BIOL 160 Exam 2 Lecture Notes
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
nucleic acids
essential to all known forms of life
DNA, RNA
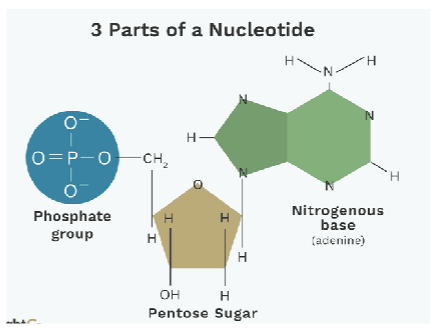
macromolecules (Nucleotide)
composed of monomers of nucleotides, which are made of three components: a 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
DNA polymerization
nucleotides bond together by dehydration reactions
result of polymerization is a single strand of DNA with two different ends
purines
adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
cytosine and thymine
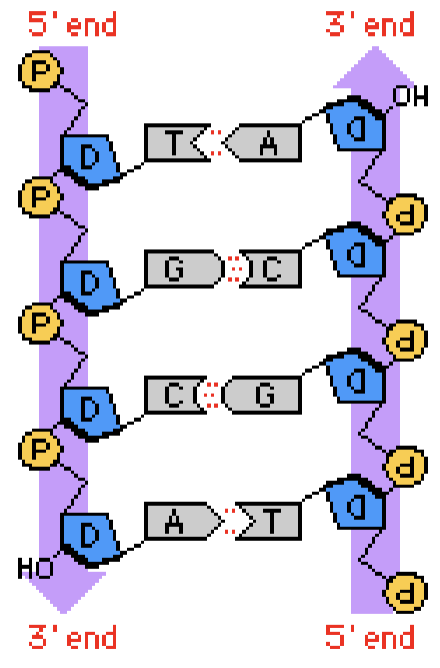
DNA
a long double-stranded molecules that curves into a helix (ladder with nitrogen bases making the rungs)
2 nucleotide strands coiled around each other form a double helix

DNA structure
because of base pairing, one strand determines the sequence of the other strand of DNA
two strands of DNA are complementary, which allows for precise duplication of DNA during cell division
antiparallel - head of one strand is laid against tail of other strand, which is important in replication (two strands replicate differently)
RNA
single-stranded and have U in place of T
coverts genetic information into proteins: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
science of heredity
study of genes and how they carry the information that makes us
how that information is replicated and passed on to the next generation
how they make all the proteins we need for life
genome
the genetic information in a cell (chromosome and plasmid)
chromosomes
DNA containing structures that contain all of our genetic information in the form of genes
genes
segments of DNA that code for a functional protein or RNA
eukaryotic chromosome
linear
2 copies - diploid
1 copy - haploid
linear strands of DNA are wrapped with histone and other proteins to form chromosomes
there are non-doing regions on the chromosomes
enclosed within a nucleus
bacteria chromosome
in cytoplasm (no nucleus)
circular
