covering the EARTH wire is...
green & yellow
Power of-, potential difference across- and current through a device are linked by the equation
power= potential difference x current
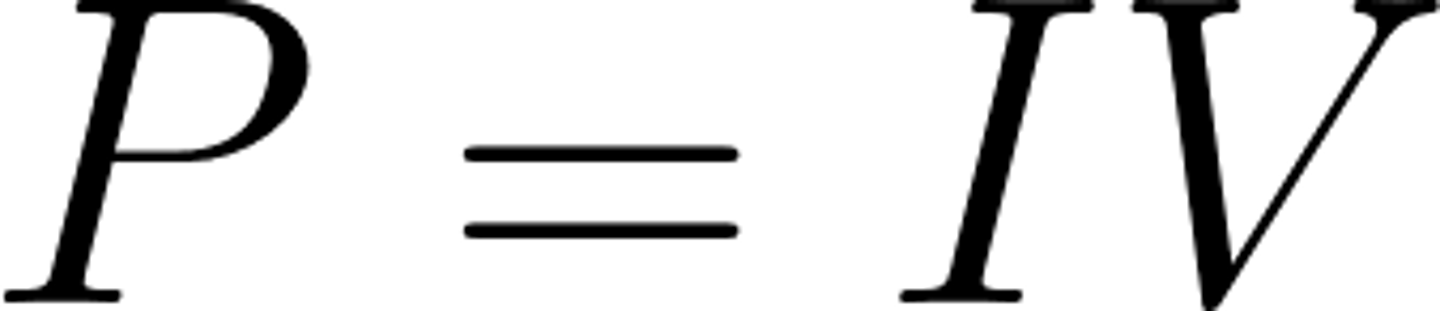
Power & resistance of a device, and current through a device are linked by the equation
Current² x Resistance
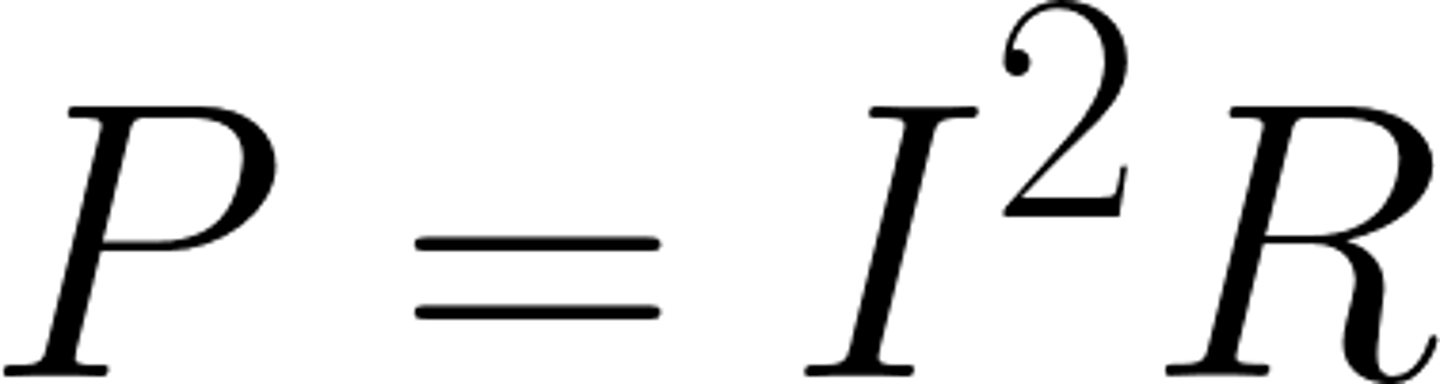
Unit of power, P
watts, W
Everyday electrical appliances are designed to bring about ______ transfers
energy
If an appliance becomes live a person could experience an...
