Ear Anatomy
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
External ear, middle ear, and inner ear
What are the three parts of the mammalian ear?
Auricle, or pinna
The large outer portion of the ear is known as the?
Tympanic membrane
The separation between the external ear and the middle ear is what structure?
Hearing and balance
The inner ear houses structures that are important for what processes?
The cochlea and the vestibular apparatus
What organs are housed within the inner ear canal?
Vertical and horizontal; external acoustic meatus
The ear canal has ___ and ___ directional portions and can also be called the?
Ceruminous glands
What structures of the ear produce earwax?
Annular cartilage
Which type of cartilage connects the auricular cartilage to the ear canal?
Muscle attachments rostral and caudal to the ears
The auricle of the ear is moveable in animals due to?
Auricular, annular, and scutiform cartilages
What cartilages are associated with the external ear?
The portion of the auricular cartilage which begins to roll up and create a scroll
The mark at which the external acoustic meatus begins is the....
Auricular muscle groups attach at this structure
What is significant about the scutiform cartilage?
Air
The middle ear cavity is ___ filled
Malleus, incus, and stapes
From largest to smallest, the ossicles are...
Pressure equalizer
The auditory tube acts as a?
External layer of stratified squamous epithelium, middle layer of connective tissue and collagen, and inner layer of simple cuboidal epithelium
What are the basic layers of the eardrum?
Malleus
Which of the ossicles is embedded in the tympanic membrane?
A flexible fold which helps the ear deal with pressure differences
What is the function of the flaccid part of the tympanic membrane?
Amplification; the cochlea is covered in a viscous fluid which is resistant to disturbance, therefore strong vibrations of sound are needed to stimulate hearing
The ossicles in the middle ear are responsible for sound ___. Why is this necessary?
Tensor tympani; prevents movement of the malleus in order to prevent the eardrum from over-amplification and loud sounds
Which muscle is attached to the malleus? What is the function of this muscle?
Stapedial m.
The ___ dampens the movement of the stapes
Epitympanic recess, tympanic cavity proper, and ventral compartment
What are the portions of the middle ear cavity?
The tympanic bulla is divided into dorsal and ventral compartments by a complete septum
What is unique about the cat's middle ear cavity?
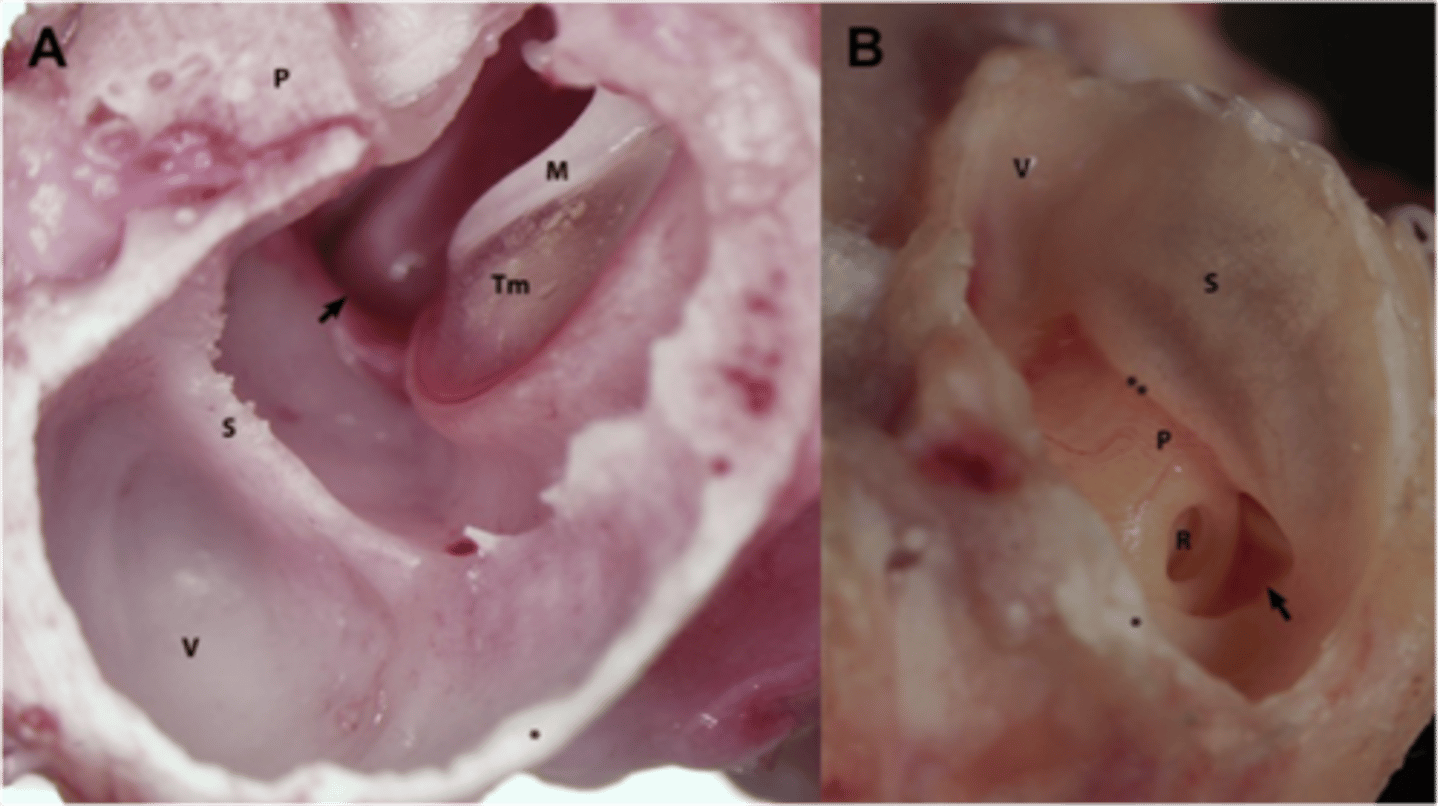
A; there is an incomplete septum
Which ear (A or B) belongs to a dog? How can you tell?
Sympathetic
Infection or truma to the middle ear can cause loss of ___ innervation to the eye
Horner's syndrome
Droopy eyelids, constricted pupils, and retracted eyes are all signs of what issue?
Petrous part of temporal bone
The inner ear is housed in what bone?
Osseous and membranous
The inner ear contains a ___ and ___ labyrinth
Promontory
The protrusion of bone which reaches into the dorsal middle ear is the?
CN VIII; vestibulocochlear n.
Information about the intensity of sound waves is relayed by what nerve?
Internal acoustic meatus
Both the cochlear and vestibular branches of CN VIII pass through the?
Caudal auricular a.
The main blood supply to the ear is the?
The rostral auricular muscles are supplied by a branch of what artery?