Sexual Differentiation🧬
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
T/F: The Y chromosome is relatively short, variable in length and is considered “gene poor”
True: The Y chromosome is relatively short, variable in length and is considered “gene poor”
If SRY is not present or its function is impaired, what occurs?
If SRY is not present or impaired,an ovary will form
SRY can act as a ________, but also as a _______.
SRY can act as a transcriptional activator, but also as a repressor
What are Sertoli cells?
Sertoli cells are somatic cells that associate with germ cells and nurture their development into sperm
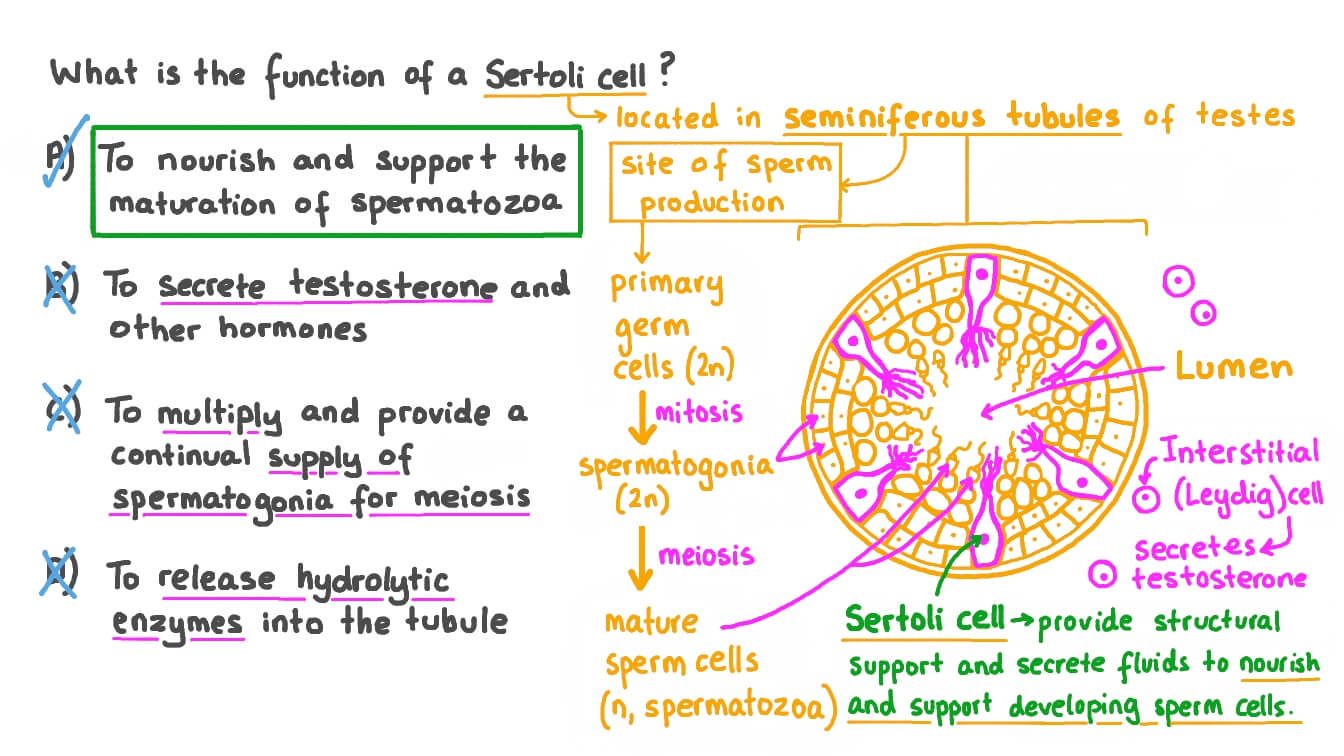
What is the differentiation from pre-sertoli cells into Sertoli cells?
The differentiation from pre-sertoli cells into Sertoli cells is marked by the polarization of the cells when they form epithelial aggregates that assemble into testis cords
Differentiation of the gonads is determined by what?