single copy
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism and its potential properties
phenotype
observable traits and characteristics
actual expressed properties
determined by the genotype
genetics
while the genotype of a cell remains constant, the phenotype may change in response to environmental signals (e.g., changes in temperature or nutrient availability that affect which genes are expressed
genomics
the sequencing and molecular characterization of genomes
first complete bacterial genomes were published in 1995
hundreds of bacterial genomes have been fully or partially sequenced
human genome project
sequencing of the entire human genome (1984-2003) completed
genetic code
the linear sequence of the bases provide the information that tells the cell what proteins to make
set of rules by which our DNA is translated into proteins
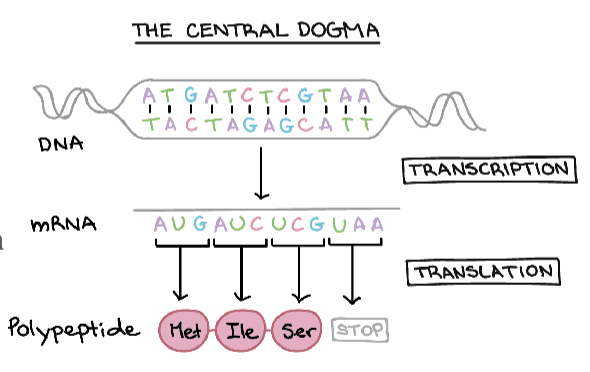
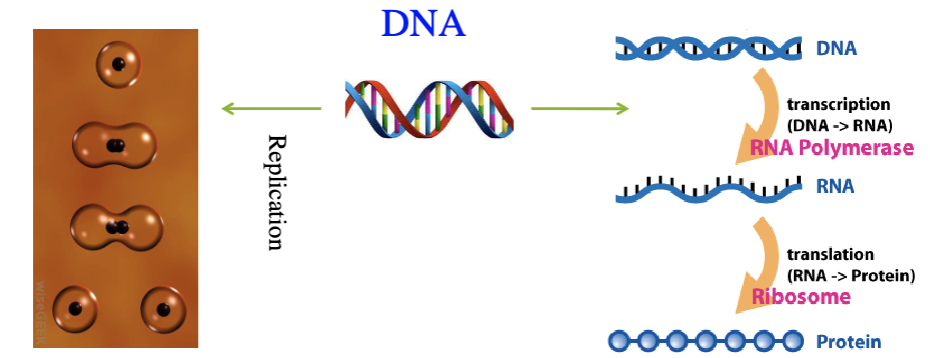
central dogma
describes the flow of information from DNA to RNA to protein:
DNA contains all the information needed to make proteins
DNA is transcribed into mRNA
mRNA is the messenger of information
mRNA is translated into proteins
how we go from information in a gene to a protein
proteins
the functional units of life (structure, carriers, and enzymes)
Why is DNA replicated?
DNA is replicated to pass on the information
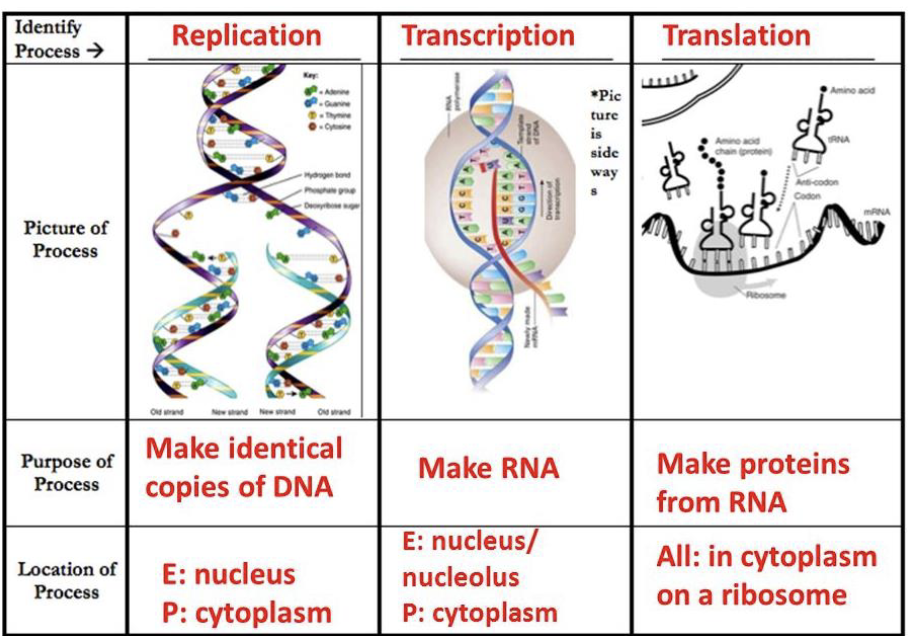
replication
when one cell divides into two, DNA must be replicated faithfully for both daughter cells
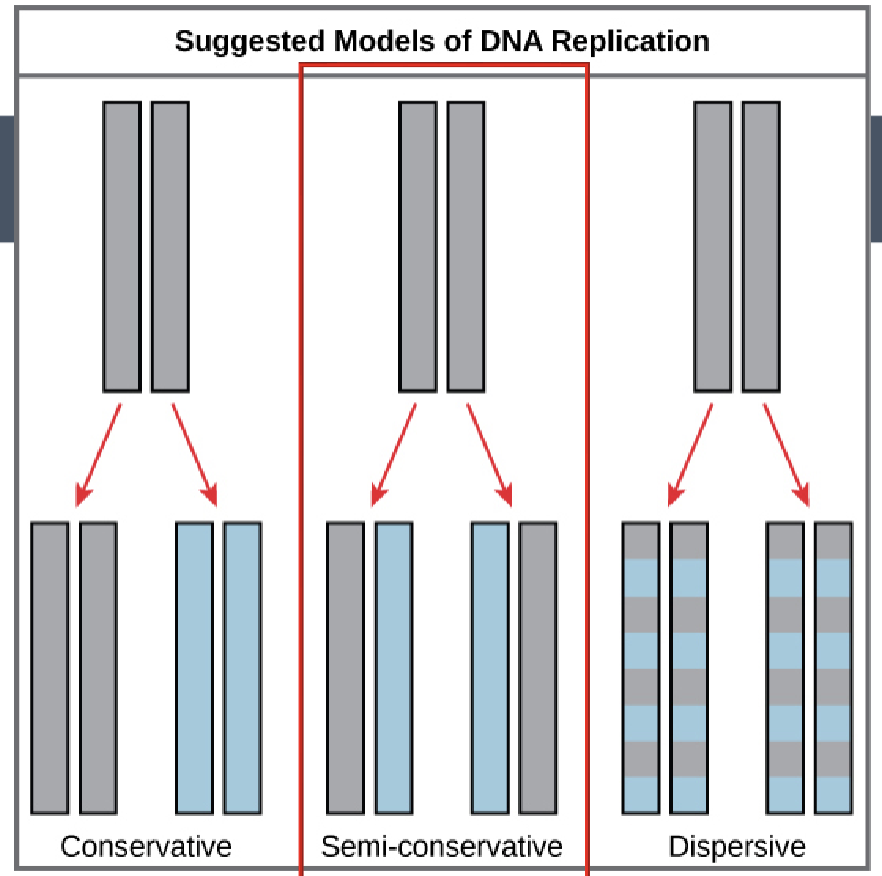
remember DNA is a double strand so looking at the dsDNA in the parental cell, each original (“old”) strand is a template that produces two new complementary strands, and each daughter inherits one new strand and one old strand (semi-conservative replication)
semi-conservative replication
each daughter inherits one new strand and one old strand
replication steps
starts: origin of replication (one or multiple)
steps: unwind, unzip, prime, replicate
