21 - Invertebrates
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What are the key characteristics that define animals?
Multicellularity, heterotrophic metabolism, internal digestion, and extracellular matrix molecules.
What is the significance of the Cambrian period in animal evolution?
It marks the dramatic increase in animal diversity and the earliest fossil appearance of many major animal groups.
Why are arthropods considered the most successful animals on Earth?
Their diverse adaptations, including exoskeletons and jointed appendages, allow them to thrive in various environments.
When did animals likely originate?
Over 700 million years ago.
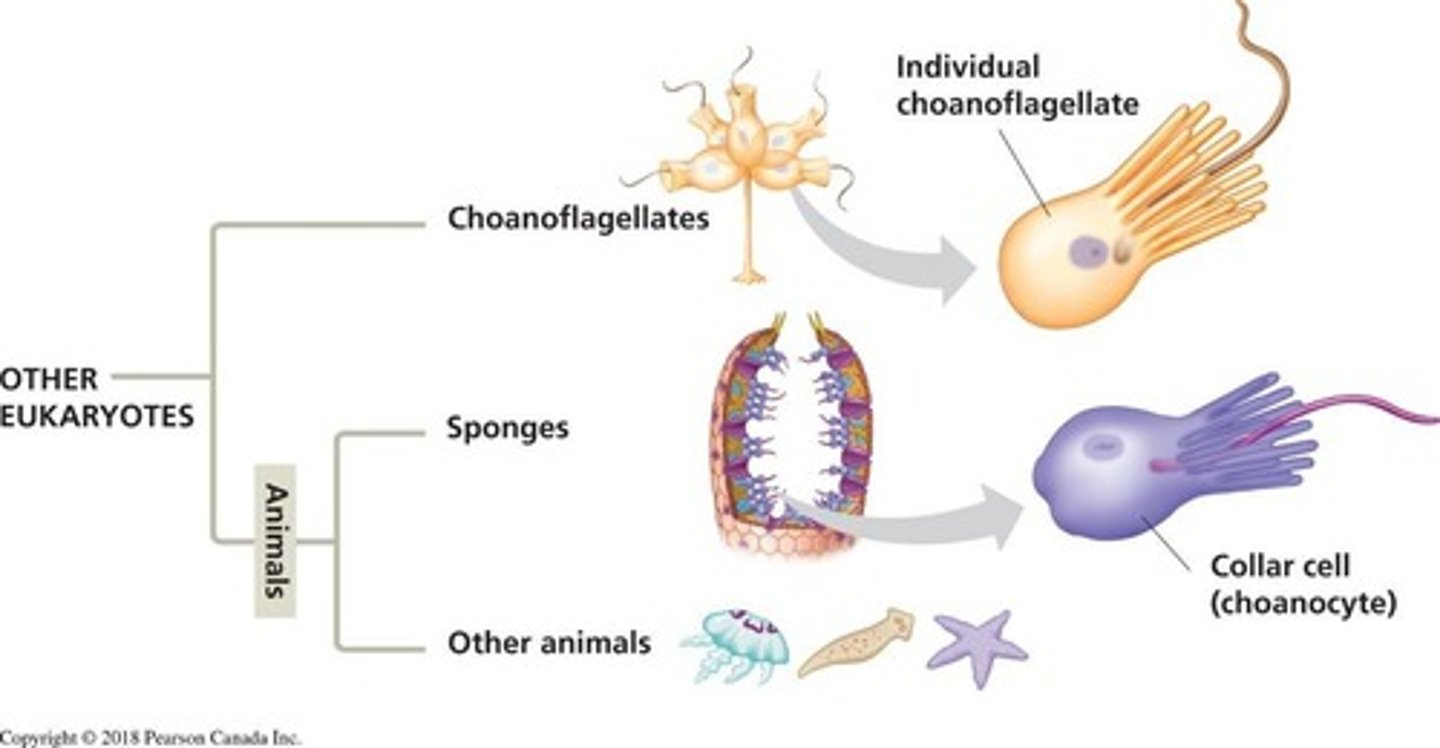
From what did animals likely evolve?
Single-celled eukaryotes similar to present-day choanoflagellate protists.