electric shock
The amount of ______ an appliance transfers depends on how long the appliance is switched on for and the power of the appliance
energy
____ is done when charge flows in a circuit
Work
Equation for energy transferred?
power x time
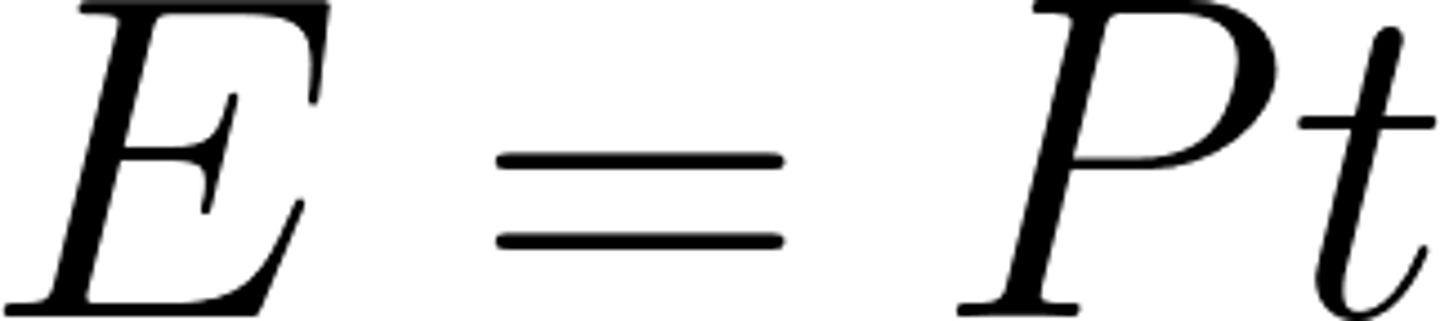
The _____ wire is at 0 Volts, it only carries a current if there is a fault
earth
What is the equation for energy transferred?
charge flow x potential difference
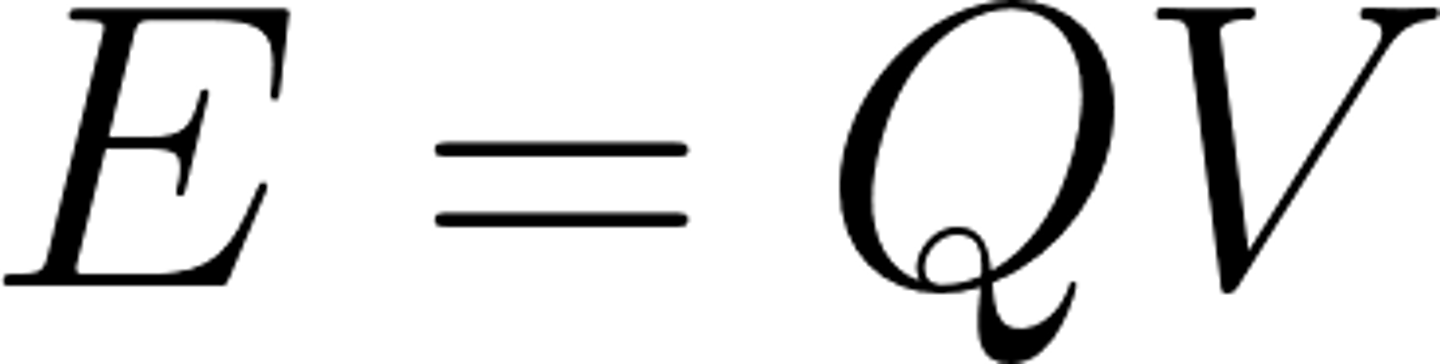