enzymes: DNA gyrase, DNA helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase
DNA gyrase
relaxes supercoiling of DNA
DNA helicase
unwinds DNA helix
opens dsDNA at origin of replication & along the replication fork
primase
reads opened strands and is a type or RNA polymerase which synthesizes small RNA primers complementary to the ssDNA to start the DNA replication
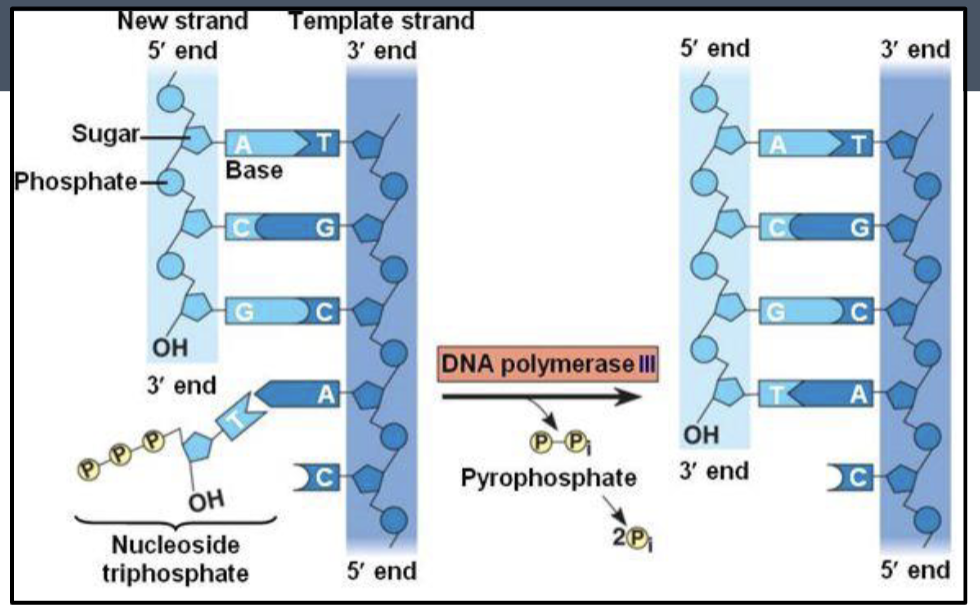
DNA polymerase
an enzyme that synthesizes (reads) new/opened strands
need a double-stranded segment to add nucleotides (hence the RNA primer)
polymerase can only add nucleotides to 3’ end. So, the newly synthesized strand only elongates/grows 5’ to 3’
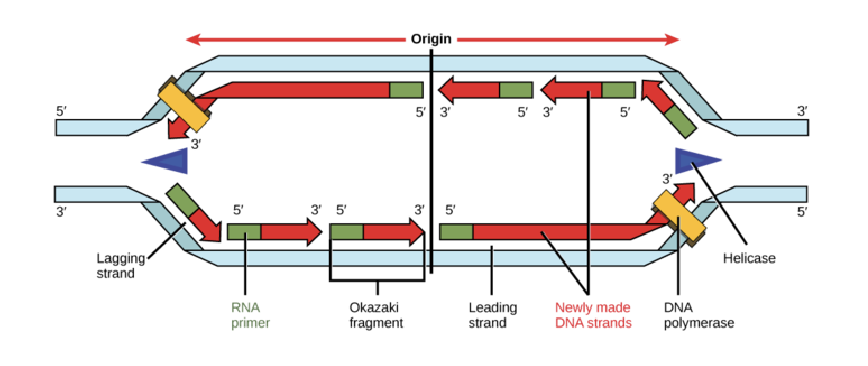
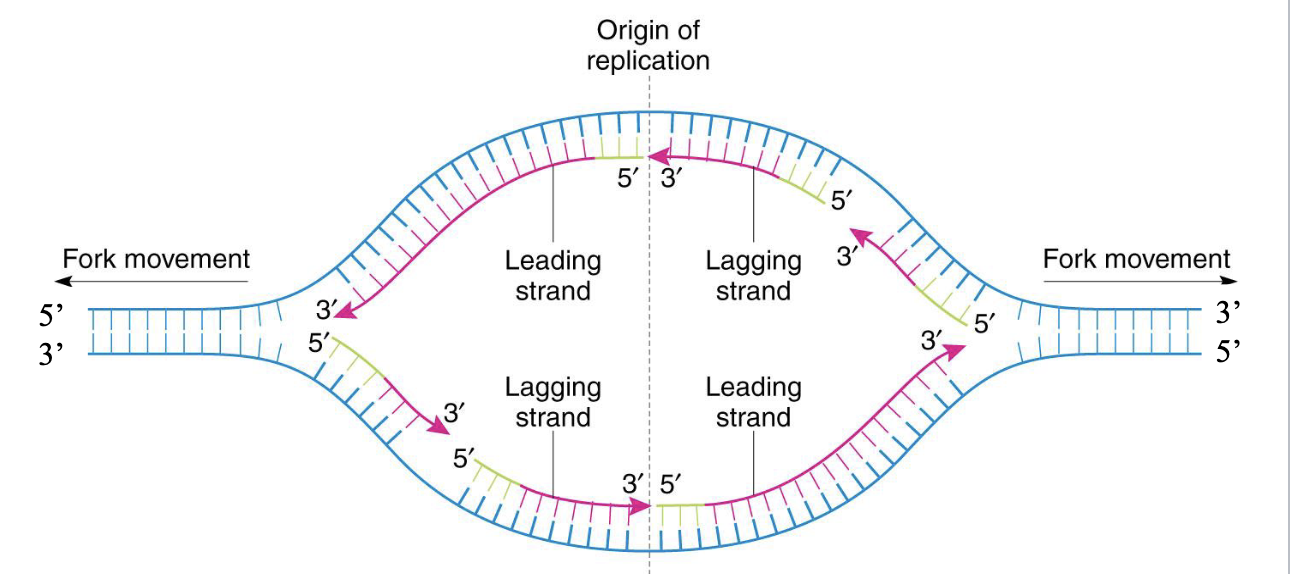
direction of replication is
bidirectional
Overview
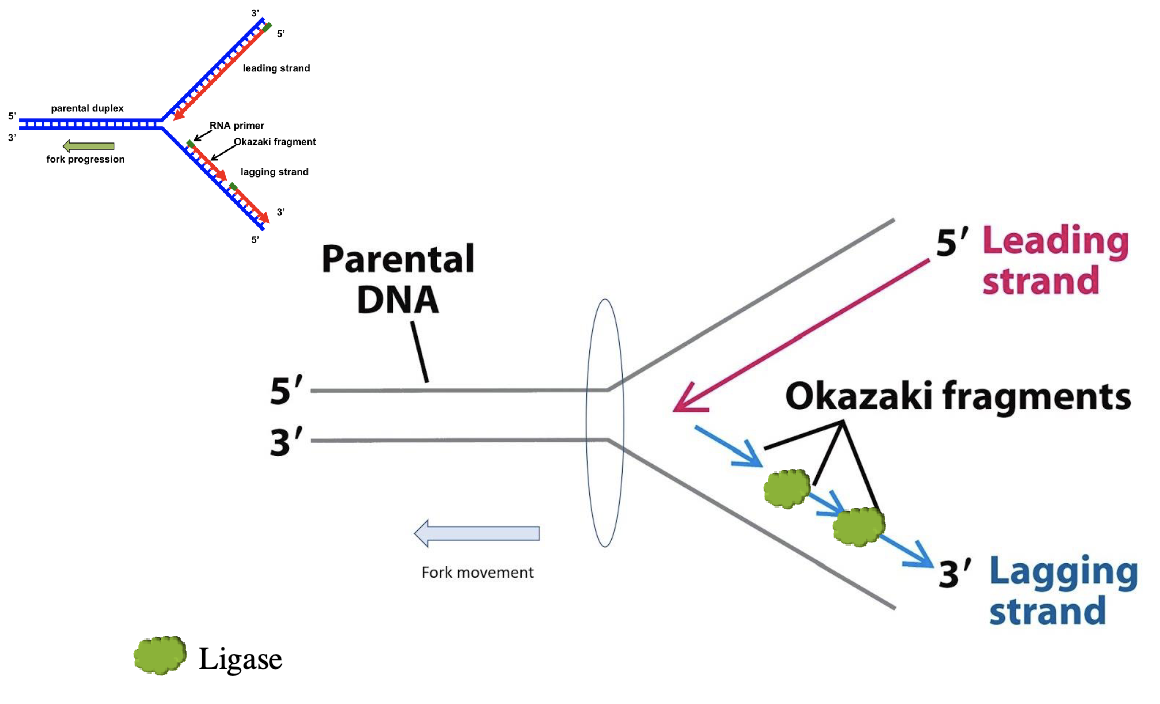
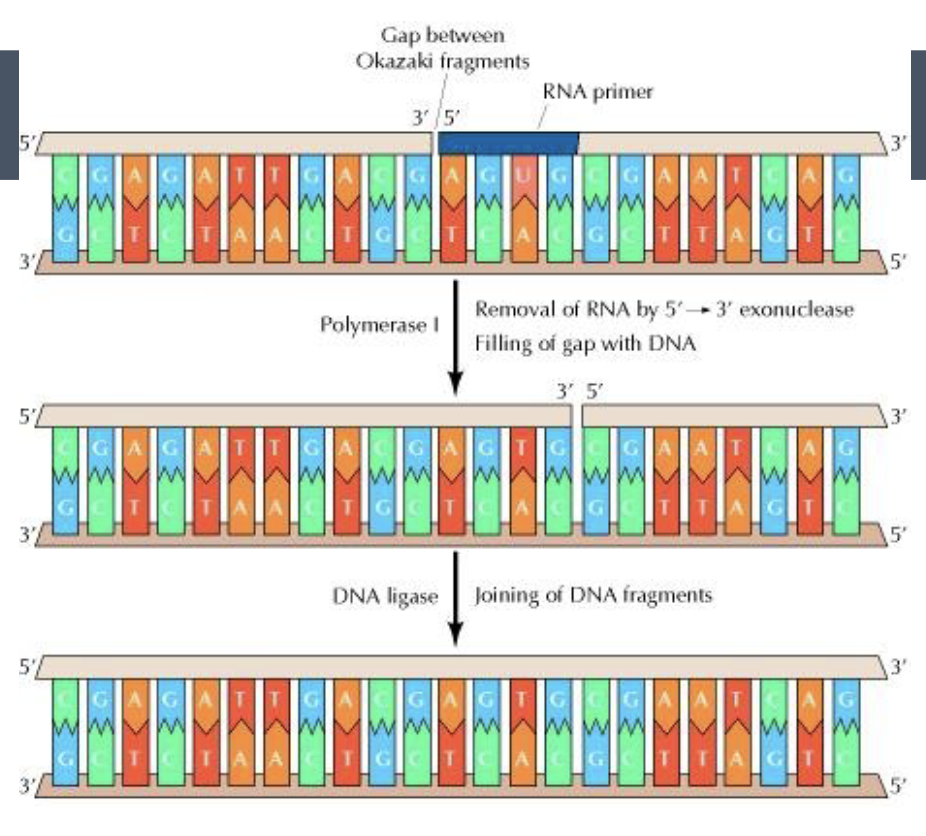
ligase
joins together the okazaki fragments
replication steps
starts at origin of replication
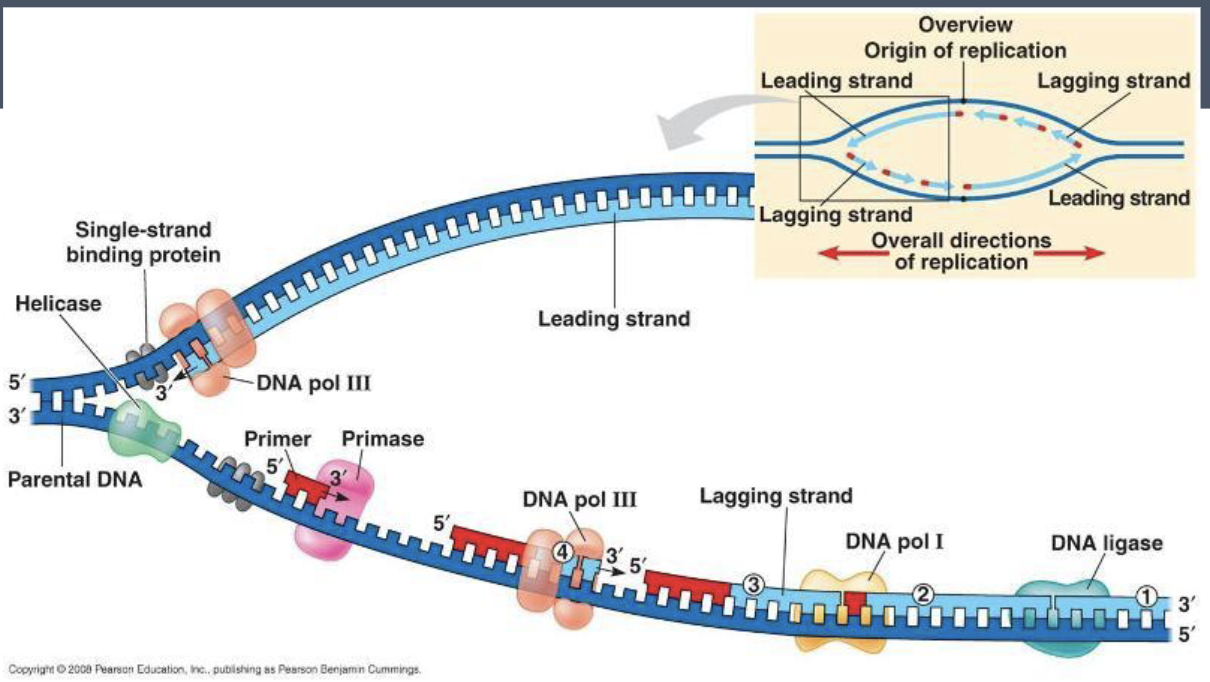
DNA helicase separates the two strands, forming a replication fork
primase lays down RNA primers
DNA polymerase uses the primer to synthesize the two strands
the synthesis of the new DNA on the leading strand is continuous in a 5’ to 3’ direction
the synthesis of new DNA on the lagging strand is done in short segments called okazaki fragments
the RNA primers are removed and replaced with DNA
DNA ligase joins all the DNA fragments
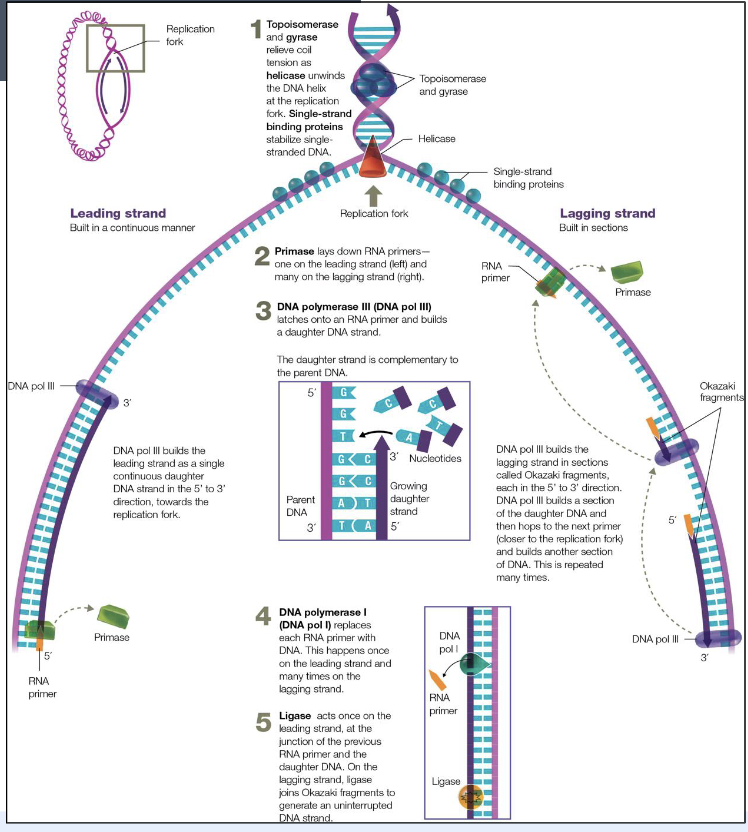
replication enzymes
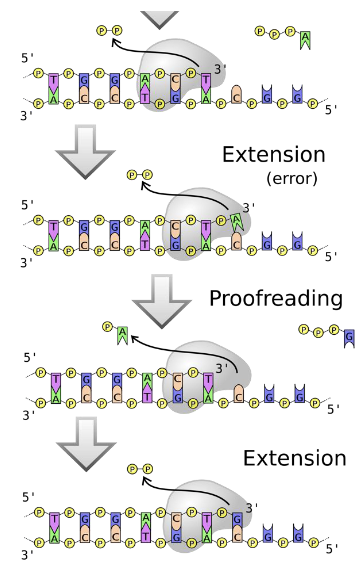
replication is amazingly accurate
error rate is 1 in 10 billion bases
proof reading by DNA polymerase not only incorporates nucleotides but also with every NTP added check to make sure there is the correct base pairing A-T, C-G and fixes any mistakes.
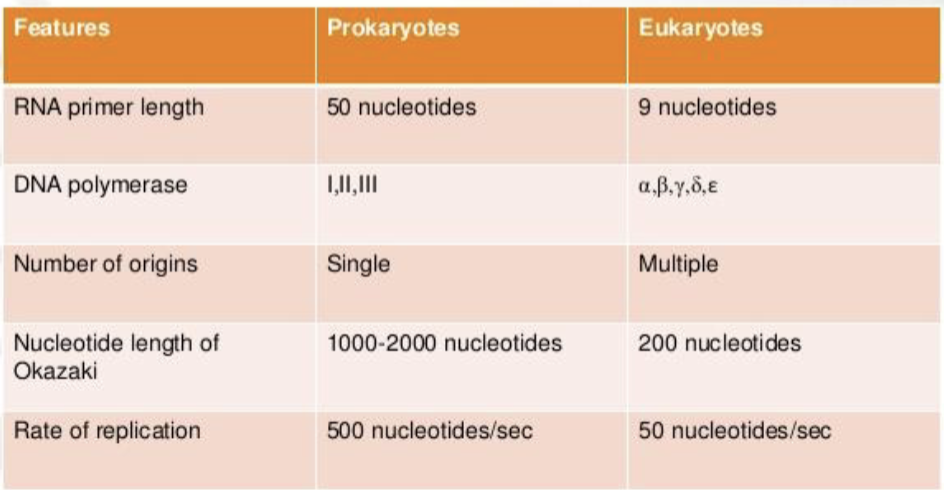
differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication
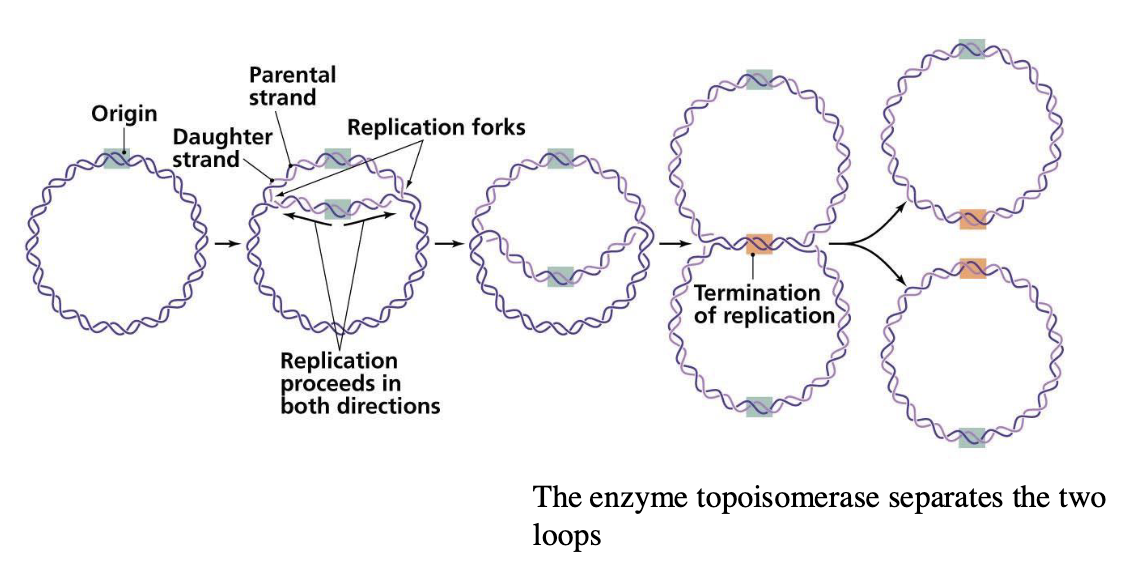
how do circular chromosomes divide?