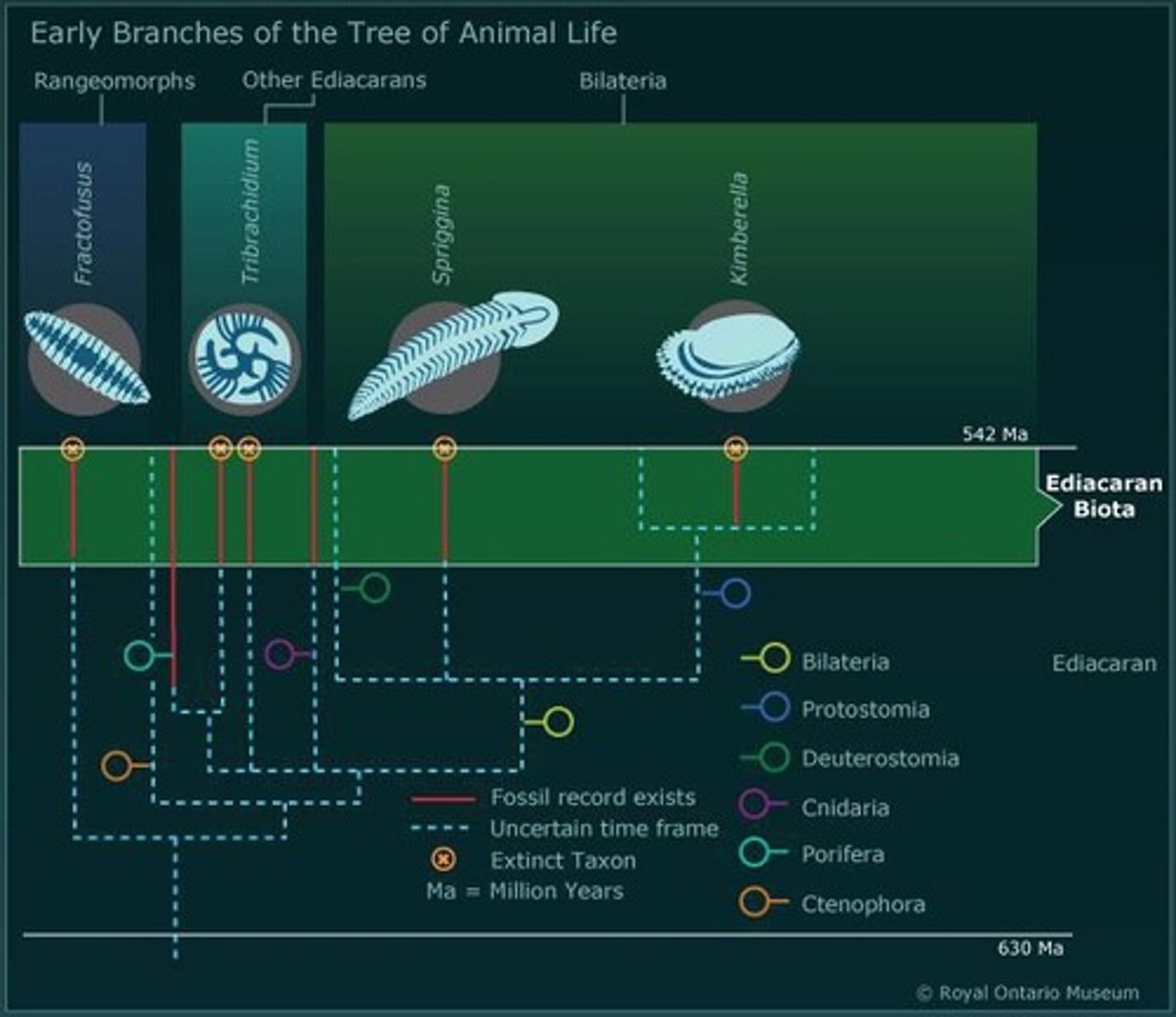
What was the Ediacaran Biota?
The first fossils of soft-bodied, mostly sessile animals living around 575-542 million years ago.
What are the two early-diverging animal groups?
Porifera (sponges) and Cnidaria (corals, sea anemones, sea jellies).
How do sponges feed?
They are filter feeders that capture particles suspended in water passing through their bodies.