Unit of energy transferred, E
joules, J
A more powerful device will transfer energy ______ than a less powerful one
quicker
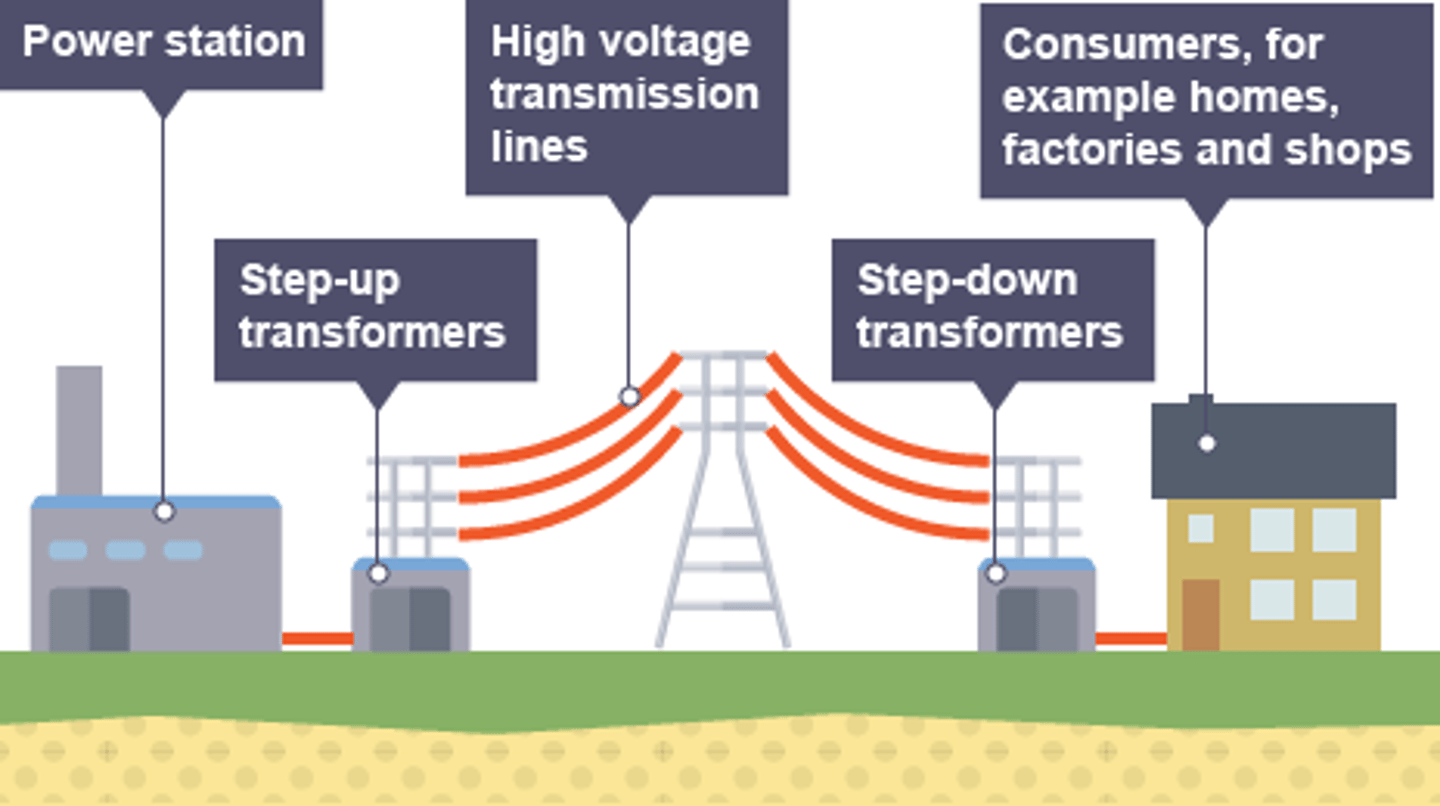
The ________ ____ is a system of cables and transformers linking power stations to consumers
National Grid
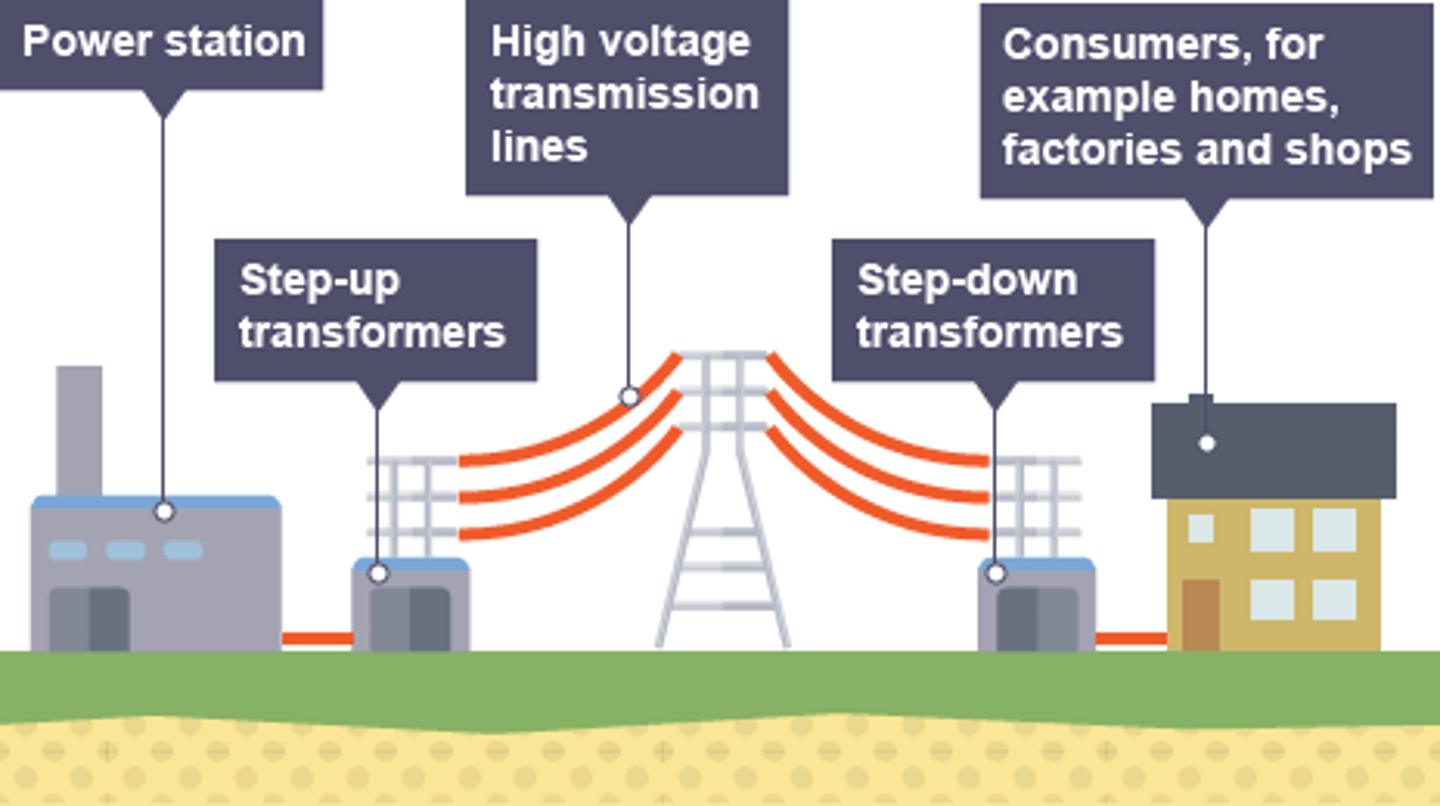
Electrical _____ is transferred from power stations to consumers using the National Grid
power
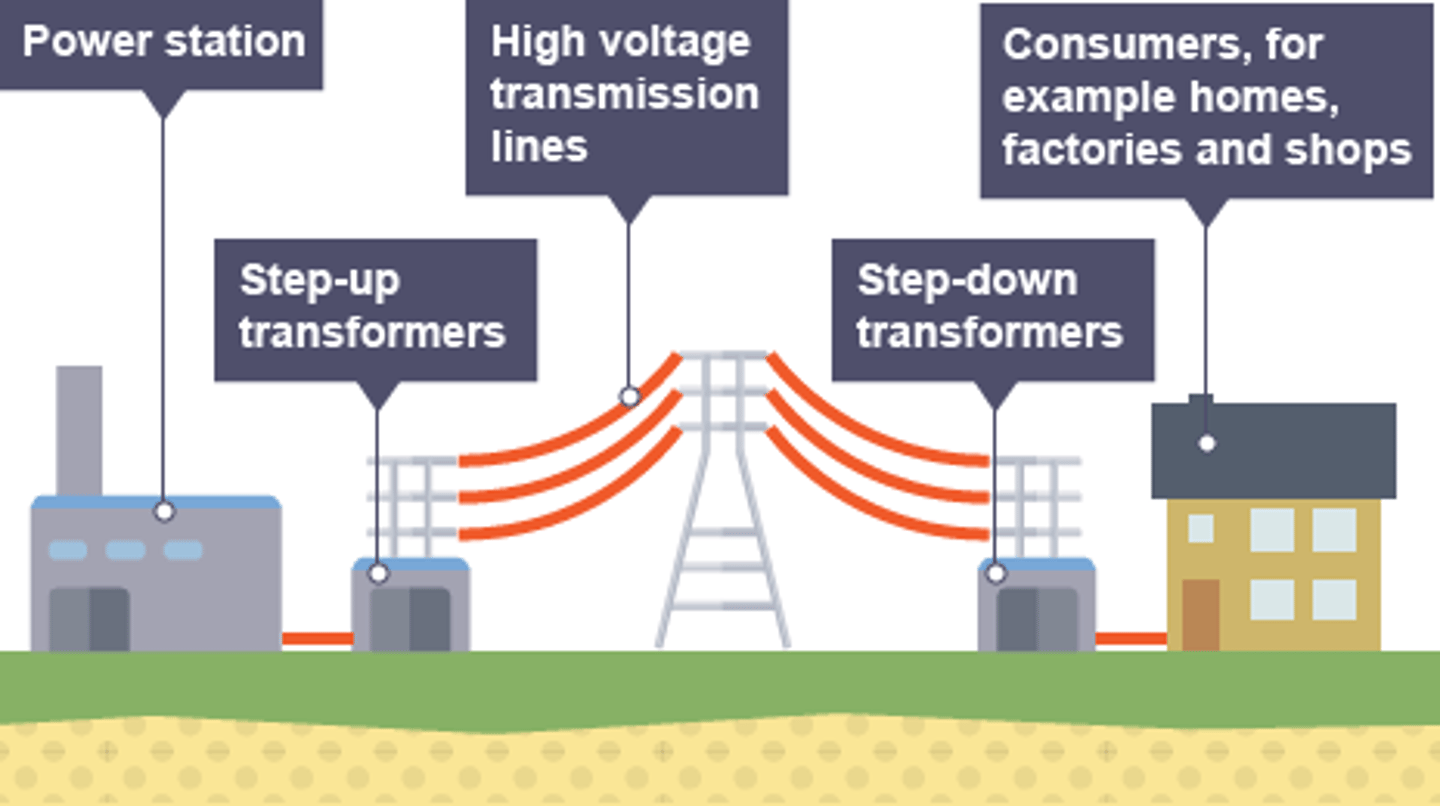
Step-up transformers are used to ________ the potential difference from the power station to the transmission cables