enzyme topoisomerase separates the two loops
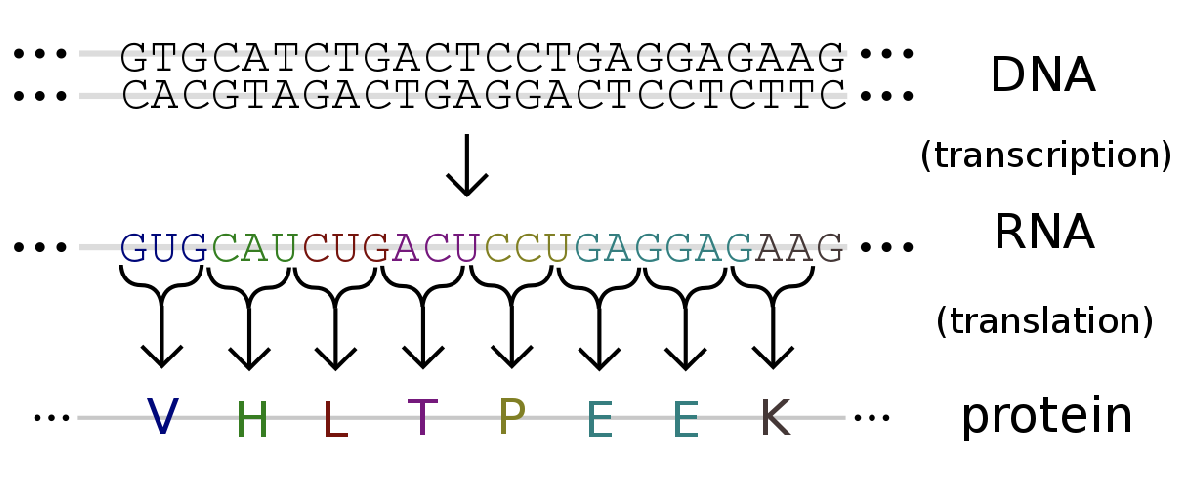
Transcription
from DNA to RNA
RNA structure
bases: cytosine, guanine, adenine, and uracil
sugar: ribose
phosphate groups
types of RNA
necessary for protein synthesis
rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA
rRNA
ribosomal RNA part of the structure of ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA functions as helper to bring correct amino acids to ribosomes to build new proteins
mRNA
messenger RNA carries the code from DNA to ribosomes where proteins are made
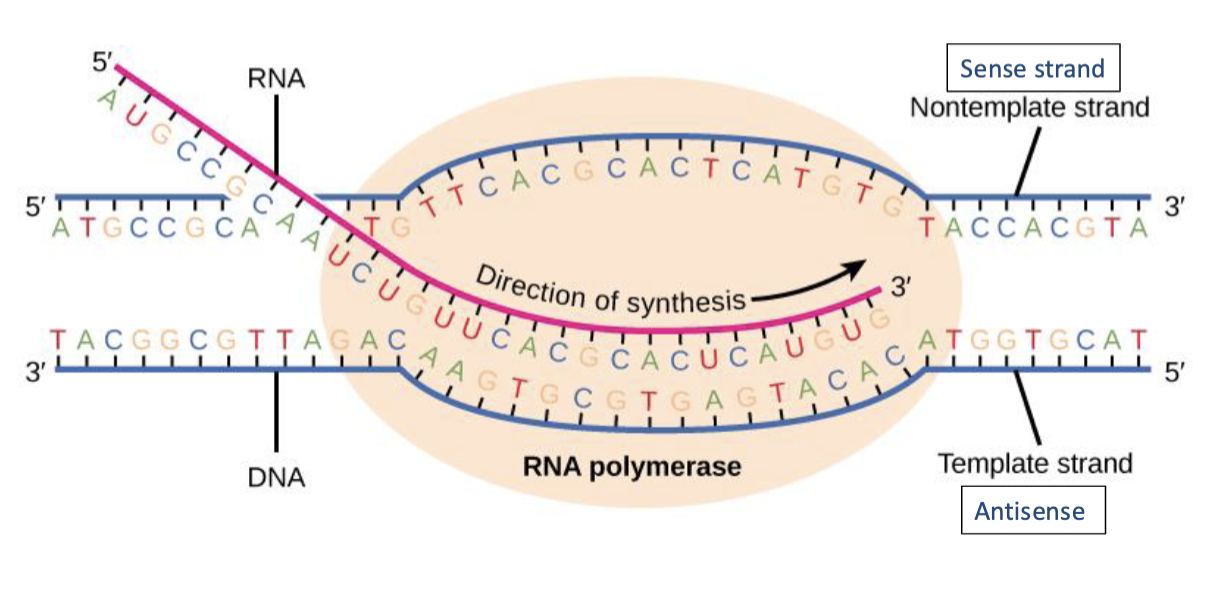
transcription
synthesis of complementary strands of RNA from DNA template
DNA cannot be read directly by the protein-making machinery. Thus, intermediary is needed - mRNA
RNA polymerase uses DNA as a template and copies/transcribes the information into mRNA
transcription only reads individual genes, not the entire genome
RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands (the template/antisense strand) as a template to make a complementary RNA molecule in a 5’ to 3’ direction
steps of transcription
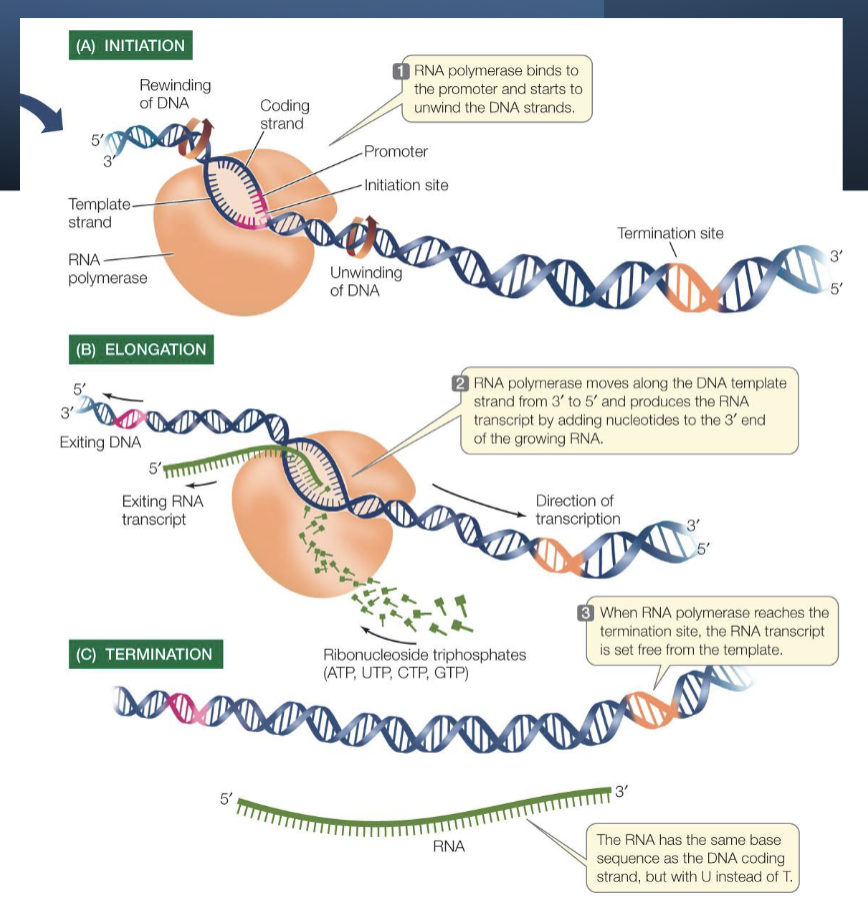
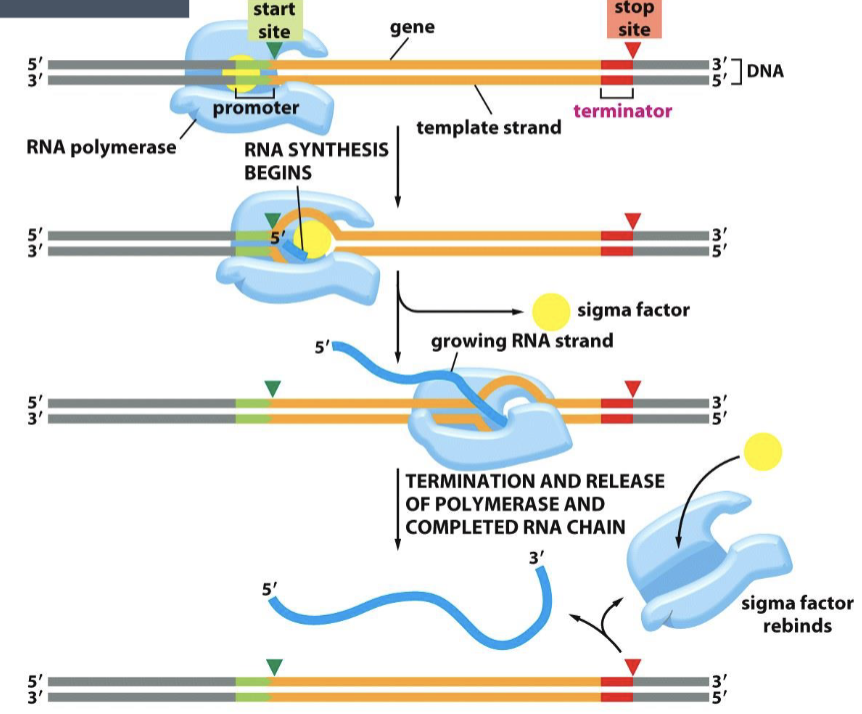
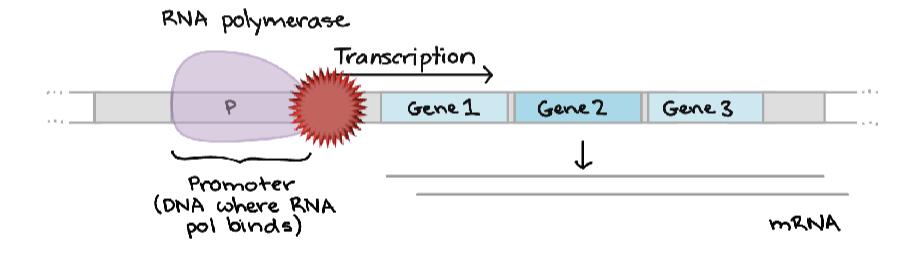
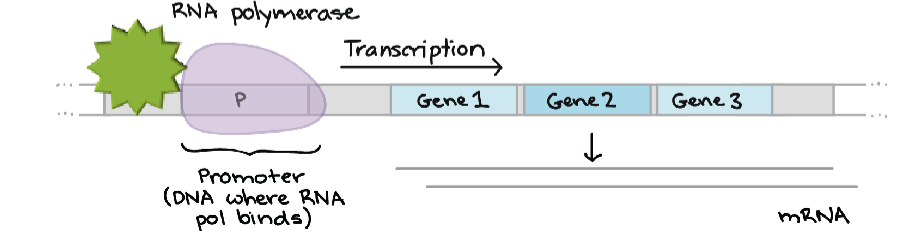
initiation - RNA polymerase binds a specific site on DNA called the promoter
promoter is a sequence of DNA that is recognized by the RNA polymerase - specific to that polymerase
elongation - RNA nucleotides are added
termination - RNA synthesis continues until RNA polymerase reaches a site called a terminator
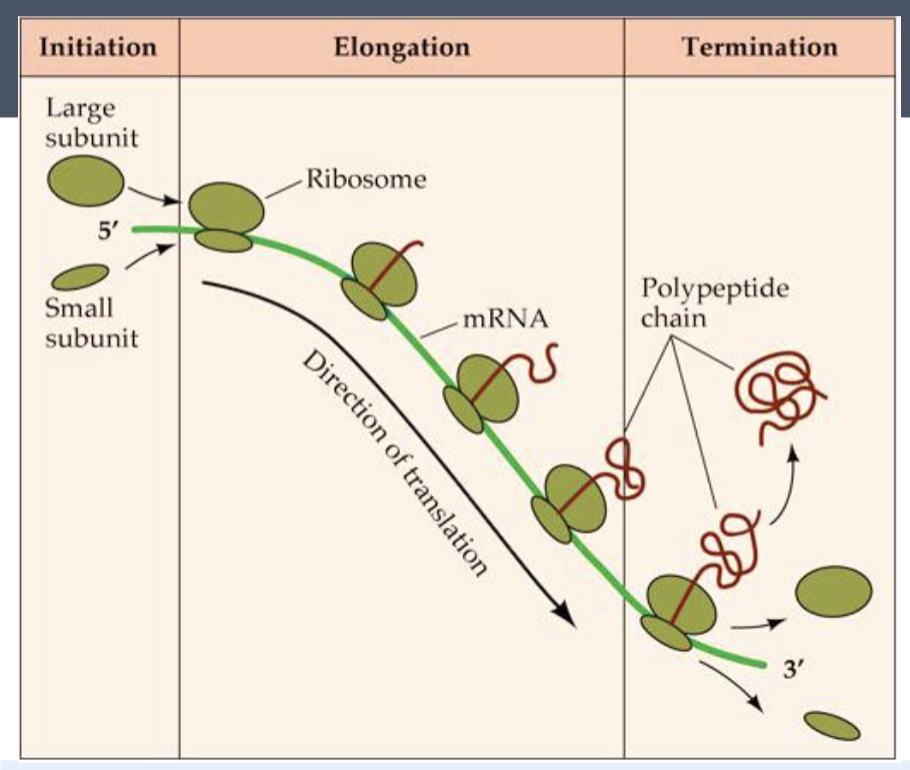
translation
expressing proteins
the process where the ribosomes read the mRNA sequence and make a protein based on the sequence
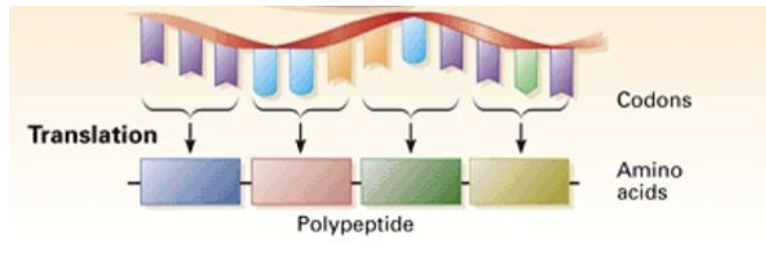
genetic code
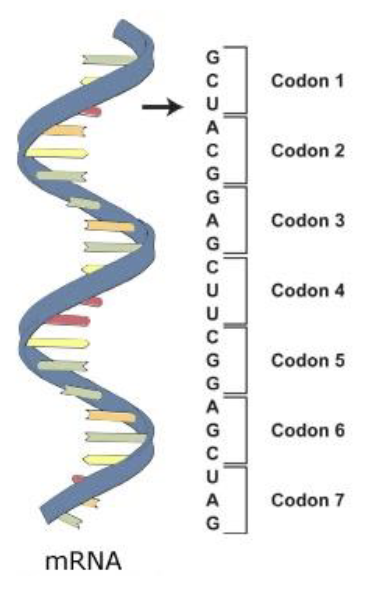
mRNA stores the information about which amino acids need to get incorporated into polypeptide chain to make a protein in the form of codons
codons are groups of 3 nucleotides that code for a particular amino acid
is redundant; a single amino acid can be represented by more than one codon
Redundancy
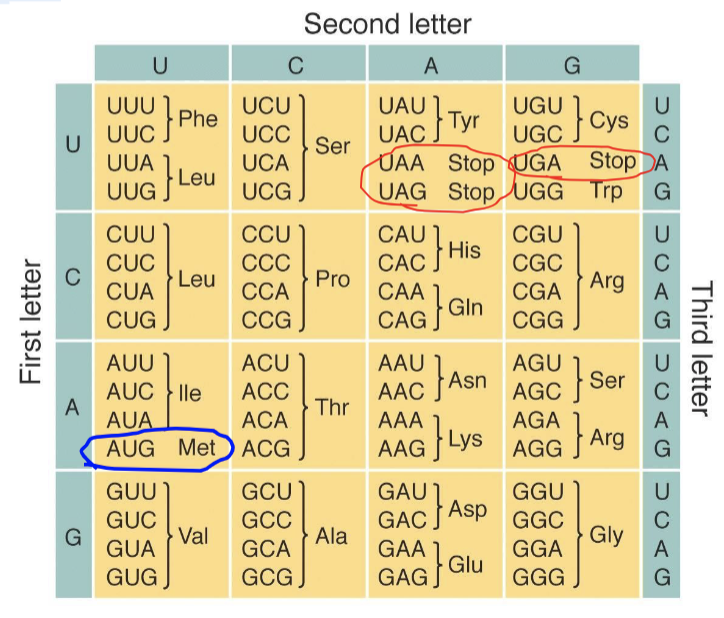
