Government intervention: price floors
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
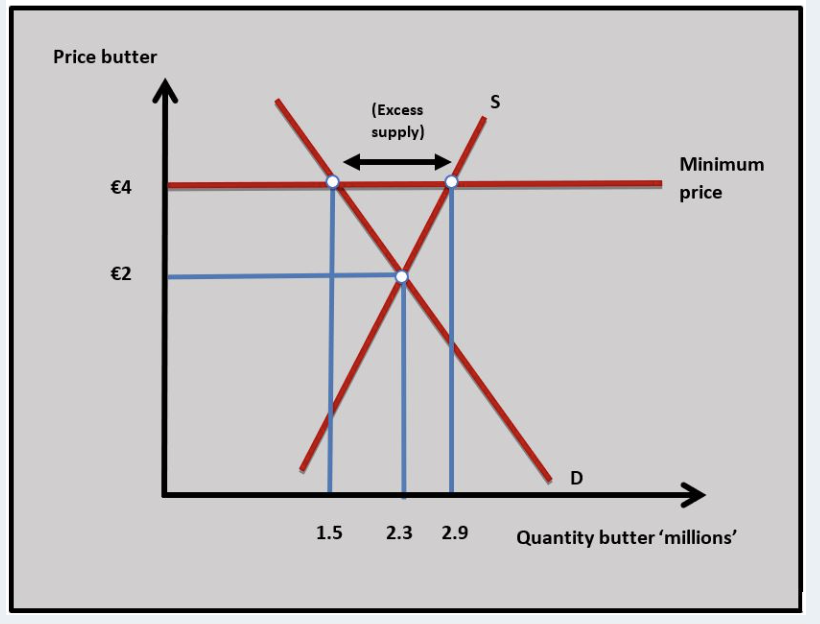
Price floor
reason
Price floor- government mandated minimum price on a good
Governments use minimum prices or guaranteed minimum prices to protect producers in markets.
This is often the case in agricultural markets where governments look to support farmers and protect the food supply.
consequences for markets
surpluses-larger quantity supplied, smaller quantity demanded; government buys excess supply
GOvernment measures to dispose of surpluses; store it or sell abroad;
Firm inefficiency:
overallocation of resources and allocative inefficienc: too many resources are alliocated to the good
Negative welfare impacts:
There is the cost of waste when excess supply is destroyed when it cannot be sold.
The gains of a minimum price tended to be concentrated amongst producers, with dispersed losses for consumers and taxpayers
consequences for stakeholders
consumers: worst off: must pay a higher price for the good
producers: gain as they receive higher price : increase revenues
workers: gain employment»greater proudction
government: government has to buy excess supply; reduce government funds; Minimum prices represent an opportunity cost to the government: buying the excess supply along with the cost of storing it and managing the system.
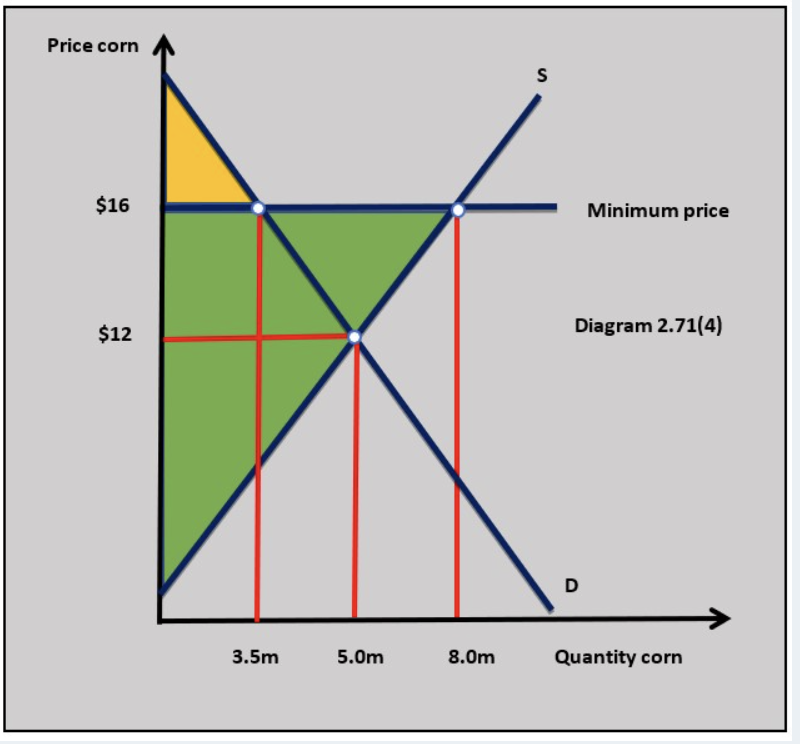
agricultural market
minimum price on butter will increase the price for consumers and lead to a reduction in their consumer surplus, which will be particularly damaging for low-income consumers.
minimum price will increase the price producers of butter will receive and will lead to an increase in their producer surplus and this should help to guarantee butter supply.
government will need to intervene in the market to buy up any excess supply to stop it from coming onto the market and causing prices to fall. This will lead to an opportunity cost to the government in terms of other areas of expenditure.