increase
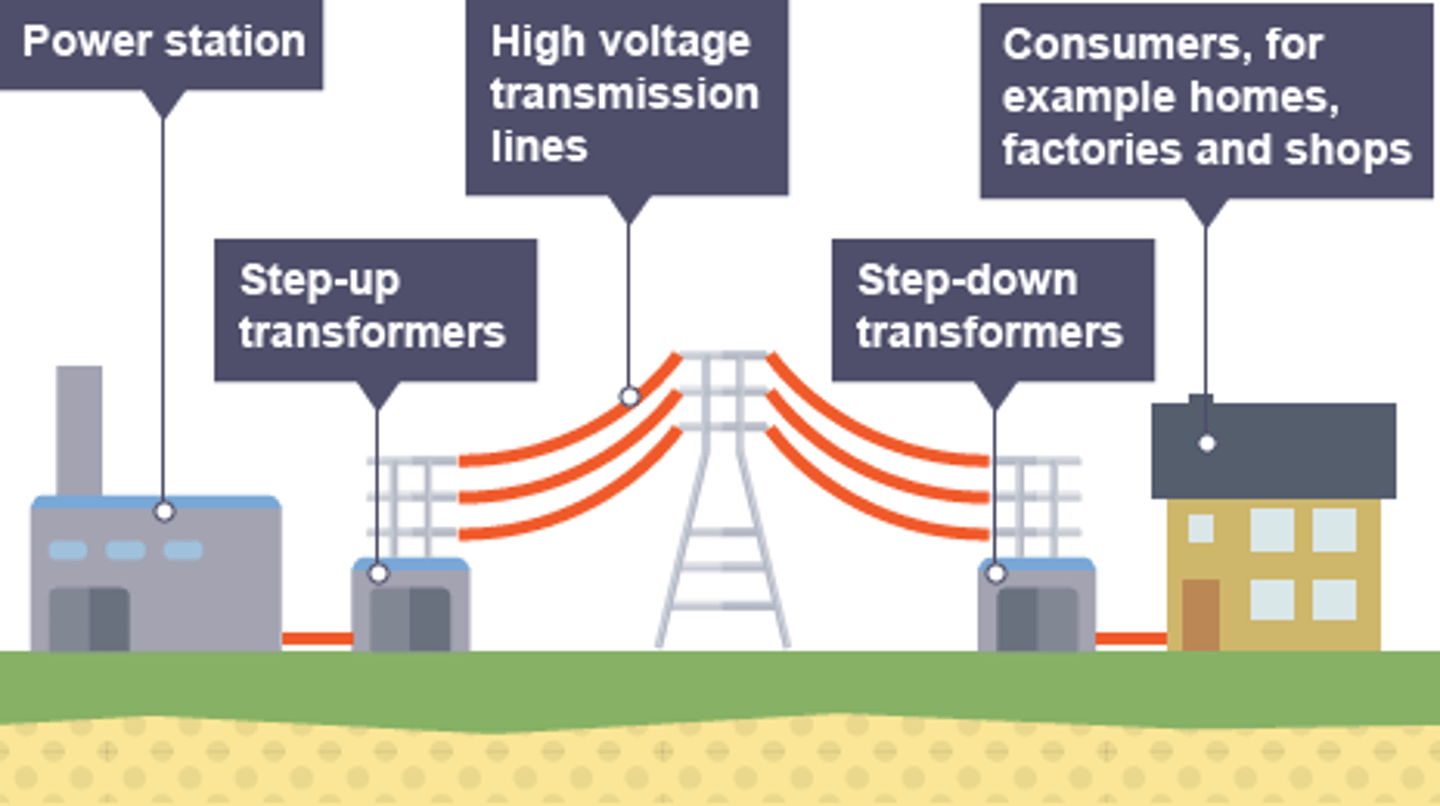
Step-down transformers are used to ________, to a safe value, the potential difference for domestic use
decrease
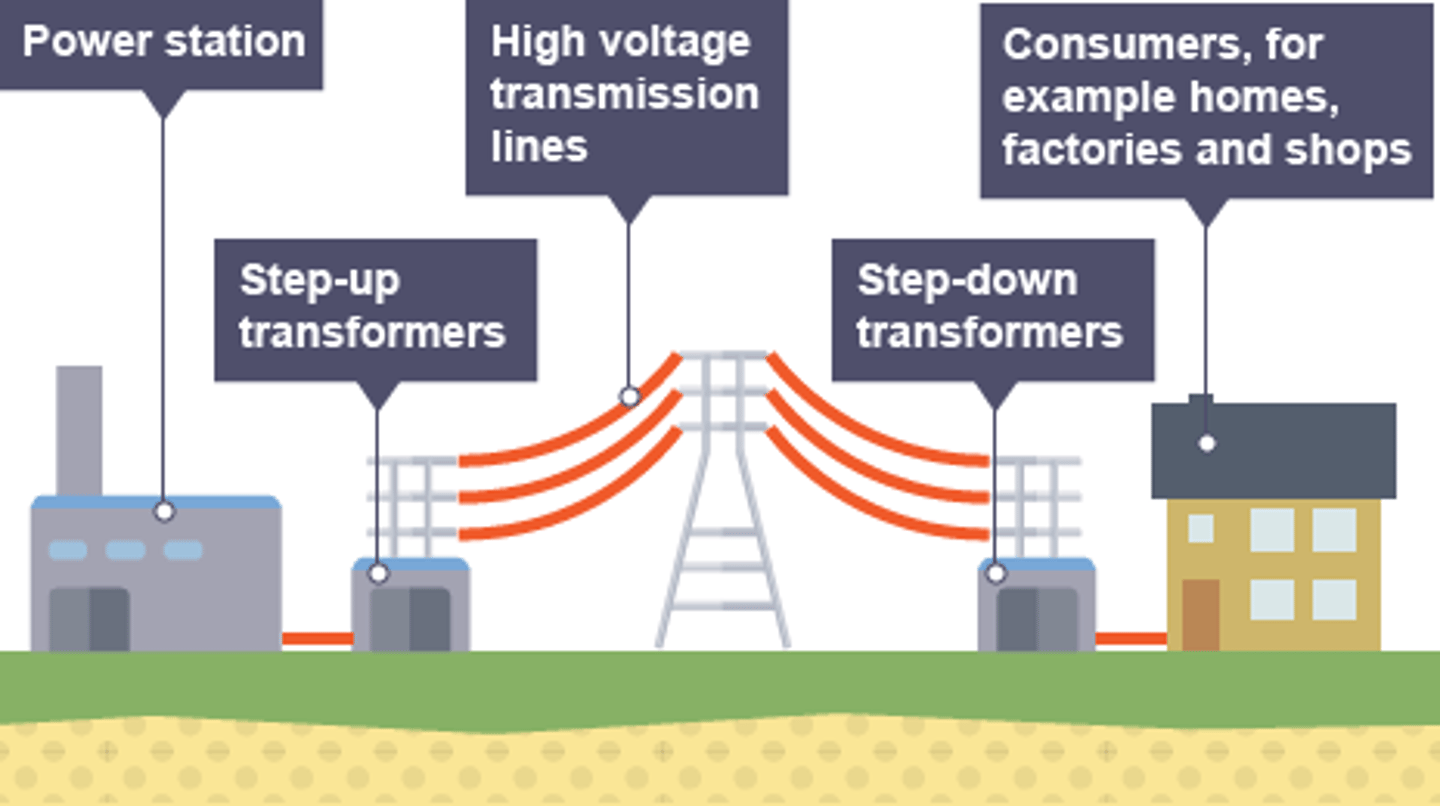
Step-up transformers dramatically decrease the _______ flowing in the transmission cables
current
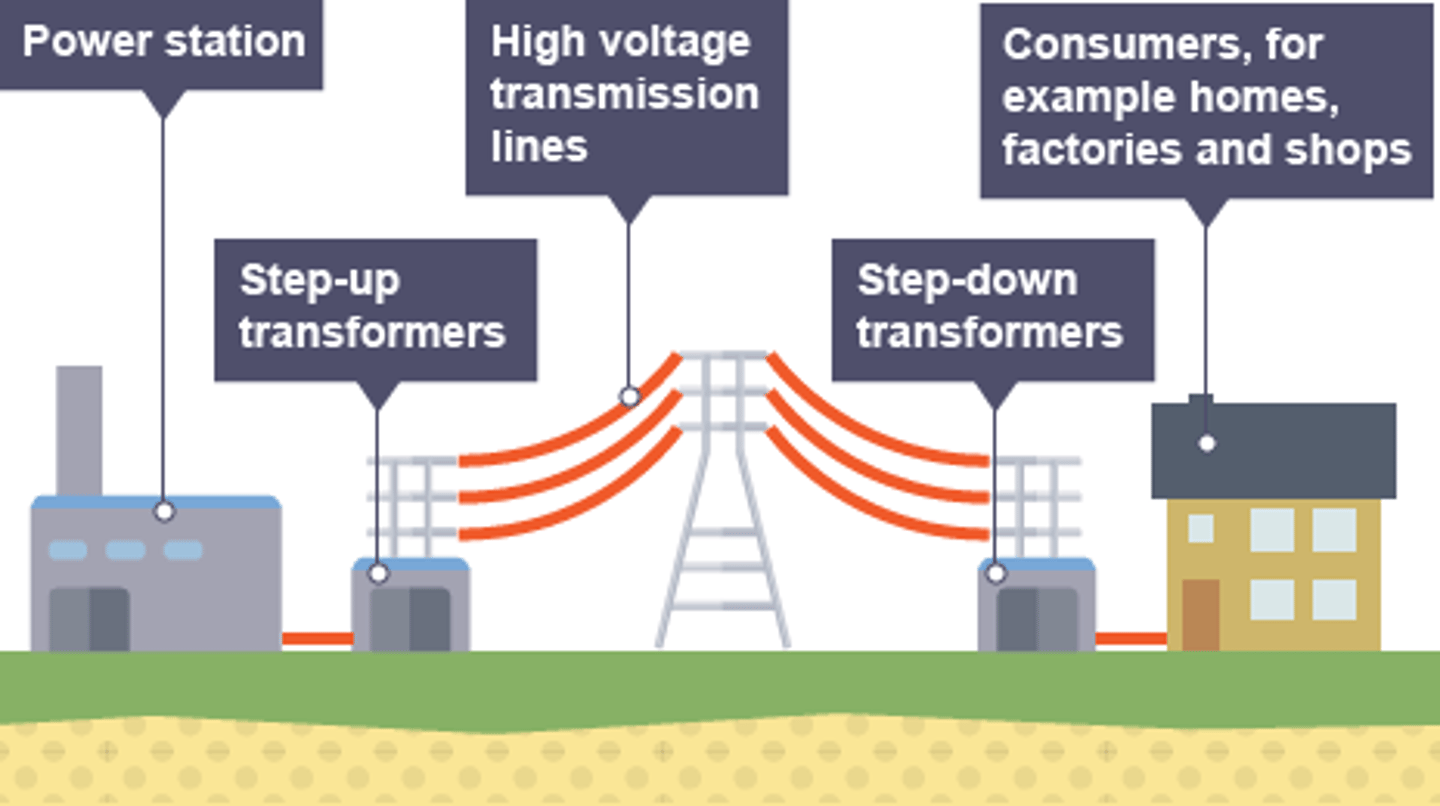
Less current flowing in the transmission cables means less _____ lost due to heating effects
power
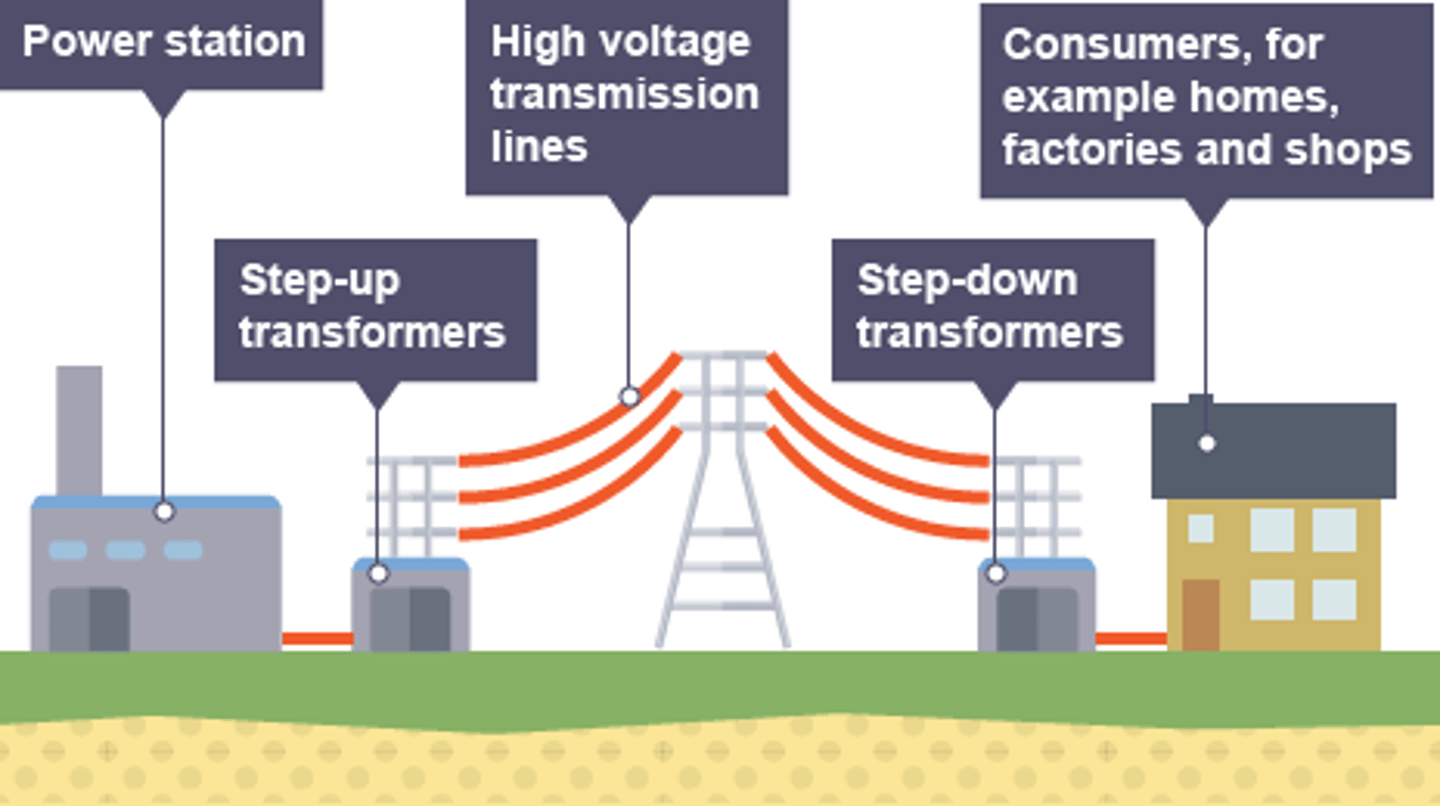