there are 64 possible permutations, or combinations, of three-letter nucleotide sequences that can be made from the four nucleotides
protects cells from genetic changes (mutations)
61 codes for AAs
1 - start codon
3 nonsense codons code for a stop codon which signals the end of a protein molecule
protects cells from genetic mutations.
codons
groups of 3 nucleotides that code for a particular amino acid
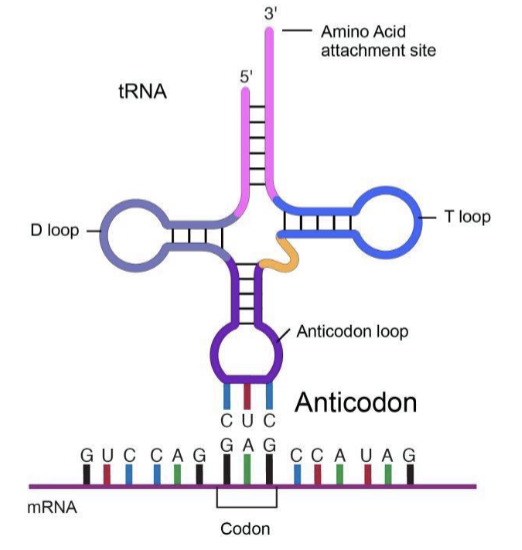
anticodon
tRNA molecule helps decode a messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence into a protein
can recognize and bind to the complementary mRNA codon.
Each tRNA has its corresponding amino acid attached to its end.
shine-dalgarno sequence
ribosomes bind mRNA at the shine-delgarno sequence and read the codons sequentially inserting the appropriate amino acid
ribosome binding site
translation starts at the AUG start codon and stops at the stop codons
Steps of translation
components needed to begin translation come together
on the assembled ribosome, a tRNA carrying the first AA is paired with he start codon on the mRNA. The place where this first tRNA site is called the P site. A tRNA carrying the second amino acid approaches.
the second codon of the mRNA pairs with a tRNA carrying the second amino acid at the A site. The first amino acid joins to the second by a peptide bond. This attaches the polypeptide to the tRNA in the P site.
the ribosome moves along the mRNA until the second tRNA is in the P site. The next codon to be translated is brought into the A site. The first tRNA now occupies the E site.
the second amino acid joins the third by another peptide bond, and the first tRNA is released from the E site.
the ribosome continues to move along the mRNA, and new amino acids are added to the polypeptide.
when the ribosome reaches a stop codon, the polypeptide is released.
finally, the last tRNA is released, and the ribosome comes apart. the released polypeptide forms a new protein.
eukaryotic transcription and translation
transcription occurs in the nucleus - mNA has to go from nucleus to cytoplasm
eukaryotic genes have non coding regions called introns