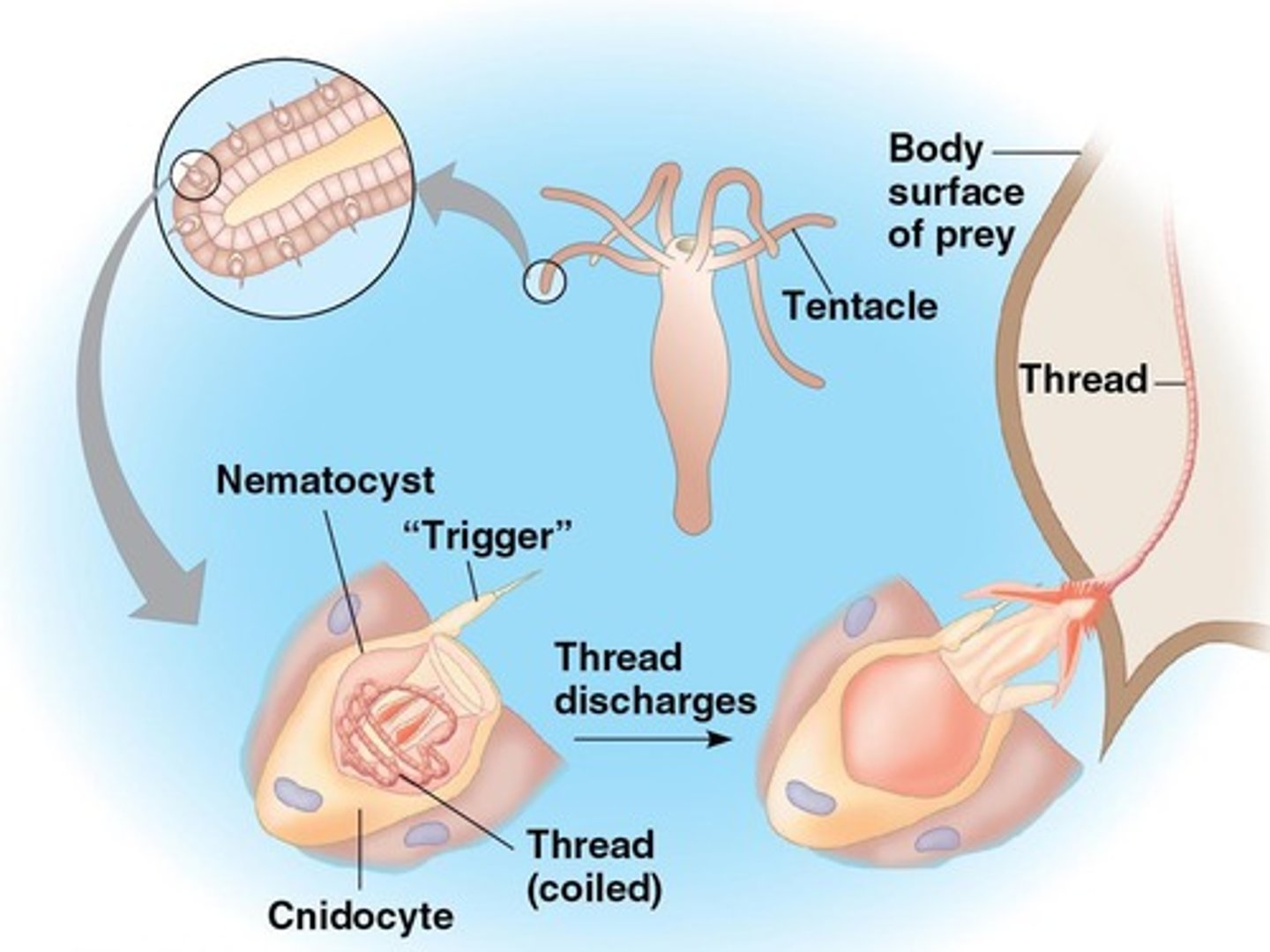
What are cnidocytes?
Specialized cells in cnidarians used for defense and prey capture, containing nematocysts that eject stinging threads.
What are the two body forms of cnidarians?
Polyp (sessile) and medusa (motile).