Less power lost in the transmission cables means the National Grid is more _________
efficient
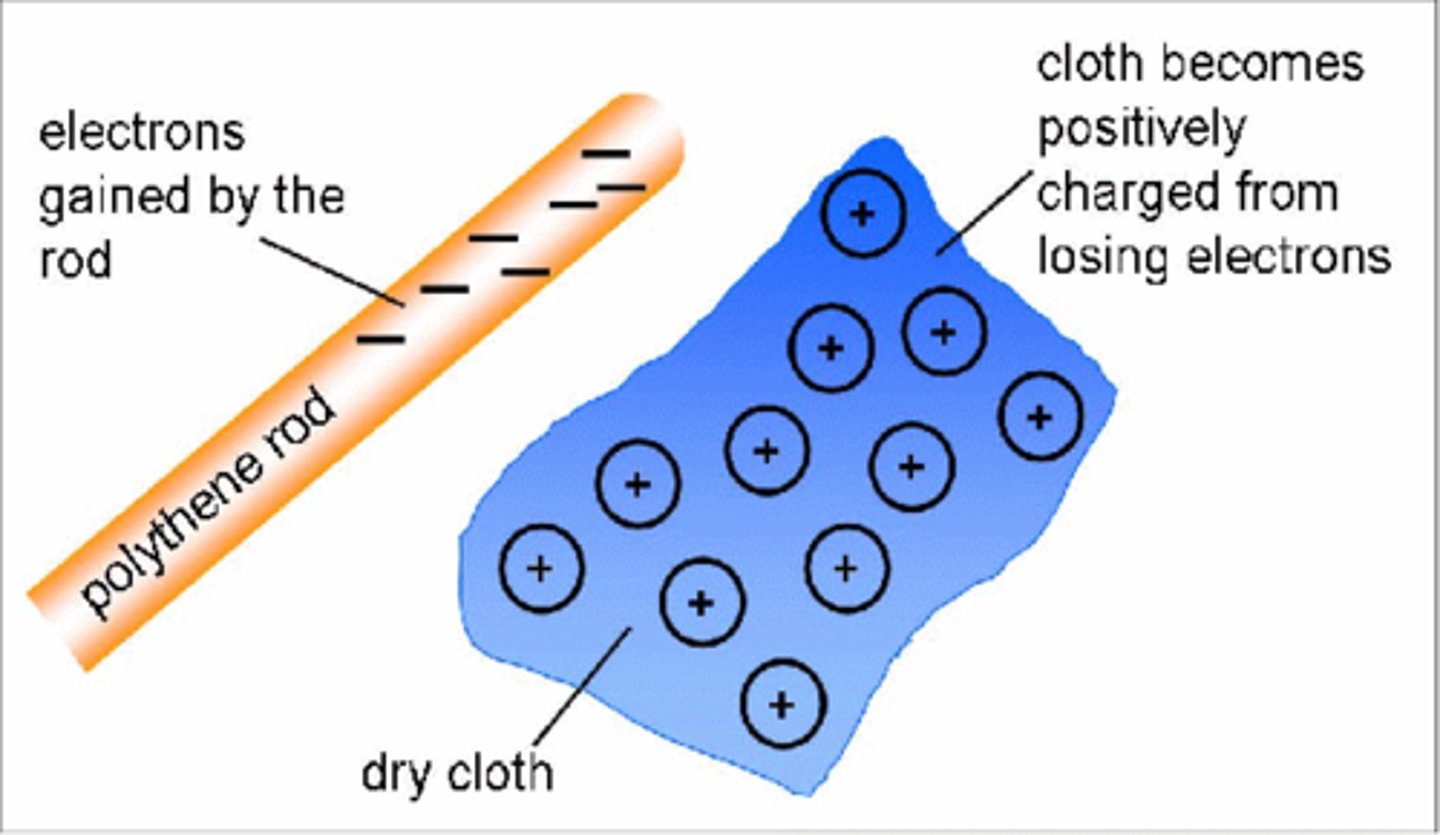
When certain __________ are rubbed against each other they become electrically charged
insulators

When two insulating materials experience friction negatively charged _________ transfer from one insulator to the other
electrons
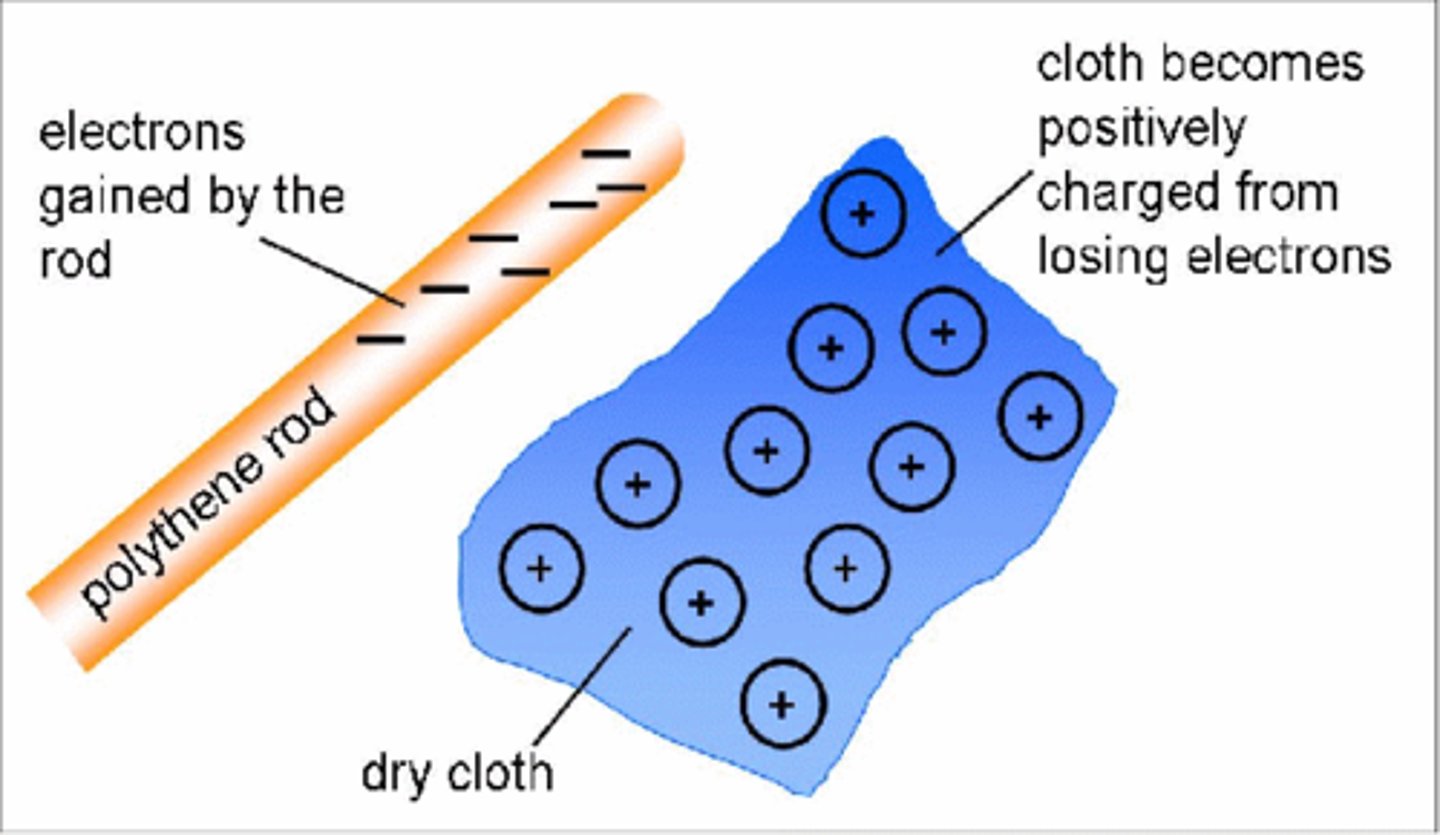
Insulators that transfer electrons to another insulator become __________ charged
positively