RNA polymerase transcribes a primary RNA transcript that includes these introns
introns are removed, spliced out, in a process called splicing to make final mRNA
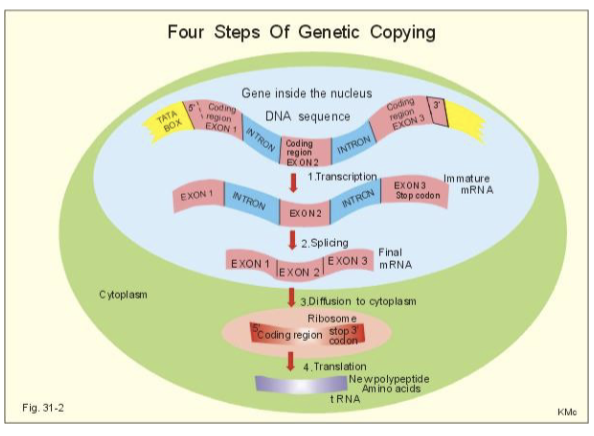
review of replication, transcription, and translation
regulation of genetic expression
production of protein from RNA
constitutive expression
relatively constance (housekeeping genes)
most genes > 60%
ex. glycolysis
regulated expression
varies under different conditions
induction and repression
transcription
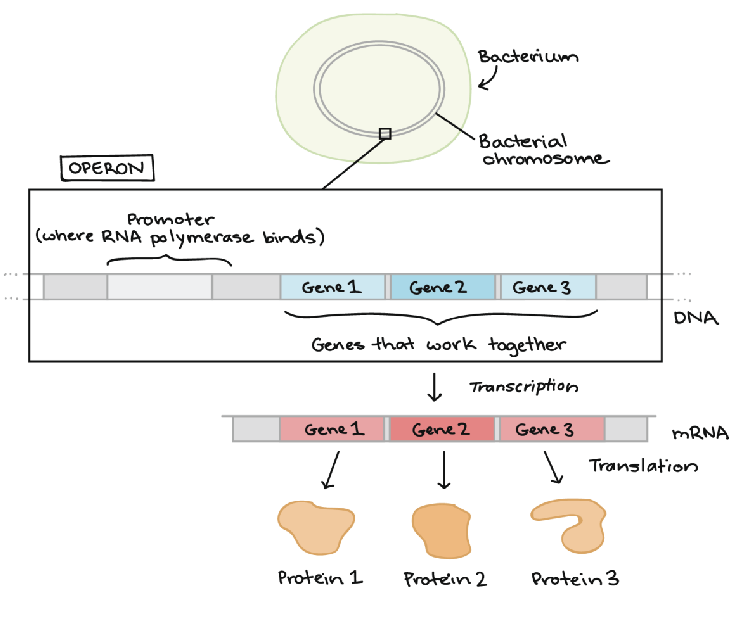
operons
a number of genes that are controlled collectively by one promoter
occurs primarily in prokaryotes
repression
activation
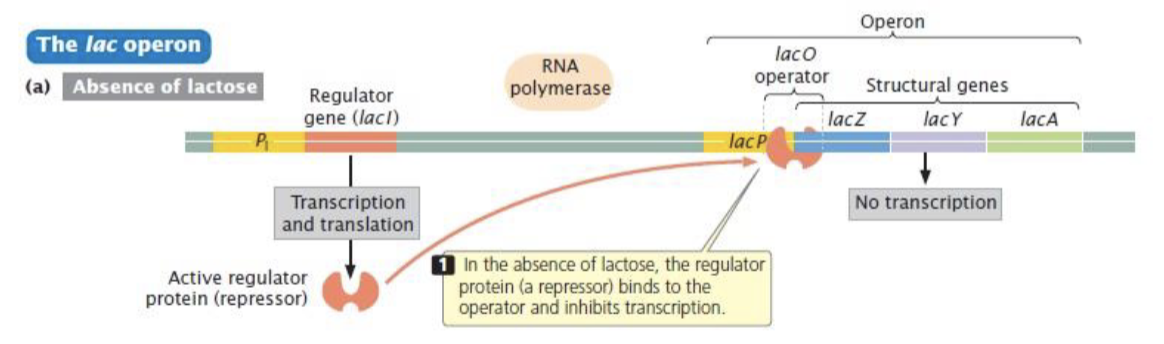
lactose operon (E.coli)
inducible operon - the structural genes are not expressed unless lactose is present
induced in the presence of lactose
genes that are required for the transport and metabolism of lactose
in the absences of glucose, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose (glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria)
3 genes in the operon: lac Z, lac Y, and lac A
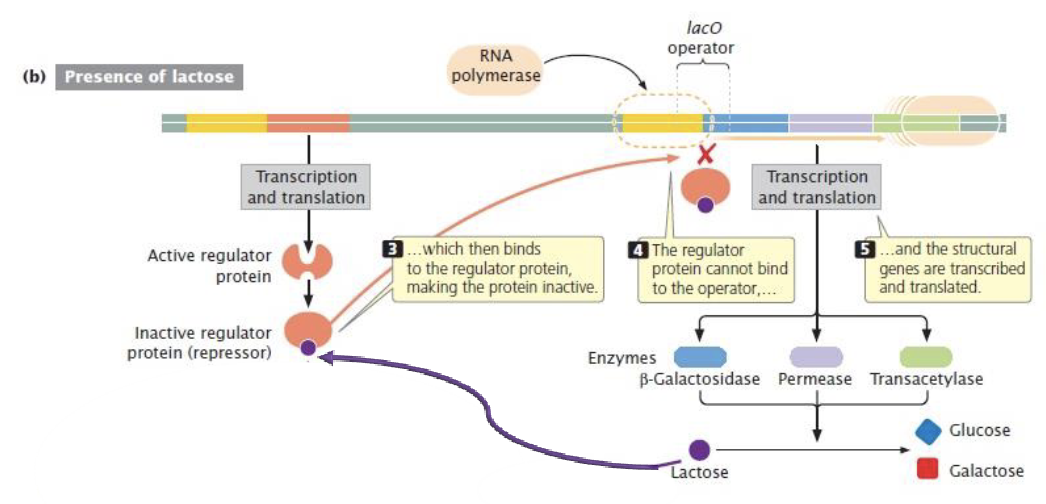
lac operon
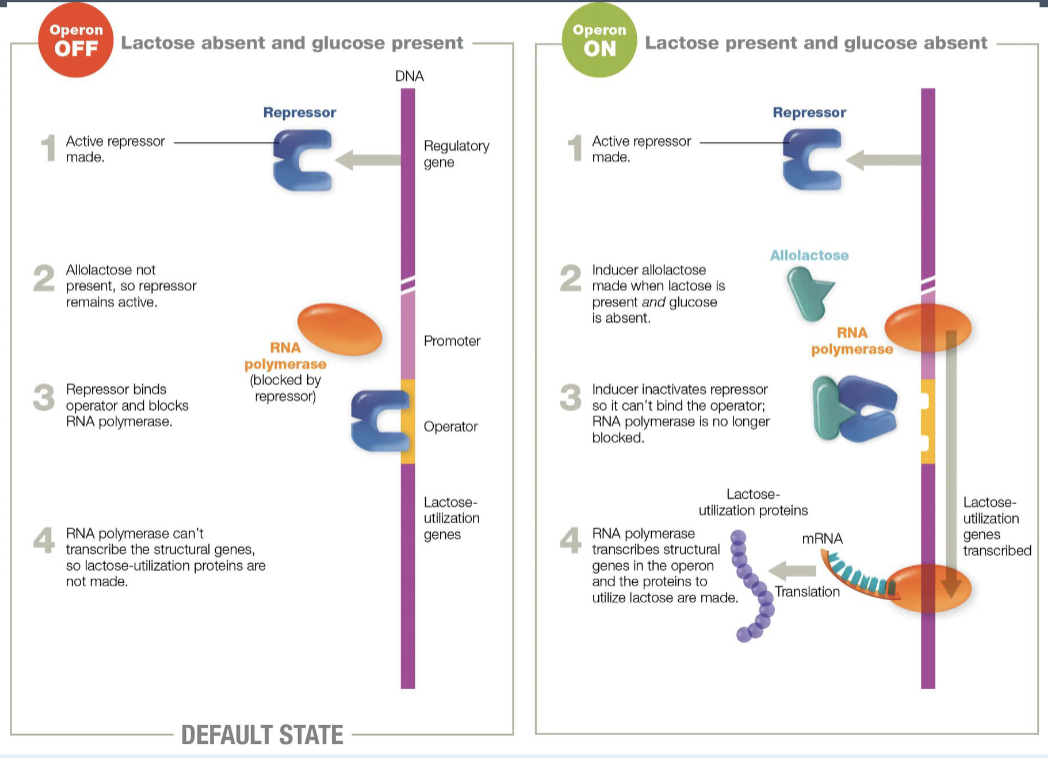
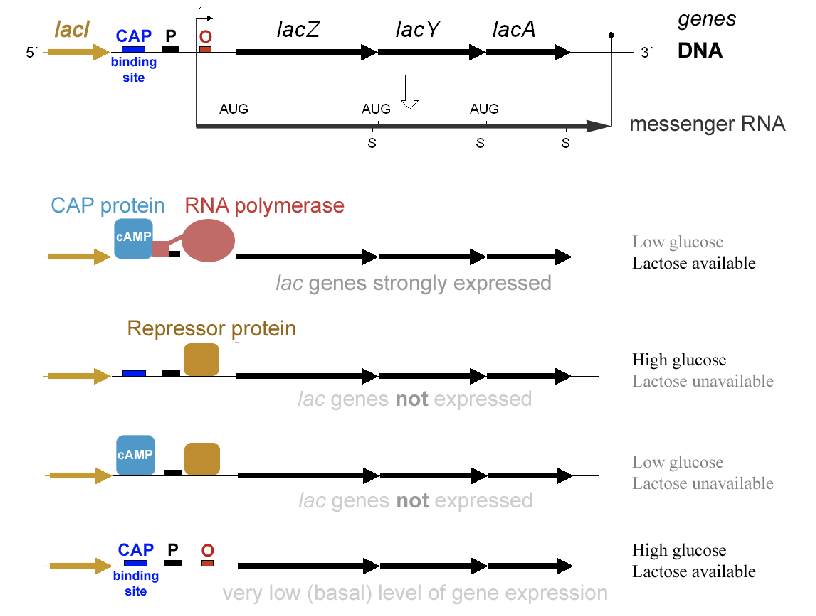
lac operon and its control elements
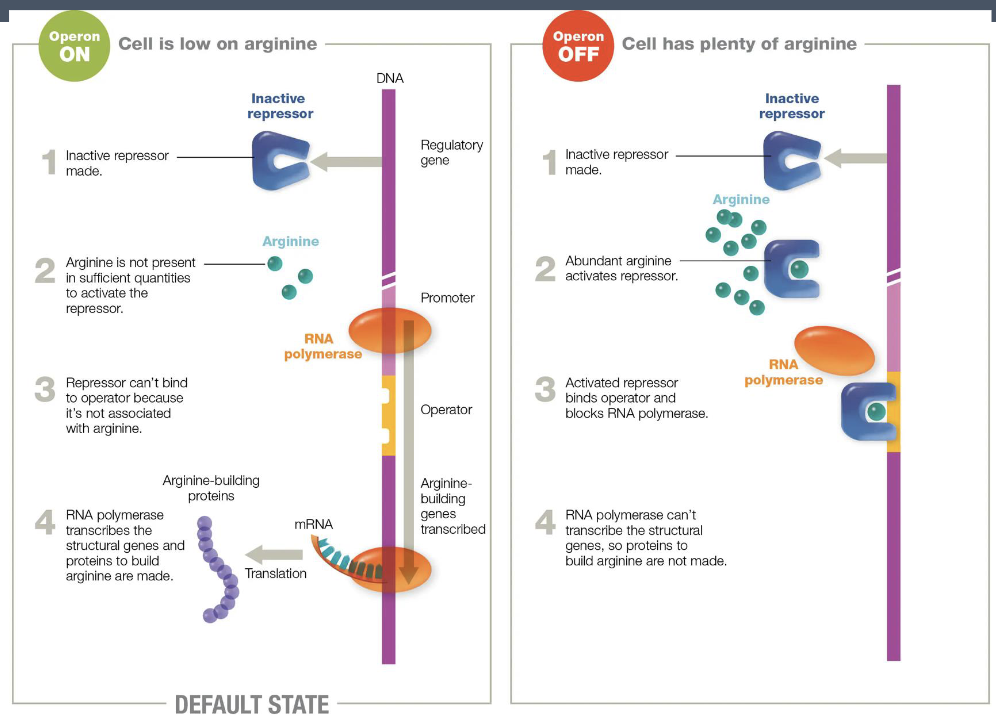
arginine operon
repressible operon - the structural genes are transcribed till they are turned off
regulated so that when arginine is present in the environment the genes for arginine synthesis are not expressed
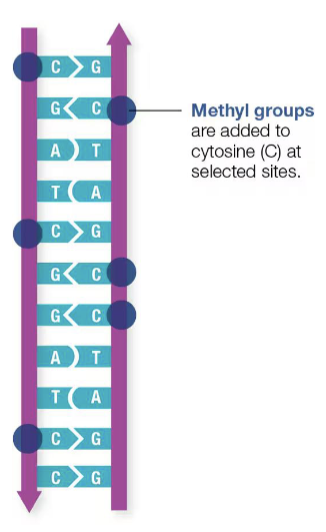
epigenetic control
changes in the regulation of gene activity and expression that are not dependent on gene sequence. epigenetic regulation is a way to control protein synthesis by directly altering the appearance of DNA without changing its sequence
methylation
can silence a gene, affect cell development, respond to stress
post transcriptional control
regulatory mechanism that stops protein synthesis after transcription has occurred
occurs mainly in eukaryotes
small singles stranded RNA called micro RNA
associates with complimentary mRNA forming double stranded RNA which is targeted for destruction
