Lab Practical (1-7)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the expectations for lab notebook assignments?
hypothesis
logic behind hypothesis
details (methods/materials)
observations and data
What are the expectations for full lab reports?
title
abstract (brief summary of each part of the report)
introduction (include brief background and hypothesis)
materials and methods
results
discussion (include why results happened+counter evidence+what you’d do differently)
acklowegments
literature cited
What should figures look like?
title
caption (explanation of what’s being showed)
standard error bars
labeled axis
What was done in lab #1? What should your lab notes look like?
work in groups of 2 and used oil immersion lenses to view prepared bacterial slides (rotate turret between 40x and 100x and put drop of oil on slide and view at 100x (should be pink)
observe 1 slide of euglena, formanifera, radiolaria, amoeba, and paramecium (protista)
write down characteristics so u can make a phylogeny
make hypothesis abt which groups are closely related
regular, but with the matrix and phylogeny with a title and caption
What is the main assumption when building a phylogeny?
organisms that are similar to one another are more closely related
parsimony: the least amt of evolutionary change is most likely correct
What did we do in lab #2? What should your lab notes look like?
invertebrate scavenger hunt (work in groups of 2)
read through clues given by lab instructor and figure out what animal fits those descriptions
include something specific to let the professor know that u actually looked at it
Draw a phylogeny
use one from online and map ur specimens onto it
- just include figures w/ a title and caption (table of phylum/characteristics/descriptions)+(phylogeny)
What did we do in lab #3? What should your lab notes look like?
work with 4-5 people and pick a question that questions plant growth
come up with ur own hypothesis (phenomenon-because)/prediction (if-then)
plant seeds (Brassica rapa=Wisconsin fast plant)
1 side of tray is control, other is experimental and water once a day over the next 2 weeks (place under
At 2nd week, measure size of each plant, use excel to calculate:
average (sum/#)
SD (mean of how far each data point is from the average)
T-test (the probability that a null hypothesis is correct) (p-value of less than or equal to 0.05 means the data is statistically significant and they’re not due to chance)
should be on graph w/ title and captions
What did we do in lab #4? What should your notes look like?
in groups of 3-4, critique 2 anonymous lab reports
1st do on ur own, then discuss w/ group, then w/ class
analysis for each report (include good and bad)
What did we do in lab #5? What should your notes look like?
worked in groups of 2 to dissect a frog (vertebrate) and learn abt their internal organs
pick one of the organs viewed during dissection and write a 1-2 page paper (focus on physiology, evolutionary history, etc)
include in-text citations
What are some important things to note about frogs?
-have general characteristics of vertebrates
-have unique adaptations that are advantageous to their lifestyle, like a 3 chambered heart, which allows them to direct blood flow to lungs while breathing air, or to bypass lungs while submerged
Should you wear gloves and wash you hands for lab #5? Why?
Yes bc the specimens are in a preservative (not specified which, but assumed its formalin, similar to formaldehyde) and u should consider the specimens to be toxic

Label the major organs.
From top to bottom:
fat body
ovaries
lungs
small intestine
spleen
stomach
large intestine
lungs
heart
liver
galbladder
Inside frog urinary bladder
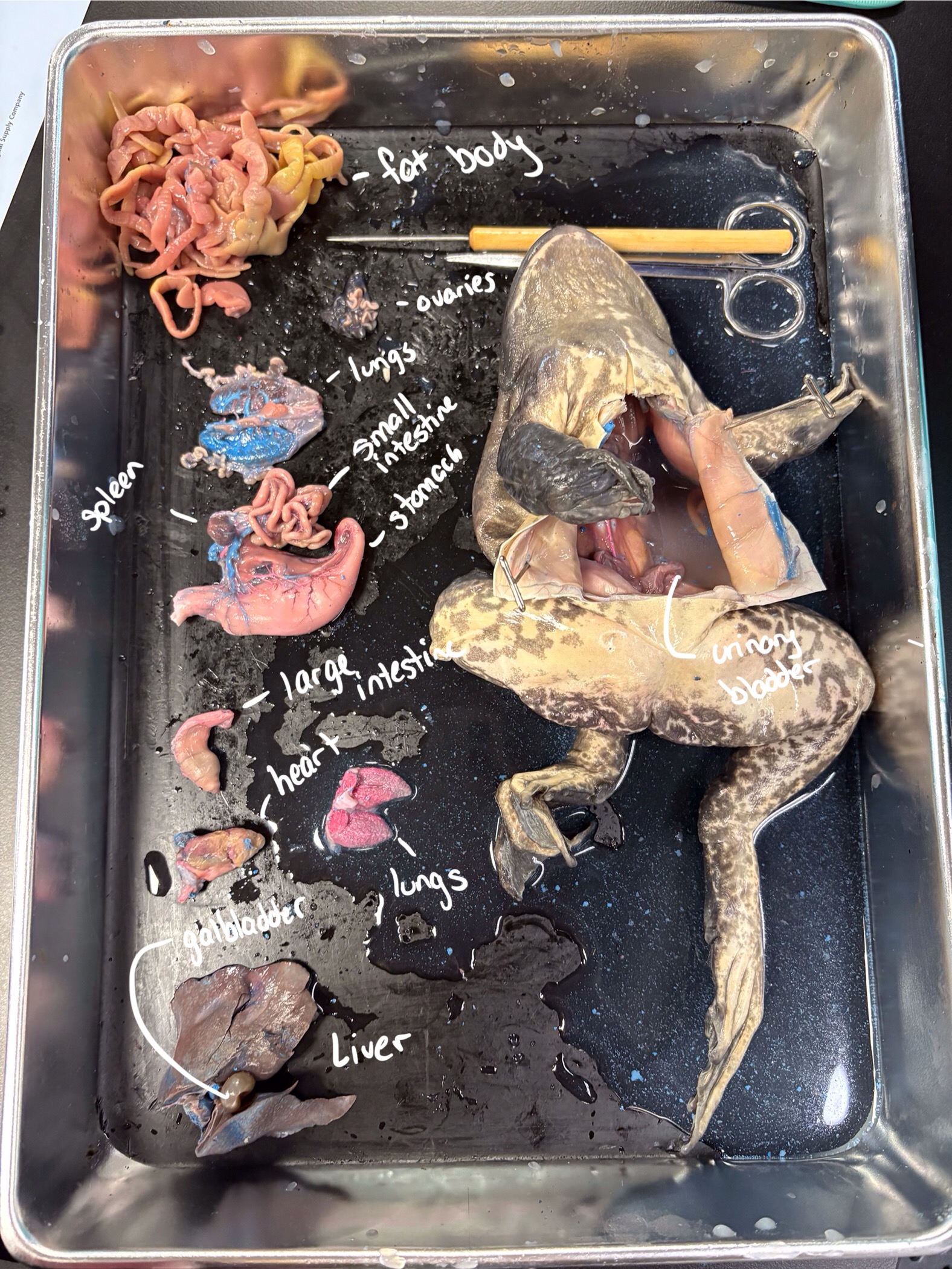
What did we do in lab #6? What should your lab notes look like?
we worked in groups of 4 and had to place a ring of petroleum jelly on a slide, put the planaria on it, then cover it w/ a coverslip…we viewed them under compound microscope (dorsal and ventral sides)