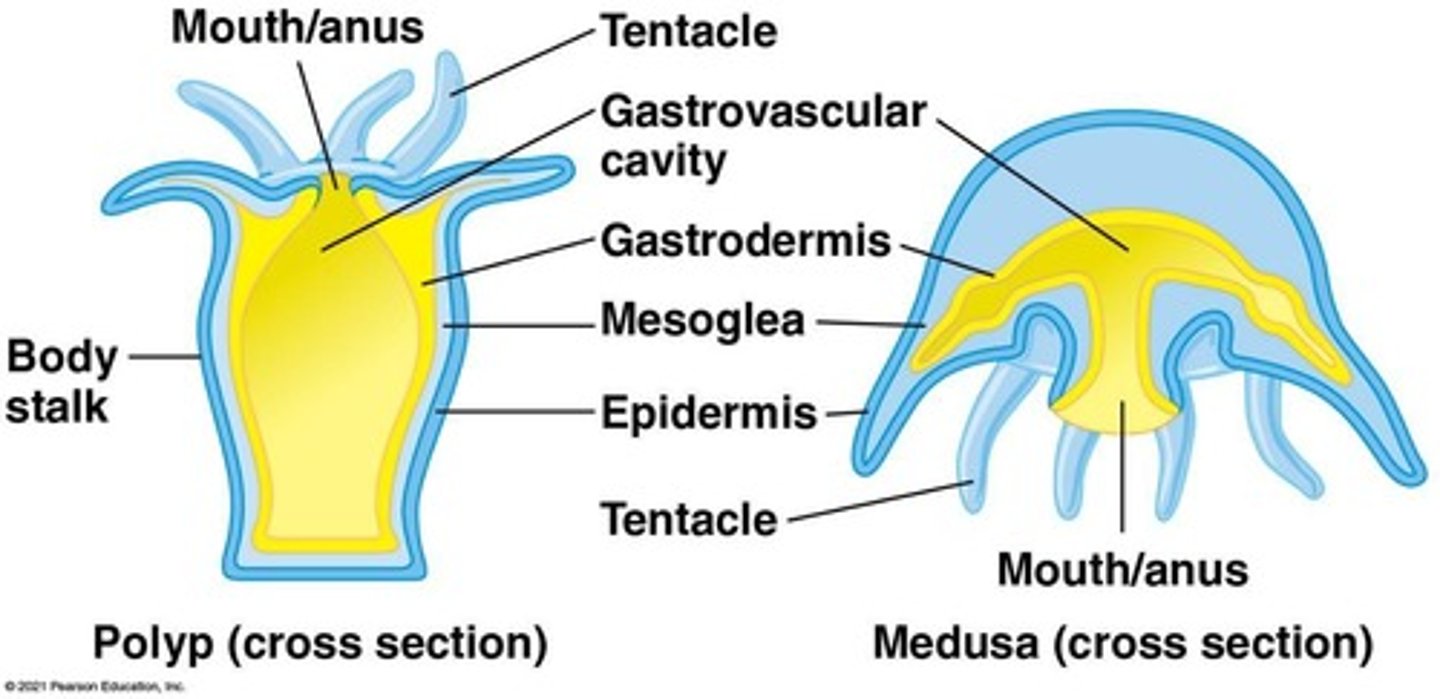
What is the role of the gastrovascular cavity in cnidarians?
It functions as both a stomach and a simple circulatory system for digestion and nutrient distribution.
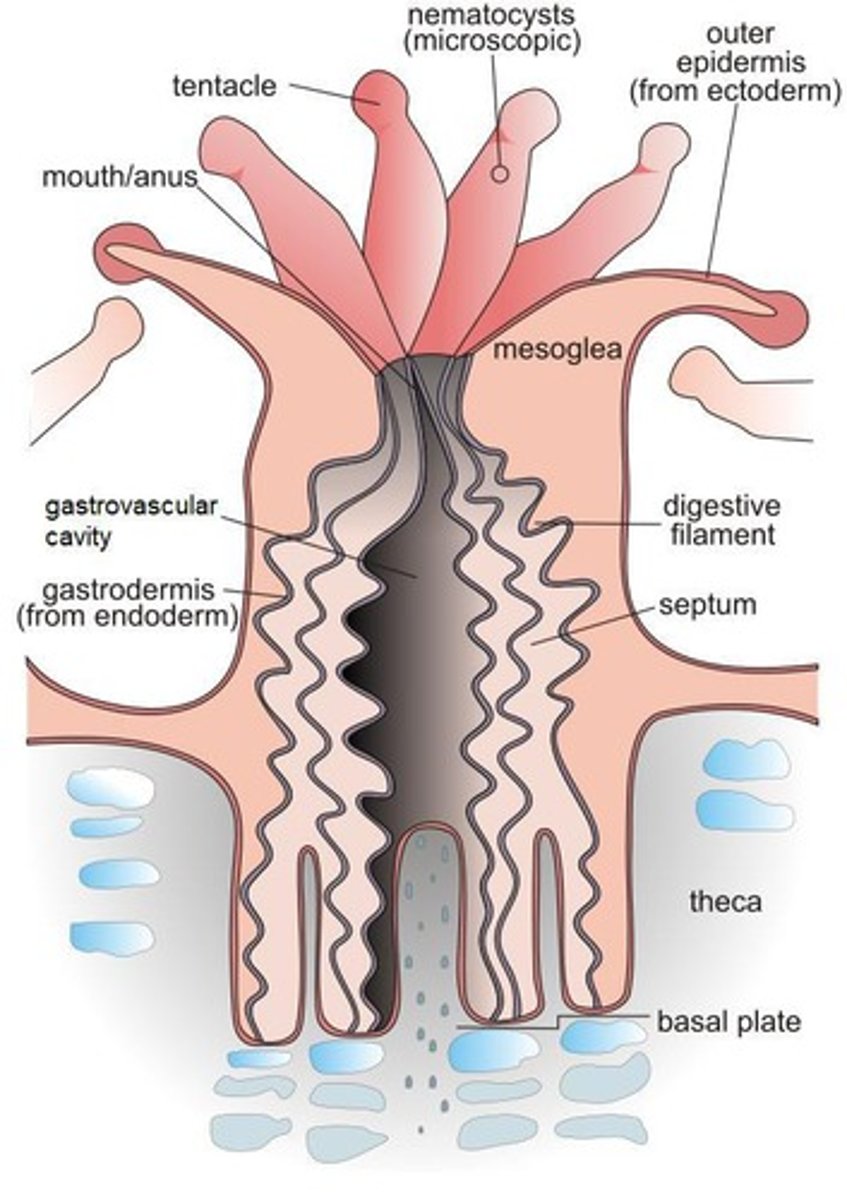