occur during development and can account for cell to cell differentiation
in bacteria, similar short RNAs enable the bacterial cell to cope with environmental stress
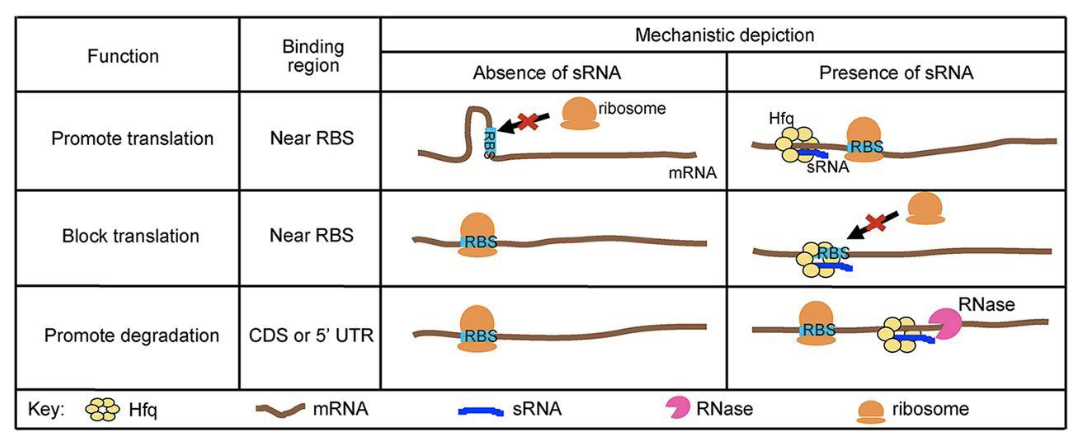
Mutation
a permanent genetic change in the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism
results in genetic variability that can impact viability, function and pathogenicity
essential to natural selection in evolution and occurs at random or in nature
can be spontaneous or induced
spontaneous mutations
results from errors in normal biological processes of DNA replication and/or transcription
important for evolution as they introduce genetic variation even in organisms that replicate asexually
occurs 1 out of every 10 billion base pairs
e.coli can divide about every 20-30 minutes = 1 million cells in 10 hours
E.coli at least 400 mutations will have occurred
induced mutations
caused by environmental factors called mutagens
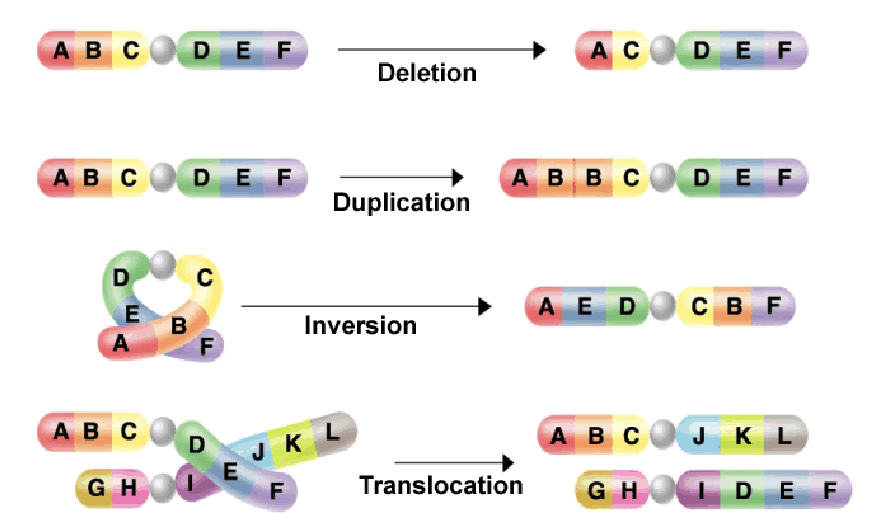
chromosomal mutations
can lead to big effects and severe phenotypic consequences
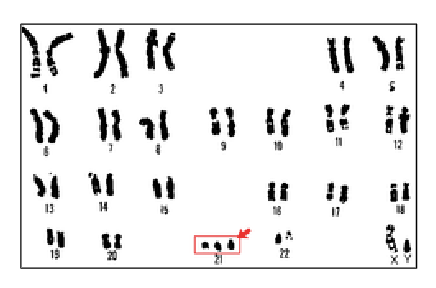
down’s syndrome - trisomy 21
wide range of developmental delays and physical disabilities
approximately half the people with down syndrome will have a congenital heart defect
duplication of 500-800 genes
phenotype is varied mainly due to variable expression of a subset of those genes
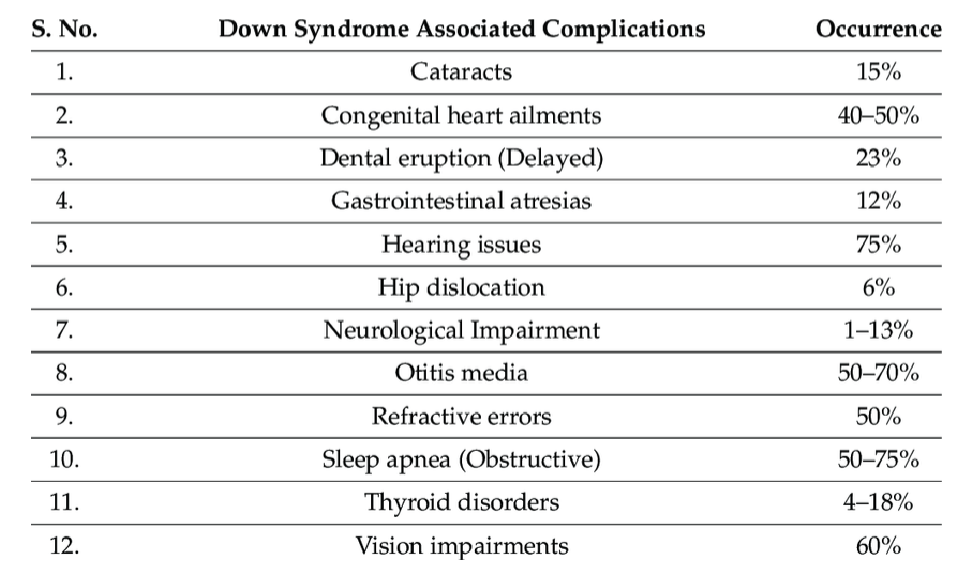
down syndrome associated complications
cri du chat syndrom - deletion in chromosome 5
microcephaly
weak muscle tone
delayed development
wolf-hirschhlorn syndrome - deletion in chromosome 4
delayed development & intellectual disability
seizures
facial characteristics
jacobsen syndrome - deletion in chromosome 11
varied symptoms
learning difficulties and cognitive impairment
distinctive facial features
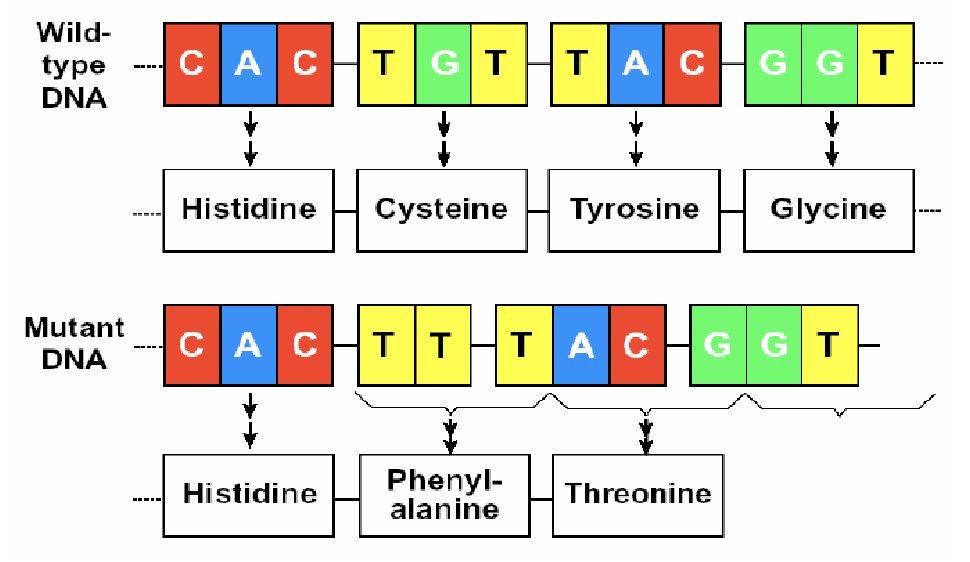
point mutations
change in a single base pair
base substitution
misense
nonsense
frameshifts
deletions
insertions
mutations can happen naturally during replication or as a result of DNA damage and improper repair
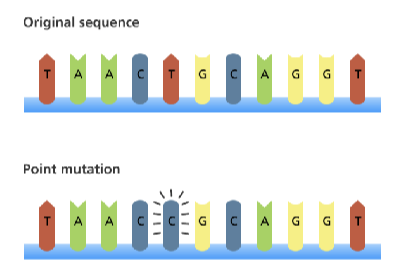
why do point mutations not always lead to phenotype?