Differentiation of the gonads is determined by the chromosomal sex
The presence of testes induces masculinization of the genital ducts and external genitalia. What induces the the development of the testes?
SRY induces development of testes
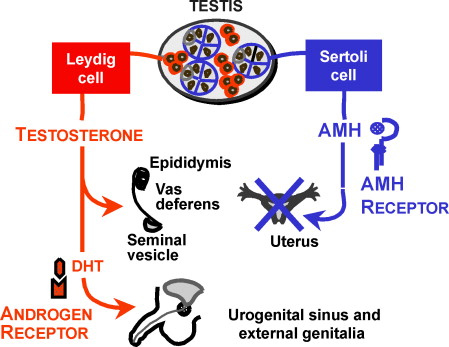
Testosterone, a steroid, stimulates the development of?
Testosterone stimulates development of the Wolffian ducts leading to the formation of the epididymis and ductus deferens, the duct system that drains the testes
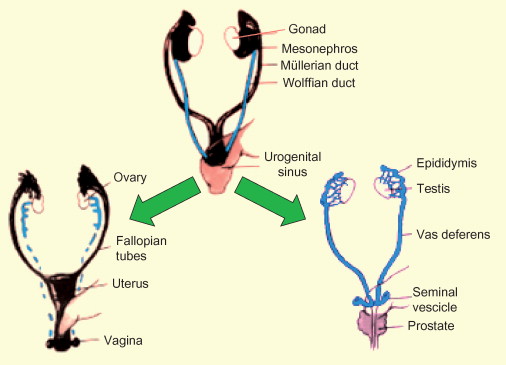
What is antimullerian hormone (AMH)?
AMH is a peptide that induces the regression of the Müllerian ducts
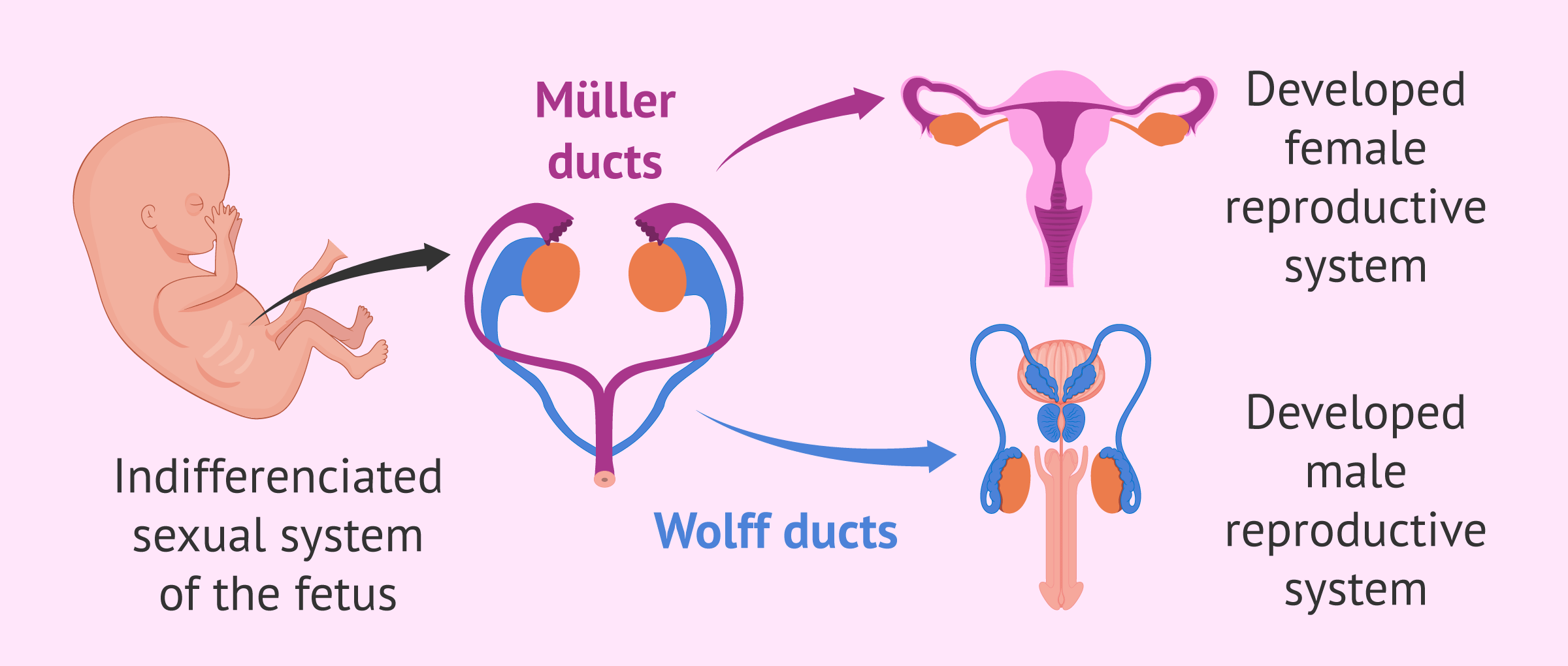
When does the development of the female genitalia occur?