What is triploblasty?
The presence of three tissue layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, found in bilaterians.
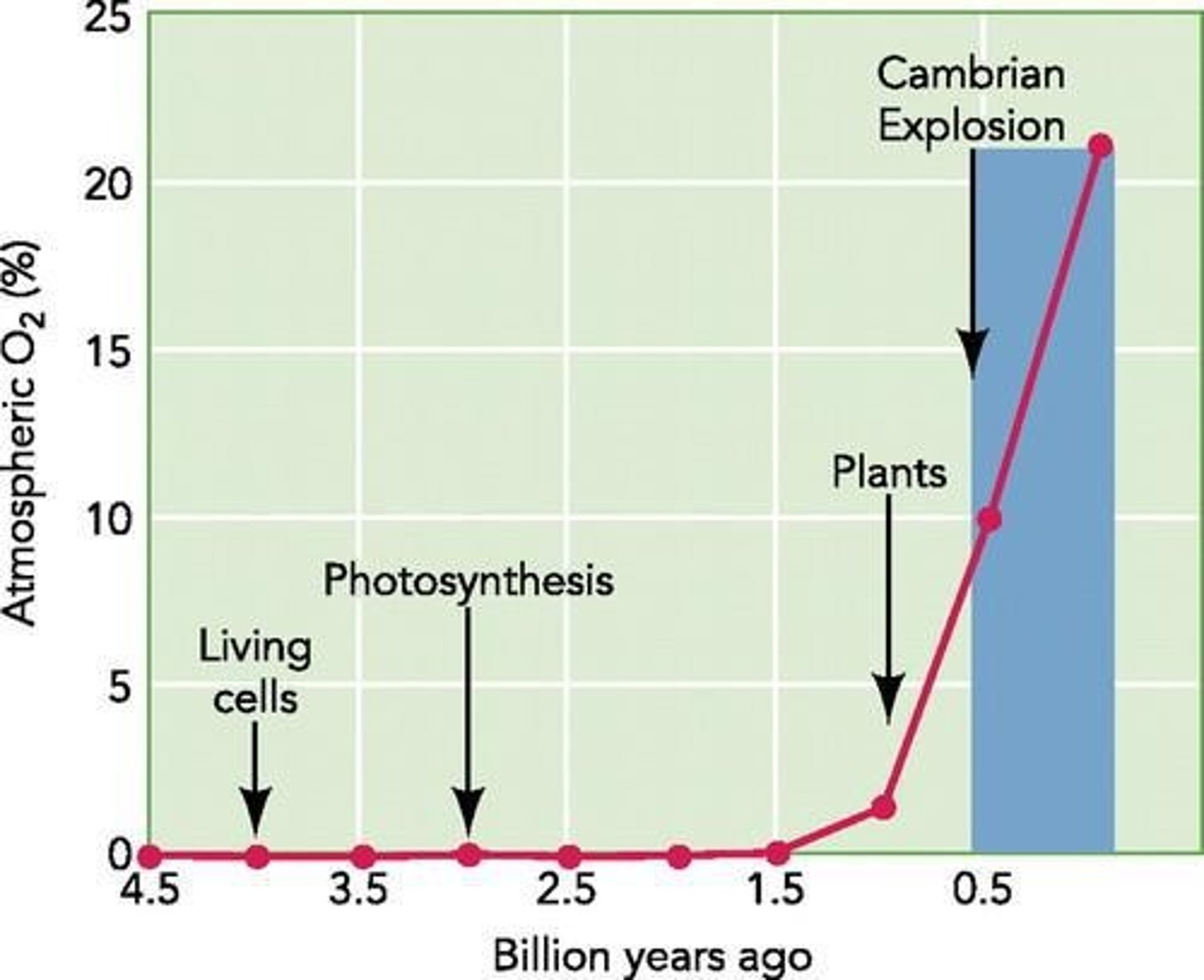
What major evolutionary advancement occurred during the Cambrian Explosion?