genetic code is redundant
every changed nucleotide does not necessarily change the amino acid sequence of the protein silent mutation
when the change in the sequence results in a change int he amino acid sequence missense mutation
even missense mutations do not always translate into phenotypic or functional changes
remember
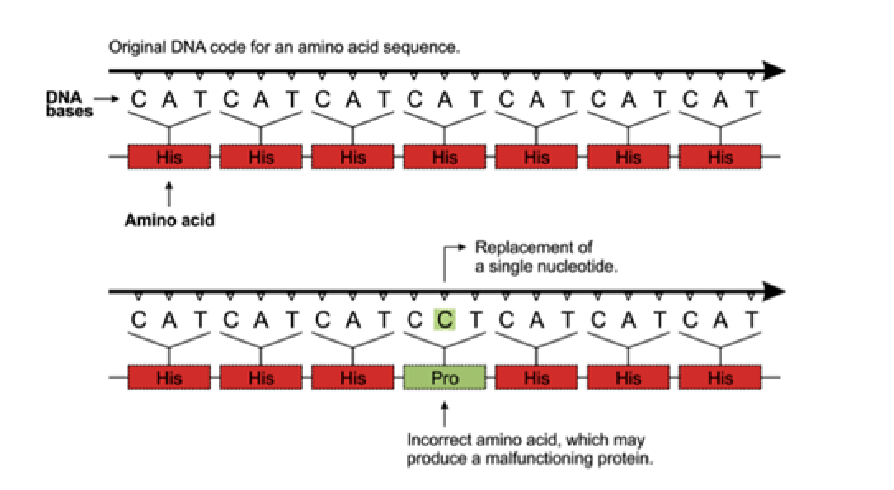
silent mutation
change in a sequence does not change the amino acid sequence of the protein
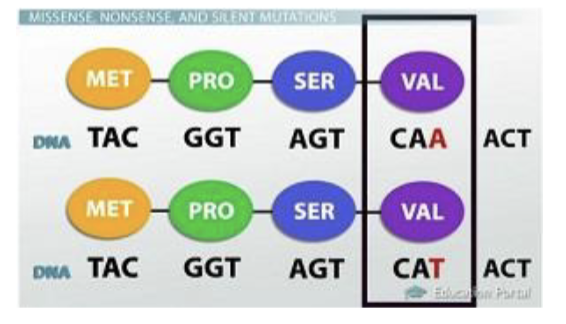
missense mutation
change in the sequence which does change the aa sequence of the protein
missense
phenotype effects may or may not occur, depending on the specific amino acid change
neutral mutation
a missense mutation that alters the amino acid sequence of the protein but does not change its function and occurs when one amino acid is replaced by another that is chemically similar or when the affected amino acid has little influence on protein function
sickle cell anemia
a single change in the globin gene
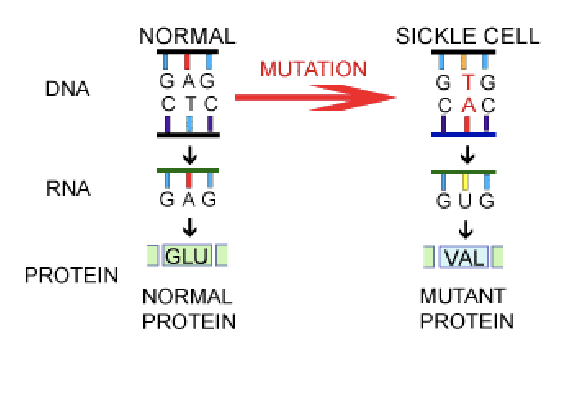
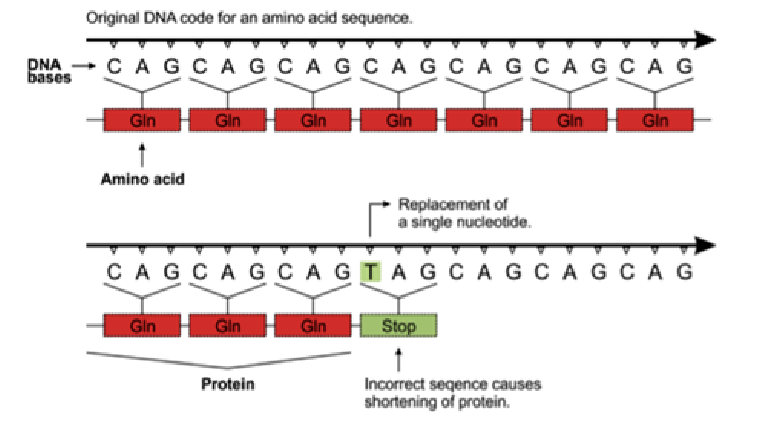
nonsense mutation
change in the sequence introduces a stop codon which will stop translation
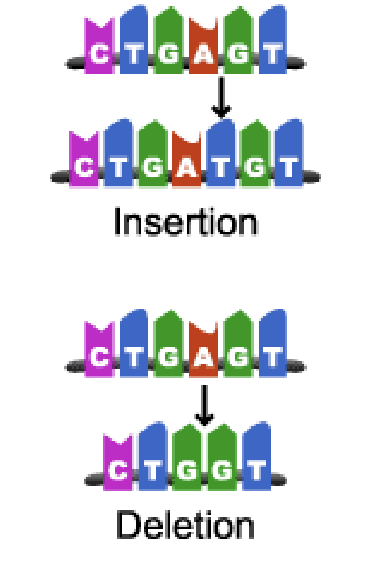
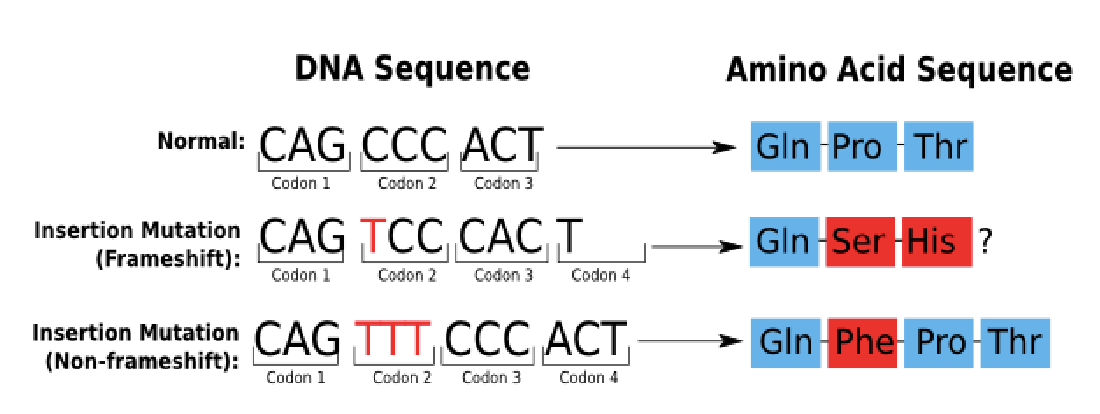
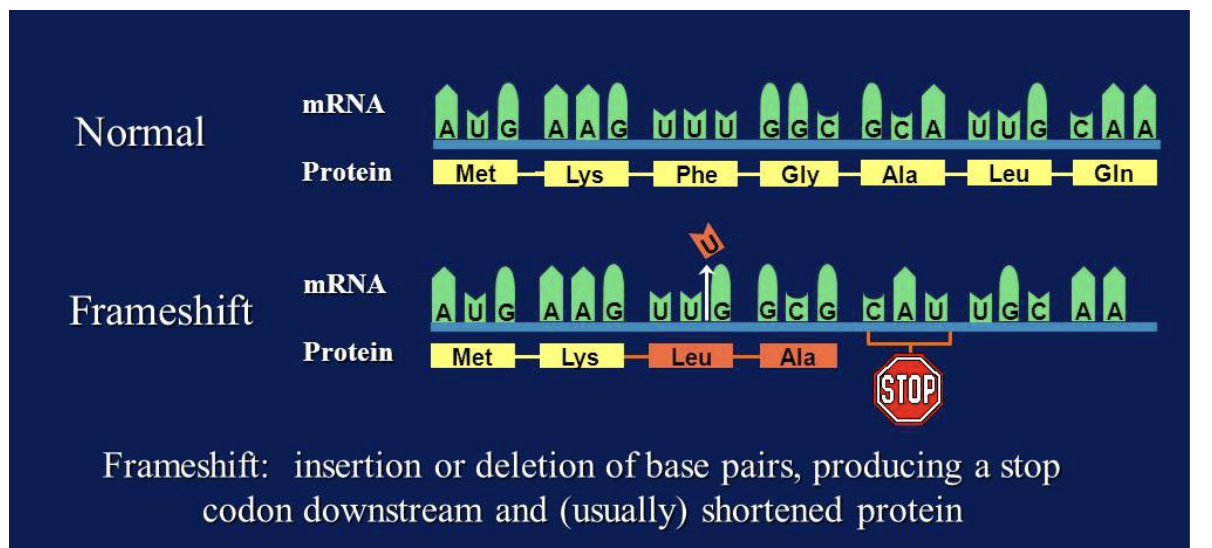
frame-shift mutations
mutations occur when ntds are either inserted into or deleted from the DNA sequence
usually, pretty severe effects because they can affect all the amino acids downstream of the insertion
can result in the introduction of a stop codon and early stop of translation
shift the reading frame of the genetic code so that proteins may not be properly synthesized and/or function

insertion
deletion
frame shift leading to stop
mutagens
can cause specific base changes
nucleoside analogs - similar to the nitrogenous bases but with slightly different base pairing
if present during growth, it can cause mistakes to occur during replication
can cause small deletions and insertions so causing frame shift mutations
radiation
x-ray and Gamma-rays
releases electrons that bombard surrounding cells and can cause damage to DNA
molecules
uv radiation
causes DNA damage by causing the formation of a covalent bond between 2 adjacent thymine’s in DNA
rate of mutagenesis

identifying mutations
mutations can be detected by selecting for an altered phenotype
positive selection
mutations results in a gains of function so can be directly selected for
antibiotic resistance
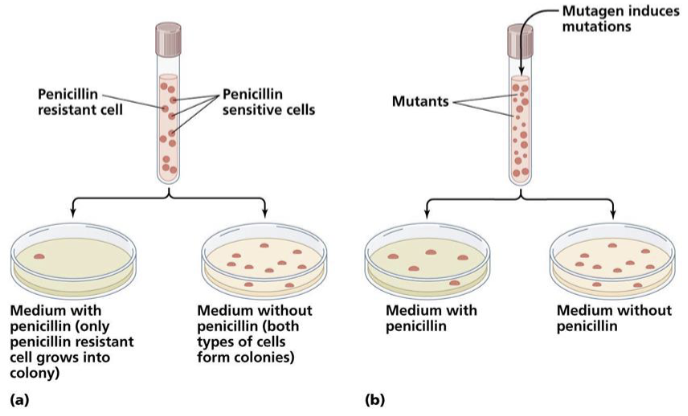
indirect selection
where the mutation results in a loss of function, screen colonies for the desired phenotype
loss of the ability to synthesize their own histidine
replica plating
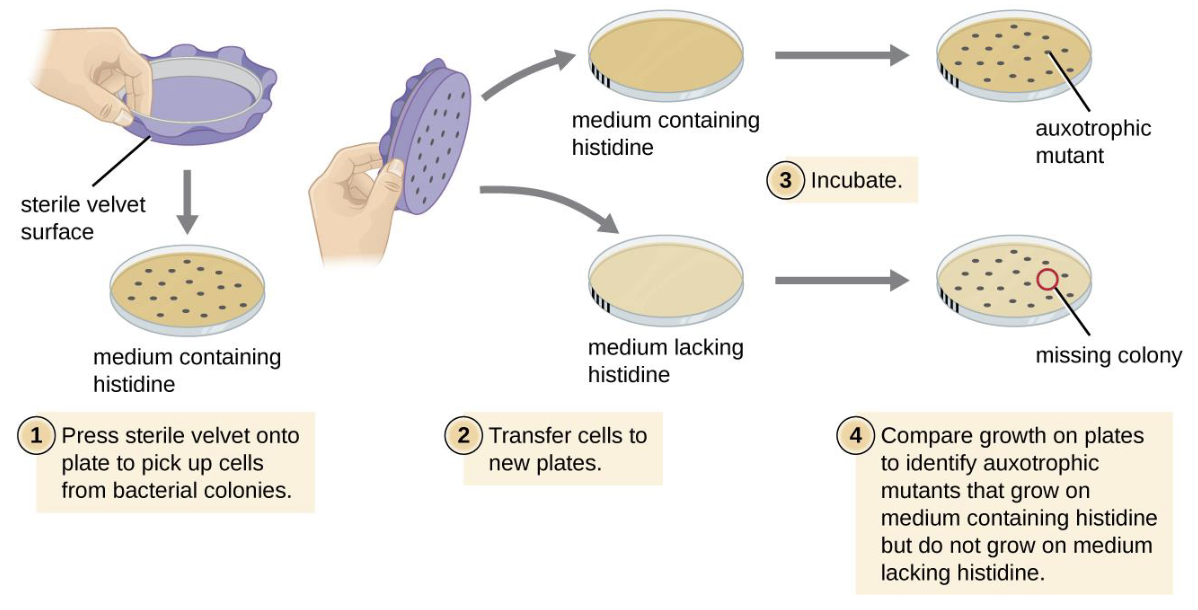
carcinogens
many known mutagens cause cancer
we can use baceria to determine if something is mutageneic hence likely carcinogenic