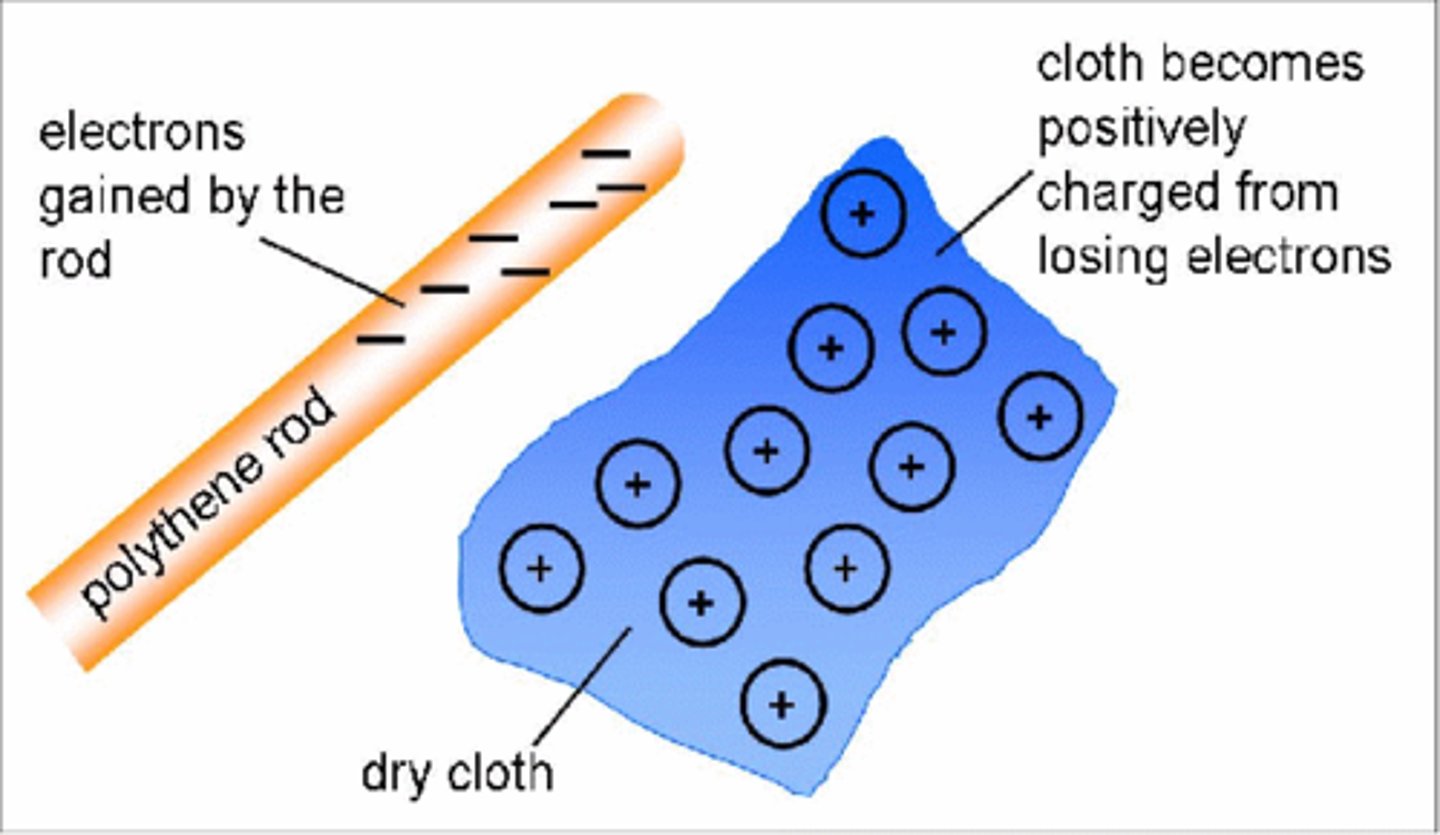
Insulators that gain electrons from another insulator become __________ charged
negatively
When two electrically charged objects are brought close together they exert a _____ on each other
force
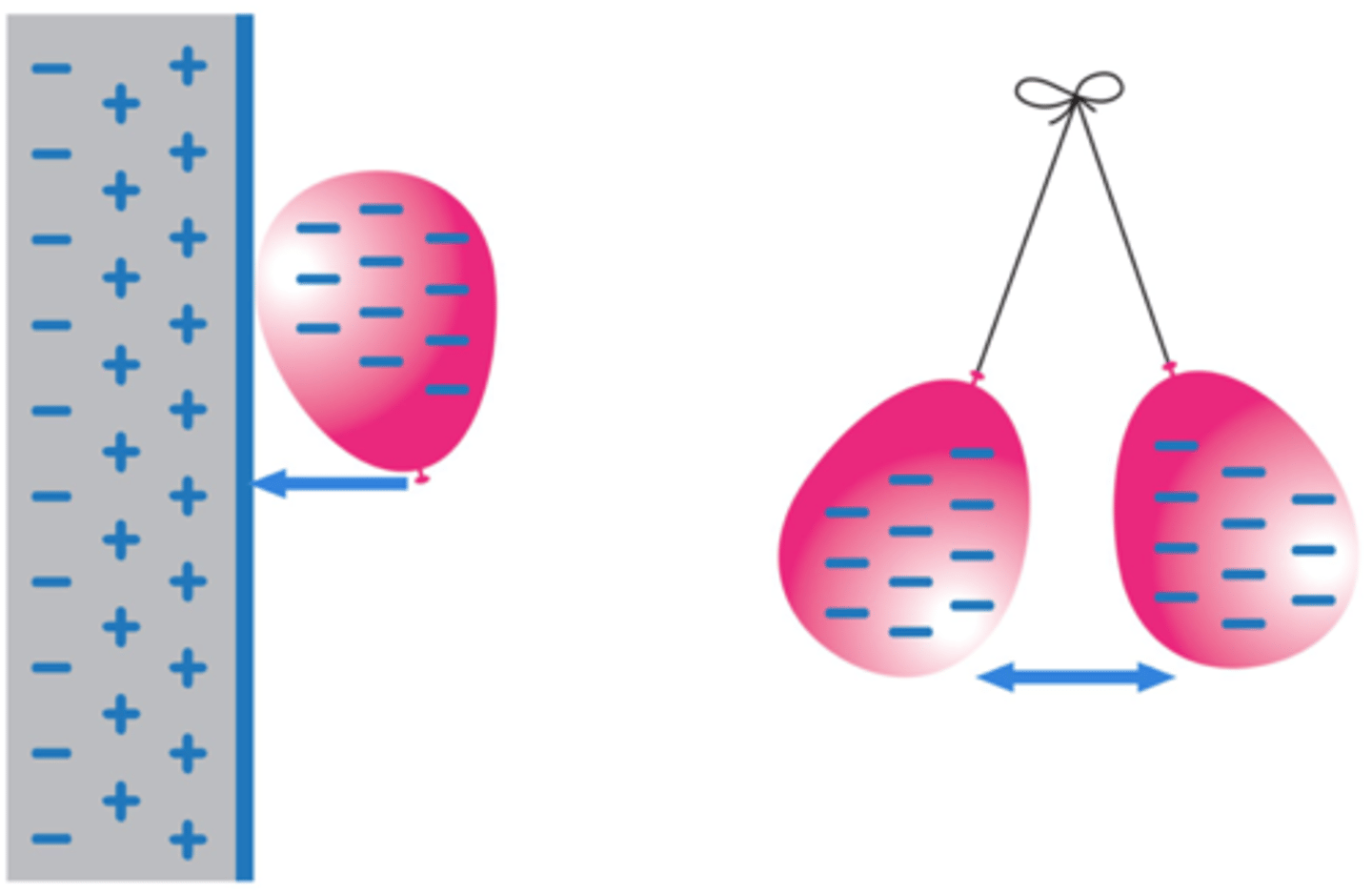
Two objects that carry the same type of charge will _____ when brought close together
repel
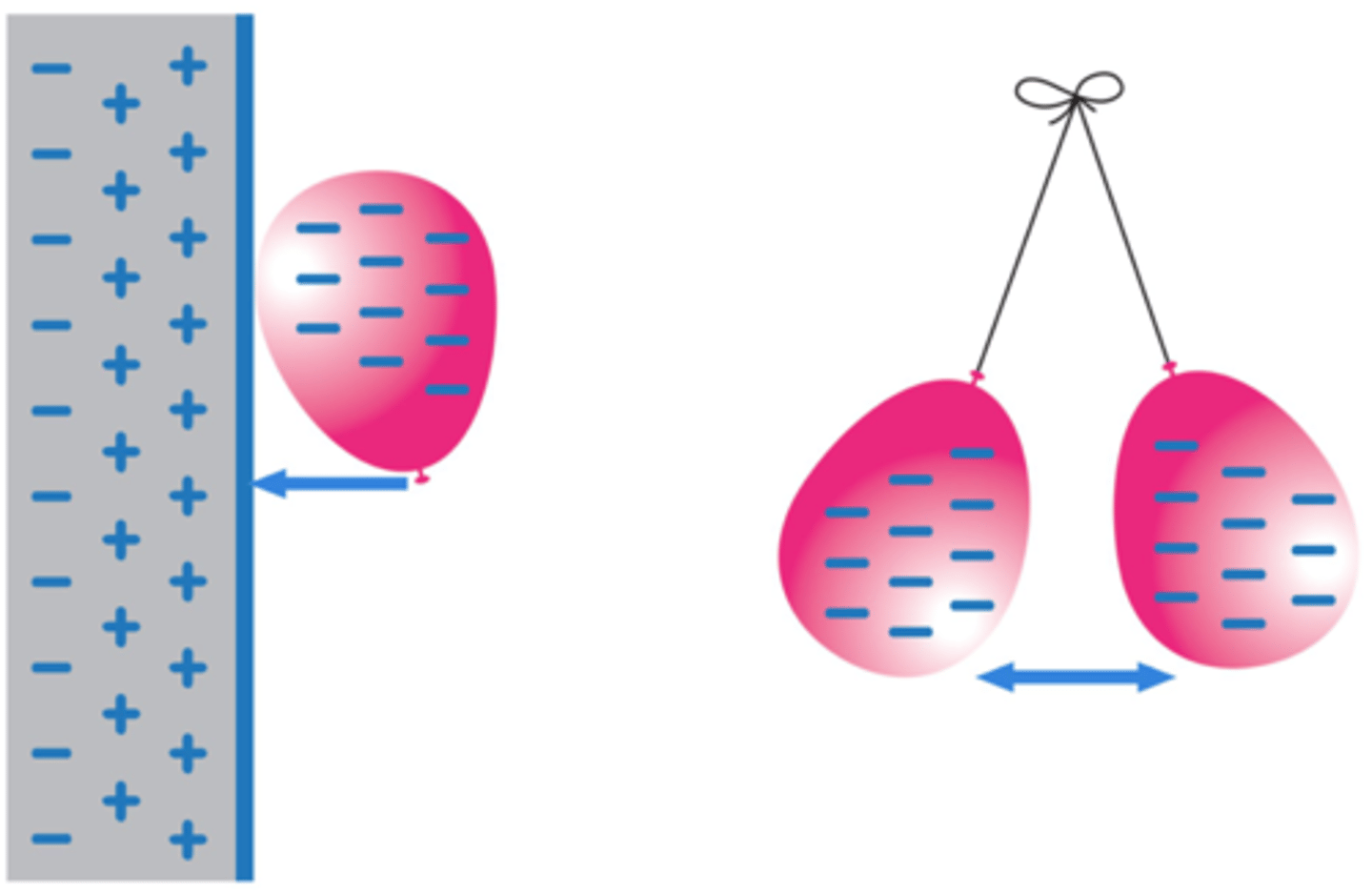
Two objects that carry different types of charge will _______ when brought close together
attract