The rapid diversification of large animals and the appearance of many major animal groups.

What environmental change contributed to the Cambrian Explosion?
The rise of atmospheric oxygen, which supported larger, more active bodies.
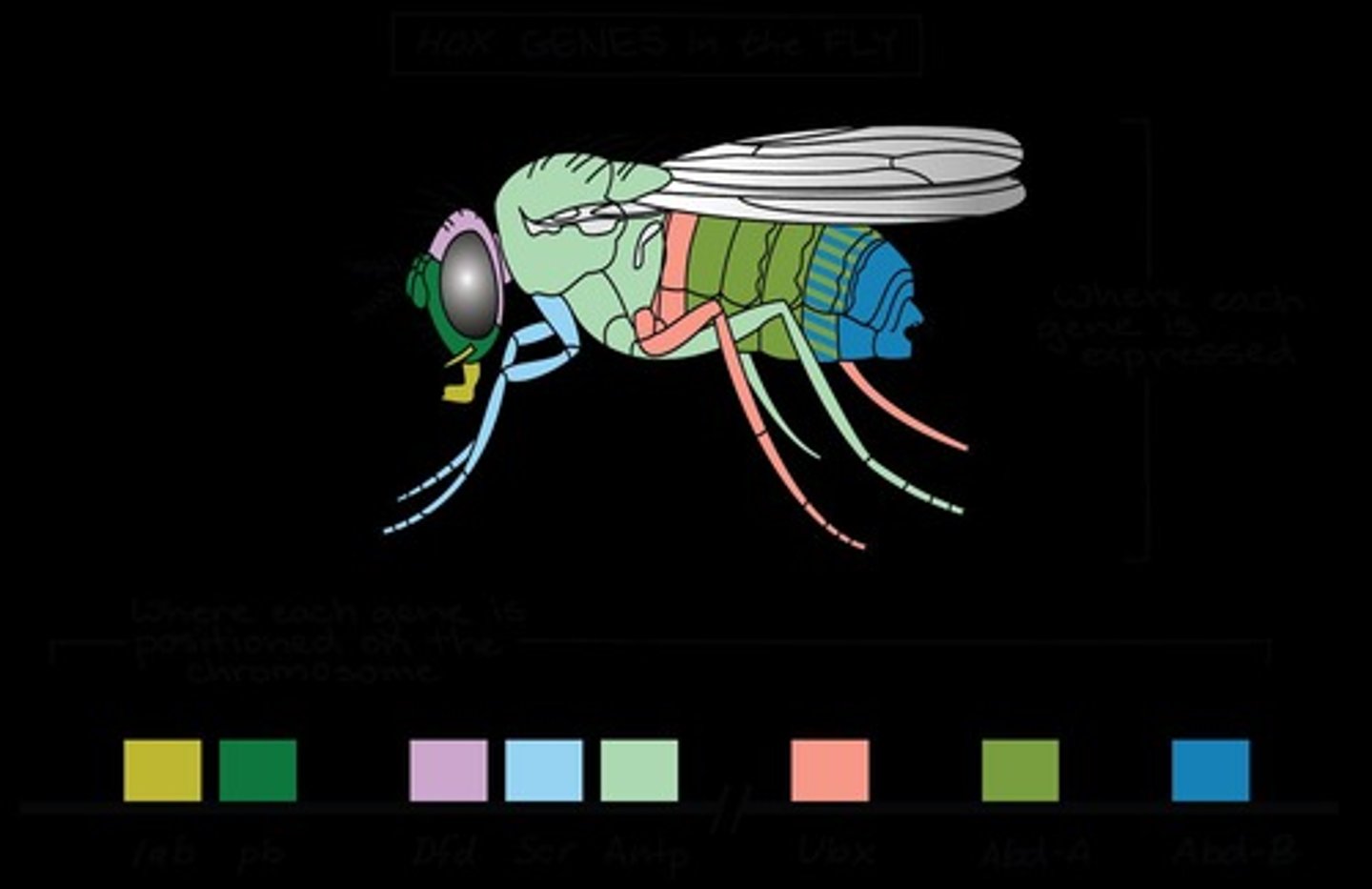
What is the Hox gene complex and its significance?