we looked at planaria w/ brush to see how they normally act (they liked shaded region bc of negative phototaxis
we designed and execute an experiment to test a hypothesized source location of a paracrine signal in the diffusion gradient model
we put plastic chambers with ice in ice, then put a drop of water and planaria on it, then cut it (use dissecting microscope)
normal w/ a discussion section to include an interpretation of data
What are planarian flatworms?
-free-living, freshwater flatworms
-asexual fission reproduction
-no apparent circulatory/respiratory systems
-has reflexes, but no brains
-usually found in clean, unpolluted water
-often inhabit small, shallow, slow-moving streams under stones or leaves
How do planarian flatworms regenerate? What is the method they use?
the animal adheres to the substrate with its posterior end, pulls forward with its anterior end (head end) and tears itself in two, each half then regenerates
epimorphosis (cells de-differentiate, and then multiply and re-differentiate)
How should planarians be maintained in the lab?
-in clean water and in dark conditions
-can't be tap water bc chlorine in it is toxic to them
-spring should be used and changed every 2-3 days and the scuzz that they secrete should be removed
-use soft paintbrush/plastic pipet to transfer animal to petri dish w/ well or spring water
-one animal will be kept as control, others are for regeneration
Why will the animals have been starved for a week?
-bc this empties the gut of food and will prevent bacterial contamination during recovery period
-they wont be fed again until regeneration is done
Explain the basics of regeneration.
1. You cut then the wound closes by muscular contractions
2. Epithelium heals over the wound
3. Neoblasts accumulate and blastema forms
4. Differentiation begins
What kind of model are we focusing on? What perspective are we exploring the model?
Diffusion gradient model
- provides information about location bc of a gradient of morphogen
-from the perspective of the endocrine system (Planarians dont have one, but they have paracrine signaling systems which function like endocrine-signals travel through cells, not blood)
What are some weird ways Planarians can regenerate? Why does this happen?
-A slice thats taken and is wider than it is long, can have 2 heads (Janus-heads)
-A slice taken from the posterior region can have 2 tails (Janus-tails)
-as ratio of length to width drops below 1.0, abnormal regenerates increase
How does sensation work?
sensory neurons/receptor cells transmit an action potential to CNS
-the perception of different senses happens bc of location of pathway experiencing action potential
Can humans "tune out" a stimulus?
What is another mechanism that allows for different perception of stimuli?
yes-if it has remained constant
-different receptors are more sensitive than others (if receptors are closer they are more sensitive)--they do become equal once an action potential
How do human eyes focus?
light is focused in fovea
-albeit is outside fovea, allows for peripheral vision (less focused bc it has less receptors)
Why is there a blind spot in everyone's peripheral vision?
bc there are no rods or cones where the optic nerve exits to the retina
What did we do in lab #7? What should your lab notes look like?
we worked in 2 conducted some experiments to explore human sensory biology
used a coin to see when we tune out a stimulus
put finger in cold a hot water, then to warm to see different reactions
use a discriminator to tap partner in 2mm intervals
cover eyes one at a time and focus on plus to find blind spot
use chart to find visual acuity
answer questions and include p-values and SD
How do you calculate the distance between the fovea and the blind spot?
x/distance between dot and plus (9cm)=4cm (distance between fovea and front of eye)/distance between eye and paper