Development of the female genitalia occurs in the absence of testosterone and with antimullerian hormone (AMH)
What occurs when their is no AMH?
Without AMH, the Müllerian ducts develop into the oviducts, uterus, and cranial vagina, and the external genitalia form the vulva, clitoris, and caudal vagina (vestibule)
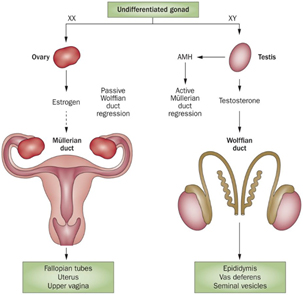
How do wolffian ducts regress?
The wolffian ducts regress when their is a lack of testosterone
What do the mullerian ducts develop into?
The mullerian ducts develop into the fallopian tubes, uterus, and cranial vagina
In a female, what does the external genitalia develp into?
External genitalia develops into the vulva, clitoris, and vestible
With the help of testosterone in males, what do the wolffian ducts turn into?
The wolffian ducts turn into the epididymis, and vas deferens, and seminal vesicles
In a male, testosterone will convert the external genitalia of a male into what?
External genitalia will transform into the penis and scrotom
When does the development of male external genitalia begin?
Development of male external genitalia occurs soon after the masculinization of the wolffian ducts and completed long before the formation of females external genitalia
Cells of the wolffian ducts do not express the 5a-reductase enzyme, so the masculinization of the wolffian ducts is controlled by what?
Testosterone controls the masculinization of the wolffian ducts
What is alpha-fetoprotein?
AFP is a large glycoprotein that cannot cross blood brain barrier produced by liver and yolk sac of developing fetus
Why is AFP important for prenatal development of the female brain?
Alpha-fetprotein (X-linked) binds to estradiol, preventing it from entering the brain, which protects it from being masculinized by estradiol
How does prenatal hormone exposure fundamentally organize the brain?
Sexual/reproductive behaviors: develpment of the hypothalamus
Problem solving
Aggression
Rough and tumble play
What cells secrete testosterone?
Leydig cells secrete testosterone
What hormone do sertoli cells secreate?
Sertoli cells secreate anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH)
SRY gene triggers differentiation into testies, what proteins does SRY also express?
SRY expresses Sox-9 and SF1
What does the y-chromosome protein Sox9 do?
SOX-9 protein binds to a promoter on the AMH gene and stops female genitals from expressing. This promotes the growth of sertoli cells. It also inhibits pathways that would lead to ovary development
What are the ovarian-promoting genes that suppress SOX-9 activity?
Wnt4 and FOXL2
What enzyme converts testosterone into estradiol?
Aromatase
What is testosterone converted into in the brain?
Estradiol and dihydrotestosterone
What hormone converts testosterone into 5alpha-DHT
5alpha-reductase
What causes the induction of AMH?
SOX-9 will cause sertoli cells to release AMH
What hormone does the female ovary produce?
Estradiol