A set of genes that control body plan development, allowing for modular segments and rapid evolution of new body plans.
What are the three major clades of bilaterians?
Lophotrochozoa, Ecdysozoa, and Deuterostomia.
What are some key innovations in the Lophotrochozoa body plan?
Segmentation in annelids and the diverse molluscan body plan (foot, visceral mass, mantle).
How do lophotrochozoans contribute to ecosystems?
They act as ecosystem engineers, with annelids bioturbating sediments and bivalves filtering water and building reefs.
What is the function of the lophophore in some lophotrochozoans?
It is a feeding structure that helps in capturing food particles.
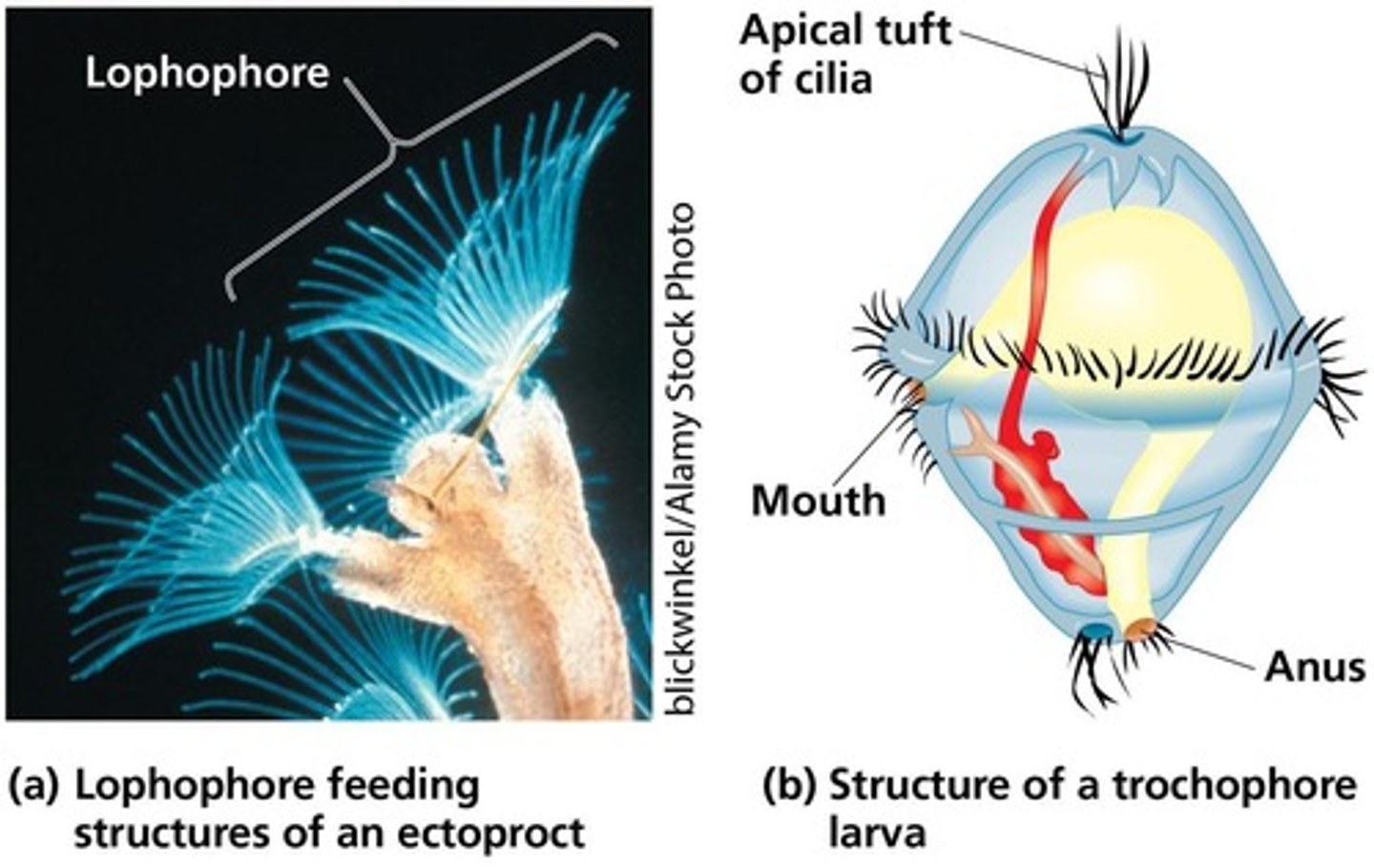
What is a trochophore larval stage?