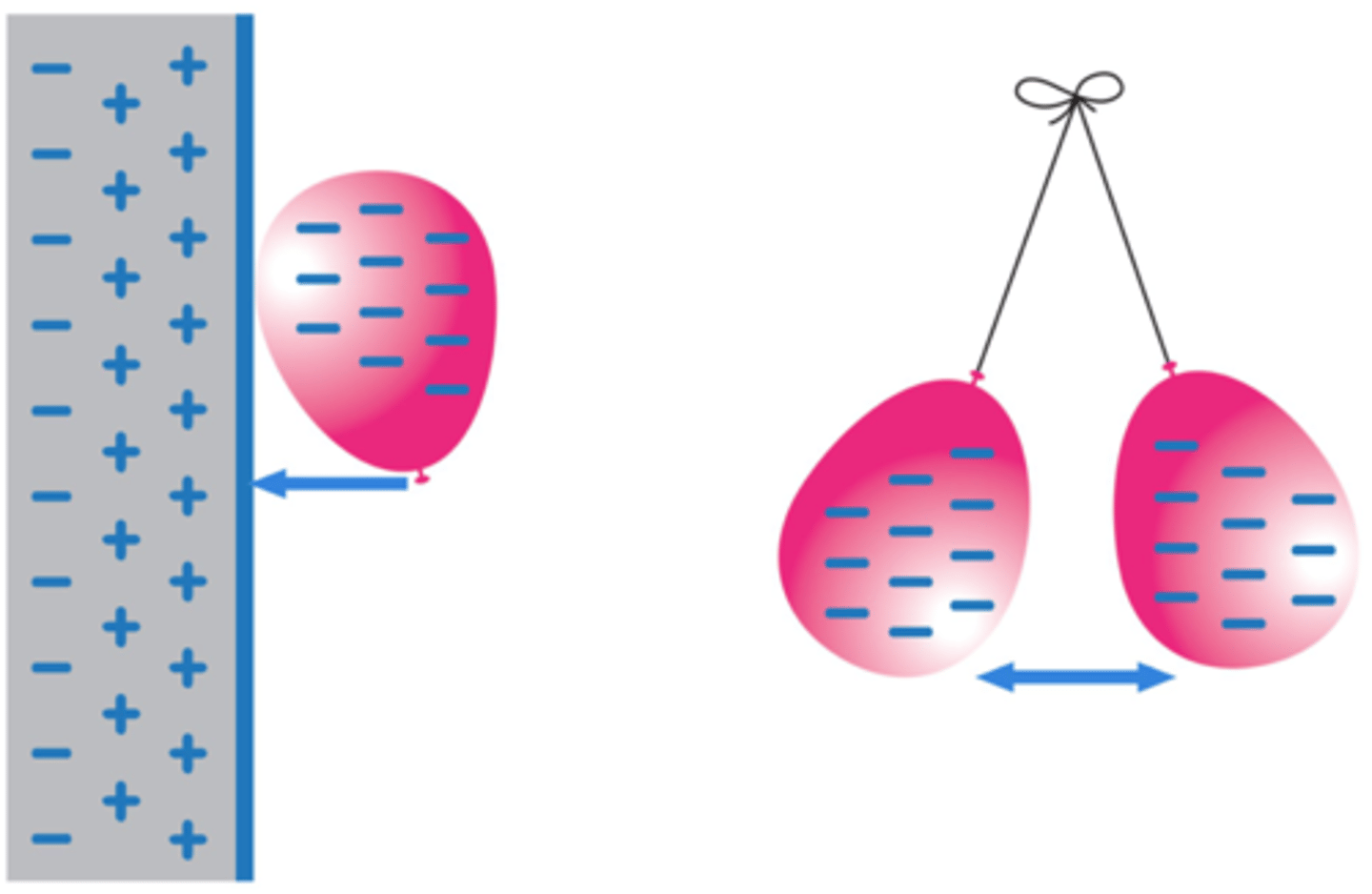
Attraction and repulsion between two charged objects are examples of ___-_______ force
non-contact
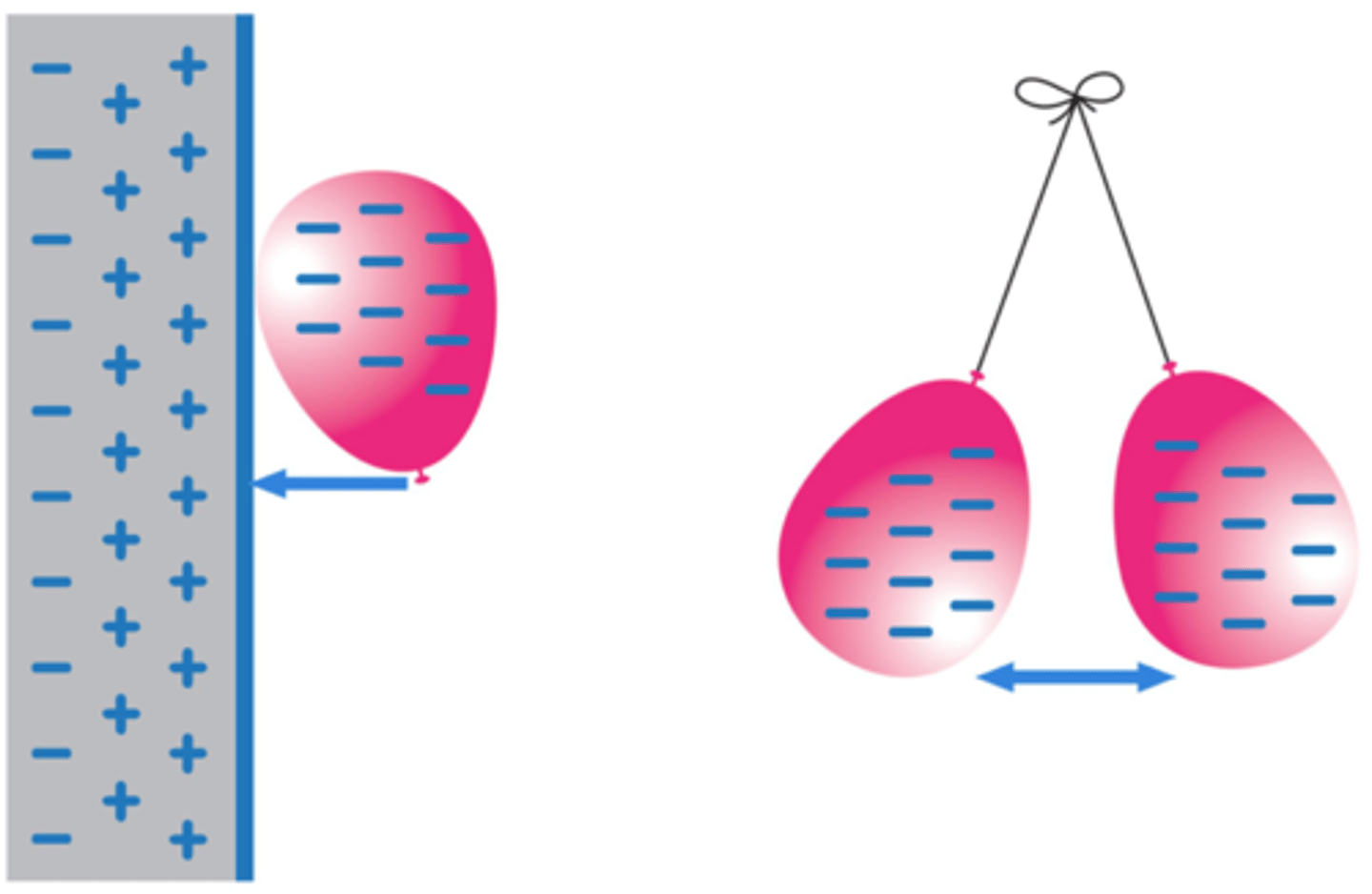
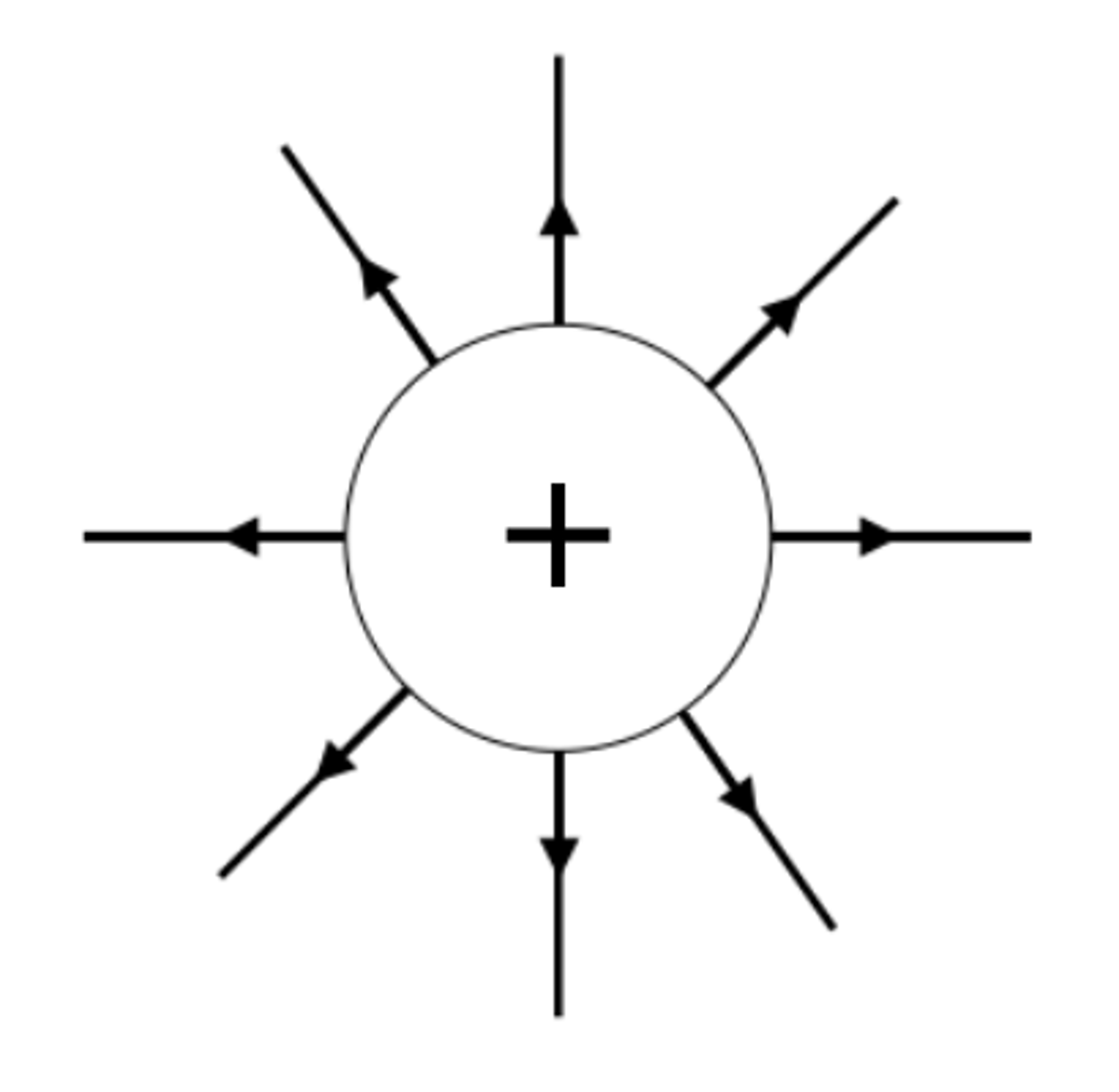
A charged object creates an ________ _____ around itself
electric field
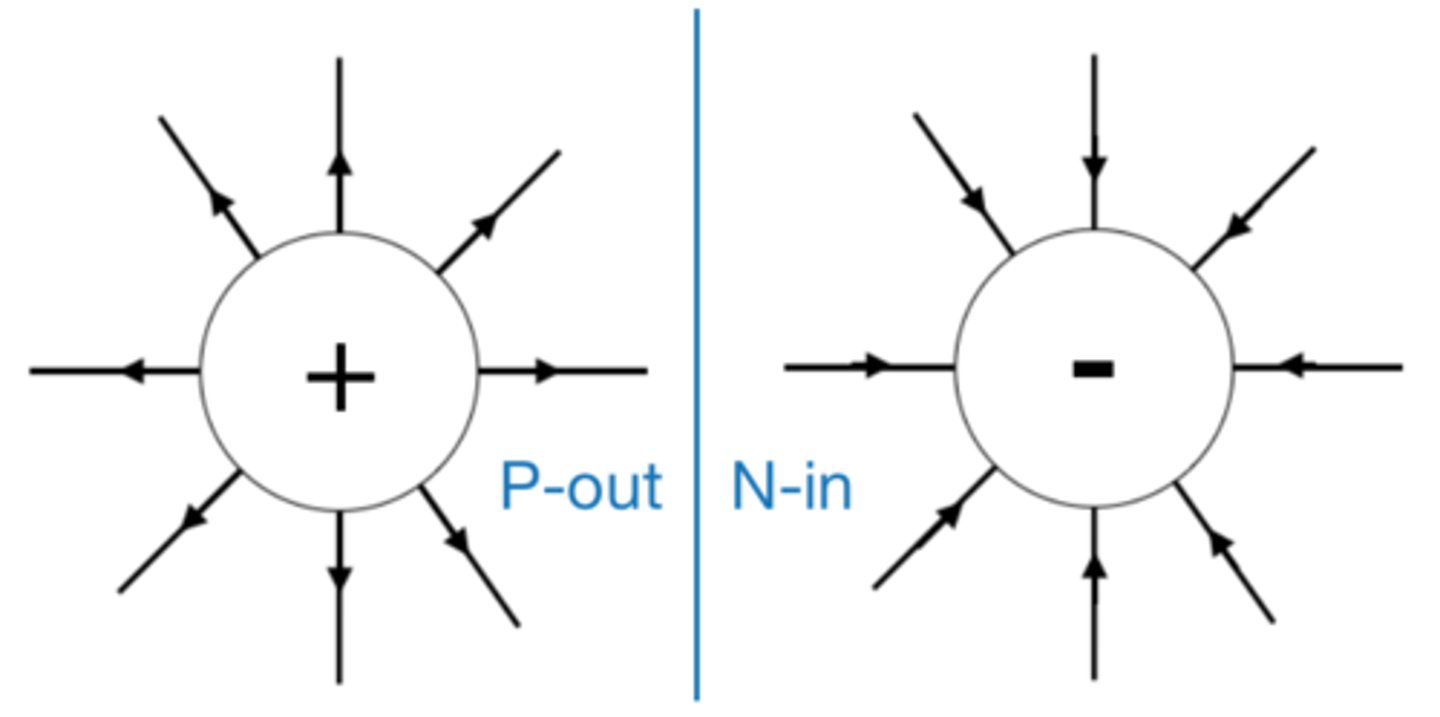
The electric field is _________ close to the charged object
strongest
The further away from the charged object, the ______ the electric field
weaker
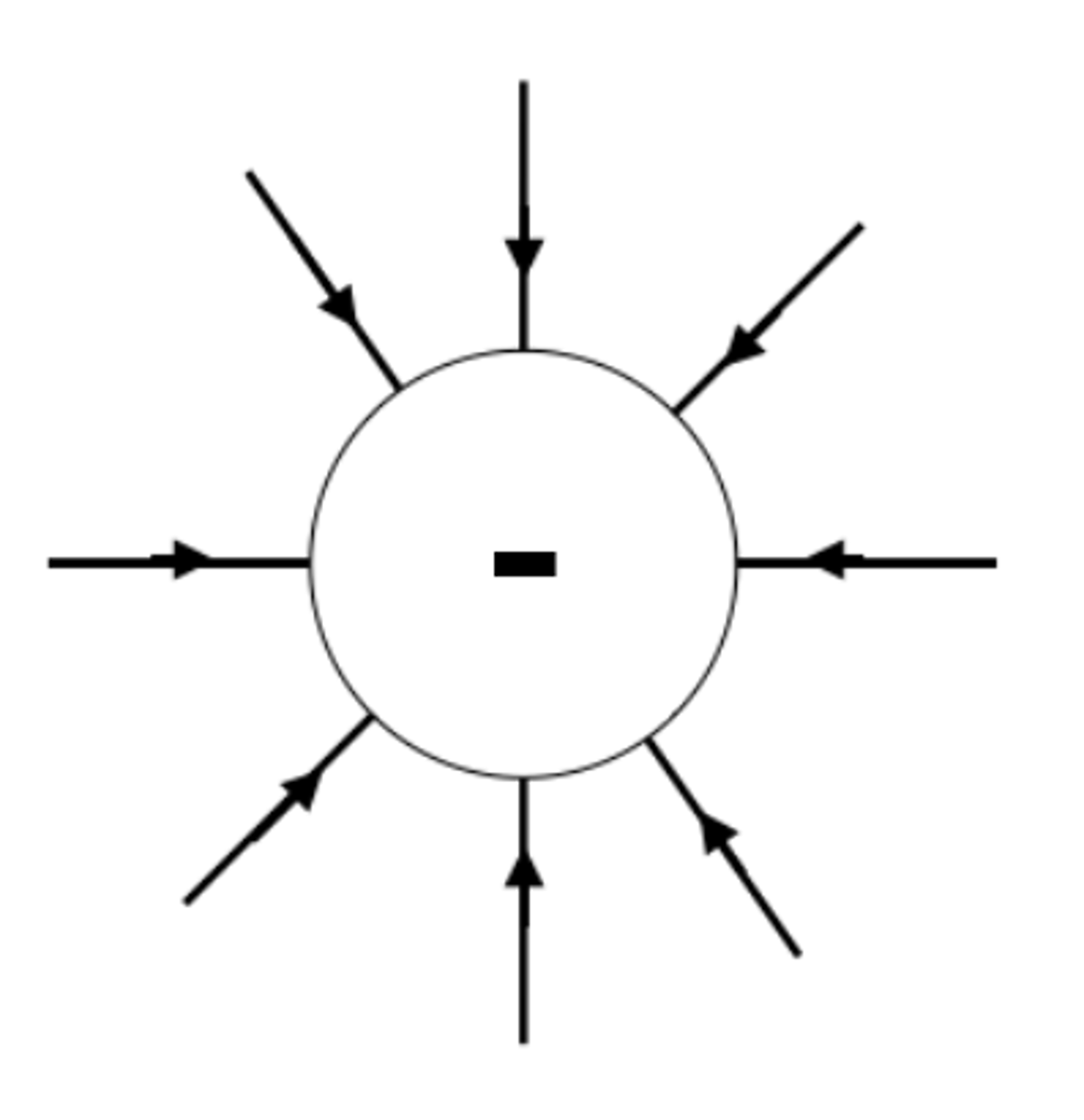
