2.1.2 Government Policies
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Fiscal policy
Manipulation of government spending and taxes in order to achieve macroeconomic objectives
Direct tax
A tax directly gained on income or profits, such as income tax or corporate tax, that is paid directly to the government.
Indirect tax
A tax that is imposed on goods and services, which can be passed on to the consumer, such as sales tax or value-added tax.
Why do governments impose taxes
Generate revenue for public services and infrastructure
Manage economic stability
Redistribute wealth to address social inequalities.
Three main areas of government spending
Capital expenditure
Current expenditure
Transfer payments
Capital expenditure
spending that impacts the long run growth of the economy (e.g. infrastructure, building hospitals etc)
Current expenditure
Day to day spending e.g. on wages for public sector staff, medicines for hospitals
Transfer payments
Government expenditures that provide financial assistance to individuals without requiring goods or services in return, such as unemployment benefits and social security.
Fiscal deficit
When government spending is higher than their tax revenue, causing a fiscal deficit or budget deficit - the accumulation of such being called ‘national debt’
Fiscal surplus
When tax revenues are greater than government spending
Fiscal debt impact
National debt gets bigger, meaning the government has to spend more of its revenue on paying off the debt.
Future generations may be burdened with the debt of ‘today’.
Fiscal surplus impact
Likely to be positive
If a government collects more revenue than it spends in a year, the surplus could be used in a number of ways. For example, it could be used to spend on the future provision of public services or used to lower taxes in the economy.
Most governments would use it to pay off some of the national debt. This would reduce future interest payments and strengthen the nation’s finances
Types of fiscal policies (2)
Expansionary fiscal policy
Contractionary fiscal policy
Expansionary fiscal policy
Increase in government spending or a decrease in tax in order to stimulate (speed up) the economy
Contractionary fiscal policy
Decrease in government spending or an increase in tax in order to slow down the economy
Expansionary fiscal policy effect
Increase in inflation
Increase in economic growth
The unemployment rate is likely to fall
Increase in demand for imports
Damage the environment
Contractionary fiscal policy effect
Decrease in inflation
Decrease in economic growth
The unemployment rate is likely to rise
Decrease in demand for imports
Monetary policy
The manipulation of interest rates and the money supply in order to achieve macroeconomic objectives.
Who controls the monetary policy
The central bank
Interest rates
Interest rates are the cost of borrowing and reward for saving
Types of monetary policies (2)
Expansionary monetary policy
Contractionary monetary policy
Expansionary monetary policy
A reduction in interest rates to boost aggregate (total) demand, therefore increasing inflation
Contractionary monetary policy
An increase in interest rates to reduce aggregate (total demand), therefore decreasing inflation.
Supply side policy
Long run policies that generally aim to increase productivity and total output.
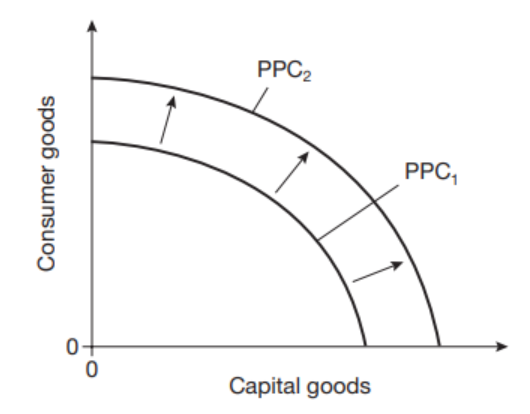
How do supply side policies affect the PPF
It will shift it out