A type of larval stage found in some lophotrochozoans that aids in dispersal.
What adaptations did predators develop during the Cambrian period?
Armor, shells, spines, and improved sensory systems to compete in the new ecological niches.
What is the role of nematocysts in cnidarians?
They are specialized organelles that eject stinging threads for capturing prey and defense.
What are the two reproductive strategies of medusozoans?
Asexual reproduction through budding and sexual reproduction through the production of medusae.
What is the ecological significance of colonial cnidarians?
They create three-dimensional habitats that structure entire marine ecosystems.
How do polyp and medusa forms differ in cnidarians?
Polyps are sessile and adhere to substrates, while medusae are free-swimming with a bell-shaped body.
What does the term 'bilaterians' refer to?
Animals with bilateral symmetry and three tissue layers, allowing for more complex structures and behaviors.
What is the significance of the complete digestive tract in bilaterians?
It allows for one-way flow of food and regional specialization, supporting larger and more active bodies.
What role do snails and bivalves play in food webs?
They act as primary consumers.
Which invertebrates are considered top predators?
Cephalopods and some flatworms.
How do parasitic flatworms affect host populations?
They shape host populations and disease dynamics.
What significance do fossil-rich groups like shelled molluscs have?
They help reconstruct past oceans and mass extinctions.
What type of nervous system did early animals like cnidarians have?
A diffuse nerve net with no true brain or nerve cord.
What evolutionary changes occurred in the nervous systems of early bilaterians?
Nervous system parts began to concentrate at two ends of the body.
What are ecdysozoans characterized by?
An external cuticle that must be shed to grow.
What is ecdysis?
The process of molting to replace the cuticle.
What is the largest group among ecdysozoans?
Arthropods.
How many arthropods are estimated to live on Earth?
About a billion billion (10^18).
What is the body plan of arthropods?
Segmented body, hard exoskeleton, and jointed appendages.
When did arthropods first appear?
During the Cambrian explosion (535-525 million years ago).
What adaptations allowed arthropods to colonize land?
Waterproof exoskeleton, jointed limbs, and internal fertilization.
What challenges did early land animals face?
Scarce water, gravity, and temperature fluctuations.
What is the function of the open circulatory system in arthropods?
It pumps hemolymph into the cavity surrounding tissues and organs.
What are the three major lineages of living arthropods?
Chelicerates, Myriapods, and Pancrustaceans.
What evolutionary advantage did the development of flight provide to insects?
It improved their ability to evade predators and disperse to new habitats.
What is the clade Hexapoda?
It includes insects and their relatives.
What is one key to the success of insects on land?
Their protective, waterproof exoskeleton.
How did arthropods adapt to gas exchange on land?
They developed a tracheal breathing system.
What are some features of octopuses' nervous systems?
They have a large central brain and ganglia in each arm.
What is the significance of the evolutionary radiations in terrestrial environments?
They led to co-evolutionary patterns, particularly between insects and angiosperms.
What adaptations allowed insects to specialize on various terrestrial resources?
Small size, rapid reproduction, metamorphosis, and diverse mouthparts.
What major transitions mark animal evolution?
From simple, mostly sessile forms to active predators and complex body plans.
What innovations did Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa contribute to animal evolution?
Segmentation, diverse molluscan forms, molting, and the arthropod body plan.