A second charged object placed in an electric field experiences a _____
force
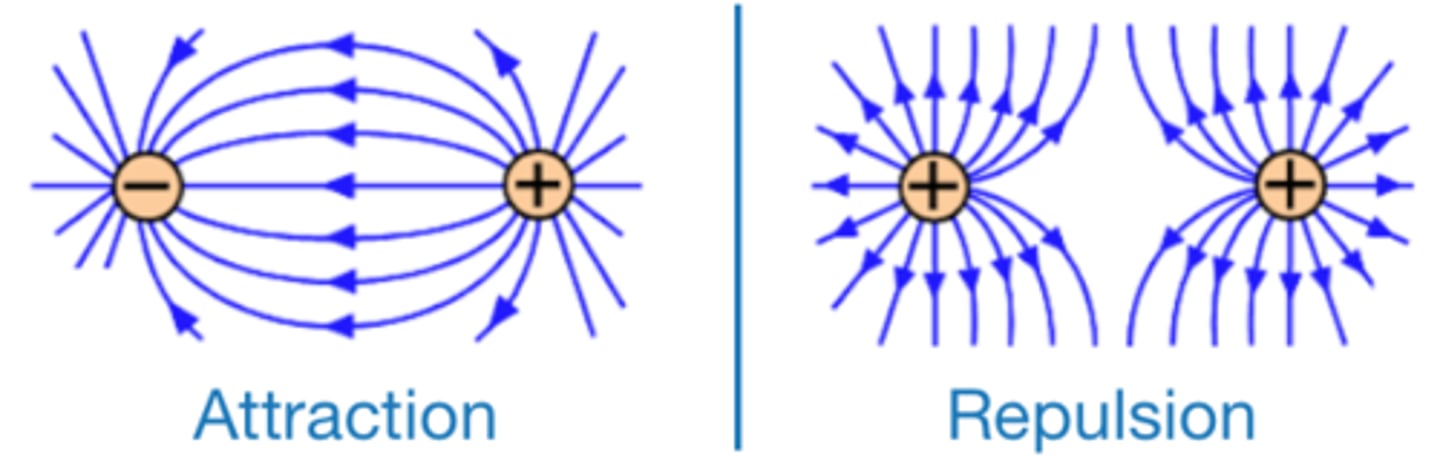
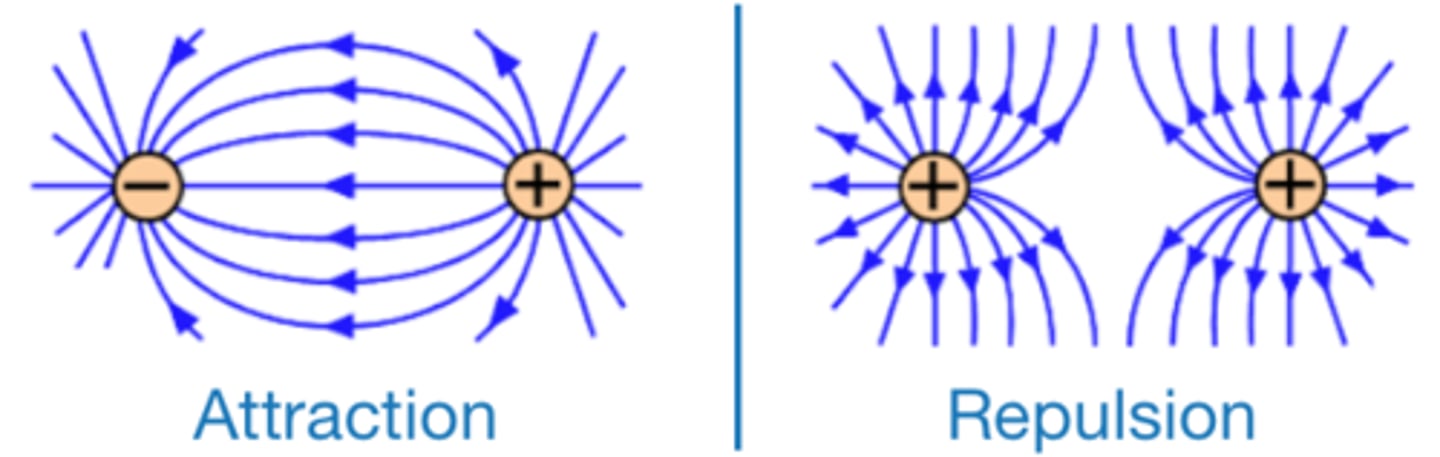
The force between two charged objects gets stronger as the distance between the objects _________
decreases
The field lines around a negatively charged sphere radiate _______ the centre
towards
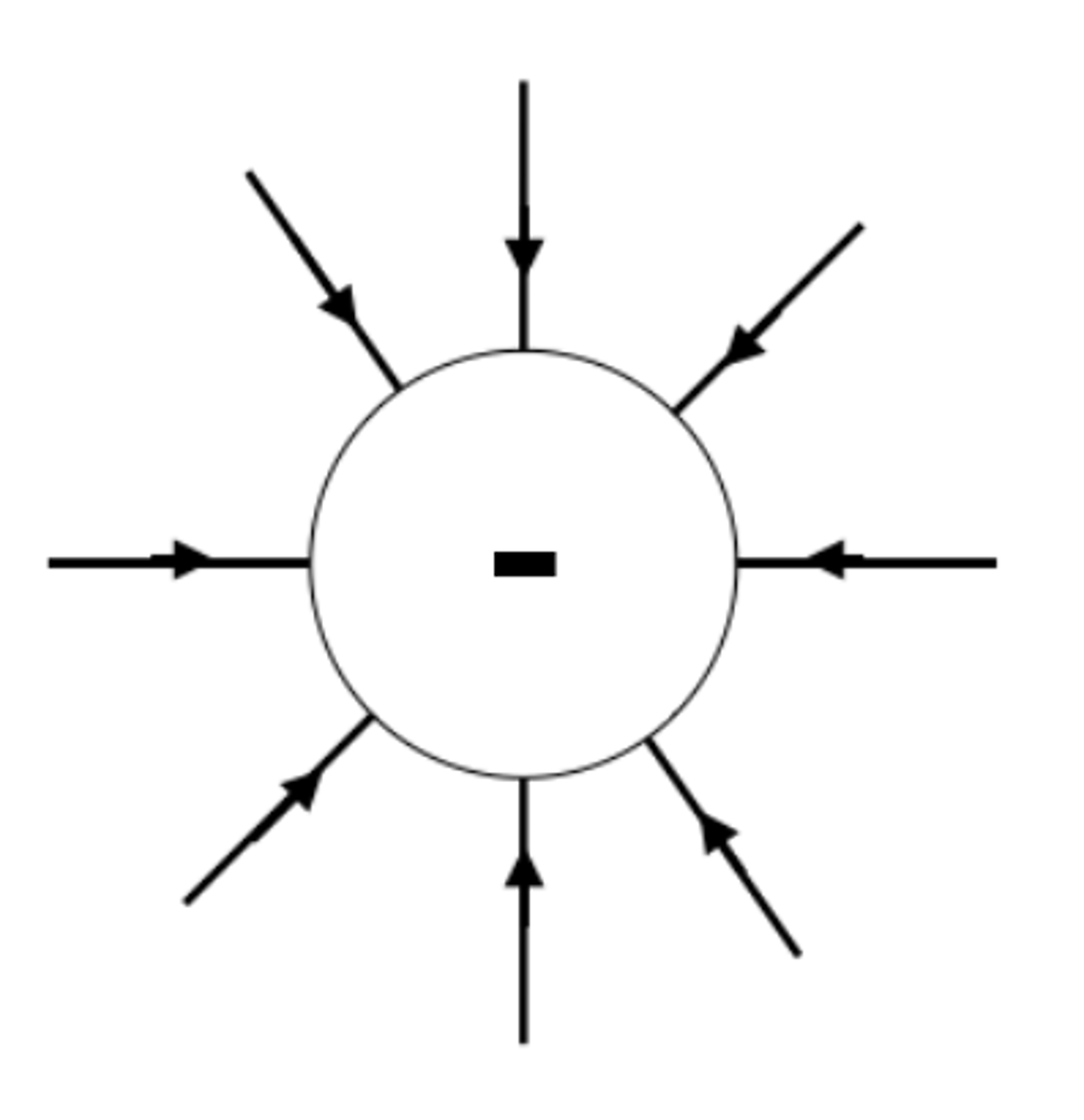
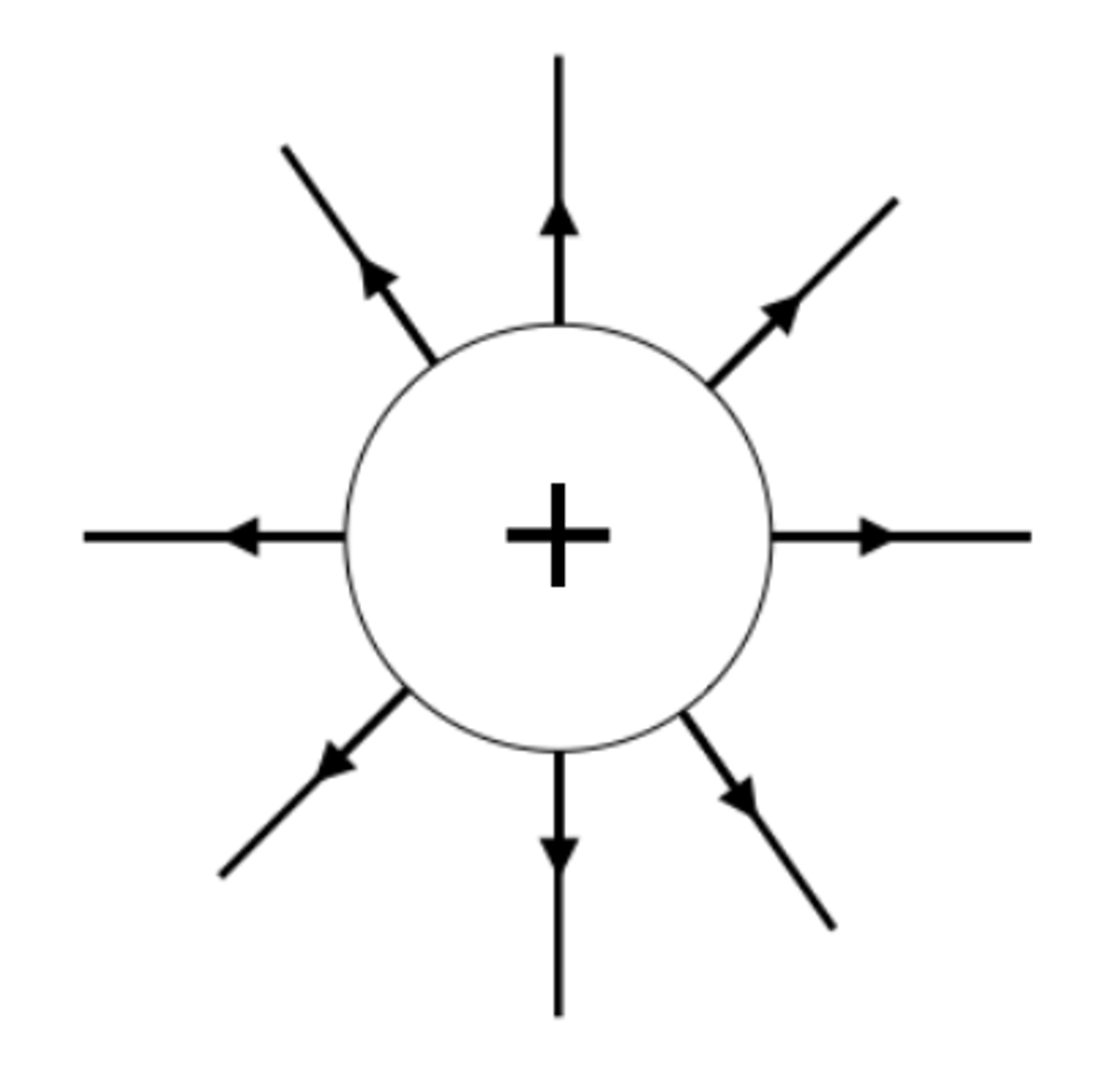
The field lines around a positively charged sphere radiate _______ from the centre
outwards